Iodine deficiency is a disorder caused by a lack of iodine in the human body. Although iodine is present in the human body in very small quantities, it cannot be avoided. Modern science knows the only function of iodine in the body: it participates in the synthesis of thyroid hormones. With a lack of iodine, this function is impaired. There may be an enlargement of the thyroid gland (goiter formation). In regions characterized by iodine deficiency, such manifestations of iodine deficiency as hypothyroidism, cretinism, decreased fertility, increased infant mortality and a relatively high number of children with mental retardation are also detected.
Causes of iodine deficiency
Iodine enters the human body mainly from food. Iodine is also contained in some medications.
If the food you eat does not contain iodine, then the body simply has nowhere to take it from. The main sources of iodine are sea fish and seaweed. Iodine is present in extremely small quantities in grain crops. If the traditional diet of residents of any region does not include fish and seafood, then their risk of developing iodine deficiency is quite high. Eastern Europe is one of these regions.
To compensate for iodine deficiency, iodized salt is sold in the Russian Federation. Salt was chosen as a carrier of iodine because its consumption is uniform across all socioeconomic classes and does not depend on the time of year. Iodine can be added to chicken feed, and then it will be contained in egg yolks, or in feed for dairy cows, and then it can be obtained by eating milk and dairy products.
Lack of iodine in the body: symptoms and prevention.
IODINE deficiency in the body: SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTION.
For the healthy functioning of the body, it is necessary to constantly maintain a balance of active substances - vitamins and minerals. One of them is iodine.
Iodine is a necessary element for the synthesis of thyroid hormones, which are responsible for the most important processes occurring in our body. If there is not enough iodine in food, almost all organs suffer. Iodine plays a vital role in the normal functioning of the thyroid gland.
Symptoms of iodine deficiency appear the same in both men and women. However, there are some peculiarities.
Signs of iodine deficiency in children. In a growing body, the need for iodine increases. Children who are deficient in this microelement often suffer from colds, their appetite is reduced, they quickly get tired from physical activity, and their school performance is poor. Iodine deficiency in children most often occurs hidden. An increase in the size of the thyroid gland and the development of a goiter indicate that the child’s body has long been experiencing iodine deficiency.
With the development of severe hypothyroidism due to iodine deficiency, the child begins to lag behind in physical, mental and mental development, and in the most severe cases, cretinism develops. If the signs described above appear, you should consult a doctor. The first symptoms of iodine deficiency are nonspecific, so it is difficult to determine the true cause of deterioration in health on your own.
External signs of iodine deficiency. As a rule, women strictly monitor their appearance. Therefore, they immediately notice such unpleasant changes as increased hair loss, brittle nails, aging skin, excessive dryness and flaking. All this may indicate a lack of iodine in the body, especially if a woman carefully takes care of herself. If iodine deficiency is confirmed, external influences are useless.
Constant fatigue from iodine deficiency. If, even if you have quality rest and a rational daily routine, you constantly feel tired, depressed, want to lie down, and are unstable to stress, then it is likely that you have an iodine deficiency. Ignoring these symptoms and trying to recover with strong tea and coffee, you can only make the situation worse. If iodine deficiency is not corrected, these unpleasant phenomena will take on more severe forms. They will develop into severe nervousness, irritability or even depression due to chronic fatigue. All this will negatively affect both your efficiency in terms of work and your appearance.
Iodine and menstrual irregularities. Some signs of iodine deficiency in the body are unique to women. So, irregular menstruation indicates a problem. As a rule, this kind of problem begins against the background of other symptoms.
Infertility due to iodine deficiency. If you have been trying to conceive a child for a long time, but are constantly failing, then get tested for iodine deficiency as soon as possible. If this suspicion is confirmed, you will be able to solve the problem and prepare for conception.
Intestinal problems due to iodine deficiency. When there is a lack of iodine in a woman’s body, the symptoms are often accompanied by intestinal upset. It manifests itself in the form of constipation, which is difficult to cope with using traditional methods.
Decreased brain activity due to iodine deficiency.
Iodine deficiency also affects mental abilities. When it occurs, it is extremely difficult for a woman to concentrate on work, and sometimes she is unable to solve complex problems. At the same time, memory deteriorates and reaction decreases.
