Instructions for use of URSOCAPS
Hepatoprotector, a drug that promotes the dissolution of cholesterol gallstones. It has hepatoprotective, choleretic, cholelitholytic, hypocholesterolemic, hypolipidemic and some immunomodulatory effects.
It is embedded in the hepatocyte membrane, stabilizes its structure and protects the hepatocyte from the damaging effects of bile salts, thus reducing the cytotoxic effect. In case of cholestasis, it activates calcium-dependent alpha protease and stimulates exocytosis, reduces the concentration of toxic bile acids (including chenodeoxycholic, lithocholic, deoxycholic), the content of which is increased in patients with chronic liver diseases.
Possessing high polarity, ursodeoxycholic acid forms non-toxic mixed micelles with apolar (toxic) bile acids, which reduces the ability of gastric refluxate to damage cell membranes in biliary reflux gastritis and reflux esophagitis. In addition, ursodeoxycholic acid forms double molecules that can be included in cell membranes (hepatocytes, cholangiocytes, epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract), stabilize them and make them immune to the action of cytotoxic micelles - a cytoprotective, hepatoprotective effect.
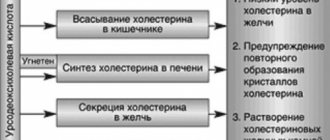
Reduces the saturation of bile with cholesterol by inhibiting its absorption in the intestine, suppressing synthesis in the liver and reducing secretion into bile; increases the solubility of cholesterol in bile, forming liquid crystals with it; reduces the lithogenic index of bile. The result is the dissolution of cholesterol gallstones (a consequence of a change in the ratio of cholesterol/bile acids in bile) and the prevention of the formation of new stones (the result of a decrease in cholesterol content in bile) - a litholytic effect.
Induces choleresis, rich in bicarbonates, which leads to an increase in the passage of bile and stimulates the excretion of toxic bile acids through the intestines, which contributes to the resolution of intrahepatic cholestasis - anticholestatic effect.
The immunomodulatory effect is due to inhibition of the expression of HLA antigens on the membranes of hepatocytes and cholangiocytes, a decrease in the activity of immunocompetent immunoglobulins (primarily IgM), normalization of the natural killer activity of lymphocytes, an effect on the formation of interleukin-2, and a decrease in the number of eosinophils.
Reliably delays the progression of fibrosis in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis, cystic fibrosis and alcoholic steatohepatitis - antifibrolytic effect. Reduces the risk of developing varicose veins of the esophagus.
Ursodeoxycholic acid slows down the processes of premature aging and cell death (including hepatocytes, cholangiocytes) - anti-apoptotic effect.
Inhibits the growth of colorectal cancer cells (antitumor effect against colon cancer).
Ursocaps - effective treatment of gallstones
Pharmacodynamics
Ursodeoxycholic acid is a natural minor component of bile acids. Oral administration of ursodeoxycholic acid leads to a dose-dependent increase in the content of this fraction in the composition of bile acids.
When using ursodeoxycholic acid in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis, a decrease in cholesterol levels is observed, which is due to improved cholestasis and changes in cholesterol metabolism. Common to the processes may be changes in the composition of endogenous bile acids when taking the drug.
Pharmacokinetics
Ursodeoxycholic acid accounts for up to 5% of the total composition of bile acids. When administered orally, most of ursodeoxycholic acid is absorbed by passive diffusion; such absorption is incomplete. After absorption, ursodeoxycholic acid is extracted in the liver by approximately 50% in the absence of liver pathology. The more severe the liver disease, the lower this indicator. In the liver, ursodeoxycholic acid is conjugated with glycine or taurine and then secreted into bile. Ursodeoxycholic acid conjugates are absorbed in the small intestine through passive and active mechanisms. Conjugates can be broken down in the small intestine by enzymes. Free ursodeoxycholic acid, which is formed again, can be absorbed and conjugated in the liver. Unutilized ursodeoxycholic acid passes to the colon, where it is primarily 7-dehydroxylated to lithocholic acid. Some of the ursodeoxycholic acid is epimerized to chenodiol via a 7-hydroxy intermediate. Chenodiol also undergoes 7-dehydroxylation to form lithocholic acid. These metabolites are poorly soluble and are excreted in the feces. A small amount of lithocholic acid is reabsorbed and conjugated in the liver with glycine or taurine and sulfated at position 3. Sulfated derivatives of lithocholic acid and its conjugates are excreted in the bile and then excreted in the feces.
