Compound
1 g of liniment or ointment contains 0.25 mg of active ingredient.
The auxiliary ingredients in liniment include:
- propylene glycol;
- anhydrous lanolin ;
- petrolatum;
- pentanol;
- stearic acid;
- nipagin;
- nipazole;
- purified water.
Excipients in the ointment:
- benzyl alcohol;
- propylene glycol;
- soft white paraffin;
- ceresin;
- lanolin.
Dosage form, composition
The active component of the drug is fluocinolone acetonide. Sinaflan is available in several forms for external use:
- liniment: yellowish viscous substance containing 0.25 mg of active substance per 1 g;
- gel: transparent yellow mass with similar content of fluocinolone acetonide;
- cream: a homogeneous oily substance.
Among the form-building compounds and stabilizers of the product: glycerin, paraffin, liquid paraffin, lanolin, ceresin, propylene glycol, purified water and other components.
All dosage forms of the drug are packaged in 10 or 15 ml tubes and cardboard boxes, equipped with instructions for its use.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Pharmacodynamics
You can often hear the question of whether Sinaflan is hormonal or not. This is a hormonal drug, but this is the reason for its high effectiveness.
Fluocinolone acetonide binds to specific receptors in the cytoplasm of cells, which provokes an increase in mRNA synthesis. The result of exposure affects all metabolic processes in the cell.
Clinically significant effects include the following aspects of influence on the cell:
- inducing the synthesis of lipocort proteins, including lipomodulin, which leads to inhibition of the activity of phospholipase A2, which is one of the factors in the progression of the inflammatory response;
- stabilizes the cell membrane, which helps prevent swelling ;
- increases the rate of protein catabolism;
- reduces the migration of B and T lymphocytes and disrupts the interaction of these cells;
- inhibits the accumulation of leukocytes and macrophages at the site of inflammation;
- suppresses the effect of hyaluronidase, reduces the level of formation of arachidonic acid and leukotrienes;
- affects the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism, reducing tissue glucose consumption, which can lead to an increase in its concentration in the blood ;
- promotes the retention of sodium and water ions, provokes the excretion of potassium and calcium, reduces the ability to absorb calcium;
- increases the synthesis of erythrypoietins.
This effect on metabolic processes in the cell contributes to a noticeable effect in those cases for which the medicine is used - for acne and other inflammatory skin lesions.
Pharmacokinetics
Fluocinolone acetonide easily penetrates into all layers of the skin, but accumulates in the stratum corneum (can be detected even 15 days after completion of treatment). It enters the bloodstream in small quantities.
Biotransformation occurs in the liver. In this case, inactive metabolites . Excretion occurs mainly due to the work of the kidneys.
Absorption of the drug occurs more intensely when treating children, when applied to large areas of skin, when used regularly, when applied to the face or damaged skin.
What is Sinaflan intended for?
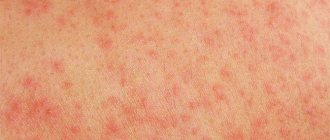
The drug reduces the manifestation of inflammatory reactions of the skin during autoimmune processes, exposure to toxins, biological and chemical allergens. Fluocinolone binds to cell cytoplasms, inhibits the production of the enzyme phospholipase A2, which provokes negative symptoms of irritation. As a result of using Sinaflan:
- the concentration of leukocytes and macrophages in the area of inflammation decreases;
- fluid outflow improves;
- metabolic processes inside cells are normalized: absorption of glucose, potassium, calcium, sodium ions;
- the production of arachidonic acid, one of the provocateurs of inflammation, is regulated.
Sinaflan inhibits the activity of cellular immunity: it reduces the accumulation of T-lymphocytes, thereby eliminating the factors of allergic manifestations. The substances of the drug act quickly directly at the sites of application, so the ointment has proven itself to be the best in the treatment of rashes and other superficial formations on the skin.
