Hyaluronic acid (HA), or hyaluronate, is one of the most important components of the intercellular fluid. It is “responsible” for retaining moisture in tissues, participates in the process of cell division, and ensures the circulation of lymphocytes, blood cells and oxygen in the body.
With age, the synthesis of hyaluronate decreases, which leads to tissue aging, including the skin. Injections of hyaluronic acid into problem areas help compensate for its deficiency and restore the skin to its former youth and elasticity. This method not only provides a significant anti-aging effect, but also allows you to correct facial features, which in general makes contouring a good alternative to plastic surgery.
Thanks to hyaluronic acid injections you can:
- eliminate wrinkles, including vertical folds between the eyebrows, wrinkles on the forehead, lips, eyes, neck and décolleté;
- smooth out nasolabial folds, nasolacrimal and lacrimal grooves;
- carry out lip contouring, that is, correct their shape;
- carry out correction of the earlobe and nose.
How to use hyaluronic acid at home
Procedures and cosmetics can be quite expensive, so many women resort to using homemade cosmetics. To do this, you will need to purchase sodium hyaluronate powder at the pharmacy and prepare a solution for external use.
To do this, you need to dilute 2 g of the active substance in 30 ml of warm drinking water. leave to infuse for 40-60 minutes. The finished solution can be used as a cream. It should be applied to previously cleansed skin. Apply any other anti-aging product of similar effect on top.
Content
- Areas corrected with fillers
- Main varieties
- Indications and contraindications
- Carrying out the procedure
- Rehabilitation
- Possible side effects
- Before/after photos
Fillers are used for the following procedures:
- bioreinforcement of the body and face;
- elimination of wrinkles;
- correction of the chin, cheekbones, nose;
- correction of certain types of scars;
- face oval lifting;
- eliminating dry, unhealthy skin color;
- correction of earlobes;
- elimination of post-acne;
- as part of a weight loss program;
- elimination of asymmetry.
Application in cosmetology
Hyaluronic acid has gained the greatest popularity in aesthetic medicine. The main indication for prescribing HA injections in cosmetology is the need to correct various deformations of skin contours, such as:
- scarring,
- deep wrinkles,
- folds,
- changing the shape of the lips.
Giving the lips additional volume by introducing hyaluronic acid does not have a lifelong effect.
The drug is administered intradermally, and the visible volume of the tissue increases. The maximum dose for correction of one area should not exceed 30 mg of active substance or 1.5 ml. If the patient requires a larger volume of the drug, then the injections are given in separate courses.
Side effects of this procedure may include:
- swelling,
- redness,
- itching,
- pain at the injection site,
- acne-like papules,
which usually go away on their own within a day or two. It should be taken into account that the administration of GC is incompatible with the use of other drugs, and when taking anticoagulants it can lead to the appearance of hematomas. There are also contraindications for the use of HA. So, hyaluronic acid cannot be injected:
- with skin hypersensitivity;
- after laser and chemical peeling;
- if there is inflammation in the area where injection is necessary;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- severe chronic diseases;
- autoimmune diseases;
- tendency to form keloid scars;
- acute form of herpes.
GC preparations should not be used before the age of 25
Biorevitalization of the face
A procedure called biorevitalization is performed in beauty salons for the purpose of rejuvenation. To correct wrinkles and folds, HA is injected into the skin linearly or a series of pinpoint injections are performed. The effect of this procedure is to moisturize the skin and rejuvenate its appearance due to the stimulation of the production of its own collagen and elastin fibers.
The technique can be used for any area of the skin that requires correction, but most often it is required in open areas exposed to ultraviolet radiation. This is the face, neck, décolleté and hands. A course of biorevitalization can be preventive or therapeutic.
The first is used to prevent dryness and early aging of the skin and includes two procedures with an interval of 3-4 weeks. This course moisturizes the skin well and helps normalize metabolic processes, thus preventing the withering of exposed skin. Typically used on the face, lips and hands.
Indications for therapeutic revitalization include the presence of pronounced age-related skin changes. The treatment course involves a deeper and more intense effect on the skin and includes three procedures performed at a similar interval. The treatment procedure effectively copes with such changes as:
- severe dehydration and aging of the skin;
- violation of skin pigmentation;
- decreased elasticity and skin turgor;
- recovery after plastic surgery and aggressive peeling.
