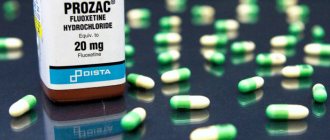
Composition and dosage form of the drug
The medication contains fluoxetine hydrochloride, a selective antipsychotic that is effective in emotionally depressed states. The drug is available in the form of tablets for oral administration: yellowish in color, film-coated. Active substance content in 1 piece: 20 mg. As auxiliary compounds, Fluoxetine contains starch, talc, silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, sucrose, and wax. The drug is sold in packages of 10 or 20 tablets, packaged in cell plates.
Mechanism of action of Fluoxetine
The drug prevents the reuptake of serotonin, helping to increase its concentration. As a result, after taking it, mood normalizes, apathy disappears, and performance increases. Fluoxetine has a slight effect on the uptake of dopamine and norepinephrine, having a selective antidepressant and pronounced stimulating effect.
The drug does not cause mental retardation, drowsiness, and does not reduce the speed of motor reactions and intellectual abilities. Fluoxetine helps get rid of dysphoria, fear, indecision, emotional instability, tension, absent-mindedness, and helps to better concentrate. The product has the property of reducing appetite until it is completely absent.
Fluoxetine is well absorbed through the mucous membranes, has high bioavailability, and binds to blood proteins. The presence or absence of food does not affect the speed of action of the medicine. The active substance is metabolized in liver tissue. The elimination period of the drug is long - up to 72 hours, during which their therapeutic effect persists. The antidepressant effect increases as the course continues. Lasting results are observed from 3-4 weeks of use and develop over several months.
Exceeding recommended doses or incorrect use of the drug can lead to withdrawal effects: increased depression, emotional swings.
Addiction treatment
Getting rid of a painful addiction to Fluoxetine may be required for patients who exceed the dosage of the drug, as well as for those who used the drug to enhance the effects of drugs or alcohol. In the latter case, the patient must undergo a full course of treatment for alcohol or drug addiction.
If your loved ones need help in treating drug addiction, then sign up for a free consultation by calling the hotline of the Zdravnitsa professional treatment and rehabilitation center: 8-800-200-27-23 . Our specialists will select an effective treatment plan and accompany you throughout the course. We guarantee results if all our recommendations are followed.
Similar articles:
Screw: what is it, the effect and consequences of use
Harmful effects of alcoholism
Laughing gas. Effects of taking nitrous oxide
Crack drug
Relapse and relapse of an alcoholic, drug addict or gambling addict
When should you take Fluoxetine?
The drug is prescribed to correct the mental state and eliminate symptoms of depression. Fluoxetine is effective for the following disorders:
- gloomy, depressed mood;
- lack of motivation;
- apathy caused by severe stress;
- obsessive-compulsive disorder;
- painful anxiety.
The drug is also indicated in the case of bulimia, a neurotic eating disorder manifested by gluttony. Improved mood and decreased appetite as a result of taking it help to switch attention from food to other things.
Contraindications to taking Fluoxetine
It is prohibited to use an antidepressant for the following disorders:
- history of seizures or epilepsy;
- prostate adenoma;
- delays in diuresis;
- glaucoma;
- intracranial pressure disorders;
- tendency to suicide attempts;
- agitated depression;
- severe kidney or liver failure.
It is also necessary to avoid using Fluoxetine if you are hypersensitive to one or more components of the drug.
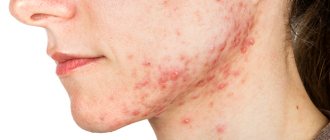
Side effects
During treatment with the drug, various reactions may develop in the vascular, nervous and digestive systems:
- headache;
- insomnia;
- increased sweating;
- tremor;
- irritability;
- violation of thermoregulation;
- panic attacks;
- tachycardia;
- hyperreflexia;
- spasms of muscles and internal organs;
- change in taste, dry mouth, nausea.
People prone to hypertension may experience increased blood pressure and associated negative symptoms.
Fluoxetine Lannacher capsules 20 mg cor x20
Trade name: Fluoxetine Lannacher International name: Fluoxetine
Release form: capsules 20 mg (blisters)
Composition: fluoxetine hydrochloride 22.36 mg
Pharmacological group: antidepressant
Pharmacological group according to ATK: N06AB03 (Fluoxetine)
Pharmacological action: H1-histamine-blocking, alpha-adrenergic blocking, anorexigenic, antidepressant, m-anticholinergic, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor,
Indications: Depression (regardless of the degree of depressive disorder - mild, moderate, severe), bulimia, anorexia, alcoholism, obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Dosage regimen: Orally, for depression, the initial dose is 20 mg/day 1 time, in the morning, if necessary, the dose is increased weekly by 20 mg/day. The maximum daily dose is 80 mg in 2-3 doses. For bulimia and for elderly patients - 60 mg in 3 doses, for obsessive disorders - 20-60 mg / day. Maintenance therapy - 20 mg/day. The course of treatment is 3-4 weeks.
Contraindications: Hypersensitivity, chronic renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 10 ml/min), severe liver failure, suicidal tendencies, simultaneous use of MAO inhibitors (in the previous 2 weeks), pregnancy, lactation.