Fluocinolone easily penetrates into the stratum corneum, accumulates in them as therapy continues and persists for up to 15–20 days from the moment the application is stopped, providing a therapeutic effect. The components of the drug penetrate into the systemic bloodstream in minute concentrations, which are not hazardous to health. They are transformed in the liver and are completely eliminated from the body.
Indications for use
Why use Sinaflan ointment and dosage forms of the drug? For the treatment of various inflammatory skin lesions of non-infectious etiology.
What does Sinaflan ointment help with in most cases? You can list the following indications for the use of ointment, gel, cream and liniment:
- eczema of various localizations;
- psoriasis of the body and scalp;
- atopic dermatitis;
- seborrheic lesions;
- lichen planus ;
- itching of the skin of unknown etiology;
- discoid form of lupus erythematosus ;
- allergic rashes;
- erythema multiforme ;
- minor burns ;
- neurodermatitis;
- inflammation at the site of an insect bite.
Contraindications
It is prohibited to use ointment or liniment in such cases;
- hypersensitivity to the active substance or auxiliary components of the drug;
- skin diseases caused by an infectious agent: bacteria, virus or fungus;
- lupus;
- skin lesions that are a manifestation of syphilis ;
- wound surface;
- diaper rash;
- precancerous skin conditions, tumors ;
- the presence of a nevus on the area of skin where the medicine should be applied;
- psoriasis that has progressed to plaque formation;
- acne (the use of Sinaflan for acne, which is actually acne, can cause an exacerbation of the disease);
- trophic ulcers on the lower extremities caused by varicose veins;
- any use for children under 2 years of age;
- use in ophthalmology and on the skin of the mammary glands is prohibited;
- pregnancy and lactation .
Sinaf ointment 0.25 mg/g 15 g No. 1
Name
Sinaf ointment dnar.prim.0.25 mgg in tubes 15g in pack No. 1
Description
The ointment is white to yellow in color, of uniform consistency.
Main active ingredient
Fluocinolone acetonide
Release form
ointment for external use
Dosage
0.025% 15 g
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Fluocinolone acetonide is a highly active synthetic corticosteroid for topical use. Has anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, antipruritic effects. Thanks to the local vasoconstrictive effect, it prevents the development of exudative reactions. Inhibits the release of inflammatory mediators, the production of cytokines, the migration of leukocytes to the site of inflammation, and suppresses proliferation processes.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption is enhanced when applied to sensitive skin in the face and anatomical folds of the body, skin with damaged epidermis or inflammation, as well as when used under an occlusive dressing. Absorption through the skin is higher in children than in adults. After absorption from the surface of the skin, it binds to plasma proteins and is metabolized in the liver to form inactive metabolites. It is excreted primarily by the kidneys.
Indications for use
For short-term treatment of inflammatory and allergic skin diseases that respond to local glucocorticosteroids and occur with persistent itching or hyperkeratosis. Anhydrous, fat-containing sinaf ointment is preferable for dry skin and chronic processes.
Directions for use and doses
The medicine is intended for topical use only. Apply a small amount of the medicine 1-2 times a day and rub in lightly. The duration of treatment depends on the nature of the disease and is usually 5–10 days, with a long course of the disease - no more than 2 weeks. Avoid applying the drug to large (more than 20% of the body surface) lesions. Combined use with non-medicinal ointment is possible: if Sinaf ointment is applied once a day, after 12 hours it is possible to apply non-medicinal ointment. The ointment should not be used under an occlusive dressing; only for psoriasis, it is allowed to use the drug under a closed dressing, which should be changed every day. Do not use on facial skin for more than 5 days. The ointment is primarily recommended for use in dry forms of dermatoses. Children Children are more sensitive than adults: with topical use of glucocorticosteroids, the drug may penetrate the body, therefore Sinaf ointment is used briefly (no more than 5 days) and with the lowest effective dose in children. In children, the drug should be used only for small areas of skin (up to 10% of the body surface area). Applying ointment to a child's face is not allowed. For children over 2 years of age, use with caution once a day under medical supervision. The drug is not used in children under 2 years of age. No specific studies have been conducted in children.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
The drug should not be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Pregnancy Animal studies have shown that fluocinolone acetonide has embryotoxic and teratogenic effects. Preclinical studies have confirmed that topical administration of glucocorticosteroids can cause intrauterine developmental disorders (eg, cleft palate, embryonic growth retardation). Controlled studies have not been conducted to evaluate the possible teratogenic effects in pregnant women when applied topically, and the potential risk to humans is unknown. Lactation It is not known whether fluocinolone acetonide passes into breast milk after topical use. Other glucocorticoids are secreted into breast milk. If long-term use or treatment of a large surface area of the body is necessary, breastfeeding should be discontinued. Contact of the infant with the treated skin surface should be avoided.
