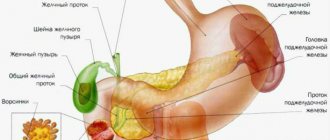
The small intestine is the part of the gastrointestinal tract that runs from the stomach to the large intestine. Its initial section is the duodenum, which is often considered as an independent unit. The small intestine consists of three membranes :
- External - connecting;
- Medium - muscular;
- Internal - mucous membrane.
The surface of the mucosa is covered with villi, and there are also excretory ducts of the digestive glands. The small intestine, like any other organ, can be susceptible to the development of cancer pathologies.
How to recognize bowel cancer? 7 risk factors Read more
““Tumors of the small intestine” is a collective term that includes formations that have different histological characteristics (characteristics obtained by examining tissue under a microscope). Moreover, the frequency of such diseases in the structure of all tumors of the gastrointestinal tract is about 5%. Almost half of them are malignant,” says Artur Kulikov, a coloproctologist at a multidisciplinary oncology center.
Types of tumors
The most frequently developing malignant neoplasms, as a coloproctologist says, include:
- adenocarcinoma (45%);
- neuroendocrine tumors (NET) (30%);
- lymphoma (10%);
- gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST/GIST);
- sarcomas.
Article on the topic
Fatal heartburn: where esophageal carcinoma and cancer begin Adenocarcinomas are more often observed in individuals with a hereditary predisposition to the development of adenomatous polyposis, with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome or Crohn's disease. The risk of developing adenocarcinoma increases in people over 60 years of age. Adenocarcinoma of the small intestine can metastasize both to regional lymph nodes and to distant organs, most often to the liver, says surgeon Kulikov.
“Carcinoid tumors mainly develop in the ileum and cecum, as well as in the appendix and duodenum. Visually, they are small nodular formations located in the intestinal wall. These tumors are hormonally active,” explains the specialist.
Lymphoma of the small intestine most often occurs in the distal sections - in the ileum and jejunum - due to the presence of a large amount of lymphoid tissue, says the specialist. Risk factors are systemic inflammatory diseases :
- Crohn's disease;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- history of lymphoma of another location.
Bacteria of death. Do antibiotics contribute to colon cancer? More details
“GISTs are most often located in the stomach, jejunum and ileum. About 20-30% of gastrointestinal tumors become malignant. This occurs more often in the small intestine than in the stomach. Tumors smaller than 2 cm are usually benign, while tumors larger than 5 cm are often malignant,” notes Artur Kulikov.
Features of the disease
Irritable bowel syndrome can occur as an independent disease or a concomitant manifestation of other pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. The main characteristic is a dysfunction of irritable bowel, accompanied by dyseptic symptoms, gastrointestinal disorders, eating disorders and other unpleasant manifestations.
Based on the totality of symptoms, three types of irritable bowel syndrome are distinguished:
- accompanied by diarrhea. Expressed in a frequent urge to defecate, especially after eating, pain, frequent loose stools;
- irritable bowel syndrome with constipation. It manifests itself as a long-term absence of stool (a week or more), pain, and in some cases, admixtures of mucus and blood in the stool;
- accompanied by flatulence. It manifests itself as bloating, a feeling of distension in the abdomen. Side symptoms include shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat. They arise due to expansion of the dome of the diaphragm and, accordingly, internal pressure.
Irritable bowel syndrome cannot exist in isolation. It leads to the development of duodenal reflux (bile entering the stomach) and gastroesophageal reflux disease (fluids entering the esophagus). This promotes inflammation of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, resulting in the development of gastritis, cholecystitis, enterocolitis, pancreatitis and even ulcers. Only timely diagnosis and correctly prescribed therapy can prevent these complications.
How to recognize
In the early stages, tumors in the small intestine, like most cancers, are asymptomatic, emphasizes surgeon Kulikov. Most often, patients complain to a doctor when the tumor has already grown deeply into the intestinal tissue and metastasizes to neighboring organs.