When used chronically in animals, lithocholic acid causes cholestatic liver damage and can lead to the death of animals that lack the process of formation of sulfate conjugates. Ursodeoxycholic acid undergoes 7-dehydroxylation more slowly than chenodiol. When comparing equimolar amounts of ursodeoxycholic acid and chenodiol, the equilibrium level of lithocholic acid in the bile acid mixture is lower when ursodeoxycholic acid is used. In humans and primates, lithocholic acid can be sulfated. Although cholestatic liver damage does not develop in humans with the use of ursodeoxycholic acid, it should be borne in mind that individual differences in the degree of sulfation of lithocholic acid are possible, although it is possible that deficient states in the ability to sulfate lithocholic acid are in fact extremely rare and have practically not been detected , despite long experience in the clinical use of ursodeoxycholic acid.
In healthy people, approximately 70% of unconjugated ursodeoxycholic acid is bound to plasma proteins. There is no information on the degree of binding of conjugated ursodeoxycholic acid to plasma proteins. The volume of distribution for ursodeoxycholic acid has not been established but is expected to be small given that this drug is concentrated primarily in the bile and small intestine.
Ursodeoxycholic acid is excreted mainly in the feces. When using ursodeoxycholic acid, the level of its excretion in urine increases, although this value remains insignificant (less than 1%) except in cases of severe cholestatic liver damage.
With chronic use of ursodeoxycholic acid, it becomes the main component of bile acids; at a dose of 13-15 mg / kg / day, its share in the total composition of bile acids accounts for up to 30-50%.
The half-life of ursodeoxycholic acid is 3.5-5.8 days.
| Body weight (kg) | Daily dose (mg/kg body weight) | Distribution of drug intake | |||
| First 3 months | Further | ||||
| Morning | Day | Evening | Evening (1 time per day) | ||
| 47-62 | 12-16 | 250 mg | 250 mg | 250 mg | 750 mg |
| 63-78 | 13-16 | 250 mg | 250 mg | 500 mg | 1000 mg |
| 79-93 | 13-16 | 250 mg | 500 mg | 500 mg | 1250 mg |
| 94-109 | 14-16 | 500 mg | 500 mg | 500 mg | 1500 mg |
| more than 110 | 500 mg | 500 mg | 750 mg | 1750 mg | |
Special instructions
In the presence of variceal bleeding, hepatic encephalopathy, ascites, as well as if a liver transplant is necessary, patients should receive appropriate specific treatment.
Use for persons over 65 years of age. No special studies have been conducted. However, given the known data, it is not expected that there will be any problems specific to the elderly that could limit the use of ursodeoxycholic acid.
Monitoring and laboratory data
Monitoring the effectiveness of ursodeoxycholic acid in the treatment of cholestatic liver diseases is based on the analysis of biochemical parameters of cholestasis, as well as identifying signs of liver cytolysis (increased activity of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase), which often accompany the progression of cholestasis.
During the first 3 months of therapy, the physician should monitor liver function parameters AST (SGOT), ALT (SGPT) and γ-GT every 4 weeks, and then every 3 months.
When used to dissolve cholesterol gallstones: to assess the therapeutic effect and for the timely detection of calcification of gallstones, depending on the size of the stone, it is necessary to visualize (using oral cholecystography) the general appearance and type of blockage of the gallbladder in a standing position and lying on the back (ultrasound control ) 6-10 months after the start of treatment.
If the gallbladder cannot be visualized on x-rays or in cases of calcification of stones, impaired contractility of the gallbladder or frequent biliary colic, ursodeoxycholic acid preparations should not be taken.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding period
There is no sufficient data on the use of ursodeoxycholic acid, in particular in the first trimester of pregnancy. Ursodeoxycholic acid should not be taken during pregnancy unless absolutely necessary. Only a doctor can make a decision about this.
Women of reproductive age can be prescribed treatment only with reliable contraception. Before starting treatment, the possibility of pregnancy should be excluded.
It is unknown whether ursodeoxycholic acid passes into breast milk. So, the drug cannot be used during breastfeeding. If it is necessary to use ursodeoxycholic acid, breastfeeding should be discontinued.
Impact on the ability to drive a car, work with equipment
There were no effects on the ability to drive vehicles or operate other machinery.
Interaction with other drugs
Bile acid sequestrants, such as cholestyramine and colestipol, may interfere with the action of ursodeoxycholic acid by reducing the level of absorption of the latter.
Antacids containing aluminum compounds and smectite can interfere with the action of ursodeoxycholic acid also by reducing the level of absorption of the latter.
Ursodeoxycholic acid may enhance the absorption of cyclosporine from the intestine. Therefore, in patients receiving cyclosporine, it is necessary to check the concentration of cyclosporine in the blood and adjust the dose of cyclosporine if necessary.