Precautionary measures
If the drug causes symptoms of irritation or allergic skin reactions (skin itching, burning or redness), its use should be stopped immediately. Do not use continuously for more than 2 weeks. With prolonged use over a large surface of the body, the frequency of side effects and the possibility of developing edema, hypertension, hyperglycemia, and decreased body resistance increases. For the treatment of skin diseases accompanied by infection, it is recommended to prescribe the drug together with antimicrobial agents. When using occlusive dressings, due to increased bioavailability, the development of general resorptive effects characteristic of glucocorticosteroids is possible. With external use of the drug, the following are possible: a decrease in the production of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) by the pituitary gland, inhibition of the adrenal-pituitary gland system, a decrease in the level of cortisol in the blood and the development of iatrogenic Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, which disappears after discontinuation of the drug. Periodic monitoring of adrenal function is indicated by determining cortisol in the blood and urine after stimulation of the adrenal glands with ACTH during long-term use. Because corticosteroids can be absorbed through the skin. Long-term treatment and use on large areas of skin under an occlusive dressing in children should be avoided. Because children have a higher body surface-to-weight ratio than adults, they are at higher risk for systemic corticosteroid side effects, including hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysfunction and Cushing's syndrome. Corticosteroid therapy may have side effects on the growth and development of children. Periodic monitoring of the function of the adrenal cortex is indicated by determining cortisol in the blood and urine after stimulation of the adrenal glands with ACTH. If an infection develops at the site of application of the ointment, appropriate antibacterial or antifungal treatment should be carried out. If symptoms of infection do not go away, you should stop using the ointment while the infection is being treated. The drug should be used with caution in the presence of subcutaneous tissue atrophy, mainly in elderly patients. It is necessary to avoid getting the drug into the eyes, mucous membranes and wounds. Do not use the drug in the area around the eyes, due to the risk of glaucoma or cataracts. Use with extreme caution in the treatment of patients with psoriasis, since topical use of glucocorticosteroids for psoriasis can be dangerous due to relapse caused by the development of drug resistance, the risk of generalized pustular psoriasis and systemic toxicity caused by impaired skin barrier function. On the skin of the face, as well as on the skin of the groin and armpits, use only in cases of special need, taking into account increased absorption and the high risk of side effects (telangiectasia, dermatitis perioralis), even after short-term use. During treatment, it is not recommended to be vaccinated against smallpox, as well as other types of immunization (especially with long-term use on large areas of the skin) due to the possible lack of an adequate immunological response in the form of production of appropriate antibodies. Corticosteroid use may change the appearance of some skin lesions, making diagnosis difficult. The drug should be used in the smallest amount for the shortest possible period necessary to achieve a therapeutic effect. It is necessary to stop treatment gradually, increasing the intervals between applications. Contains propylene glycol. May cause skin irritation. Due to the lanolin content, it may cause local skin reactions (eg contact dermatitis).
