According to statistics, every third person experiences joint diseases. And among them are not only elderly people, but also young people - 30-35 years old. The problem also affects bodybuilders, overweight people, sedentary office workers and representatives of certain professions (loaders, builders, workers). The rate of degradation of cartilage tissue is different for all people, but they have one thing in common - a lack of glucosamine. This is an organic substance, due to the lack of which arthritis, osteoarthritis, osteochondrosis and other characteristic diseases develop. Preparations with glucosamine for joints restore cartilage, relieve swelling and restore previous mobility.
Glucosamine is an important component for joint health
Glucosamine for joints: what is this substance?
Articular cartilage
– a smooth and durable fabric that acts as a shock absorber pillow. It prevents bones from rubbing against each other, reduces pressure during movement, and consists of 60-65% water.
Glucosamine
– a monosaccharide that is contained and accumulates in the connective tissue of the musculoskeletal system, making it stronger and more elastic. The body mainly uses its reserves to form cartilage cells and maintain joint ligaments. In other words, it is a building material for cartilage. Its highest concentration is found in mollusk shells, bones and bone marrow of animals. All shells and shells of crustaceans are also sources of glucosamine. It is usually made from the chitinous shells of crabs, lobsters, shrimp and crayfish.
Glucosamine - a substance for strengthening joints?
This is a monosaccharide used for the synthesis of complex organic substances, in other words, a building element of connective tissues
(cartilage and ligamentous apparatus). The substance glucosamine is present in all living organisms; in high concentrations it can be found in the shells of crustaceans, as well as in the brain and bones of animals. In diseases of the musculoskeletal system, our body produces catastrophically little of it. To replenish its reserves, take medications containing glucosamine.
The substance glucosamine has a unique property - it is responsible for stimulating cartilage cells
.
Thanks to it, cells produce proteoglycans, building blocks that restore joint tissue. It has a positive effect on joints, bones, ligaments, cartilage, tendons and blood vessels. The effect of glucosamine also extends to synovial fluid - the so-called “lubricant”, which ensures painless sliding of articular cartilage. Creaking and crunching of joints during movement is evidence of low quality lubricating fluid, and therefore a deficiency of the substance glucosamine
.
As a result, what happens is this: heavy physical activity and some concomitant diseases lead to microtraumas of cartilage tissue, which can only be regenerated due to the optimal amount of glucosamine. If it is not enough, recovery does not occur, and diseases in the form of arthritis, arthrosis and osteochondrosis begin to develop. The body of an elderly person is not able to synthesize glucosamine in the required volumes, so such patients more often than others complain of joint pain. They especially need preparations with glucosamine.
A deficiency of the substance glucosamine leads to creaking and crunching of joints.
The benefits of glucosamine: how does it affect joints?
Over time, the cartilage wears out, dries out, and becomes thinner. External sources of glucosamine (from food) are most often insufficient; an age-related decrease in the rate of metabolic processes does not allow the body to independently synthesize it in the required volume. That is, the cartilage does not recover on its own and begins to perform its functions poorly. When sources of glucosamine disappear, pain and inflammation inevitably follow.
Injuries, excess weight, genetic predisposition, abnormal loads (heavy lifting) or lack of physical activity accelerate the process of cartilage degradation. This does not happen immediately in 2-3 weeks, but imperceptibly stretches over years or decades.
For example, at the age of 35, a person begins to be bothered by pain and unhealthy crunching in the knee joints, which he does not pay attention to, because they go away after a short rest. However, after 3-4 years, the intensity of the pain syndrome increases, the person becomes less mobile, and movements become limited. Further - worse. Destruction of the joint leads to coxarthrosis, gonarthrosis, osteochondrosis and other diseases associated with damage to cartilage. Their extreme stage is complete disability.
Conclusion:
supporting the optimal amount of glucosamine for joints in the body - protecting cartilage from wear and drying! The less it is, the faster the cartilage tissue is depleted and the joints hurt more.
