Ringworm (microsporia) is a disease manifested as a fungal infection of the skin, nail plates and hair follicles. The pathogen is a mold fungus of the genus Microsporum. Its colonies form in keratinized substrates. Microsporia remains a relatively common disease - dermatologists identify 60-75 cases for every hundred thousand Moscow residents. The pathology has a pronounced seasonality. The peak incidence occurs at the end of summer and beginning of autumn - the period of breeding of offspring in cats and other animals.
What is ringworm?
Ringworm is an infectious skin disease caused by the parasitic fungi Microsporum canis and Trichophyton tonsurans, it is part of the group of ringworms that primarily affect the skin, hair and nails. This is an infectious dermatological pathology caused by dermatophyte fungi. It is also called dermatomycosis, scab, micro- and dermatophytosis.
Doctors distinguish several types of ringworm, depending on the location, nature of the course and the causative agent.
The main types of the disease are:
- chronic or ringworm of smooth skin;
- surface;
- ringworm of the nail plate;
- infiltrative-suppurative.
Since ringworm is caused by two types of fungi, in medicine it is diagnosed as microsporia and trichophytosis. These fungi have persistent pathogenicity, pronounced virulence and often cause acute diseases with varied clinical manifestations.
A disease caused by fungi of the genus Microsporum canis is microsporia. Depending on the location, there is microsporia of smooth skin and microsporia of the scalp.
Trichophytosis is caused by the activity of the dermatophyte Trichophyton tonsurans, which, through the anthroponotic route of infection, causes inflammation of the scalp and smooth skin, and through the zootroponotic route, inflammation in the deep layers of the dermis, accompanied by suppuration.
The presence of fungal spores does not always provoke damage to the skin and its appendages. The transition of the fungus from an inactive state to a pathogenic state is facilitated by metabolic and endocrine disorders, immune diseases, hypovitaminosis or vegetative-vascular dystonia. This increase in the pathogenicity of dermatophytes provokes an exacerbation of inflammatory processes, the spread of the fungus through the blood and lymph flow.
The disease is weakly expressed during the development of a latent infection and when localized in previously affected areas, and the high virulence of the fungus is formed during a relapse, gradually decreasing during the course of the infection.
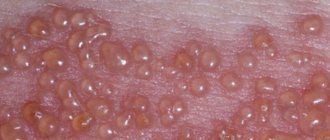
Symptoms of ringworm: At the end of the incubation period, itchy ring-shaped spots of red-pink color appear on the skin, on the surface of which bubbles appear, after which a crust and peeling remain. The hair at the site of the lesion breaks and falls out.
Normally, the immune system is able to cope with the pathogen and prevent its activity, but there are a number of factors that increase the risk of ringworm, namely:
- skin microtraumas;
- lack of vitamins and microelements;
- prolonged contact with the source of infection;
- high humidity and air temperature;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases, etc.
In a situation where there is an adult or child with lichen at home, it is necessary to take preventive measures to reduce the likelihood of its spread, namely:
- use separate towels and bed linen;
- wash your hands thoroughly with soap, especially if you touched the patient’s things;
- use gloves when touching areas of disease;
- undergo examination and take tests to identify pathogens, etc.
The main method for diagnosing ringworm is the use of a Wood's lamp, under the light of which the affected areas acquire a characteristic greenish glow. Microscopic examination and culture of skin and hair scales are effective to confirm the diagnosis.
Timely diagnosis and a properly selected treatment regimen can effectively eliminate ringworm in children and adults, preventing its spread. The pathology is prone to relapse, since the presence of spores of viable fungi can cause repeated damage. It is extremely important to complete the course of treatment and follow all doctor’s recommendations.
Signs and clinical forms
The symptoms of trichophytosis are quite recognizable. The main one is the appearance of reddish spots on the body, sharply demarcated from the surface of healthy skin. The spots may be round or shapeless. Color varies from pale pink to red-violet. The surface can be smooth or rough. Often, a slight pityriasis-like peeling forms in the center of the spot, which disappears closer to the edges. The boundaries of the spot can be blurred or pronounced. In the second case, blisters or purulent hemorrhagic crusts are clearly visible.