Interaction with other drugs
Compatible with antimicrobial drugs. Reduces the activity of antihypertensive, diuretic, antiarrhythmic drugs, potassium supplements. Diuretic drugs (except potassium-sparing drugs) increase the risk of hypokalemia. The drug may enhance the effect of immunosuppressive drugs and weaken the effect of immunostimulating drugs.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or other components of the drug. Bacterial, viral, fungal infections of the skin (including skin manifestations of syphilis, skin tuberculosis, pyoderma, chicken pox, herpes, actinomycosis, blastomycosis, sporotrichosis). Rosacea and vulgaris, diaper dermatitis, perioral dermatitis, anogenital itching, post-vaccination reactions, wounds and ulcerative skin lesions at the application sites, trophic ulcers associated with varicose veins. Skin tumors (including nevus, hemangioma, xanthoma, atheroma, skin cancer, melanoma, sarcoma). Pregnancy, breastfeeding, children under 2 years of age. The drug is not used in ophthalmology.
Compound
Each tube (15 g) contains: active ingredient: fluocinolone acetonide – 3.75 mg; excipients: propylene glycol, soft white paraffin, anhydrous lanolin, ceresin.
Overdose
Symptoms: itching and burning of the skin at the site of application of the drug, hyperglycemia, glucosuria, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome. Treatment: symptomatic with gradual withdrawal of the drug.
Side effect
Adverse reactions are listed according to the classification of undesirable side effects in accordance with damage to organs and organ systems and the frequency of their occurrence: very often (? 1/10), often (? 1/100 to
Storage conditions
At temperatures from 8 °C to 15 °C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Side effects
The question of whether an ointment is hormonal or not is often due to the fact that it is known that hormonal drugs actively affect the entire body. This also applies to Sinaflan. Side effects are not very common, but they can be quite varied.
On the part of the skin and subcutaneous fatty tissue, the following may appear:
- hives;
- allergic contact dermatitis;
- skin irritation;
- peeling of the skin or rashes in the form of papules or spots at the site of application of the medicine;
- hyperkeratosis;
- furunculosis;
- exacerbations of pathological skin conditions that were present at the start of treatment;
- atrophic changes in the skin;
- burning sensation;
- itching;
- steroid acne ;
- folliculitis;
- hair loss or excessive growth in the area where Sinaflan was applied;
- pigmentation disorders.
From the digestive system (occurs when used on large areas of the skin):
- gastritis;
- steroid gastric ulcer .
From the endocrine organs:
- increased blood glucose levels;
- glucosuria;
- in children – slower growth and development;
- when applied to large areas of skin, the development of adrenal insufficiency , Itsenko-Cushing syndrome , and steroid diabetes mellitus .
From the immune :
- allergic reactions;
- hypersensitivity reactions;
- decreased immunity ;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- generalization of infectious lesions;
- slowing down repair processes.
From the heart and blood vessels:
- increased blood pressure ;
- swelling.
When applied to the outer surface of the eyelids, there is a risk of developing cataracts and glaucoma .
Possible adverse reactions
When using the drug Sinaflan, the following are rarely possible:
- increased itching, flaking, dry skin;
- the appearance of keratosis;
- swelling, redness, burning.
With long-term use, there are isolated cases of impaired carbohydrate metabolism, increased blood pressure, and decreased immunity. The risk of side effects is higher when Sinaflan is combined with other hormonal ointments or when taking systemic glucocorticoid drugs.
Instructions for use of Sinaflan (Method and dosage)
Sinaflan ointment, instructions for use
The ointment is applied to the affected area 1 or 2 times a day and lightly rubbed in. The course of treatment for adults is up to 10 days, for children – no more than 5 days, for facial skin – no more than 1 day.
It is not advisable to use ointment under a bandage, with the exception of some forms of psoriasis . But in this case, it is very important to change it regularly.
The drug in the form of an ointment is recommended for use in dry forms of dermatoses .
Liniment Sinaflan, instructions for use
Liniment can be applied 2-4 times a day. The course of treatment is the same in duration as when using the ointment.
Do not use under a closed bandage, but can be applied to a small area of skin under an occlusive one.
It is advisable to use for dry dermatoses .
How to use Sinaflan cream or gel
Apply to affected areas 1-4 times a day. The course lasts no more than 2 weeks.
The cream is more often used for wet dermatoses , and the gel is used for lesions of the scalp.