The benefit of glucosamine is that it directly participates in the construction of cartilage elements, stimulates recovery, affects metabolism in cartilage tissue, improves calcium absorption and the protective functions of intra-articular fluid. Preparations with glucosamine prevent the occurrence of joint diseases, strengthen ligaments and tendons, bone tissue, nails and hair, heart muscle, blood vessels, and also improve the quality of synovial fluid.
Main properties of glucosamine for joints
- Improves cartilage metabolism and limb mobility.
- Pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. Reduce stiffness, swelling and pain.
- Elimination of hypersensitivity.
- Suspension of destructive changes.
- Preservation of water cushions in cartilage.
Preparations with glucosamine slow down the further development of diseases, alleviate the general condition both in the early and later stages, when pharmacological treatment is still possible and functionality is not lost.
Glucosamine
for joints of any kind - not an instant pain reliever only for symptomatic treatment, but a slow-acting drug that gradually accumulates in the body and regenerates cartilage. What does this mean? The effect and benefits of glucosamine are noticeable not after 1-2 days, but approximately 4-8 weeks after starting use. Thanks to it, the need for NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) is significantly reduced.
Treatment or prevention?
Based on the above, we can conclude that glucosamine can be used not only to treat joint diseases, but also to prevent further progression of cartilage destruction. In order to curb dystrophic changes, the drug is prescribed when the first signs of the disease appear, as a rule, to athletes and people over 40, since these groups are most susceptible to the development of joint diseases. Glucosamine has established itself as an excellent substance in terms of effectiveness and safety profile, which has been popular for several decades.
The effectiveness of taking glucosamine in maintaining joint health has also been proven in combination with chondroitin. The combination of these substances promotes the restoration of cartilage tissue, increases the cartilage’s resistance to destruction and helps reduce pain1.
This combination is presented in the line of drugs “Teraflex” and “Teraflex Advance”, which helps reduce pain due to the presence of ibuprofen (a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug) in the composition, and the combination of glucosamine and chondroitin simultaneously begins to stimulate the renewal of cartilage tissue.
Preparations with glucosamine: indications for use
Glucosamine for joints is taken both for prevention and directly for the treatment of diseases. First of all, it is responsible for the high-quality restoration of cartilage, and as a result, it relieves moderate and mild joint pain.
Taking medications with glucosamine restores cartilage tissue
What diseases does glucosamine help with?
- Osteoarthritis of joints (ankle, knee, elbow, shoulder, hip, wrist, jaw).
- Osteochondrosis (cervical, thoracic, lumbar).
- Arthritis (rheumatoid, reactive, gouty, traumatic and others).
Doctors recommend additional sources of glucosamine:
- Overweight people. Excess weight creates additional stress on the joint capsules.
- Sedentary people.
- People with an active lifestyle, which is accompanied by heavy physical activity. These could be professional athletes, loaders or miners. Relevant for extreme sports enthusiasts, travelers and those who regularly visit the gym.
People over 35 years of age and strict vegetarians, whose diet lacks sources of glucosamine, are especially deficient in the substance. The risk group also includes patients who have been diagnosed with joint diseases of an infectious autoimmune nature. Timely prevention helps to avoid the destruction of cartilage tissue, which means keeping joints healthy and mobile.
How to use?
When choosing glucosamine, pay attention not only to the manufacturer, but also to the amount of active ingredient in one tablet or capsule. There are supplements that contain 240-360 tablets per package, but the dosage is low. In this case, you will have to take 4-6 tablets per day. It is more convenient and more profitable to purchase glucosamine, albeit in 90 capsules, but with a daily portion of 2 tablets.
The daily intake of glucosamine for an adult is 700 mg. Athletes are recommended to take 1500 mg/day, dividing the total amount into several doses. Doctors advise taking it with or after meals. You should never take it on an empty stomach as this may cause intestinal irritation.
The duration of taking glucosamine for preventive purposes is 4 weeks, with an interval of 2-3 months. However, for the best effect or in the presence of joint diseases, it is recommended to increase the duration of use of the supplement, since it has a cumulative property. It is better to take glucosamine for a course of 12 weeks, but no more than 16, then take a break for 6-8 weeks and resume taking it again.