If you find several signs of iodine deficiency in your body, the best course of action would be to consult a doctor. Only a specialist can confirm or refute your guesses, and also prescribe the most effective drug.
To avoid unpleasant symptoms of iodine deficiency, you should consider your daily diet.
It should contain in sufficient quantities: seafood and sea fish - they are the richest sources of this microelement; river fish, but it is worth considering that it contains less iodine than sea fish; beef; chicken or quail eggs; milk and dairy products; mushrooms; cereals; vegetables and herbs - potatoes, garlic, beets, radishes, tomatoes, eggplants, spinach, green onions, sorrel; fruits - oranges, lemons, melons, pineapples, persimmons. You can also use iodized salt when cooking. But you need to understand that during heat treatment a significant part of the beneficial substance is lost.
Now there are other products artificially fortified with iodine - mineral water, eggs, baby food, etc.
Rest in ecologically clean areas. A person receives iodine not only from foods, but also from air and water. Therefore, it is so important to regularly relax at sea or in a region whose soil is rich in this microelement. As a result, during your vacation you will be able to replenish your iodine deficiency without making any effort.
Iodine and preparation for pregnancy. A lack of iodine in a woman’s body, the symptoms of which you now know, is especially undesirable during the period of preparation for conception. Therefore, it is advisable to plan your pregnancy in advance; the exact plan of action should be discussed with your doctor. Signs of iodine deficiency may appear very mild. But it is important to detect them in the early stages to avoid complications. Even if you have vague suspicions, you can immediately take preventive measures by adjusting your diet. If there are obvious symptoms of iodine deficiency, you should not act at random; it is better to immediately consult a specialist. Delays in general development and defects in the organization of the nervous system are the possible consequences of iodine deficiency for a baby. And the expectant mother herself will suffer if there is not enough iodine in her body. In particular, high blood pressure will accompany pregnancy. Fortunately, not so often, but there are cases where a lack of iodine leads to the development of cretinism in a child.
How much iodine does a woman's body need during pregnancy? The daily requirement for pregnant women is 250-300 mcg of iodine.
Even if the expectant mother eats foods rich in iodine every day, it is rarely possible to completely replenish the reserves of this element in the body through food alone. The second half of pregnancy automatically, so to speak, increases the body's need for iodine. Oysters and squid, shrimp and scallops, mussels and crabs in small quantities may well be present in a pregnant woman’s diet. Why small? Still, for our table these are still exotic products; the body must learn to perceive them correctly. And the expectant mother does not need to experiment on herself, so you should not overeat with these seafood. Therefore, in addition to foods high in iodine, a pregnant woman must take special medications. They are prescribed by an endocrinologist, and every expectant mother should attend an appointment. In most cases, iodine preparations are used in combination with other microelements and vitamins. Perhaps the most common prescription is the drug Iodomarin 200 mcg/1 tab.
There may be certain contraindications to this prescription, so you cannot prescribe preventive treatment for yourself.
Iodomarin is prescribed to many expectant mothers; your task is not to skip taking the drug and to strictly follow the dosage. If the doctor has not prescribed anything else, there is no need for amateur activities. You can ask your doctor about this or that iodine-containing product, and he will tell you how and in what quantities the expectant mother can consume this product.
The consequences of iodine deficiency during pregnancy can be very serious. Among them: miscarriage in the first trimester, frozen pregnancy, impaired metabolism of the pregnant woman (excess weight), intrauterine growth retardation, late toxicosis, weakness of labor. A baby who does not receive enough iodine during uterine development may have disturbances in the functioning of the brain, disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid gland, excess weight of the fetus, as well as delayed sexual development of the child. Since most regions of the country are considered iodine deficient, all expectant mothers need to worry about iodine reserves in the body even before pregnancy.
When prescribing medications with iodine, you cannot refuse to take them. Any problematic issues regarding the supply of iodine in the body can be resolved by an endocrinologist, whom a pregnant woman should contact at least once in 9 months.
Symptoms of iodine deficiency
The first sign of iodine deficiency is a uniform enlargement of the thyroid gland (subsequently a multinodular goiter is formed). Severe iodine deficiency leads to hypothyroidism (decreased thyroid function).