Sinaflan-Akrikhin ointment (tube 0.025% 15g)
A country
Russia
The country of production may vary depending on the batch of goods. Please check with the operator for detailed information when confirming your order.
Compound
Tube 15 g
Fluocinolone acetonide in terms of 100% substance - 0.025 g per 100 g. Excipients: propylene glycol 4.975 g, petroleum jelly 80 g, lanolin 5 g, paraffin paraffin 10 g.
pharmachologic effect
Pharmacodynamics The active component of Sinaflan-Akrikhin, fluocinolone acetonide, is a glucocorticosteroid for external use.
When exposed to the skin, the drug inhibits the release of inflammatory mediators and also prevents the marginal accumulation of neutrophils, as a result of which the inflammatory exudate and the production of cytokines are reduced, the migration of macrophages is delayed, and the process of infiltration and granulation is reduced. Sinaflan-Akrikhin has anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effects. Pharmacokinetics After absorption from the skin surface, fluocinolone acetonide binds to plasma proteins. The substance is metabolized in the liver, resulting in the formation of metabolites that do not have pharmacological activity. It is excreted primarily by the kidneys.
Indications for use
Inflammatory and allergic skin diseases of non-microbial etiology: eczema, atopic dermatitis, simple chronic lichen (limited neurodermatitis), itching, psoriasis and other chronic diseases accompanied by dry skin.
Side effects
Burning, itching, steroid acne, stretch marks, dry skin, folliculitis. With long-term use, skin atrophy, local hirsutism, hypertrichosis, telangiectasia, purpura, skin pigmentation disorders, alopecia, especially in women, secondary immunodeficiency (exacerbation of chronic infectious diseases, generalization of the infectious process, development of opportunistic infections); when applied to large surfaces, systemic manifestations are possible (gastritis, “steroid” gastric ulcer, adrenal insufficiency, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, “steroid” diabetes mellitus, slowdown of reparative processes).
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, skin manifestations - syphilis, skin tuberculosis, diaper rash, rosacea, extensive psoriatic plaques, anogenital itching; skin infections caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi - pyoderma, chickenpox, Herpes, actinomycosis, blastomycosis, sporotrichosis, trophic leg ulcers associated with varicose veins, erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, ulcers and wounds at application sites , skin cancer, nevus, atheroma, melanoma, hemangioma, xanthoma, sarcoma, pregnancy, lactation, children (up to 2 years). With caution: In girls during puberty.
Mode of application
Externally. A small amount of the drug is applied to the skin, previously wiped with a swab moistened with an antiseptic liquid, 2-4 times a day and lightly rubbed. If necessary, you can apply an occlusive dressing, leaving it on the affected surface for up to 3-4 days: It is not allowed to use more than 2 g/day under the dressing. - The duration of treatment depends on the nature of the disease and the effectiveness of therapy, usually 5-10 days; If the disease persists, the course of treatment can be extended to 25 days or more. In children, it is recommended to use the minimum effective dose, no more than 5 days.
special instructions
Use only in short courses on small areas of skin. It is recommended to wear loose clothing during treatment. The drug should not be applied to the face. Avoid getting the drug into your eyes. When local infectious complications develop, it is used in combination with antimicrobial drugs. Effect of the drug on the ability to drive vehicles and other mechanisms: No effect
Overdose
Itching and burning of the skin at the site of application of the drug, hyperglycemia, glucosuria, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome. Treatment: symptomatic with gradual withdrawal of the drug.
Interaction with other drugs
Compatible with antimicrobial drugs. Reduces the activity of antihypertensive, diuretic, antiarrhythmic drugs, potassium supplements. Diuretic drugs (except potassium-sparing drugs) increase the risk of hypokalemia.
Overdose
An overdose can easily occur when the medicine is applied to large areas of the skin, in case of long-term treatment, or when applied to particularly sensitive areas, such as the skin of the face. There is also a high risk when treating children with Sinaflan.