Glucosamine release forms for joints
Based on the clinical manifestations and lifestyle of the patient, the doctor individually selects chondroprotectors in different forms.
Glucosamine is available as:
- Injections.
- Mazey.
- Tablets and capsules.
- Powder.
For intramuscular administration, you will need the help of a health care professional - daily injections, unlike taking tablets or powder, can cause inconvenience. External agents (creams and balms) act locally, are characterized by low bioavailability and relatively low efficiency. As for the tablets, you need to take several of them at once.
With powder everything is much simpler: 1 sachet at a time. The composition includes excipients that enhance the effect and benefits of glucosamine. It does not affect the gastric mucosa, contains a daily dose of glucosamine for joints, quickly penetrates the cells and is easily absorbed.
Has the healing effect of glucosamine been proven in humans?
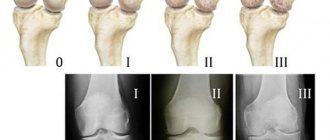
The first studies of glucosamine were carried out in the 80s of the last century in Italy. Clinical studies found that with long-term oral use of glucosamine, it reduced pain and improved joint movement, and slowed the progression of osteoarthritis. Most patients noticed a significant reduction in pain after just a month of taking glucosamine. The results were also confirmed when studying X-rays of patients after a course of glucosamine: a slowdown in joint destruction was noted. Subsequent experiments confirmed the data obtained and even showed an increase in the effect when combined with glucosamine and chondroitin.
In addition, it should be mentioned that glucosamine is recommended by the European Society for the Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis as first-line therapy for osteoarthritis and other degenerative joint diseases due to its ability to control pain and slow the progression of structural changes in the joints.
At the same time, glucosamine with another chondroprotective substance, chondroitin sulfate, showed particularly high effectiveness in osteoarthritis. The effectiveness of the combined use of these substances has been well studied in various comparative studies. It has been shown that in terms of effectiveness against the symptoms of osteoarthritis - pain, joint dysfunction - the combination of glucosamine and chondroitin, when used systematically, is not inferior to the most modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and at the same time has a positive effect on the structure of joint tissues. In this case, one should take into account the doses of glucosamine and chondroitin, which were used in the largest foreign studies and are currently considered sufficient or therapeutic. For example, a therapeutic daily dose of glucosamine (1500 mg) and chondroitin (1200 mg) is contained in 3 capsules of the Teraflex drug and is therefore recommended for use in the first 3 weeks of treatment.
Artracam is a working drug with glucosamine!
Artracam is a drug that belongs to the group of chondroprotectors.
The drug with glucosamine is designed for the long term - Artracam slowly but surely restores mobility by accumulating in the body. It affects all joints at once, relieves symptoms (pain and swelling), and has a direct effect on cartilage regeneration. The powder has a neutral taste, consists of glucosamine sulfate sodium chloride and glucosamine sulfate, made from natural raw materials. It can be combined with chondroitin.
To achieve lasting and maximum results, it is advisable to take it in courses (1 course = 6 weeks). If necessary, taking glucosamine for joints is combined with NSAIDs, physiotherapy, exercise therapy (physical therapy), and proper nutrition.
Artracam is an effective and safe drug
with glucosamine, which is enough to take once a day so that the joints work properly, and most importantly... painlessly!
Images designed by Freepik
Positive Action
Additional intake of glucosamine helps restore damaged cartilage and ligament tissue. Thanks to it, the production of hyaluronic acid, which forms synovial fluid, improves. This is extremely important for preventing joint injuries.
Regular use of glucosamine for osteoarthritis reduces the risk of arthrosis. Its effectiveness is partly comparable to taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. During the first three weeks of use, pronounced pain decreases and mobility in damaged joints improves.
Glucosamine sulfate fights infection. In combination with other drugs, it reduces inflammatory processes in affected tissues. Rheumatologists often prescribe glucosamine to patients who have nothing to do with sports.