Angina pectoris: general information
If, as you age, you begin to notice that heart pain occurs after physical activity, immediately consult a cardiologist. There is a high probability that you are developing a heart disease called angina pectoris FC 2. Attacks of pain pass, so many people tend to ignore them. However, the result and direct consequence is myocardial infarction. An even worse option: sudden cardiac arrest. Do not expose yourself to mortal risk - get examined using professional diagnostic equipment at the first symptoms of angina pectoris! Now you have a unique opportunity to undergo a free consultation with a specialist and a set of preparatory examinations when enrolling in a course of enhanced external counterpulsation or shock wave therapy of the heart:
Promotion
Just until the end of autumn, undergo a free consultation and a set of preparatory examinations* when registering for a course of enhanced external counterpulsation or shock wave therapy of the heart.**
Send a request
* Check the details of the Promotion by phone. **Has contraindications; consultation with a doctor is required.
Enhanced external counterpulsation (EECP) Cardiac shock wave therapy (SWTS)
Hurry up to apply, the promotion period is limited.
Treatment
Treatment of unstable angina is carried out in an inpatient setting in a therapeutic or cardiology department.
Treatment goals:
- restore the patency of the coronary vessels as early as possible;
- stabilize clinical manifestations, relieve pain;
- prevent acute heart attack and sudden death;
- provide the opportunity for rehabilitation and adaptation to living conditions.
As first aid, the patient can take up to two Nitrogrycerin tablets. Some people prefer a spray under the tongue. It is recommended to take two Aspirin tablets to prevent thrombosis.
"Old Man" Aspirin is still in demand
In the hospital, the patient is prescribed bed rest, gradually increasing as his condition improves.
The diet comes down to frequent meals in small portions, limiting spicy and fatty foods, foods that contribute to bloating and elevation of the diaphragm.
Recommended are porridge, stewed vegetables, kefir, cottage cheese, low-fat soups, beef meat dishes, boiled chicken, and unsalted fish.
Treatment with medications
In an acute condition, nitro-containing drugs (isosorbide dinitrate, Nitroglycerin) are administered intravenously, then the dose for internal use is selected.
Anticoagulants (Heparin subcutaneously, Aspirin orally) to reduce coagulation and prevent the development of thrombosis. Modern aspirin-containing drugs can protect the stomach from harmful effects (Aspirin Cardio, Thrombo Ass, Cardiomagnyl).
A group of adrenergic blockers is prescribed in all cases except Prinzmetal's angina. These drugs are contraindicated for bronchial asthma, chronic bronchitis with respiratory failure.
Calcium channel antagonists are indicated in the absence of severe vascular damage (Cordafen, Nifidipine, Verapamil).
Symptomatic medications (painkillers, diuretics) are prescribed by the doctor on an inconsistent basis.
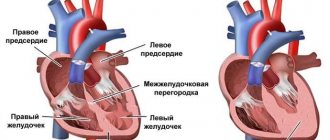
What is cardiac angina?
The disease is the most common form of coronary heart disease. Its danger should not be underestimated, because against its background heart failure develops quite quickly. Not far from a heart attack!
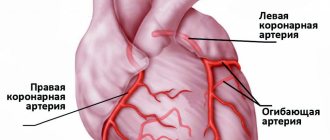
The disease develops in men after 55 years, in women - after 64. The reason is a partial (50-70%) narrowing of the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart tissue. The narrowing occurs due to the deposition of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of blood vessels and the formation of blood clots. They impede blood circulation, the heart lacks oxygen and nutrients. Especially during times of physical and emotional stress, when the heart muscle works actively and requires more oxygen. The arteries are not able to satisfy her need. That's when you experience attacks of pain.
Diagnostic procedures
The absence of specific symptoms does not allow the cardiologist to confirm the diagnosis during a physical examination. The doctor carries out differential diagnosis to exclude heart attack and non-ischemic heart pathologies from the patient’s history. Clinical guidelines suggest the following tests to confirm unstable angina:
- electrocardiography;
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- echocardiography;
- coronary angiography.
