Nephrology is a medical branch that specializes in the study of the normal and pathological functioning of the kidneys and related diseases, as well as developing and implementing methods for diagnosing and eliminating (treating) such diseases. The professional interests of nephrology include the study of not only the kidneys, but also the urethra, ureters and bladder. What does a nephrologist treat?
In this informational article we will look at who a nephrologist is and what he treats.
Who is a nephrologist
Everyone knows that the human body is a complex, harmonious system of interaction between internal organs and their systems. It should be understood that nephrology problems can be related to neurology, hematology, dermatovenerology, urology, gynecology, etc. In addition, prolonged kidney disease increases the risk of developing diseases of organs that are part of the circulatory system.
A nephrologist is a doctor who treats diseases of important paired organs that are part of the urinary system, diagnoses such diseases, and also develops and implements individual preventive methods. Nephrology is an additional specialization; accordingly, the doctor must have a diploma of higher medical education in the field of pediatrics or in the specialty of general medicine, and only then can he choose an additional, narrower specialization.
If the doctor has previously received education in the specialty of pediatrics, then after receiving additional specialization in the field of nephrology, he will have the specialty of pediatric nephrologist. If a specialist initially received an education in the specialty “general medicine”, and subsequently underwent training in “surgery” and only after that chose a specialization in the field of nephrology, then such a doctor will have the specialty “nephrologist surgeon”. If a doctor, having a basic education in the specialty “general medicine”, completed an internship in the field of surgery, subsequently received residency training in the field of urology and only after that underwent specialization in the field of nephrology, then such a specialist is a urologist-nephrologist.
What symptoms should you see a doctor for?
The kidneys are a kind of filter in the body. They pass through and process harmful substances, which then leave the body naturally. In a healthy body, these functions are performed, but if health is impaired, all toxic substances remain in the body and poison it. This can be very dangerous - in serious cases it can even be fatal.
Therefore, at the first signs of disturbances in the functioning of the urinary system, it is necessary to urgently visit a nephrologist, undergo a full diagnosis and, if necessary, immediately begin treatment. Remember that any pathology is much easier to cure at the initial stage. Whereas in advanced cases, surgical intervention may be necessary for treatment.
What does a nephrologist do and what does he do?
The activities of a nephrologist are closely related to such areas of medicine as surgery and urology. Let us note that a nephrologist is, first of all, a general practitioner, and therefore carries out medication or any other treatment not related to surgery.
A nephrologist carries out professional activities in public medical institutions, as well as in private medical institutions, conducting outpatient visits.
What is the difference between a urologist and a nephrologist? A urologist is a doctor with a broader specialization, since the area of medical activity of a urologist includes therapy and diagnosis of diseases of the genitourinary system, as well as individual organs (kidneys, prostate, etc.). It is the urologist who performs surgical operations, if necessary, for diseases of the paired organs included in the urinary system.
What does a nephrologist do during an appointment? The appointment with a nephrologist does not have a specific focus. Initially, the doctor conducts a survey of the patient to collect information and identify complaints. The nephrologist will be interested in previous infectious diseases, rhythm of life, nutrition, systematic use of drugs, hereditary diseases, etc. Subsequently, the nephrologist performs an external examination and palpation, and also, often, taps the kidneys with a finger.
Often, to make an adequate diagnosis, the results of laboratory tests and diagnostic hardware procedures are evaluated. Types of diagnostics that may need to be performed at the discretion of the nephrologist:
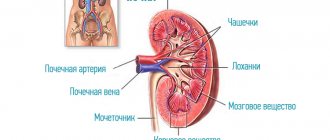
- Retrograde pyelography;
- Scintigraphy;
- Biopsy;
- X-ray, as well as a specific X-ray examination, in which a certain substance is injected into a blood vessel;
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys, as well as (if necessary) abdominal organs;
- Pneumoperitoneum (injection of gas into the abdominal cavity);
- ECG;
- CT scan;
- Radioisotope radiography;
- Study of blood pressure in dynamics;
Our service will select the best nephrologist for you for free when you call our Unified Appointment Center by phone. We will find an experienced doctor near you, and the price will be lower than if you contact the clinic directly.
Necessary tests:
- Daily diuresis;
- Research on Nechiporenko;
- OAM and UAC;
- BAC for creatinine, uric acid and urea levels;
- Analysis for cholesterol and triglycerides;
- Samples of Reberg and Zemnitsky;
- Urine culture for bioflora;
Since many kidney diseases occur due to various disorders and infectious lesions of the body, additional consultation with other specialized specialists may be required.
If diseases are detected, the nephrologist prescribes treatment, which will usually have 2 basic directions:
- Direct treatment of the disease;
- Nephroprotective treatment aimed at protecting this paired organ and normalizing its functioning;
What laboratory diagnostic methods does a nephrologist use?