Possible symptoms of overdose:
- swelling;
- increased blood pressure ;
- burning , itching at the site of application of the drug;
- increased levels of glucose in the blood and urine;
- Itsenko-Cushing syndrome.
Treatment for overdose is symptomatic. In this case, gradual withdrawal of Sinaflan is indicated.
Sinaflan (ointment)
If there are signs of hypersensitivity or skin irritation associated with the use of the drug, you should stop treatment and consult a doctor.
Avoid getting the ointment in your eyes.
Do not apply ointment to mucous membranes or wounds.
It is recommended to use Sinaflan ointment in short courses on small areas of the skin. Loose clothing should be worn during treatment.
With prolonged use of the ointment and/or application to large surfaces of the skin, damaged skin, when using large doses, using occlusive dressings and during therapy in children, systemic absorption of the glucocorticosteroid is possible; it is possible to suppress the function of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system and develop symptoms of hypercortisolism (Itsenko-Cushing syndrome).
Atrophic changes may appear on the skin of the face more often than on other surfaces of the body after long-term treatment with topical glucocorticosteroids; the course of treatment in this case should not exceed 5 days.
With long-term therapy with glucocorticosteroids, sudden cessation of therapy can lead to the development of “rebound syndrome,” manifested in the form of dermatitis with intense redness of the skin and a burning sensation. Therefore, after long-term treatment, drug withdrawal should be carried out gradually, for example, by switching to an intermittent treatment regimen before stopping it completely.
During drug therapy, periodic monitoring of the function of the adrenal cortex is necessary by determining the level of cortisol in the blood and urine after stimulation of the adrenal glands with adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH).
In patients with acne vulgaris or rosacea, an exacerbation of the disease may occur during drug therapy.
To prevent local infectious complications, the drug is recommended to be prescribed in combination with antimicrobial agents.
The ointment should be applied with caution to the skin around the eyes or eyelids due to the risk of developing glaucoma or cataracts, as well as in patients with a history of these diseases, who may experience an exacerbation of these diseases.
If a patient experiences symptoms such as blurred vision or other visual disturbances, consider referring the patient to an ophthalmologist to investigate possible causes of the disturbance, which may include cataracts, glaucoma, or rare diseases such as central serous chorioretinopathy.
The ointment should be used with extreme caution on the skin of the face, areas with thin skin and intertriginous skin (skin folds, armpits, groin, folds of the arms and legs), due to increased absorption of glucocorticosteroids through thin skin and the possibility of side effects (telangiectasia, skin atrophy, perioral dermatitis) even after short-term use.
The drug should be used with caution in case of atrophic changes in the subcutaneous tissue, especially in the elderly.
The ointment should be used with extreme caution in patients with psoriasis, due to possible relapse of the disease caused by the development of tolerance, the risk of generalized pustular psoriasis and general toxicity due to pressure ulcers.
Use in pediatrics
The drug can be used in children over 2 years of age. It must be taken into account that in young children, skin folds, diapers, diapers can have an effect similar to the effect of an occlusive dressing and increase the systemic absorption of the glucocorticosteroid. In addition, a greater degree of systemic absorption is possible in children due to the relationship between the surface of the skin and body weight, as well as due to insufficient skin maturity. Long-term use of glucocorticosteroids in children can lead to disturbances in their growth and development. Therefore, long-term use of the drug should be carried out under the supervision of a physician. Children should receive the minimum dose of the drug sufficient to achieve an effect. In children, the course of treatment should not exceed 5 days.
Propylene glycol and lanolin contained in Sinaflan may cause irritation at the site of application. In such cases, you should stop using the drug.