Side effects: From the nervous system: dizziness, headache, drowsiness or insomnia, lethargy, increased fatigue, asthenia, tremor, agitation, anxiety, suicidality (typical of patients with depressive disorders), mania or hypomania. From the digestive system: loss of appetite, dry mouth or hypersalivation, nausea, diarrhea. Allergic reactions: skin rash, urticaria. Other: increased sweating, weight loss, decreased libido, systemic disorders of the lungs, kidneys or liver, vasculitis. Overdose. Symptoms: nausea, vomiting, agitation, convulsions. Treatment: gastric lavage, administration of activated carbon, for convulsions - anxiolytic drugs (tranquilizers), symptomatic therapy.
Pharmacodynamics: Antidepressant, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor. Improves mood, reduces tension, anxiety and fear, eliminates dysphoria. Does not cause orthostatic hypotension, sedation, and is noncardiotoxic. A lasting clinical effect occurs after 1-2 weeks of treatment.
Pharmacokinetics: Absorption is high, TCmax after oral administration of 40 mg is 6-8 hours, Cmax value is 15-55 ng/ml. Capsules and an aqueous solution of the drug are bioequivalent; food intake does not affect bioavailability. Plasma protein binding is 94.5% (including albumin and alpha1-glycoprotein). The volume of distribution is high, easily penetrates the BBB. Both enantiomeric forms are equieffective, but S-fluoxetine is eliminated more slowly and predominates over the R-form at Css. In the liver, the enantiomers are metabolized to the active metabolite, norfluoxetine. Metabolites are excreted by the kidneys (80%) and feces (15%), mainly in the form of glucuronides. It is an inhibitor of the isoenzymes CYP2C19, CYP3A2, CYP3A3, CYP3A5 and CYP3A7. T1/2 of fluoxetine is 1-4 days with a single dose and 4-6 days after reaching Css. T1/2 of norfluoxetine with a single dose and after reaching Css is 4-16 days, which causes a significant accumulation of active forms, slow achievement of their Css in plasma and long-term presence in the body after withdrawal. In patients with liver cirrhosis, T1/2 is prolonged by 3-4 times.
Special instructions: When treating patients with underweight, anorexigenic effects should be taken into account (progressive weight loss is possible). In patients with diabetes mellitus, the use of fluoxetine increases the risk of developing hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia when it is discontinued. In this regard, the dose of insulin and/or any other hypoglycemic drugs used orally should be adjusted. Until significant improvement in treatment occurs, patients should be under medical supervision. During treatment, you should refrain from taking ethanol and engaging in potentially hazardous activities that require increased attention and speed of mental and motor reactions. The interval between the end of therapy with MAO inhibitors and the start of treatment with fluoxetine should be at least 14 days, and between the end of treatment with fluoxetine and the start of therapy with MAO inhibitors - at least 5 weeks. For liver diseases and in old age, treatment should begin with 1/2 dose. Carefully. Diabetes mellitus, epileptic syndrome of various origins and epilepsy (including a history), Parkinson's disease, compensated renal and/or liver failure, cachexia.
Interaction: Enhances the effects of alprazolam, diazepam, ethanol and hypoglycemic drugs. Increases the plasma concentration of phenytoin, tricyclic antidepressants, maprotiline, trazodone by 2 times (it is necessary to reduce the dose of tricyclic antidepressants by 50% when used simultaneously). During electroconvulsive therapy, prolonged epileptic seizures may develop. Tryptophan enhances the serotonergic properties of fluoxetine (increased agitation, motor restlessness, gastrointestinal disorders). MAO inhibitors increase the risk of developing serotonin syndrome (hyperthermia, chills, increased sweating, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, tremor, diarrhea, incoordination, autonomic lability, agitation, delirium and coma). Drugs that have a depressant effect on the central nervous system increase the risk of side effects and increased depressive effects on the central nervous system. When used simultaneously with drugs that have a high degree of protein binding, especially with anticoagulants and digitoxin, it is possible to increase the plasma concentration of free (unbound) drugs and increase the risk of adverse effects.
Drug registration number: P No. 015843/01
Date of registration (re-registration) of the drug: 07/15/2004
How to take Fluoxetine
The tablets are taken in the dose prescribed by the doctor, washed down with water. It is not necessary to associate the medicine with periods of eating. It is preferable to take Fluoxetine in the morning, as it has a pronounced stimulating effect.
The treatment regimen depends on the identified disorders. General recommendations:
- 1 tablet once a day: to eliminate symptoms of apathy and depression;
- 1 tablet 2-3 times a day: for the treatment of bulimia.
In some cases, the dosage may be increased to 5-6 or 8 tablets per day. Their intake is divided into 3-4 times.
The course of treatment for acute stress is 3–4 weeks. For prolonged depression, it is necessary to take Fluoxetine for at least 3-4 months, sometimes up to six months. It is necessary to discontinue therapy according to a specific regimen, gradually reducing the dose. Abrupt withdrawal of the drug can cause a relapse of negative conditions.
Why is the drug dangerous?
Side effects occur if a person does not follow the dosage prescribed by the doctor. Over time, a person becomes addicted, and then develops a number of side effects that destroy the nervous system.
It is almost impossible to get rid of such addiction on your own and requires long-term therapy and the help of doctors, narcologists and psychologists.