For two days after the procedure, you should not touch your face, much less use cosmetics. The exception is those medications prescribed by the doctor. For a week after the procedure, you should not go to the bathhouse or sauna or play sports. Within two weeks from the date of injection, the skin should be protected from exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
Reviews from those who have undergone this procedure confirm its effectiveness and quick results, although many find it quite painful. In this case, bruises and papules can persist for up to three days.
In addition to the solution for intradermal injection, produced in ampoules, hyaluronic acid is included in various anti-aging creams, gels, and masks, which are used both in beauty salons and at home.
Application methods for using HA are available at home
Indications and contraindications
Any medical and cosmetic drug must be used according to indications, as well as taking into account certain restrictions.
Indications for the use of HA fillers:
- scars, wrinkles, deep nasolabial folds;
- uneven skin;
- dark circles under the eyes;
- unaesthetic shape of lips, cheeks, cheekbones, etc.;
- eyebrow folds;
- various traces of injuries, post-acne.
Contraindications:
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- severe autoimmune diseases;
- allergy to fillers;
- skin diseases in the intended treatment area;
- influenza, ARVI, etc.;
- increased body temperature;
- tendency of the skin to form keloid scars;
- herpes in the acute stage;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- diabetes;
- dysfunction of internal organs;
- blood clotting disorder;
- recent laser resurfacing, deep or medium peeling, photorejuvenation.
Introduction
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a joint disease, the main pathogenesis of which is cellular stress and degradation of the extracellular matrix. They arise as a result of macro- or microdamage that activates pathological adaptive recovery reactions, including pro-inflammatory pathways of the immune system [1]. According to estimates by the Federal State Statistics Service of the Russian Federation for 2021, diseases of the musculoskeletal system occupy a significant place in the structure of disability along with cardiovascular diseases and cancer. OA plays an important role among these diseases [2]. Currently, the prevalence of the disease is steadily increasing. OA accounts for 36 million outpatient visits and 750 thousand hospitalizations per year. In developed countries, the economic costs of OA amount to 1.5–2% of GDP per year [3]. Clinical manifestations and progression of OA do not pose a threat to the life of patients, but pain, which is a constant symptom of the disease, and limitation of joint function lead to a marked deterioration in the quality of life, the development of temporary and permanent disability. Against this background, there is a progression of concomitant diseases, which leads to an increased risk of overall mortality. In 2021, the Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI), together with the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), recognized OA as a serious disease [4]. In Russia, the prevalence of OA is also high and reaches 13%. According to the Russian Ministry of Health, over 5 years (2011–2016) there was an increase in the incidence of OA from 32.3 to 35.7 per 1000 population. In recent years, in the process of studying OA, ideas about its pathogenesis have changed significantly. Currently, OA is considered not as a degenerative disease, but as an inflammatory disease. The diversity and varying degrees of severity of individual pathogenesis links have led to the identification of several OA phenotypes. Changing understanding of the pathogenesis of the disease is also changing approaches to therapy, with an emphasis on personalized treatment.
The effect of hyaluronic injections in the face
Contour plastic surgery with hyaluronic acid is a procedure during which a cosmetologist injects filler under a wrinkle or skin fold and fills the insufficient volume with the drug. This allows you to model your appearance, correct facial asymmetry, smooth out wrinkles, scars, scars, moisturize and rejuvenate the skin.
Hyaluronic facial injections are also popular among women who want to increase the size and volume of their lips.
To prevent pain and discomfort, half an hour before the injections, the cosmetologist applies an anesthetic cream to the affected area.
The result of contouring with hyaluronic acid is noticeable immediately after injection correction, but the final assessment of the result can be made in a couple of days, after the slight swelling in the injection area has subsided.
Recommendations for the management of patients with OA
Currently, OA therapy is regulated by documents developed by professional communities. ESCEO (European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis and Musculoskeletal Diseases) has developed guidelines that guide consistent treatment choices for patients with knee OA . They were presented in 2014 [5], and expanded in 2021 [6]. New recommendations were published in 2021, taking into account the latest evidence on the safety and effectiveness of drugs currently used to treat OA [7]. The developed scheme recommends step-by-step administration of therapy (Fig. 1).