The most severe manifestation of iodine deficiency is cretinism. This condition develops as a result of iodine deficiency during fetal development and is manifested by mental retardation, gait disturbance, deafness, and short stature.
Iodine deficiency is the most common potentially preventable cause of mental retardation in the world. Reduced speech skills and memory in children can be observed even in cases where the results of a functional examination of the thyroid gland remain normal.
Symptoms indicating an enlarged thyroid gland
An enlarged thyroid gland puts pressure on surrounding tissues. As a result, symptoms such as a feeling of a lump in the throat, hoarseness, shortness of breath, cough, and difficulty swallowing may be observed.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is manifested by abnormal fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, constipation or depression. Symptoms may also include dry skin, swelling around the eyes, and changes in deep tendon reflexes.
Where to buy iodine
Iodine is an essential substance for the proper functioning of many processes in a woman’s body. Unfortunately, in our climate there is no way to obtain iodine from the air or fresh seafood, so it is important to monitor its level yourself. In our online store you can find a wide range of high-quality supplements and vitamin complexes for you and your family, get advice and choose exactly what you need!
Thank you for reading the article and wish you good health! Sincerely, )
Perhaps you will
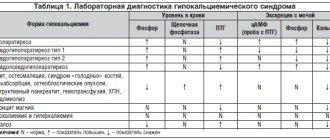
Methods for diagnosing iodine deficiency
Testing to detect iodine deficiency includes a thyroid test, urine iodine levels, blood thyroglobulin levels, and dietary assessment. It is very important for pregnant women and school-age children to be examined promptly, since the risk of iodine deficiency is especially high for them.
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland
An enlarged thyroid gland, determined by ultrasound, may be due to iodine deficiency. If mass examinations reveal an enlarged thyroid gland in 5% of the population of a particular area, there is a possibility that the cause of this is iodine deficiency. However, in a single case, an enlarged thyroid gland in itself is not enough to draw a conclusion about iodine deficiency.
More information about the diagnostic method
Determination of iodine in urine
The kidneys excrete 90% of the iodine obtained from food. Thus, the best way to detect iodine deficiency is to determine the average iodine content in 24-hour urine. An iodine content of 50 - 100 mKg per liter of urine indicates a moderate degree of iodine deficiency, 20 - 49 mKg - a moderate degree of severity, and an iodine concentration of less than 20 mKg per liter of urine indicates severe iodine deficiency.
More information about the diagnostic method
Blood test for thyroglobulin
Thyroglobulin is a protein containing iodine. Produced by the follicles of the thyroid gland. The test that determines the level of thyroglobulin in the blood is a hormone test.
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Iodine during pregnancy
Pregnant women need more iodine in their diet. Iodine is essential for proper brain development in babies. Research has shown that children born to women who do not get enough iodine during pregnancy are more likely to have intellectual delays and lower IQ than children born to mothers who get enough iodine during pregnancy.
Women who breastfeed also have higher iodine requirements because they supply the element to their babies through breast milk . A mother who receives a sufficient amount of it can fully pass it on to her child, which has an extremely beneficial effect on the proper development of the baby’s brain.
The recommended daily intake of iodine during pregnancy is 220 mcg . By comparison, the recommended amount for non-pregnant women is 150 mcg per day.
The recommended daily amount of iodine during breastfeeding is 290 mcg . The iodine that a mother obtains from food and supplements is passed through breast milk to her infant. This is a critical period of brain development, so babies need 110 mcg per day until they reach 6 months of age.
The same benefits of iodine for brain development in developing babies and toddlers extend into early childhood. Children who do not get enough iodine are at increased risk of mental retardation.
What can iodine deficiency lead to?
Iodine deficiency is especially harmful to pregnant women; iodine plays a key role in the development of the fetus and the cognitive functions of the infant. In the first four months of development, the fetus does not yet have a thyroid gland separate from the mother, so the mother must provide the child with iodine. Iodine deficiency can lead to the development of serious diseases: problems with vision, hearing, paralysis, cretinism and mental disability. True, we are talking about a high degree of iodine deficiency, while residents of Russia are characterized by moderate iodine deficiency, although it is dangerous.