Article on the topic
A bad sign of a well-fed life.
What is colorectal cancer and who is at risk from it? The earliest symptoms , as the specialist notes, are:
- nausea or vomiting;
- bloating;
- spasmodic pain in the intestinal area.
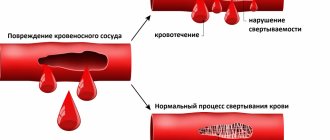
“Then the patient begins to lose weight and intestinal bleeding appears. If the tumor grows strongly, it can block the intestinal lumen, and then obstruction occurs, accompanied by bloating, vomiting, and dehydration. Also, the tumor can compress neighboring organs and tissues, this can cause the development of jaundice, pancreatitis, intestinal ischemia, etc. In some situations, the tumor can rupture the intestinal wall, and then the patient will need urgent surgery, otherwise he may die,” says Artur Kulikov .
Diverticular disease of the small intestine
Diverticular disease of the small intestine is caused by pathological changes in one or more diverticula.
The cause of the disease: impaired emptying of diverticula, development of bacterial colonization syndrome of the small intestine.
Diverticula form in various parts of the small intestine, and therefore the clinical symptoms of inflammation are determined by their location.
For inflammation of diverticula:
a) duodenum, pain appears in the right hypochondrium, accompanied by bad breath. b) duodenum near the papilla of Vater, through which bile and pancreatic enzymes enter the intestine, the development of obstructive jaundice and a picture of acute pancreatitis is possible; c) Meckel's diverticulum in the ileum may cause bleeding, in children - intestinal volvulus, obstruction, in the elderly - symptoms of appendicitis may appear. Multiple diverticula of the jejunum are most often asymptomatic. When they become inflamed, excessive growth of microbes develops, absorption is impaired, swelling occurs, and water-electrolyte metabolism is disrupted.
Clinical symptoms that make one suspect the disease include :
- cramping abdominal pain
- smell from the mouth
- flatulence
- diarrhea
- constipation
- intestinal bleeding
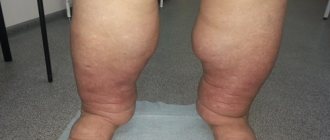
- swelling of the lower extremities
If you have these symptoms, you should consult a doctor. The specialist will assess the condition and prescribe an examination.
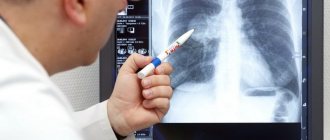
The main method of examination is x-ray examination of the small intestine. This study will determine the violation of emptying of diverticula, the degree of their filling with contrast, thereby confirming or excluding the diagnosis.
The danger of the disease lies in the possibility of progression of the inflammatory process, the development of bleeding, obstruction, abscess and rupture of the diverticulum, complicated by peritonitis.
Treatment consists of following a special diet and using antibacterial drugs. If there are complications, surgical treatment is possible.
At the Moscow Clinical Scientific and Practical Center named after. A.S. Loginova, treatment of diverticular disease of the small intestine is carried out jointly by gastroenterologists and surgeons .
Do not delay your visit to the specialists of our Center. This will help to diagnose this condition in a timely manner and choose the right treatment tactics. Doctors of the department of non-inflammatory intestinal pathology of the State Budgetary Healthcare Institution MKSC named after A.S. Loginova DZM are always ready to help you.
Disease prevention
Preventing irritable bowel syndrome is much easier and cheaper than treating it. Reconsider your lifestyle. Reduce the consumption of fatty, fried, smoked, spicy foods to a minimum, stop smoking and frequent alcohol consumption. Try to have breakfast, lunch and dinner at the same time, avoid snacking on the go. Follow a daily routine. Don't neglect physical activity, including walking and abdominal exercises. Positive attitudes will help reduce the level of anxiety; in difficult cases, consultations with a psychologist or psychotherapist.