If OA symptoms persist, the use of hyaluronic acid (HA) is indicated, both as monotherapy and in combination with drugs from other groups. Let's take a closer look at the effects of HA.
Rehabilitation period
To avoid complications and enhance the effect after any injection procedures with hyaluronic acid, you should adhere to the following rules:
- During the day, try not to touch the injection areas and avoid exposure to them during sleep;
- use antiseptic drugs recommended by a specialist;
- do not use cosmetics unless otherwise prescribed by a doctor;
- avoid exposure to ultraviolet radiation, after the ban on the use of cosmetics is lifted, apply sunscreen to the skin;
- do not overheat, do not visit the sauna and bathhouse;
- refuse any care and therapeutic procedures, unless otherwise recommended by the cosmetologist;
- If you suspect complications, contact a specialist.
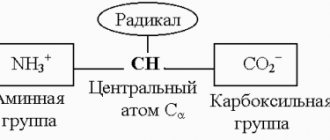
Glycosaminoglycans[edit | edit code]
Formula of chondroitin sulfate, one of the glycosaminoglycans.
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are unbranched polysaccharide chains built from repeating disaccharide units in which one of the two sugar residues is an amino sugar (N-acetylglucosamine or N-acetylgalactosamine), which in most cases is sulfated. The presence of sulfate or carboxyl groups (or both) on many sugar residues gives glycosaminoglycans a large negative charge. The second sugar is usually an uronic acid (glucuronic or iduronic). There are four main groups of GAGs:
1) Hyaluronate.
2) Chondroitin sulfate and dermatan sulfate.
3) Heparan sulfate and heparin.
4) Keratan sulfate.
GAGs carry a large negative charge, are highly hydrophilic, have a highly elongated conformation, and form gels even at low concentrations. The recruitment of osmotically active cations by GAG causes swelling pressure (matrix turgor), which gives the matrix the ability to resist compressive forces. Because GAGs form porous hydrated gels, they fill most of the available space and provide tissue support while allowing water-soluble molecules to diffuse and cells to migrate.
Anti-inflammatory and regenerating mechanisms of action of GCs
The physiological role of HA has been well described by many researchers [8–10]. In general, HA can participate in various cellular processes (cell differentiation, proliferation, etc.) and perform physiological functions (lubrication, hydration balance) [9, 10]. HA has unique rheological properties and is an integral part of articular cartilage; the important role of HA in the functioning of joints, not only healthy ones, but also joints with OA [11], as well as other body tissues, has been well studied [12]. Studying the pharmacological action of GC, E. Maheu [13], GM Campo [14] and J. Jerosch. [15] in their studies proved that GC reduces the activity of proinflammatory mediators that produce neuropeptides released by activated synovial cells. The authors also described the interaction of HA with pain receptors and its analgesic properties.
LW Moreland [10] noted in his study that HA can reduce the mechanosensitivity of pain receptors. GC may also reduce OA pain by reducing the synthesis of prostaglandin E2 and bradykinin.
In OA, synovitis plays an important role in inducing pain, swelling and stiffness [16], and the severity of synovitis correlates with a high risk of progression to knee OA [17]. A study was conducted that showed that GC inhibits the activity of matrix metalloproteinases and aggrecanases, which are at least partially involved in the degradation of OA cartilage as a result of their induction by proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1 (IL-1) [18]. . Therefore, it is hypothesized that GC modifies structural joint damage and the rate of progression of OA in addition to its symptom-modifying effect [19].
Regarding the reparative function of HA, JL Cook et al. [20] suggested that intra-articular administration of GC has a direct effect on chondrocytes or synoviocytes and the production of Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β), basic fibroblast growth factors (FGF) and insulin-like growth factor (Insulin-β). like growth factor, IGF). Histological data confirmed that HA prevents cartilage degradation and may promote cartilage regeneration. Other authors [14] have also provided evidence that GC treatment mitigates synovial hypertrophy and increases the number of synovial fibroblast-like cells while reducing the number of macrophages, lymphocytes, mast cells and adipocytes. HA, according to them, provides cartilage protection by suppressing the production of proinflammatory cytokines, free radicals and proteolytic enzymes in the synovial fluid.