The most common diagnostic methods are blood and urine tests. The kidneys filter excess fluid and waste from the blood, forming urine. This means that blood and urine tests can often tell whether the kidneys are working properly.
Blood tests include:
Serum creatinine
The body produces creatinine as a byproduct of daily muscle damage. Having high levels of creatinine in the blood is a sign of advanced kidney disease. Serum creatinine levels vary with factors such as age, body size, and race. A value greater than 1.2 for women or greater than 1.4 for men may indicate kidney problems.
Glomerular filtration rate
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) indicates how well the kidneys are able to filter excess fluid and waste from the blood. Nephrologists can determine this value by calculating the serum creatinine level and taking into account age, sex, and race. The value usually decreases with age, but GFR values include:
- Above 90 is normal
- Below 60 – kidney dysfunction
- Below 15 - the need for dialysis or kidney transplantation
Blood urea nitrogen
Urea nitrogen is a waste product from the body that breaks down protein in foods and drinks. Typically, blood urea nitrogen levels increase when kidney function is poor. Urea nitrogen levels normally range from 7 to 20.
Analysis of urine
The nephrologist will usually send the urine sample for microscopic examination to check for abnormalities.
A 24-hour urine test is often analyzed. A person's urine is collected over a 24-hour period to show how much urine the kidneys can produce and how much protein and electrolytes are released into the urine each day.
Estimation of creatinine clearance
Estimating creatinine clearance helps compare the amount of creatinine in a 24-hour urine sample with that in blood samples to determine how much waste the kidneys are filtering each minute.
Albumin in urine (Microalbuminuria)
The microalbuminuria test is a sensitive diagnostic test that can detect small amounts of albumin protein in the urine. People at risk for kidney disease, including those with high blood pressure or metabolic disorders such as diabetes, may benefit from this test.
What does a nephrologist treat?
The competence of a nephrologist includes the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of many diseases. Below we provide a small list of problems that a nephrologist treats. What does a nephrologist treat?
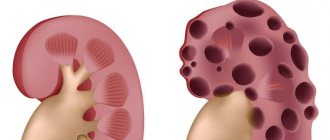
- Pyelonephritis (acute/chronic) – inflammation of the kidneys, which has a bacterial etiology, is characterized by damage to the calyces, pelvis and parenchyma;
- Glomerulonephritis (acute/chronic), also called glomerular nephritis. Characterized by inflammation of the glomeruli;
- Diabetic, urate nephropathy. In general, nephropathy includes many pathological processes characterized by bilateral kidney damage and varying degrees of failure;
- Partial/absolute inability of the kidneys to secrete/form urine;
- Kidney amyloidosis is a disease in which the functioning of these organs is disrupted due to metabolic disorders, in connection with which a specific substance (amyloid) is formed;
- Interstitial nephritis, lupus;
- Toxic damage to paired organs of the urinary system due to medications;
- Kidney damage due to vasculitis;
- Vascular nephropathies;
- Urolithiasis, etc.;
What does a nephrologist treat in children:
- Children's glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis;
- Tubolopathies are a group of diseases characterized by impaired functioning of the renal tubules;
- Familial nephropathies;
- Urinary incontinence (enuresis);
- Kidney dysplasia is a pathological development of the genitourinary system in newborns, characterized by a reduced size of one or two kidneys at once and the phenomena arising from this pathology;
- Abnormal pathologies of the urinary system;
- Hemolytic-uremic syndrome is a combination of renal failure (acute) with thrombocytopenia and hemolytic anemia;
- Nephritis against the background of hemorrhagic vasculitis;
- Dysmetabolic nephropathy is a group of diseases caused by metabolic disorders;
Complications
In the absence of timely consultation with a doctor, complications often develop. For example, kidney failure.
The mechanism of its formation is different. First, swelling of the kidney substance occurs. After which it shrinks and ceases to function properly. This leads to disruption of the excretion of urine and metabolic products.
Against this background, deficiency develops. It is accompanied by a general deterioration of the condition, nausea, vomiting, and lack of urine. Without medical help, this condition will lead to irreversible consequences, including removal of the affected kidney.
With urolithiasis, a kidney blockage by a stone is possible. Proper outflow of urine does not occur, pressure in the kidney increases, and tissue compression develops from the inside. Impaired blood flow leads to ischemia and tissue death.
Treatment of complications in nephrology is long and expensive. These are regular hemodialysis procedures or a donor kidney transplant.
When to see a nephrologist
Regular visits to a nephrologist are provided for persons who have suffered from the following diseases:
- Impaired urine outflow, accompanied by acute pain;
- Destabilization of kidney function;
- Inflammation of the paired bean-shaped organ;
- Infections of the urinary system;
If you have the following symptoms, you should visit a nephrologist as soon as possible.
