Causes of chilly feet
Hypothermia
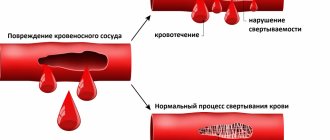
A decrease in body temperature to 35°C or below causes chilliness in the distal parts of the legs and arms. The symptom is caused by increased heat loss when the body’s own heat production mechanisms fail to maintain equilibrium. When hypothermia occurs, a person feels severe cold, tingling or numbness in the lower extremities. The situation is aggravated if you wear tight, uncomfortable shoes, which impair blood circulation in the tissues of the feet.
Nutrient deficiency
Feet begin to freeze more than usual if a person follows a low-calorie diet for a long time and lacks vitamins and microelements. Nutritional deficiency is complemented by metabolic and heat exchange disorders, which leads to chilliness of the lower extremities. Most often, symptoms are detected in those suffering from deficiency anemia - a decrease in hemoglobin levels impairs the flow of oxygen to the legs, which causes discomfort.
Arterial diseases
A typical pathological cause of chilliness is obliterating atherosclerosis. Lipid plaques spread from large vessels to peripheral arteries and impair blood flow in them, which is accompanied by trophic disorders. The feet are constantly cold to the touch and are difficult to warm up in a hot bath or with a heating pad. The skin on the legs and feet becomes pale, dry, and thinned. The clinical picture mainly develops in older people.
The above symptoms, found in young and middle-aged people, are more characteristic of obliterating endarteritis. A distinctive feature of the disease is the spread of changes from the distal parts of the limb to the hips. Patients also feel constant chilliness; their feet become very cold outside in cold weather, even if they are wearing warm socks and suitable shoes. The sensitivity of the feet decreases, tingling and paresthesia occur periodically.
Cold feet
Chronic venous insufficiency
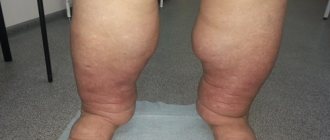
Coldness of the legs, combined with increased fatigue and heaviness in the limbs, are typical signs of impaired venous outflow. Patients notice that their feet feel cold to the touch, even when the room is hot. Periodic tingling, crawling, and numbness are felt. The skin of the legs becomes pale or bluish, and swelling is noted. In the later stages of CVI, trophic ulcers form.
Arterial hypotension
With reduced blood pressure, blood circulates worse throughout the body, so moderate ischemia of the distal parts of the lower extremities is possible. Patients with hypotension do not tolerate cold well, freeze faster and feel chilly, and therefore do not like long walks in winter. Despite wearing insulated shoes, the feet remain cold, and after entering a warm room they do not warm up for a long time.
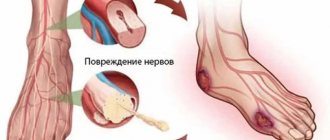
Polyneuropathy
Damage to the peripheral nerves is accompanied by disturbances in the perception of heat and cold, so chilliness constantly bothers patients. A variety of uncomfortable sensations are possible: tingling in the legs, heaviness, increased fatigue. Coldness first occurs in the feet in a “sock-like” manner and spreads proximally. If motor nerve fibers are affected, changes in gait, paresis and paralysis of the legs are noticeable.
Rare causes
- Endocrine pathologies
: hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus. - Neurological problems
: lumbosacral osteochondrosis with intervertebral hernia, vegetative-vascular dystonia. - Cardiac diseases
: heart failure, arrhythmias.
Parasitic infestation
A common reason why women's feet get very cold is worms. The thing is that during their life, worms produce a huge amount of toxins. In turn, toxins lead to vasospasm. People who constantly come into contact with animals, namely milkmaids, veterinarians and animal lovers, are especially prone to infection with worms.
reasons why feet are cold
Diagnostics
The examination of a patient with complaints of chilly feet begins with a family doctor (therapist), who, if necessary, involves highly specialized specialists in the diagnostic search - vascular surgeons, neurologists, endocrinologists. During a physical examination, the color and temperature of the extremities are assessed and signs of venous stasis or ischemia are identified. For diagnostic purposes, the following instrumental and laboratory research methods are used:
- Doppler ultrasound of leg vessels.