The mycelium growth zone can be in the same plane as the skin, 2-3 mm above it. When the deep layers of the dermis are involved in the inflammatory process, a spherical “bump” appears at the site of the spot. It protrudes over healthy skin. There may be discharge on the surface:
- bloody;
- purulent;
- hemorrhagic.
The lump consists of an inflammatory infiltrate. As the disease progresses, pus accumulates in the skin.
Trichophytosis is characterized by a particularly recognizable symptom - the presence of “stumps” over the entire surface of fungal spots. “Stumps” are broken hairs that have been infected by a fungus. The appendages break off 2-3 mm from the skin, and their remains are clearly visible to the naked eye. Sometimes the “stumps” become covered with a grayish coating.
The second scenario is lysis of the hair sheath by the fungus and destruction of the hair directly near the hair follicle. In this case, there are no stumps, but black dots are visible on the skin - fungus-filled passages that remain from lost hair.
How is ringworm transmitted?
Ringworm is transmitted in two ways:
- from a sick animal – zoonotic with an incubation period of one week;
- from an infected person – anthroponotic with an incubation period of up to 6 weeks.
Children are at risk because they most often come into contact with the carriers of the pathogens of this disease - cats and dogs. Children's skin is characterized by low density of the stratum corneum and weak protective properties of the water-lipid mantle. The stratum corneum prevents the penetration of the fungus into the layers of the skin, since its spores are located between the horny scales, and the water-lipid mantle forms a barrier to the penetration of pathogens.
The infection is also transmitted by non-compliance with personal hygiene standards and the use of other people's personal belongings containing fungal spores (hats, combs, bed linen, etc.).
Reasons for development
The main causes of ringworm are contact with the pathogen:
- A child aged 4–11 years whose sweat reaction is predominantly alkaline.
- A child or adult with reduced immunity, the presence of scratches, scabs, microtraumas that can become infected.
Most often the carrier is an animal, less often a person. Infection also occurs through objects or personal belongings on which infected hairs, hairs or skin scales remain. Infection is possible through undisinfected hairdressing tools, through soil on which the causative agent of the disease can persist for up to 3 months, during processing of hay. According to statistics, up to 70–80% of cases of the disease occur as a result of contact with stray young cats and kittens.
How does ringworm begin?
Favorable conditions contribute to the introduction and reproduction of a pathogenic fungus in the skin, triggering the infectious process. In the initial stages, this period is asymptomatic. After which the development of the pathology acquires clinical manifestations, the signs of which depend on the stage of the pathology.
The stages of the infectious process during the development of ringworm are:
- incubation period;
- period of mushroom growth;
- refractory stage (period of insensitivity, rest);
- regression.
In the skin, the fungus forms branched mycelium, which gradually invades new areas of the skin, while old lesions become the location of its spores. This period of fungal growth is determined by the rapid increase in the colony of the pathogen, active division of skin cells and the high rate of exfoliation of the affected epidermis.
Since most often the growth of the colony outstrips the rate of change of the stratum corneum, the infectious process spreads. An intense immune reaction (inflammation) in the lesion is displayed in the form of a red ring, which, in the chronic course of mycosis, becomes the permanent residence of the pathogen.
Diagnostics
It is not difficult to make a primary diagnosis if you know what ringworm looks like. To clarify the diagnosis use:
- analysis of clinical data;
- results of luminescent analysis;
- microscopic studies;
- sowing material.
In some cases, the source of infection is difficult to determine, since the incubation period ranges from 2 to 45 days. Symptoms may appear on the head, neck, arms, legs, including the palms, soles of the feet, groin areas and folds. Fungal infection causes itching, discomfort in the area of inflammation, and creates psychological discomfort.
What does ringworm look like?
Clinical manifestations of ringworm depend on the type of pathogen, course and stage of the disease. Dermatophytes secrete enzymes and toxins that destroy keratin protein (they feed on it), so the severity of symptoms directly depends on the ability of fungi to produce these substances.
Common symptoms of ringworm on the scalp are:
- hair thinning;
- the appearance of localized peeling of the skin;
- redness of the epidermis;
- hair breaking off at the root;
- the appearance of small bubbles with cloudy contents along the edges of bald patches, after opening which yellow crusts form.
