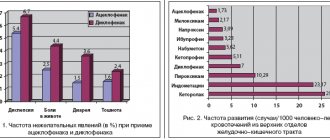
Drugs from the NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) group are used to treat acute back and joint pain. Nemulex and Nimesil are two medications that are similar in their therapeutic effects. They contain nimesulide, a substance that can reduce pain, lower temperature and relieve inflammation. A special release form (powder for dissolution in water) ensures rapid absorption of drugs, and their effect manifests itself quite quickly.
Compound similarities
These drugs have the same release form - water-soluble powder. Their therapeutic effects are similar. Both drugs effectively reduce temperature and eliminate pain.
Nemulex contains the active substance – nimesulide.
Additional components:
- macrogol;
- sucrose;
- flavoring agents;
- citric acid;
- silicon.
The medicine has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, and antiaggregation properties. The product has good digestibility. The medicine remains at its highest concentration in the blood for 2.5 hours.
The drug quickly enters the lesion and is excreted by the liver and kidneys. Nemulex suppresses prostaglandins in the inflammatory focus. The medicine is used to treat negative symptoms. The medication eliminates pain and prevents the development of inflammation.
Indications for use:
- arthritis;
- muscle pain;
- joint pain;
- bursitis;
- tenosynovitis;
- pain during menstruation;
- headache;
- toothache;
- pain syndrome during the development of intervertebral hernia;
- pain after injuries and operations.
The product does not have a therapeutic effect, but eliminates pain and inflammation of an episodic nature.
Indications for use of Nemulex: arthritis, muscle pain, joint pain.
Nimesil is produced in the form of granules for oral administration and suspension. The active substance is the same - nimesulide.
Additional components:
- macrogol;
- maltodextrin;
- lemon acid;
- sucrose;
- flavorings.
The medicine is a non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drug. It has anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and analgesic properties.
The drug reduces the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting cyclooxygenase. After oral administration, the drug is well absorbed, reaching its highest concentration in the blood after 2-3 hours. The drug is metabolized in the liver.
Indications for use:
- elimination of pain syndrome;
- relief from primary dysmenorrhea.
How do they work?
When injury, infection, or degenerative changes occur in the spine and joints, tissue cells are damaged. When cell membranes are destroyed, phospholipids are released. They break down into fatty acids, among which is arachidonic acid. Further, under the action of the enzyme COX-2 (cyclooxygenase type 2), arachidonic acid is converted into biologically active substances, including prostaglandins. They organize the inflammatory response.
Inflammation is accompanied by swelling and pain. To relieve inflammation, you need to reduce prostaglandin production. Drugs from the NSAID group block (inhibit) the work of cyclooxygenase, and without it prostaglandin is not formed.
Nimesulide is a selective (selective) COX-2 inhibitor. That is, the active substance of both drugs acts selectively, affecting predominantly this type of enzyme. This is important because it is COX-2 that is triggered in response to damage, causing an inflammatory response. There is also the enzyme COX-1: it is formed normally in the body and is needed for the synthesis of those prostaglandins that are involved in normal physiological reactions. Non-selective inhibitors, such as acetylsalicylic acid or ketorolac, act on COX-1 and COX-2; at the same time, the number of side effects associated with suppression of prostaglandin production in the gastric mucosa and kidneys increases.
So, Nemulex and Nimesil have the same effect. It is based on reducing the synthesis of prostaglandins - the main participants in inflammation, pain and fever.
Differences between Nimesil and Nemulex
Despite the fact that these drugs are analogues, they also have differences.
Main differences:
- the price of Nemulex is less than Nimesil;
- they are made by various manufacturers;
- the taste and smell of the powder differs;
- Nemulex granules are larger than Nimesil;
- Nemulex in powder form often takes longer to dissolve in water.
But these differences are not significant; they do not affect the effectiveness of the drugs. Thus, apart from the price and slight differences in the composition of the components, these drugs do not differ in anything else. Both medications effectively eliminate pain and alleviate the patient's condition.
These medications should not be taken together, because they both contain the active ingredient nimesulide, and if taken at the same time, there may be an overdose that will cause side effects.
Both drugs have the same indications for use:
- osteoarthritis;
- arthritis;
- myalgia;
- arthralgia;
- headache and toothache.
When are these drugs used?
Both medications relieve symptoms of inflammation, reduce fever and relieve pain. Indications for the use of drugs are general - symptomatic treatment of acute pain in diseases of the joints and spine of an inflammatory, degenerative, autoimmune and traumatic nature:
- arthrosis (dystrophic change in articular cartilage);
- osteochondrosis with pain syndrome;
- inflammation of joints of various etiologies;
- inflammation of tendons (tendinitis), muscles (myositis), joint capsule (bursitis);
- injuries, bruises, sprains.
In addition, both medications are prescribed to relieve toothache and painful menstruation.
Occurring side effects: diarrhea, nausea, exacerbation of bronchial asthma, allergic reactions. Hepatitis and jaundice rarely occur, and the activity of liver enzymes increases.
Nimesulide is hepatotoxic, so drugs based on it are not prescribed to people with liver diseases.
Like any NSAIDs, Nimesil and Nemulex have an impressive list of contraindications, including age under 12 years, pregnancy and breastfeeding. Before taking, please read the instructions carefully.
Contraindications
Nemulex and Nimesil have the following contraindications:
- intolerance to the components of the drug;
- bronchospasm;
- alcoholism;
- gastrointestinal bleeding;
- stomach and duodenal ulcers;
- cerebrovascular bleeding;
- increased bleeding;
- bleeding disorders;
- severe heart failure;
- liver and kidney dysfunction;
- flu;
- high body temperature;
- children under 12 years of age;
- pregnancy in the third trimester;
- lactation;
- hyperkalemia;
- if the patient has undergone coronary artery bypass surgery;
- diabetes.
Nimesil has the following contraindications: intolerance to the components of the drug, bronchospasm.
These drugs should not be used simultaneously with antiplatelet agents, glucocorticosteroids and anticoagulants.
Nemulex® (Nemuleks®)
Undesirable side effects can be minimized by using the drug in the minimum effective dose with the minimum duration of use necessary to relieve pain.
There is evidence of very rare cases of serious reactions from the liver, including cases of death, associated with the use of nimesulide-containing drugs. If symptoms similar to signs of liver damage appear (anorexia, itching, yellowing of the skin, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark urine, increased activity of liver transaminases), you should immediately stop using the drug NEMULEX® and consult a doctor. Repeated use of NEMULEX® in such patients is contraindicated.
Liver reactions, which are in most cases reversible, have been reported with short-term use of the drug.
While using NEMULEX®, the patient should refrain from taking other analgesics, including NSAIDs (including selective COX-2 inhibitors).
NEMULEX® should be used with caution in patients with a history of gastrointestinal diseases (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease), since exacerbation of these diseases is possible.
The risk of gastrointestinal bleeding, peptic ulcer/perforation of the stomach or duodenum increases in patients with a history of ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease), as well as in elderly patients, with an increase in the dose of PPVP. Therefore, treatment should be started with the lowest possible dose. In such patients, as well as in patients who require the simultaneous use of low doses of acetylsalicylic acid or other drugs that increase the risk of complications from the gastrointestinal tract, it is recommended to additionally prescribe gastroprotectors (misoprostol or proton pump blockers). Patients with a history of gastrointestinal disease, especially older patients, should report new gastrointestinal symptoms (especially symptoms that may indicate possible gastrointestinal bleeding) to their physician.
NEMULEX® should be administered with caution to patients taking drugs that increase the risk of ulceration or bleeding (oral corticosteroids, anticoagulants such as warfarin, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors or antiplatelet agents such as acetylsalicylic acid).
If gastrointestinal bleeding or gastrointestinal ulceration occurs in patients taking NEMULEX®, treatment with the drug must be stopped immediately.
Given reports of visual impairment in patients taking other NSAIDs, if any visual impairment occurs, use of NEMULEX® should be immediately discontinued and an ophthalmological examination performed.
Nimesulide can cause fluid retention, therefore, in patients with arterial hypertension, renal and/or heart failure, NEMULEX® should be used with extreme caution. If the condition worsens, treatment with NEMULEX® should be discontinued.
Clinical studies and epidemiological data allow us to conclude that. that NSAIDs, especially in high doses and with long-term use, may lead to a small risk of myocardial infarction or stroke. There is insufficient data to exclude the risk of such events when using nimesulide.
In patients with arterial hypertension, renal and/or heart failure, coronary heart disease, peripheral arterial disease and/or cerebrovascular diseases, with risk factors for the development of cardiovascular diseases (for example, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, smoking patients), NEMULEX® should be used with special caution. If the condition worsens, treatment with NEMULEX® should be discontinued.
The drug contains sucrose, this should be taken into account by patients suffering from diabetes (0.15 XE in one sachet) and those on a low-calorie diet. NEMULEX® is not recommended for use in patients with fructose intolerance, sucrose-isomaltase deficiency, or glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome.
If signs of a “cold” or acute respiratory viral infection occur while using the drug 11EMULEXk, the drug should be discontinued. Nimesulide can change the properties of platelets, so caution must be exercised when using the drug in people with hemorrhagic diathesis, however, the drug does not replace the preventive effect of acetylsalicylic acid in cardiovascular diseases.
Elderly patients are especially susceptible to adverse reactions to NSAIDs, including life-threatening gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation, and decreased renal, liver, and cardiac function. When taking NEMULEX® for this category of patients, proper clinical monitoring is necessary.
There is evidence of rare cases of skin reactions (such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis) when taking NSAIDs. including nimesulide. At the first manifestations of a skin rash, damage to the mucous membranes or other signs of an allergic reaction, taking NEMULEX® should be stopped immediately.
How to take Nimesil and Nemulex
Nemulex is taken as follows. It is necessary to dissolve the contents of the package in 0.5 cups of boiled water. For adult patients and children over 14 years of age, take 100 mg 2 times a day. The medicine is taken after meals. The course of treatment should last no more than two weeks.
Nimesil is taken in a short course. The product is drunk after meals. The course of treatment should not last more than 14 days. For adults, 100 ml of the active substance (1 sachet of powder) is prescribed 2 times a day. Children and the elderly are prescribed the same dosages. Before taking the medicine, you need to pour the contents of the sachet into a glass of water, dissolve and drink the product.
What is the difference?
Nemulex (instructions) is produced in granules for the preparation of a suspension by Romanian pharmaceuticals, and is produced in Russia. The sachets contain 2 g of granules; packed in 4, 10 or 30 pieces per pack.
Nimesil (instructions) is produced in Italy;
it is also produced in bags of granules (2 g each), 9 or 30 bags per pack. Comparative table of compositions
| Nemulex | Nimesil |
| Active ingredient | |
| Nimesulide (100 mg per 2 g) | |
| Excipients | |
| Macrogol cetostearate; colloidal silicon dioxide (aerosil); lemon acid; orange flavor; sucrose | Ketomacrogol 1000; maltodextrin; lemon acid; sucrose; orange flavor |
Nemulex and Nimesil contain nimesulide in the same amount. A comparison of drugs by auxiliary components shows that, although their difference is not significant, it exists. Various components are used as emulsifiers and a base for the powder. Perhaps because of this, there is some difference in the pharmacokinetics of the drugs:
- Nemulex reaches its maximum concentration in the systemic circulation after 1.5–2.5 hours, and Nimesil slightly later, after 2–3 hours.
- The half-life of Nemulex is 3–5 hours, Nimesil is 3–6 hours.
- Nimesulide is excreted by the kidneys. In Nimesil, the amount of nimesulide metabolite excreted by the kidneys is 50%; Nemulex has 65%. The rest comes out with bile.
Changes in the concentration of the active drug substance in organs and tissues over time occur with slight differences.
The same components are added to give the granules flavor.
Nemulex granules are slightly larger than Nimesil, so they take longer to dissolve in water.
Comparison of granules
Conclusion
If you need to provide a quick anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect using a drug from the NSAID group, doctors often prescribe Nemulex or Nimesil, which contain the same active substance and have a similar effect. The release form is also the same: powders for dissolution in water. The differences in pharmacokinetics are very minor and do not affect the therapeutic effect of the drugs. Therefore, which of these drugs is better depends on the patient’s preferences and the availability of the drug in the pharmacy.
The cost of drugs can be
Side effects of drugs Nimesil and Nemulex
Side effects of Nemulex are:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- sleep disorders;
- increased blood pressure;
- dyspnea;
- stomach bleeding;
- depression.
Side effects of Nimesil:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- pain in the epigastrium;
- sleep disorders;
- gastrointestinal bleeding;
- arterial hypertension;
- acute renal failure;
- breathing problems;
- anaphylaxis.
Buy Nemulex granules for suspension 100 mg 2 g No. 30 in pharmacies
Nemulex Buy Nemulex in pharmacies Nemulex in the drug directory DOSAGE FORMS granules for the preparation of suspension for oral administration 100 mg
MANUFACTURERS Sotex PharmFirm (Russia)
GROUP Anti-inflammatory drugs of different groups
COMPOSITION Active substance: nimesulide.
INTERNATIONAL NON-PROPENTED NAME Nimesulide
SYNONYMS Actasulide, Aponil, Koxtral, Mesulide, Nise, Nimegesic, Nimesil, Nimesulide, Nimica, Nimulid, Prolid, Flolid
PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTION Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It has anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antipyretic and antiplatelet effects. Unlike other NSAIDs, it selectively suppresses COX-2 and inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins at the site of inflammation; has a less pronounced inhibitory effect on COX-1 (less likely to cause side effects associated with inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis in healthy tissues). Absorption when taken orally is high. Eating reduces the rate of absorption without affecting its extent. The maximum concentration in blood plasma is 3.5-6.5 mg/l. Binding to plasma proteins - 95%, to erythrocytes - 2%, to lipoproteins - 1%, to acidic alpha1-glycoprotein 1%. Metabolized in the liver by tissue monooxygenases. The main metabolite, 4-hydroxynimesulide (25%), has similar pharmacological activity, but due to a decrease in molecular size, it is able to quickly diffuse through the hydrophobic COX-2 channel to the active binding site of the methyl group. 4-hydroxynimesulide is a water-soluble compound, the elimination of which does not require glutathione and phase II metabolic conjugation reactions (including sulfation, glucuronidation). 4-hydroxynimesulide undergoes enterohepatic recirculation. The half-life of nimesulide is 1.56-4.95 hours, 4-hydroxynimesulide is 2.89-4.78 hours. 4-hydroxynimesulide is excreted by the kidneys (65%) and bile (35%).
INDICATIONS FOR USE Rheumatoid arthritis; osteoarthritis; arthritis of various etiologies; arthralgia; myalgia; postoperative and post-traumatic pain; bursitis; tendinitis; algodismenorrhea; toothache and headache. The drug is intended for symptomatic therapy, reduces pain and inflammation at the time of use, and does not affect the progression of the disease.
CONTRAINDICATIONS Hypersensitivity; complete or incomplete combination of bronchial asthma, recurrent nasal polyposis or paranasal sinuses and intolerance to acetylsalicylic acid and other NSAIDs (including a history); erosive and ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum; active gastrointestinal bleeding; cerebrovascular or other bleeding; inflammatory bowel diseases (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis) in the acute phase; hemophilia and other bleeding disorders; decompensated chronic heart failure; liver failure or any active liver disease; history of hepatotoxic reactions when using nimesulide; alcoholism; addiction; severe chronic renal failure (CR
SIDE EFFECTS Allergic reactions: hypersensitivity reactions, anaphylactoid reactions. From the side of the central nervous system: dizziness, feeling of fear, nervousness, nightmares, headache, drowsiness, encephalopathy (Reye's syndrome). From the skin: itching, skin rash, increased sweating, erythema, dermatitis, erythema multiforme exudative, incl. Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's syndrome). From the urinary system: edema, dysuria, hematuria, urinary retention, hyperkalemia, renal failure, oliguria, interstitial nephritis. From the digestive system: diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, constipation, flatulence, gastritis, abdominal pain, stomatitis, tarry stools, gastrointestinal bleeding, ulcer and/or perforation of the stomach or duodenum, increased liver transaminases, hepatitis, fulminant hepatitis, jaundice, cholestasis. From the hematopoietic system: anemia, eosinophilia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, purpura, prolongation of bleeding time. From the respiratory system: shortness of breath, exacerbation of bronchial asthma, bronchospasm. From the senses: blurred vision. From the cardiovascular system: arterial hypertension, tachycardia, hemorrhages, hot flashes. Other: general weakness, hypothermia.
INTERACTION There is evidence that nimesulide can reduce the bioavailability of furosemide and compete for binding to plasma proteins of fenofibrate, salicylic acid, and tolbutamides. May replace salicylic acid and furosemide (but not warfarin) in plasma proteins. In the presence of the drug, the free fractions of methotrexate may increase significantly. Taking the drug in therapeutic doses orally for a short period does not change the serum profile of digoxin in patients with mild heart failure. Plasma lithium concentrations increase when lithium and nonmex are taken concomitantly. It is not recommended to take Nemex at the same time as diuretics, which have a damaging effect on renal hemodynamics. May enhance the effect of cyclosporine on the kidneys. When using the drug simultaneously with corticosteroids and serotonin reuptake inhibitors, the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding increases.
METHOD OF APPLICATION AND DOSAGE The drug is taken orally. The contents of 1 sachet of granulate are dissolved in 80-100 ml of water. The recommended dose for adults and adolescents aged 12-18 years is 100 mg (1 sachet) 2 times a day after meals. The maximum daily dose for adults and adolescents aged 12-18 years is 200 mg.
OVERDOSE Symptoms: nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, apathy, gastrointestinal bleeding, increased blood pressure, acute renal failure, respiratory depression. Treatment: Symptomatic and supportive treatment is recommended. There is no specific antidote. Patients admitted to the hospital with symptoms of a drug overdose (within 4 hours after taking it or after taking a high dose) are recommended to lavage the stomach, take activated charcoal (adults - 60-100 mg) and/or an osmotic laxative. Regular monitoring of liver and kidney function is necessary. There is no data on the possibility of removing nimesulide using hemodialysis. Forced diuresis and hemodialysis are ineffective due to the high degree of binding of the drug to proteins.
SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS To reduce the risk of side effects, it is necessary to use the drug in the minimum effective dose for the shortest duration. If the patient's condition does not improve, treatment should be stopped. It is necessary to stop taking the drug if the temperature rises or flu-like symptoms develop while taking it. If patients taking the drug develop symptoms indicating liver damage (for example, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fatigue, dark urine), or increased liver transaminases, the drug should be discontinued. Such patients are not recommended to be prescribed this drug in the future. Gastrointestinal bleeding or ulcer/perforation of the stomach or duodenum can develop at any time while using the drug and is not accompanied by clinically significant symptoms (including pain). If gastrointestinal bleeding or ulcers occur, or if renal function deteriorates, the drug should be discontinued. If the drug is used for more than 2 weeks, monitoring of liver function indicators is necessary. In patients with liver cirrhosis or renal failure, with hypoalbuminemia or hyperbilirubinemia, the binding of nimesulide is reduced. Elderly patients most often develop side effects when taking the drug, incl. gastrointestinal bleeding, perforation, dysfunction of the heart, kidneys and liver. Therefore, regular clinical monitoring of the patient’s condition is recommended. If, when using the drug, undesirable effects from the central nervous system and sensory organs occur, then patients should refrain from driving vehicles and engaging in activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
STORAGE CONDITIONS Store out of reach of children, in a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 C.
Reviews from doctors
Svetlana Anatolyevna, therapist
These drugs are prescribed when the patient urgently needs relief from pain. Medicines effectively eliminate headaches, toothaches, and pain during menstruation. Patients tolerate these medications well, but they cannot be taken for a long time. The course of treatment should not last more than two weeks.
Arkady Mikhailovich, rheumatologist
In patients with rheumatoid arthritis, when the disease worsens, joint pain intensifies and the inflammatory process worsens, these drugs are prescribed. They effectively cope with pain and inflammation.
Patient reviews
Alla, 35 years old
If pulpitis occurs, the doctor recommended taking Nimesil. He quickly eliminated severe toothache. The next day, when the severe pain had already disappeared, I went to see a dentist to treat a bad tooth.
Sergey Ivanovich, 60 years old
I have been suffering from osteoarthritis of the knee joints for several years. When the disease worsens, severe pain occurs and it becomes impossible to walk. In this case, the doctor advised taking Nemulex. I take the drug according to the instructions prescribed by the doctor. After a few days, the pain subsides.