Duplex scanning of the arteries and veins of the lower extremities shows the speed of blood flow, pathological reverse blood flow, visualizes blood clots and lipid plaques blocking the lumen of blood vessels. Features of microcirculation are assessed according to rheovasography and capillaroscopy. - Angiography.
The method is used to diagnose obliterating processes of the lower extremities that cause chilliness. Peripheral arteriography shows narrowing or blockage of the lumen of the arteries and helps assess the size and extent of plaques. Ascending phlebography of the legs is indicated for studying venous blood flow, the condition of the deep and superficial veins. - ECG.
To confirm arterial hypotension, arrhythmia and other cardiac pathologies, a cardiogram is recorded at rest and with stress tests. To clarify the diagnosis, an orthostatic test and echocardiography are recommended. To assess daily fluctuations in blood pressure, Holter monitoring is performed. - Neurological diagnostics.
A standard examination includes testing of superficial and deep sensation, reflexes, muscle tone and strength. For a qualitative assessment of neuromuscular transmission, electroneuromyography is prescribed. In case of osteochondrosis, the results of an MRI or CT scan of the spine are informative for a neurologist. - Laboratory techniques.
Based on the results of a clinical blood test, anemia and its probable causes are diagnosed. Biochemical research is aimed at identifying nutritional deficiency. When cold feet are of endocrine origin, an expanded hormonal profile is studied.
Consultation with a vascular surgeon
Thyroid diseases
The thyroid gland is a key link in the hormonal regulation of the entire body. With hypothyroidism (lack of thyroid hormones), metabolic processes slow down. Lethargy and lethargy, drowsiness, and excess weight appear. The person feels depressed. The face, especially the eyelids, swells, and the pulse slows down. The skin becomes dry, often flakes, and thickens. The functioning of the mechanisms responsible for maintaining normal body temperature is disrupted. When thyroid hormone levels are low, a person often feels cold.
What to do?
It is important to undergo an examination by an endocrinologist, do an ultrasound of the thyroid gland, and take a general blood and urine test. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe additional X-ray and magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, etc.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
If chilliness occurs against the background of banal hypothermia, the person needs to be warmed up as soon as possible. For mild hypothermia, use warm drinks, baths, and heating pads. The temperature must be increased gradually. For superficial frostbite, warming bandages are applied to the legs. With moderate and severe hypothermia, the patient requires comprehensive medical care.
To correct vegetative-vascular dysfunction or physiological hypotension, non-drug measures are sufficient. Patients experiencing chilliness are advised to normalize their work and rest schedule, walk more in the fresh air, and begin dosed training in the gym. It is recommended to limit watching TV and surfing social networks. A balanced diet high in vitamins helps improve your well-being.
Conservative therapy
Medicines are selected taking into account the etiological factors of chilly feet. In cases of arterial circulation disorders, infusions of saline solutions and antiplatelet agents, which prevent the adhesion of red blood cells and increase blood fluidity, show a good effect. To prevent thrombosis, anticoagulants are included in therapy. Dilatation of peripheral vessels and improvement of blood flow is achieved by taking antispasmodics.
For obliterating atherosclerosis, which causes chilly legs, lipid-lowering drugs are effective, reducing cholesterol and LDL levels and preventing the appearance of new lipid plaques. For endarteritis, pathogenetic treatment includes anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroids, which neutralize pathological changes in the vascular wall.
In case of insufficient venous outflow, phlebotropic agents are used in combination with elastic compression. To influence trophic ulcerative defects, local effects in the form of creams or ointments are indicated. Patients with polyneuropathy are recommended to take B vitamins, which improve neuromuscular transmission. The therapeutic regimen is supplemented with neurotrophic drugs.