Symptoms
If the form of the disease is mild, it may not be recognized. However, as the situation worsens, symptoms can become quite pronounced. You should contact your doctor for a more detailed examination if even one of the following symptoms is observed:
- Discomfort in the intestines of varying severity
- Anemia according to blood tests
- Deficiency of vitamins B12, B9, C and others
- Increased dryness of skin and hair, brittle nails and other signs of vitamin deficiency, especially if you are taking special medications
- Deficiency of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, K
- Hypocalcemia
- Weakness
- Increased excitability or, conversely, apathy
- Losing weight for no apparent reason
Article on the topicFor gastritis, contagious and inherited. Debunking myths about stomach ulcers
You should also pay attention to pain. In this case, the pain may radiate to the lower back, be cramping in nature, or be girdling (it is often compared to intestinal colic). It starts to hurt after eating, and at the same time you can notice bloating and rumbling. The stool changes, becomes more frequent and has an unpleasant odor. The syndrome also leads to a feeling of nausea and affects appetite.
Non-pharmacological therapy
In combination with drug treatment of the disease, additional methods and techniques are recommended that speed up the healing process:
- physical activity within acceptable limits (for example, yoga). If you are overweight, it is also necessary to use programs to reduce your body mass index;
- dietary nutrition that excludes the use of poorly digestible substances, but includes foods enriched with soluble dietary fiber. In addition, it is necessary to exclude the use of products that cause gas formation;
- psychological consultations, stress management training programs.
Drug therapy
The following drugs are used in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome:
- peppermint oil – used to reduce the severity of symptoms;
- antispasmodics - hyoscine, drotaverine and other drugs that have proven effective in treating this disease;
- antidepressants – can be prescribed as part of complex treatment to reduce the severity of symptoms. Tricyclics or SSRIs are used. As a rule, treatment involves taking the minimum effective dose. The course of admission is from 4 to 12 weeks. If the symptoms of the disease decrease, the duration of the course can be increased by the attending physician;
- probiotics – included in treatment if symptoms such as bloating and diarrhea are present. Monostrains or combination drugs are used that have a beneficial effect on the intestinal microflora;
- Rifaximin - the course of treatment for irritable bowel syndrome is about 4 weeks. The main condition for treatment with rifaximin is the absence of symptoms such as constipation;
- polyethylene glycol preparations - used in the treatment of constipation. Other symptoms are not affected;
- loperamide - reduces the severity of diarrhea. It has no effect on other symptoms.
Therapy in our clinics
In our clinics you will receive an appointment with leading specialists - therapists, gastroenterologists, as well as a comprehensive examination using modern methods. At the first stage, you should consult with a therapist, who will conduct an initial examination and refer you to a specialized specialist.
Doctors from the Medcom network of clinics prescribe treatment after a comprehensive examination of the patient and an accurate diagnosis. An individual diet is developed for each patient, including boiled meat, fish, vegetable and fruit purees, natural kefir and other products that normalize intestinal function. If nervous system dysfunction is identified among the causes of irritable bowel syndrome, the doctor prescribes sedatives. For constipation, laxatives are selected taking into account the severity of symptoms and the individual characteristics of the body. The treatment process for irritable bowel syndrome may also include niacin injections, physical therapy, and other medical treatments.
At all stages of treatment for irritable bowel syndrome, the doctor maintains contact with the patient - this is necessary to monitor the effectiveness and make timely adjustments.
What is the problem
Malabsorption, or malabsorption in the intestine, is a malfunction in the functioning of this organ, which is manifested by a number of symptoms resulting from a violation of the digestive and transport functions of the small intestine. This definitely affects metabolism. Malabsorption syndrome is often congenital and manifests itself in children in the first 10 years of life. But there are also cases of acquired disease.
Article on the topic The intestines have neurosis. How to properly treat irritation?
Diagnosis directly depends on symptoms. So, for example, if the clinical manifestations of the congenital variant and the moderate and severe form of the acquired variant can actively manifest themselves, then the latent forms of the syndrome do not have clear manifestations and require a different diagnostic approach.