Interaction
The drug interacts with many other medications, so caution is necessary when using at the same time:
- with systemic glucocorticosteroids – the effectiveness of Sinaflan increases and the likelihood of developing side effects from its use increases;
- with non-hormonal anti-inflammatory medications – the risk of developing both local and systemic adverse reactions of the body to each of the drugs increases;
- with antihypertensive, antirhythmic drugs, diuretics, potassium supplements - the effectiveness of these medications decreases;
- with diuretics (except potassium-sparing ones) – the likelihood of developing hypokalemia ;
- with vaccines - an inadequate immune response is possible due to the fact that the immune system is weakened and is not able to synthesize the necessary antibodies in normal quantities;
- with immunosuppressants – enhances the effect;
- with immunostimulants - suppresses the effect of these drugs on the immune system.
special instructions
When treating with Sinaflan, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- avoid getting the medicine into your eyes;
- do not apply to wounds or breast skin;
- it is strictly forbidden to exceed the recommended duration of treatment;
- do not use with other topical medications;
- it is undesirable to use under a bandage, since in this case the adsorption of the drug and the risk of developing systemic side effects increases;
- If necessary, undergo a course of treatment several times, you need to take tests to monitor the functioning of the adrenal glands.
Sinaflan FT (gel)
- If the drug causes symptoms of irritation or allergic skin reactions (skin itching, burning or redness), its use should be discontinued immediately. Do not use continuously for more than 2 weeks. With prolonged use over a large surface of the body, the frequency of side effects and the possibility of developing edema, hypertension, hyperglycemia, and decreased body resistance increases. The drug should not be applied to the face. Avoid contact with eyes. For the treatment of skin diseases accompanied by infection, it is recommended to prescribe the drug together with antimicrobial agents. When using occlusive dressings, due to increased bioavailability, the development of general resorptive effects characteristic of GCS is possible. With external use of the drug, the following are possible: a decrease in the production of ACTH by the pituitary gland, inhibition of the adrenal-pituitary gland system, a decrease in the level of cortisol in the blood and the development of iatrogenic Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, which disappears after discontinuation of the drug. Periodic monitoring of adrenal function is indicated by determining cortisol in the blood and urine after stimulation of the adrenal glands with AC TG during long-term use. If an infection develops at the site of application of the drug, treatment should be discontinued and appropriate antibacterial or antifungal treatment should be administered. Avoid applying the gel to the eyelids or skin around the eyes in patients with closed-angle and open-angle glaucoma, as well as in patients with cataracts. Considering the possibility of increased symptoms of the disease. Because corticosteroids can be absorbed through the skin. Long-term treatment and use on large areas of skin under an occlusive dressing in children should be avoided. Because children have a higher body surface-to-weight ratio than adults, they are at higher risk for systemic corticosteroid side effects, including hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysfunction and Cushing's syndrome. Corticosteroid therapy may have side effects on the growth and development of children. Periodic monitoring of the function of the adrenal cortex is indicated by determining cortisol in the blood and urine after stimulation of the adrenal glands with ACTH. If an infection develops at the site of application of the gel, appropriate antibacterial or antifungal treatment should be carried out. If symptoms of infection do not go away, you should stop using the gel while the infection is being treated. The drug should be used with caution in the presence of subcutaneous tissue atrophy, mainly in elderly patients. Avoid contact of the drug with eyes, mucous membranes and wounds. Do not use the drug in the areas around the eyes, due to the risk of glaucoma or cataracts. Use with extreme caution in the treatment of patients with psoriasis, since topical use of glucocorticosteroids for psoriasis can be dangerous due to relapse caused by the development of drug resistance, the risk of generalized pustular psoriasis and systemic toxicity caused by skin dysfunction. On the skin of the face, as well as on the skin of the groin and armpits, use only in cases of special need, taking into account increased absorption and the high risk of side effects (telangiectasia, dermatitis perioralis), even after short-term use. Use with caution in existing conditions of subcutaneous tissue atrophy, especially in the elderly. During treatment, it is not recommended to be vaccinated against smallpox, as well as other types of immunization (especially with long-term use on large areas of the skin) due to the possible lack of an adequate immunological response in the form of production of appropriate antibodies. Contains methyl parahydroxybenzoate and propyl parahydroxybenzoate, which may cause allergic reactions. Contains propylene glycol. May cause skin irritation. Do not use on breast skin.