A large number of clinical studies have found that GC reduces the progression of OA. GC is a slow-acting drug that can be used prophylactically or therapeutically as an anti-inflammatory symptom-modifying drug [20, 21].
Several clinical studies have found that intra-articular HA injections slow joint space narrowing on x-ray and stop the progression of cartilage degeneration on subsequent arthroscopy [22, 23].
Main types of fillers
The advantages of hyaluronic fillers for the face and body are that hyaluronic acid is a substance contained in skin cells and is responsible for retaining moisture in the intercellular space. With age, its synthesis slows down, and a deficiency of this substance develops. The skin becomes less elastic, dry, wrinkles and other imperfections appear. Fillers replenish the deficiency of hyaluronic acid, restoring skin elasticity, beautiful color and pleasant texture. Moisturizing occurs, the production of elastin and collagen is stimulated, and regeneration processes begin. Moreover, the drugs have a gel structure, due to which they fill the intercellular space well and are slowly absorbed (biodegradation takes from 6 to 24 months).
Types of hyaluronic fillers
The results of recent studies indicate that the optimal concentration of hyaluronic acid in filler is 22 mg/g. Preparations based on it also contain a stabilizer. Its concentration is considered optimal at the rate of 0.5 mg/g. Most often, the stabilizer is BBDE, that is, butanediol diglycidyl ether, less often - DVS (divinyl sulfone). It is the concentration of the stabilizer that provides the desired cosmetic effect, but the higher it is, the higher the risk of an undesirable consequence in the form of an allergic reaction, since these substances are no longer “native” to the skin.
Fillers are divided into:
- Monophasic (hyaluronic acid content – 15-26 mg/g). Examples: Teosyal, Juviderm, Stylage. Evenly distributed in the folds of the skin and under it. They are distinguished by elasticity, are easier to insert under the skin and are corrected after insertion by manual action. Secondary correction after use is almost never necessary. Biodegradation occurs evenly. They are used to correct and enlarge lips, fill wrinkles, including facial wrinkles, post-acne, scars, and improve skin tone.
- Biphasic (GK – 22-23 mg/g). Examples: Restylane, Perfectha Derm. They allow you to work with larger-scale imperfections than single-phase ones. They have a high density, so manual correction is difficult, they have a smooth consistency, and are more difficult to insert and distribute under the skin. Biodegradation occurs unevenly. Primary – up to 30%, so contour plastic surgery requires correction after some time. The main advantage is long-term preservation of the effect due to high density. Even if deep lifting was performed, the primary result will last up to 1 year. Used to correct and lift the oval of the face, fill deep wrinkles, correct the tip and back of the nose, chin, cheekbones, and lip modeling.
Carrying out the procedure
Today, the use of hyaluronic acid fillers is one of the safest and fastest methods for solving aesthetic and some medical problems.
The duration of the procedure is from 5 to 60 minutes. On average - half an hour. Pain relief is by application, and some fillers include Lidocaine. Before the session, the doctor cleans and marks the face, places dots in the areas where the drug is administered. Photos may be taken to compare the condition of the problem area before and after the intervention. The ampoule is shown to the patient - its expiration date, integrity of the packaging, dosage. After this, the filler is injected in a targeted manner using a very thin needle, for example, under a wrinkle. Sometimes the drug is administered perpendicularly - this enhances the effect due to the formation of a reinforcing frame.
After the session, a facial massage is performed to evenly distribute the filler. The achieved effect is fully manifested after two weeks, when the skin is enriched with moisture.
Areas corrected with fillers
One of the most popular uses of hyaluronic fillers is lip augmentation and/or correction of their shape and contour, elimination of drooping corners and wrinkles.
Video about lip augmentation
In addition, hyaluronic acid injections (“beauty injections”) are performed on the following areas of the face and body:
- eyebrows (removal of interbrow folds, or so-called “wrinkles of anger”);
- eyes (to eliminate crow's feet, adding volume to eyelids);
- forehead (removal of facial wrinkles);
- face (oval correction);
- cheekbones (adding volume);
- back of the hands (rejuvenation);
- any area of skin (filling scars);
- ears (lobe correction);
- cheeks (replenishing volume, giving relief).