Cardiologists detect changes in the condition of the coronary arteries and decreased left ventricular function. Based on these data, the diagnosis is confirmed.
How does the disease develop?
It is at such moments that common signs of angina pectoris appear in women and men: you feel a lack of air, arrhythmia. At this time, chemical changes occur in the myocardium associated with metabolic disorders, a decrease in the synthesis of substances, and the accumulation of acids. The functions of the myocardium are gradually disrupted, and its metabolism changes.
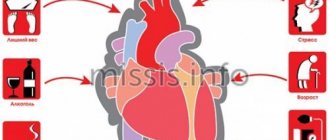
What causes this disease? There are certain factors:
- high cholesterol levels;
- obesity when consuming excessive amounts of fats and carbohydrates;
- physical inactivity disrupts lipid volume;
- smoking causes oxygen starvation of cells and arterial spasm;
- arterial hypertension causes myocardial tension;
- anemia, intoxication contribute to oxygen starvation;
- diabetes mellitus increases the risk of ischemia;
- increased blood viscosity is a direct risk of blood clots;
- psycho-emotional stress (especially in women) worsens myocardial nutrition.
Stable angina (tension): signs and symptoms
If periodic attacks that occur as a result of exercise last more than 1 month, doctors diagnose “stable angina.” The pain is relieved after taking nitroglycerin.
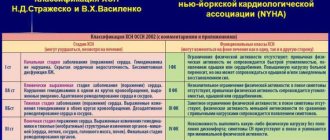
Depending on how strong the load can cause an attack in the patient, functional classes of the disease are distinguished.
- Angina pectoris FC 1 is characterized by good tolerability, and signs of angina in men and women are noticeable only with excessive stress.
- Angina pectoris FC 2 is manifested by some limitation in normal activities: an attack begins when walking more than 500 m, climbing to the 1st floor, or emotional excitement. With coronary artery disease and angina pectoris FC 2, the first hours after waking up are difficult to bear. Cold weather also has a negative effect.
- Angina pectoris FC 3 is already a serious limitation of normal physical and emotional activity. Obvious signs appear during normal walking at a distance of 150-200 m on level ground, or climbing one floor. Also, angina pectoris FC 3 develops due to anxiety.
- Stable angina pectoris FC 4 occurs after minimal exertion. The patient is unable to perform simple physical activities. This class closely borders on resting angina, i.e. one that is not associated with loads.
This classification allows the doctor to act more accurately when prescribing medications and treatments.
Angina at rest: signs and symptoms
It is characterized by the manifestation of characteristic symptoms in a calm state - at night and especially in the morning after waking up. Typically, angina at rest is diagnosed using 24-hour monitoring. Most often, attacks are caused by increased blood pressure and psycho-emotional stress. Unfortunately, any troubles at work or family quarrel can provoke an attack. And sometimes it is enough to change the position of the body.
This type includes vasospastic angina, the cause of which is a sudden spasm of the coronary vessels. And also post-infarction - manifesting itself 10-14 days after the heart attack.
Unstable angina: signs and symptoms
Unlike stable angina, this type of disease changes its behavior, so it is important to constantly be under medical supervision in the first two months after the first attack. Obvious symptoms of unstable angina: changing frequency, duration, intensity of attacks. They can also start at night.
In turn, unstable angina is divided into:
- into classes depending on the nature and severity (initial, subacute and acute stages);
- into groups according to the conditions of occurrence (primary, secondary, post-infarction);
- into groups during therapy (the disease develops during procedures, medication, intensive treatment).
Therapeutic measures
Conservative treatment involves prescribing several groups of drugs to the patient. Antianginal drugs relieve symptoms of angina pectoris. In acute attacks accompanied by intense pain, intravenous infusion of painkillers is performed.
Thrombolytics reduce the likelihood of blood clots. A similar goal is pursued when prescribing direct anticoagulants to a patient.