Use only in short courses on small areas of skin. The drug should not be applied to the face. Avoid getting the drug into your eyes.
Use during pregnancy and lactation Animal studies have shown that fluocinolone acetonide has embryotoxic and teratogenic effects. Animal studies with other glucocorticoids have found evidence of fetal damage (eg, cleft palate, skeletal abnormalities, and fetal mortality). When using glucocorticoids during pregnancy, especially during the first three months, the benefits and risks must be weighed. Animal studies have shown that the use of glucocorticoids at subteratogenic doses during pregnancy is associated with an increased risk of intrauterine growth restriction, as well as cardiovascular disease and/or metabolic disorders. In addition, the risk may be increased by permanent changes in glucocorticoid receptors, changes in neurotransmitter turnover. The use of the drug during pregnancy is contraindicated. If the use of glucocorticoids during pregnancy is unavoidable, hydrocortisone and prednisolone should be used because these substances are inactivated in the placenta by the 11βHSD enzyme and therefore there is greater protection from these substances compared to most synthetic glucocorticoids. Lactation There is no data on the penetration of fluocinolone acetonide into human breast milk. Other glucocorticoids are secreted into breast milk. When using for a long time or treating large surfaces of the body, a woman should not resort to breastfeeding. Contact of the infant with the treated skin surface should be avoided.
Effect on the ability to drive a car and operate machinery No effect.
Sinaflan's analogs
Level 4 ATC code matches:
Gistan-N
Sinalar
Avecourt
Mesoderm
Momederm
Betazon
Silkaren
Elokom
Flucinar
Celestoderm
Cutivate
Advantan
Betamethasone
Beloderm
Mometasone Furoate
Uniderm
Momat
Analogues of Sinoflana:
- Sinoflan-Fitofarm ointment (an analogue with an identical composition, manufactured by the manufacturer PJSC Fitofarm);
- Flutsar-Darnitsa;
- Flucederm;
- Flucinar (gel and ointment).
Sinaflan price, where to buy
The price of Sinaflan ointment and other dosage forms of this drug is low. In Russian pharmacies the cost is 10-90 rubles, depending on the form of release. In Ukrainian pharmacies, the price of medicine ranges from 10 to 30 hryvnia.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
ZdravCity
- Sinaflan-Akrikhin ointment for external use.
approx. 0.025% tube 15gAO Akrikhin 83 rub.order - Sinaflan ointment 0.025% tube 10 gAO Akrikhin
81 RUR order
- Sinaflan ointment 0.025% 10gAltaivitaminy JSC
33 rub. order
- Sinaflan ointment 0.025% 15gBiokhimik OJSC
76 RUR order
- Sinaflan ointment 0.025% 10g JSC Murom Instrument-Making Plant
30 rub. order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Sinaflan-Akrikhin ointment (tube 0.025% 15g) Akrikhin OJSC
92 rub. order
- Sinaflan-Akrikhin ointment (tube 0.025% 10g) Akrikhin OJSC
69 RUR order
- Sinaflan ointment (tube 0.025% 15g) Nizhpharm JSC
70 rub. order
- Sinaflan ointment (tube 0.025% 10g) Nizhpharm JSC
72 RUR order
- Sinaflan ointment (tube 0.025% 15g) Muromsky PZ
44 RUR order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Sinaflan 0.025% 15 g ointment
27 UAH. order - Sinaflan 0.025% 10 g ointment TOV DKP Pharm.Fabrika, Ukraine
20 UAH order
- Sinaflan-Fitofarm 0.025% 15 g ointment PRAT "Fitofarm", Ukraine
21 UAH order
PaniPharmacy
- Sinaflan ointment Sinaflan ointment 0.025% 15g Russia, Nizhpharm
35 UAH order
- Sinaflan ointment Sinaflan ointment 0.025% 10g tube Ukraine, Zhytomyr FF LLC
27 UAH order
- Sinaflan ointment Sinaflan ointment 0.025% 15g Ukraine, Fitofarm ChAO
24 UAH order
show more