Ringworm of smooth skin includes the following symptoms:
- pronounced itching;
- the appearance of round red spots;
- light epidermis at the site of damage, surrounded by gray scales;
- the edges of the damaged area consist of pink-red bubbles;
- growth of the lesion in diameter.
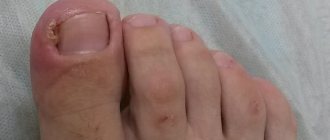
The chronic form of the disease is accompanied by the presence of microscopic blisters on the affected areas, the formation of scars after their opening and severe itching. In a situation where the site of the lesion is the nail plate, its separation, discoloration and thickening are observed.
Ringworm of the infiltrative-suppurative form is characterized by the appearance of large bright red spots up to 10 cm in diameter, the outer surface of which is lumpy and uneven, and purulent follicles form along the edges. Pain, swelling and hyperemia of the affected areas are also observed.
The appearance of the first signs of the disease requires a mandatory visit to a dermatologist. The lack of qualified treatment can lead to the rapid spread of infection throughout the body and cause a number of complications: tissue scarring, death of hair follicles, allergic reactions and the addition of a secondary infection.
How is ringworm treated?
In each case, treatment for ringworm should be selected individually, since its composition and duration have their own specifics and are determined by the type, location and stage of the pathology.
Only prescriptions from a dermatologist are effective; they take into account the current clinical picture, the characteristics of the patient’s physical health and his age.
Therapy is aimed not only at relieving the symptoms of the pathology, but also at inactivating the pathogen. The chronic form of the disease also provides support for the immune system, normalization of metabolism and hormonal levels.
The following groups of drugs are used to treat ringworm:
- systemic and local antimycotics;
- antiseptic solutions;
- multivitamin complexes.
How long does it take to treat ringworm?
The treatment process for ringworm is lengthy, usually taking at least six weeks, with systemic therapy lasting mainly 15-25 days.
The effectiveness of therapy is assessed using laboratory tests. In a situation where tests indicate a significant decrease in the number of fungal spores after 2 weeks of a medication course, it is necessary to continue the chosen treatment. In some cases, fungal shedding can last for several months.
After the signs of pathology disappear, you need to scrape the epidermis three times in previously damaged areas:
- immediately after completion of therapy;
- 7 days after therapy;
- after 2-3 months.
The result of therapy is considered successful if all three tests show negative results.
How to treat ringworm in children?
Treatment of ringworm in a child is the responsibility of a pediatric dermatologist, since the characteristics of the child’s body require special doses and composition of medications.
Hygiene and child care are also important elements of pathology therapy:
- boiling and ironing clothes in contact with affected areas of the skin;
- treating household surfaces with disinfectants to prevent the spread of spores;
- frequent change of bed linen;
- washing in the shower rather than the bath, etc.
Can I go to work or school with ringworm?
The presence of this diagnosis requires isolation of the patient from the team for at least two weeks. In schools and other children's institutions, it is mandatory to notify parents for timely detection of the disease in other children.
The disappearance of ringworm symptoms and 3 negative tests for the presence of fungus are a reason to return to school or work.
If a dermatomycosis infection has been detected in a team, then to prevent pathology, you can use antifungal shampoos for some time, carry out wet cleaning with the addition of antiseptic solutions, and strictly observe personal hygiene.
- Treatment of lichen in Kharkov;
- treatment of lichen in Uzhgorod;
- treatment of deprivation in Sumy;
- treatment of lichen in Poltava;
- treatment of lichen in Odessa;
- treatment of deprivation in Nikolaev;
- treatment of lichen in Mariupol;
- treatment of deprivation in the Dnieper.
3
1
0
Article rating:
3.8 out of 5 based on 5 ratings
Author: Mangusheva Victoria Yurievna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist. Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category. Work experience more than 10 years.
Preventive measures
Prevention of ringworm is based on regular medical examinations of children attending preschool educational institutions. Parents should talk to their children about the inadmissibility of contact with stray animals. An important preventive measure is compliance with personal hygiene rules by patients of all age groups.
When purchasing pets, you must visit a veterinarian. The doctor will examine the cat or dog and give recommendations on how to eliminate any health problems with the pet. Following your veterinarian's advice will help prevent microscopic outbreaks within your family.