- Pain during the natural process of urination;
- Producing an excessively large volume of urine during urination (polyuria);
- Problems with urination, cessation of urine output (anuria);
- Acquisition of unnatural color in urine, turbidity;
- Detection of blood clots, blood, mucus in the urine;
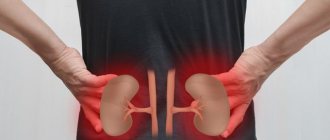
- Pain in the lumbar region that does not have any obvious cause. Pain may radiate to the hip joint;
- The appearance of swelling (in particular in women during pregnancy);
- Change in the smell of urine, unpleasant odor of urine;
Symptoms of kidney disease
- Pain in the lower back and side (sharp or dull, constant or worsened by physical activity, light tapping on the back and ribs);
- change in urine color;
- strong smell of urine;
- the appearance of blood in the urine;
- cloudiness of the urine, the appearance of sediment and sand in it when standing;
- pain and stinging when urinating;
- swelling of the face and other parts of the body, most pronounced in the morning;
- increasing weakness, shortness of breath, increased blood pressure, dry mouth, itchy skin;
- high blood pressure, difficult to correct with antihypertensive drugs;
- a decrease in the amount of urine excreted by a third of the usual daily norm when drinking the same amount of liquid;
- a sharp increase in the amount of urine excreted, its discoloration.
The appearance of one or more symptoms is a reason to contact a nephrologist.
How to prepare for an appointment with a nephrologist
When visiting this specialist, it is advisable to take a medical card with you, since the doctor will certainly ask various questions, and the presence of a medical card will allow the nephrologist to collect more information about the patient. In addition, you should first give urine and blood (OAM and UAC), and take the results of these tests with you. You should also measure your blood pressure for several days and, upon admission, provide complete information about the studies performed.
Preparing for an appointment with a nephrologist is as follows:
- It is necessary to reduce fluid intake the day before the appointment with the nephrologist;
- Smoking should be avoided ½ day before the medical appointment;
- The day before your medical appointment, you must completely avoid drinking alcohol;
- ½ day before your appointment with a nephrologist, it is not advisable to eat a lot of food;
- A woman needs to remember all the nuances of pregnancy, since the nephrologist will be interested in this;
Instrumental diagnostic methods in nephrology
Nephrologists use several types of imaging techniques to diagnose, monitor, and treat kidney disease. These procedures include:
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound)
An ultrasound uses sound waves to create a picture of the kidneys. This diagnostic test helps detect changes in the size or position of the kidneys, as well as the presence of tumors and other abnormal growths such as cysts or kidney stones.
CT scan
A CT scan uses X-rays to create a picture of the kidneys, sometimes with the help of intravenous contrast dye. However, contrast dyes may cause intolerance in people with kidney disease.
Biopsy
A biopsy involves inserting a thin needle that has a cutting edge to take small samples of kidney tissue that the doctor will examine. Indications for biopsy:
- kidney damage assessment
- determination of the disease process
- understand the complications of transplantation
Field of activity
The main objects that a nephrologist deals with are the kidneys and the organs adjacent to them anatomically or functionally: the ureters, bladder and urethra.
The activities of nephrologists are divided into the following areas:
- General nephrologist – deals with acute or chronic diseases.
- Nephrologist-urologist – examines kidney diseases associated with pathologies of the urogenital tract. This specialization is quite rare and, as a rule, occurs only in large specialized centers.
- Pediatric nephrologist – the structure and physiology of a child’s body differs from an adult’s, so this specialist has the necessary knowledge about the age-related characteristics of the kidneys.
- Nephrologist surgeon - specializes in cases requiring urgent or planned surgical intervention to preserve the health and life of the patient.
How is the appointment going?
During the appointment, the nephrologist listens to the patient’s complaints and examines his skin for the presence of swelling and pallor, which accompany many kidney diseases. Tapping of the lumbar region is performed to identify pain in this area. Based on the examination results, the following tests may be needed:
- urine analysis (general, according to Zimnitsky, according to Nechiporenko, Volhard and Reberg-Tareev test);
- Ultrasound;
- angiography;
- biopsy;
- MRI.
After clarification of the diagnosis, treatment is prescribed. In the most difficult cases, an operation is needed that can return the patient to a full life.
The cost of an initial appointment with a doctor starts from 1200 rubles. and reaches 16,000 rubles. depending on the diagnostic equipment at the place of consultation or with the possibility of visiting your home.
An appointment with a nephrologist cannot be postponed, since normal kidney function is associated with the functioning of the entire body and is the key to its normal functioning, and sometimes to the patient’s life.
Consultations with a doctor online Taking care of your health is a life priority for everyone. Communicate with doctors online and receive qualified assistance without leaving your home. Try it Please note! The information on this page is provided for informational purposes only. To prescribe treatment, you must consult a doctor.