In some cases, ursodeoxycholic acid may reduce the absorption of ciprofloxacin.
Ursodeoxycholic acid reduces the maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) and area under the curve (AUC) of the calcium antagonist nitrendipine. Based on this, as well as from the only report of interaction with the substance dapsone (reduced therapeutic effect) and from in vitro studies, it can be assumed that ursodeoxycholic acid induces the activity of cytochrome P450 3A4, which metabolizes the drug.
Thus, when concomitantly using drugs that are metabolized by this enzyme, caution must be exercised and keep in mind that dosage adjustment may be required.
Side effect
From the gastrointestinal tract:
dyspepsia; noted nausea and abdominal pain, cases of anorexia, esophagitis, peptic ulcer; diarrhea, pasty stool, severe abdominal pain localized in the right hypochondrium.
From the liver and gallbladder:
When treated with ursodeoxycholic acid, calcification of gallstones may occur.
In the treatment of advanced stages of primary biliary cirrhosis
decompensation of liver cirrhosis may occur, which partially regressed after cessation of treatment.
From the skin:
cases of itching and skin rashes.
Metabolic disorders:
cases of increased creatinine and increased blood glucose.
General violation:
asthenia, chest pain and peripheral edema.
From the cardiovascular system:
increased blood pressure.
From the hematopoietic system:
cases of leukopenia.
Overdose
In case of overdose, diarrhea may occur. In general, overdose is unlikely because the absorption of ursodeoxycholic acid decreases with increasing doses and it is mainly excreted in the feces.
If diarrhea occurs, the dose should be reduced, and if diarrhea continues, ursodeoxycholic acid should be discontinued. The effects of diarrhea should be treated symptomatically while maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance.
»
Ursocaps capsules 250 mg No. 10x5
Name
Ursocaps caps. 250 mg in container pack No. 10x5
Description
Soft gelatin capsules, oval in shape with a seam, elastic, light brown in color.
Main active ingredient
Release form
Soft gelatin capsules, 10 capsules in a blister pack, 5 blister packs in a pack.
Dosage
250 mg.
Indications for use
— Symptomatic treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) in the absence of signs of decompensation; - dissolution of cholesterol gallstones. Cholesterol stones should not appear as shadows on an x-ray and should not exceed 15 mm in diameter. Despite the presence of stones, the function of the gallbladder should not be impaired; - toxic (including alcoholic, medicinal) liver damage; — cholestatic liver diseases in children; — hepatitis (chronic, active, including atypical forms of chronic autoimmune, chronic and acute viral); - treatment of gastritis with bile reflux.
Directions for use and doses
For various indications for use, the following daily dosage regimens are recommended: For the dissolution of cholesterol gallstones, approximately 10 mg of ursodeoxycholic acid per 1 kg of human body weight: up to 60 kg 2 capsules up to 80 kg 3 capsules up to 100 kg 4 capsules over 100 kg 5 capsules Capsules required Take in the evening, before bed, without chewing and with a small amount of liquid. Capsules should be used regularly. The duration of treatment to dissolve stones is 6-12 months. If the size of the stones does not decrease after 12 months, treatment should not be continued. The success of treatment should be monitored with ultrasound or x-ray examinations every 6 months. At a subsequent examination, you should check whether calcification of the stones has occurred in the interim. If this occurs, treatment should be stopped. For the treatment of gastritis with bile reflux: prescribe one capsule, which is taken daily, in the evening, before bedtime, without chewing and with a small amount of liquid. The treatment period is 10-14 days. In general, the duration of use depends on the course of the disease. For the symptomatic treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC): The daily dose of the drug depends on the patient’s body weight, and varies from 3 to 7 capsules (14±2 mg of ursodeoxycholic acid per 1 kg of body weight). In the first 3 months of treatment with Ursocaps, 250 mg capsules, the drug intake should be divided throughout the day. After liver parameters improve, the daily dose of the drug can be taken once, in the evening. Capsules should be taken without chewing, with a small amount of liquid. It is necessary to observe regular intake. The use of Ursocaps capsules for the treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis may not be limited in time. In rare cases, in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis, clinical symptoms may worsen at the beginning of treatment, for example, itching may become more frequent. In this case, treatment should be continued by taking one Ursocaps capsule daily, then the dosage should be gradually increased (increasing the daily dose by one capsule weekly) until the recommended dosage regimen is achieved again. Chronic liver diseases: in a daily dose of 10 mg/kg to 12-15 mg/kg (2-5 drops) for 4-6 weeks. Toxic and alcoholic liver damage: 10-15 mg/kg/day for 14-21 days.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
There is not enough data on the use of ursodeoxycholic acid, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy. Animal studies have demonstrated evidence of teratogenicity during early pregnancy. Ursocaps capsules should not be used during pregnancy unless absolutely necessary. A decision about this can only be made by a doctor after assessing the benefits/risks. Women of childbearing age should take the drug only if they are using reliable contraception. Before starting treatment, the possibility of pregnancy must be excluded. It is unknown whether ursodeoxycholic acid passes into mother's milk. The drug should not be taken during breastfeeding. If there is a need for treatment with Ursocaps, 250 mg capsules, breastfeeding should be discontinued.