Lipid-lowering drugs remain an integral component in the drug treatment of unstable angina. They help normalize cholesterol levels in the patient’s blood. Constant use of such drugs reduces the likelihood of complications and recurrent attacks.
If conservative treatment is ineffective, the patient is prescribed surgery. The type of surgical intervention is determined by a cardiologist based on coronary angiography data. Imaging will allow us to understand the extent of damage to the coronary arteries. The most common methods of surgical treatment of angina remain coronary bypass surgery and coronary angioplasty.
Symptoms of angina in women and men
Pain
Most patients report the following symptoms of an angina attack. First of all, cutting, pressing pain in the chest. Many people complain that their heart “burns” or their throat “tightens.” At the same time, you instinctively want to press your hand or fist to your chest. Often the pain migrates to the left shoulder, neck, arm, and shoulder blade. It may grow or disappear suddenly. Symptoms clearly and distinctly appear during exercise, when the patient is diagnosed with IHD angina pectoris FC 2.
Pain can occur after physical exertion, stress, high blood pressure, or overeating. At night - due to stuffiness or low air temperature. Often the attack is accompanied by arrhythmia.
External symptoms and signs of angina pectoris
It is quite simple to identify an attack by its external manifestations. Pay attention to the following signs of angina: the person turns pale, sweat appears on the forehead, his face expresses suffering; fingers lose sensitivity, hands become cold; the patient breathes intermittently and rarely; the onset of an attack is accompanied by a rapid pulse.
Causes
Unstable angina has the same causes as all manifestations of myocardial ischemia:
- Damage to the coronary vessels by the atherosclerotic process when the diameter is narrowed by ½. Risk factors should be taken into account here (age after 45 years, predominantly male gender, presence of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, cigarette smoking, alcohol dependence).
- Thrombosis of cardiac vessels with increased blood clotting, decreased blood flow speed (heart failure), thromboembolism from various sources.
According to cardiologists, it is the addition of thrombosis that plays a major role in the instability of vasoconstriction. This possibility increases in patients with thyrotoxicosis and anemia.
Morning jogging can cause pain
What can the disease be confused with?
As for diseases not related to the cardiovascular system, based on the symptoms and signs, angina pectoris can be mistaken for:
- osteochondrosis of the cervical or thoracic spine;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- gastrointestinal diseases (diaphragmatic hiatal hernia);
- pleurisy, pulmonary embolism;
- pinched nerves.
Usually this disease is confused with the onset of myocardial infarction. The signs are really very similar. The main difference is that an attack of angina is relieved by taking nitroglycerin. In case of a heart attack, the medicine does not work or relieves pain only slightly and temporarily.
Possible complications
Untreated angina can cause:
- sudden ventricular fibrillation with fatal outcome;
- acute myocardial infarction;
- acute failure of the heart muscle with pulmonary edema;
- thromboembolism of the pulmonary arteries.
Therefore, an increase in attacks and the appearance of unusual symptoms are important reasons for urgent medical attention.
When referred for inpatient treatment, refusal is considered as the patient’s responsibility for his own life.
Where can I get diagnosed and treated?
Rest assured that your heart is not in danger! If the first symptoms and signs of angina appear, consult a qualified healthcare provider. Cardiologists at the CBCP Center for Circulatory Pathology are ready to help you. The clinic will offer professional consultation and modern types of diagnostics, through which the doctor will receive objective, detailed and accurate information about the disease.
If you discover serious violations, do not despair! The level of medicine at CBCP makes it possible to effectively treat complex cardiovascular diseases using medicinal and non-surgical methods.
Diagnostics
In diagnosing angina, a balanced and competent approach is necessary, because with unstable angina, the patient's condition may worsen until the development of myocardial infarction. Each study must be substantiated.
- ECG
- 24-hour ECG monitoring
- bicycle ergometry or treadmill (stress test with simultaneous ECG recording)
- EchoCG
- stress echocardiography
- coronary angiography
- myocardial scintigraphy
At the EXPERT Clinic, cardiologists are also functional diagnostics doctors. They will weigh all the risks before conducting the examination.