To eliminate chilliness associated with obliteration of the vessels of the legs, physiotherapy is used: electrophoresis with medicinal solutions, ozokerite applications, diadynamic currents. Hyperbaric oxygenation helps improve tissue oxygen supply. General strengthening balneological procedures are actively prescribed: pine, pearl or radon baths.
Atherosclerosis
There is a thickening and loss of elasticity of the walls of the arteries, a narrowing of their lumen with subsequent disruption of the blood supply to the organs. Hence the cold hands. When cerebral vessels are damaged, tinnitus, dizziness, memory loss, and headache are noted. Eating with an excess amount of animal fat, a sedentary lifestyle, and psycho-emotional stress can lead to this disease.
What to do?
An ECG, ultrasound of the heart and blood vessels, rheovasography, angiography, coronary angiography are performed, blood pressure is measured, lipid levels (cholesterol, etc.) and blood sugar are examined.
Etiology
Most common causes of numbness in the legs
consist in the presence of pathological processes in the spine - however, this is not all. The etiology of this symptom may be as follows:
- arthritis;
- pathological conditions of a systemic nature;
- multiple sclerosis;
- blood flow disturbances.
The area in which the feeling of numbness is localized will help to more accurately determine the cause.
| Numb area | Diseases characterized by this symptom |
| Hips/thigh |
|
| Above the knees |
|
| Calves of the legs |
|
| Below the knees |
|
| Foot/feet |
|
| Numbness in left leg |
|
| Numbness in right leg |
|
Osteochondrosis
Deformation and thinning of the intervertebral discs, muscle spasm lead to compression of the spinal cord, surrounding nerves and blood vessels. Blood circulation is disrupted, hands and feet become cold, a feeling of numbness and aches appears, constant aching pain in the back, headache, and dizziness occur.
What to do?
It is necessary to consult a neurologist. Complex treatment includes physical therapy, physiotherapy, massage, manual therapy, spinal traction (traction), reflexology, and drug therapy. In difficult cases, surgery is possible.
Clinical manifestations
In pathological conditions, numbness of the legs is a symptom that is always accompanied by a number of others. Depending on the etiology, they may be different, but the general picture is approximately as follows:
- Feeling of heaviness in the lower extremities;
- Gait disturbances;
- Inability to distinguish cold from hot;
- Fatigue, constant weakness and weakness;
- Tingling and goosebumps;
- Cramps and increased pain at night;
- Sudden and sharp appearance of pain in the chest and spine;
- Itching and burning of the skin, sometimes blueness;
- Severe headaches and dizziness.
Scleroderma, Raynaud's syndrome
The fingers or toes become cold, numb, a tingling sensation appears in them, and they become white or even bluish in color. This occurs under the influence of stress or temperature exposure and can last from several minutes to several hours. At the end of the attack, the bluish skin turns red, fever and pain appear. This is Raynaud's syndrome - one of the manifestations of scleroderma. As a result of damage to the blood vessels, many organs and tissues of the body are affected, especially the skin. The face takes on a mask-like appearance, and it is difficult to open the mouth. It is believed that scleroderma is stimulated by viruses, poisoning, and congenital predisposition. This disease occurs 5 times more often in women than in men.
What to do?
At the first symptoms, you should urgently consult a dermatologist. They conduct laboratory tests of blood, urine, immunodiagnostics, X-ray examination of bones and joints, ultrasound of internal organs, and cardiac diagnostics.
Prevention
In order to eliminate such a manifestation as numbness of the legs, you must adhere to simple rules, which are as follows:
- Rejection of bad habits;
- Reducing salt intake;
- Active lifestyle;
- Proper, balanced nutrition;
- Providing the body with all the microelements and vitamins it needs;
- Avoiding high-heeled shoes or keeping them to a minimum;
- Sports activities;
- Attention to your health;
- Timely seeking professional help if certain symptoms occur.
MC CELT specialists give a positive prognosis for timely treatment of numbness in the legs. Trust your health to professionals!
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions