This is a special category of bacterial cultures, many species of which are dangerous to human health. Staphylococci are commonly called opportunistic microbes. Living in the body constantly, they are under the control of the immune system. But when the protection is weakened, they can provoke an inflammatory process. Some bacteria are extremely resistant to antimicrobial agents and often cause superinfections.
About the disease
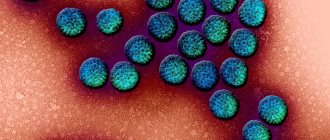
When grown in a petri dish containing blood agar, Staphylococcus aureus colonies have a characteristic golden yellow color, hence the name. This microorganism is extremely common, colonizing about a quarter of the world's population.
It usually spreads in the nasal cavity, groin area, armpits and other parts of the skin, but in most cases it is a normal part of human skin flora and does not cause any problems.
However, as the number of bacteria on the skin increases, they begin to penetrate into the deeper layers of the skin through microcracks and can lead to skin infections and abscesses.
Pathological processes can affect not only various internal organs, such as the liver, kidneys, spleen, brain, but also muscles, bones and joints, which leads to extremely disastrous consequences, therefore, if you suspect an infection, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Types of staphylococcal infections
There are several most common types of staphylococci:
● Hemolytic staphylococcus.
Most often, this infection affects the upper respiratory tract, causing purulent sore throat, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, bronchitis and other inflammatory diseases. These bacteria are very resistant and difficult to treat.
● Golden.
This microorganism is extremely resistant to almost all types of penicillin antibiotics, antiseptics, high temperatures, and active direct sunlight. It causes various skin lesions, such as eczema, abscess, boils, lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, upper respiratory tract, mucous membranes, and in the worst case leads to toxic shock.
● Epidermal.
This microorganism lives on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes of any healthy person and does not cause any harm. But, if this bacterium enters the blood of a person with a weakened immune system, which most often occurs during surgical operations, the use of improperly processed instruments, catheters, blood poisoning occurs, which leads to inflammation of the inner lining of the heart.
● Saprophytic.
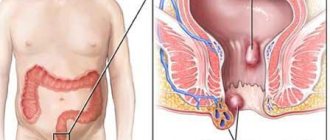
Despite the fact that this species is the least dangerous, when infected it leads to general intoxication of the body due to the release of dangerous toxins and enzymes during its life processes. These microorganisms often cause inflammation of the urethra and bladder. This is mainly typical for women due to the anatomical features of the structure of their genitourinary system. If left untreated, cystitis leads to kidney inflammation and problems conceiving a child.
Prevention
Compliance with basic rules of personal hygiene is the main preventive measure. In addition, it is recommended:
- Healthy food;
- sunbathing;
- avoid stress and overwork;
- regularly carry out vitamin therapy;
- maintain a daily routine;
- provide the child with adequate sleep;
- cut your nails regularly;
- strengthen immunity;
- promptly treat any damage to children's skin;
- fight excessive sweating.
All preventive measures that help avoid infection of children with pyoderma are familiar to parents. These are their direct parental responsibilities. If a child is instilled with a healthy lifestyle from childhood, he will not be afraid of any cocci. The only exceptions are unforeseen external circumstances that cannot be predicted (accidental microtrauma of the skin, contact with a pathogen carrier, etc.).
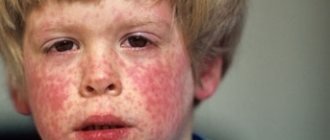
Symptoms and forms of staphylococcus in adults and children
The symptoms experienced by the patient vary greatly depending on the method and location of infection and the state of the immune system. But a number of the most characteristic features can be identified:
● elevated temperature;
● suppuration of cuts, swelling, purulent rashes on the skin and mucous membranes, itching and redness of the eyes;
● lack of sense of smell and nasal breathing;
● sore throat, pain when swallowing, dry cough;
● nausea, vomiting, general weakened state;
● severe headaches, epileptic attacks, severe shortness of breath;
● painful sensations in the joints.
One of the most common forms of staphylococcus in adults is its asymptomatic carriage. A healthy person does not feel any signs of the disease until a provoking factor appears that gives impetus to the development of the disease.
For women, the most dangerous form is the saprophytic form, which can lead to cystitis. This is due to the fact that the women’s urethra is located very close to the vagina, which is why there is a high probability of pathogenic microflora, including staphylococcus bacilli, entering the urethral canal, and then into the bladder, causing its inflammation.
Since young children do not have a strong immune system, the risk of developing an infection in a child is quite high. Moreover, even those types of staphylococcus that cause practically no problems in adults can lead to serious complications in children. Staphylococcus is especially dangerous in children under one year of age, as it can easily spread throughout the body in the shortest possible time and lead to serious consequences, including death.
Classification
The main microorganisms that cause pyoderma are streptococcus (Streptococcus pyogenes) and staphylococcus (Staphylococcus aureus). The percentage of diseases caused by other microflora (pseudomonas or Escherichia coli, pseudomonas infection, pneumococci, etc.) is very small.
Therefore, the main classification according to the nature of the pathogen is divided into:
- staphyloderma - purulent inflammation;
- streptoderma - serous inflammation;
- strepto-staphyloderma - purulent-serous inflammation.
In addition, any pyoderma differs in its mechanism of occurrence:
- primary - manifested on healthy skin;
- secondary - which has become a complication of other diseases (most often accompanied by itching).
In addition, pyoderma is divided according to the depth of infection. Therefore, the general classification of pyoderma looks like this:
- with superficial depth of infection (streptococcal impetigo, syphilide-like impetigo, bullous impetigo, intertriginous impetigo (slit-shaped), annular impetigo, streptococcal impetigo, superficial panaritium, dry streptoderma);
- with deep penetration (acute streptococcal cellulitis, vulgar ecthyma).
Staphyloderma includes:
- with superficial depth of infection (superficial folliculitis, ostiofolliculitis, acne vulgaris, sycosis vulgaris, epidemic pemphigus of newborns);
- with deep penetration (deep folliculitis, furuncle, furunculosis, carbuncle, hidradenitis).
Strepto-staphyloderma includes:
- with superficial depth of infection (impetigo vulgar);
- with deep penetration (chronic ulcerative pyoderma, chancriform pyoderma).
Causes
Most often, the bacterium enters the human body through wounds and microcracks in the skin. The infection, having penetrated through the wound, begins to multiply in the blood, spreading throughout the body and affecting the lungs, heart, brain, liver, kidneys, and joints.
With staphylococcus, diseases can be very different, such as pneumonia, meningitis, osteomyelitis, endocarditis, sepsis and many others.
Staphylococcus infection can occur in the following ways:
● Through contact and household use when using the patient’s personal items;
● Airborne droplets during close contact with an infected person;
● Fecal-oral on dirty fruits, vegetables and other food products, dirty dishes and hands;
● Vertical when a child passes through the birth canal of an infected mother during childbirth.
● Infection often occurs during surgery through medical instruments and during various manipulations.
How to treat pyoderma?
Treatment of pyoderma is carried out under the supervision of qualified specialists. As a rule, the doctor prescribes medications for external and internal use, including restoration of immune strength.
General uses:
- diagnosis and treatment of concomitant diseases (hormonal imbalance, diabetes, immunodeficiency);
- elimination of adverse effects on the skin (damage, pollution, exposure to high or low temperature);
- nutrition with a limitation of refined carbohydrates, a predominance of proteins, plant fiber, and fermented milk products;
- prohibition of washing (shower, bath), you can only wash local unaffected areas of the skin with great care so as not to spread the infection;
- trimming hair in the affected area;
- treating the skin around the ulcers twice a day with a solution of salicylic alcohol.
A special low-carbohydrate diet must be followed. The following medications are used to treat various types of pyoderma:
- It is recommended to carry out antibiotic therapy using semisynthetic macrolides, Penicillin, Tetracycline, aminoglycosides, and latest generation cephalosporins);
- in case of severe development of the disease, glucocorticosteroid drugs are used (Hydrocortisone, Metipred, etc.);
- for pyoderma, hepatoprotectors are prescribed (Essentiale Forte, Silibor, etc.);
- the use of angioprotectors (Actovegin, Trental) is recommended;
- cytostatics (Methotrexate) are prescribed.
To antisepticize erosive ulcerations, it is necessary to use ointments with a bactericidal effect. Most often used in the treatment of pyoderma:
- zinc ointment or salicylic-zinc paste;
- Levomekol;
- tetracycline ointment;
- lincomycin ointment;
- erythromycin ointment;
- hyoxysone ointment, etc.
In addition, there are drugs for complex treatment that have antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and antifungal effects. The most popular ointments are Thymogen and Triderm.
When pyodermatitis is accompanied by the appearance of ulcers, the inflammatory foci should be washed with aseptics after removing the scab (Tannin, Furacilin, boric acid, Dioxidine, Chlorhexidine, etc.).
For carbuncles, boils, hidradenitis, you can apply a sterile bandage with Ichthyol + Dimexide, Chymotrypsin and Trypsin to the affected area. In addition, a Tomicide bandage is often applied to the affected parts of the body.
Diagnostics
Only a doctor can diagnose the presence of infection based on the results of a staphylococcus test.
It is worth remembering that testing is recommended only if symptoms of the disease are present. The presence of bacteria in biological material may mean that a person is its carrier, which in itself is the norm.
For analysis, material is taken from the area where the infection is believed to be developing. To detect a pathological process, several tests are carried out to track the dynamics of bacterial growth. If their number increases rapidly, the presence of a staphylococcal infection can be diagnosed. Also, additional analysis will determine the specific type of infection so that the doctor can choose a personal treatment regimen.
Competition “Bio/Mol/Text”-2020/2021
This work was published in the nomination “Visually about the beloved” of the competition “Bio/Mol/Text”-2020/2021.
The general partner of the competition is the annual biotechnology conference BiotechClub, organized by the international innovative biotechnology company BIOCAD.
The sponsor of the competition is SkyGen: a leading distributor of life science products on the Russian market.
Competition sponsor: the largest supplier of equipment, reagents and consumables for biological research and production.
"Book" sponsor of the competition - "Alpina Non-Fiction"
Treatment
Staphylococcus can be treated surgically if there is a purulent lesion in the area of infection. It may also be necessary to remove an infected implant, catheter, etc.
As a conservative treatment for staphylococcus, antibiotics and antibacterial agents are used in combination with immunomodulatory therapy. The drugs are selected taking into account the resistance of staphylococcus to a wide range of medications. The use of brilliant green solution for treating infected wounds has shown greater effectiveness.
What tests need to be taken
First of all, to determine the presence of infection, a staphylococcus test is taken.
For diseases of the respiratory tract, a swab is taken from the nasopharynx and oropharynx, for cystitis - urine, for gastrointestinal disorders - feces, for skin lesions - a scraping from the skin, and if there is a suspicion of extensive infection, they donate blood.
Also, before starting treatment with antibiotics, it is required to be tested for resistance to these medications.
Which doctor should I contact?
Advanced cases of the disease are dealt with by an infectious disease specialist.
But if you just have suspicions and want to get an accurate diagnosis, first you should consult a therapist, or with children, a pediatrician. The doctor will conduct a diagnosis and, based on the results obtained, will write you a referral to the necessary doctor.