Precautionary measures
In case of cholelithiasis, the effectiveness of treatment is monitored every 6 months. by conducting x-ray and ultrasound examination of the biliary tract in order to prevent relapses of cholelithiasis. — Positive results can be obtained only in the presence of purely cholesterol (X-ray negative) gallstones no larger than 15-20 mm in size, with preserved gallbladder function and patency of the cystic and common bile ducts. With long-term (more than 1 month) treatment, it is necessary to conduct a monthly biochemical blood test to determine the activity of liver transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, gamma-glutamyltransferase and bilirubin (especially in the first 3 months of therapy). If elevated levels persist, the drug should be discontinued. After complete dissolution of the stones, it is recommended to continue use for at least 3 months in order to promote the dissolution of stone remains that are too small to be detected. If within 6-12 months. after the start of therapy, partial dissolution of the stones has not occurred, it is unlikely that the treatment will be effective. The discovery of a non-visualized gallbladder during treatment is evidence that complete dissolution of the stones has not occurred and treatment should be stopped. If the gallbladder cannot be visualized on x-rays or in cases of calcified stones, poor contractility of the gallbladder or frequent attacks of colic, Ursocaps should not be used.
Interaction with other drugs
Cholestyramine, cholesterol and antacids containing aluminum hydroxide bind ursodeoxycholic acid in the intestine, reduce its absorption and weaken its effectiveness. If simultaneous treatment with the above drugs is necessary, it is recommended to use them 2 hours before or after taking Ursocaps. Lipid-lowering drugs (especially clofibrate), estrogens, neomycin, progestins can increase the saturation of bile with cholesterol and reduce the ability of ursodeoxycholic acid to dissolve cholesterol gallstones. Ursocaps may increase the absorption of cyclosporine in the intestine. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor cyclosporine levels and adjust the dose in people taking this drug concomitantly. In some cases, Ursocaps may reduce the absorption of ciprofloxacin. Ursodeoxycholic acid reduces peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) and the area under the concentration-time pharmacokinetic curve (AUG) of nitrendipine, a calcium antagonist. From the interaction report with diaphenylsulfone (reduced therapeutic effect) and in-vitro studies, it can be assumed that ursodeoxycholic acid affects the metabolism of diaphenylsulfone by cytochrome P450 ZA4 enzymes. Therefore, precautions should be taken when coadministering drugs metabolized by this enzyme and adjustments may be necessary.
Contraindications
- hypersensitivity; - X-ray positive (high calcium content) gallstones; - acute inflammatory diseases of the gallbladder, bile ducts and intestines, Crohn's disease; - non-functioning gallbladder; - complete obstruction of the biliary tract; — liver cirrhosis in the stage of decompensation; - severe dysfunction of the kidneys, liver, pancreas; - bile-gastrointestinal fistula; - acute cholecystitis; - acute cholangitis; - pregnancy; - lactation period; - children under 6 years of age; - frequent biliary colic.
Compound
one capsule contains: ursodeoxycholic acid - 250 mg. Excipients: lecithin (Solek B-10), beeswax, sunflower oil. Composition of the capsule shell: gelatin, glycerin, purified water, methyl parahydroxybenzoate, titanium dioxide, dye: sunset yellow E-110.
Overdose
In case of overdose, diarrhea may occur. In general, other symptoms of overdose are unlikely because the absorption of ursodeoxycholic acid decreases as the dose is increased and thus it is excreted in the feces. If diarrhea occurs, the dose should be reduced, but if diarrhea continues, treatment should be discontinued. No special preventative measures are required, and the consequences of diarrhea should be treated symptomatically by restoring fluid and water-salt balance.
Side effect
Ursocaps is quite well tolerated by patients. The assessment of undesirable effects is based on the following data on the frequency of occurrence: very often (>1/10), often (>1/100 to 1/1, LLC up to 1/10, 000
Storage conditions
Buy Ursocaps caps.250mg in container pack No. 10x5 in the pharmacy
Price for Ursocaps caps. 250 mg in container pack No. 10x5
Instructions for use for Ursocaps caps. 250 mg in container pack No. 10x5