Giardiasis in adults: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
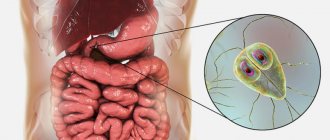
Giardiasis is a common parasitic infection caused by protozoa from the class of flagellates. For the first time, intestinal parasites as pathogens of the disease were studied and described by the Russian scientist D. Lambl in 1859 and were subsequently named in his honor.
Parasites can exist in two forms: immobile (cysts) and mobile (vegetative). According to statistics, it is enough for a person to receive only 10 cysts from the external environment to become infected and after some time begin to excrete a huge amount of Giardia during bowel movements. At first, the disease is often asymptomatic and the carrier of the parasites, without knowing it, infects the people around them.
To successfully fight an infection, you need to know as much as possible about it. Let's find out what giardiasis is, learn all about the routes of infection, the characteristic symptoms of the disease and treatment methods.
How can you get infected?
Ways of Giardia to enter the body:
- Water – you can become infected by drinking insufficiently purified tap water or water from open reservoirs;
- Contact household - pathogens accumulate on the surface of household items: toys, dishes, linen, clothes;
- Food – sources of contamination are a variety of food products. Giardiasis is especially often detected after eating food that has not undergone heat treatment: vegetables, fruits, berries.
As a rule, giardiasis in children and adults occurs after contact with a sick person, however, scientists have found that rodents, dogs and cats can also act as carriers of parasites. In addition, Giardia is often found in polluted water bodies and even chlorinated tap water. In order for giardiasis to begin to develop, a person only needs to ingest 10 parasite cysts and have a low level of gastric acidity.
Is Giardia transmitted?
- Is Giardia transmitted from person to person? Giardia is transmitted from person to person.
- Is Giardia transmitted through kissing or saliva? Transmission of Giardia through a kiss is theoretically possible, provided that parasite cysts are present in the person’s saliva during the kiss.
- Is Giardia transmitted from cats to humans? Giardia can be transmitted from cats to humans.
- Can Giardia be seen in feces? It is impossible to see Giardia in feces on your own, since their size is very small. Therefore, parasites in feces can only be visualized under a microscope.
What happens after infection?
To become infected, it is enough to swallow several dozen cysts (the patient secretes millions of them per day, so you can imagine the likelihood of infecting others if he does not follow the rules of personal hygiene). After entering the small intestine, each cyst is divided into two halves, from which two lamblia are formed, which also begin to actively multiply.
Further development of parasitic infestation can follow two scenarios:
- Symptoms of the disease will appear.
- The person will become an asymptomatic carrier.
The likelihood of developing clinical giardiasis is influenced by a number of factors:
- state of human immunity;
- acidity of gastric juice (low acidity contributes to high activity of Giardia and the manifestation of giardiasis);
- the presence of problems with the secretion of bile (if there is not enough of it in the small intestine, it will be easier for Giardia to take root in the body).
In case of carriage, cleansing of the intestines from the parasite can occur spontaneously, without any treatment. The only condition is that self-infection should not occur, that is, the person must carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene.
If Giardia takes root and begins to multiply, the first thing that happens in the intestines is a violation of parietal digestion, as a result of which various intestinal disorders and signs of a lack of certain substances in the body arise. In addition, Giardia can influence intestinal motility by irritating nerve endings. This causes painful cramps in the abdomen.
In people prone to allergies, the products secreted by parasites in the process of vital activity sensitize the body, so patients develop various allergic reactions. These same products also poison a person, causing symptoms of intoxication.
Causes
Giardia is the simplest microscopic unicellular parasite from the class of flagellates.
In the human intestine it can be in two forms - vegetative and spore. Giardia reproduces by division and doubles in number every 10-12 hours. The habitat of vegetative forms is the upper section of the small intestine. Cysts are immobile, oval in shape and protected by a capsule. In this form, Giardia exists in the colon, as well as in the external environment. This way they can remain viable for a long time. The main causes of giardiasis are the entry of cysts into the human body. This happens when eating unwashed vegetables and fruits, violating hygiene rules, and using unboiled water. This route of transmission is called fecal-oral, since the source of the spread of giardiasis pathogens is an infected person who excretes cysts along with feces. Pets can also be carriers of giardiasis, and flies and cockroaches act as carriers.
Provoking factors can be overcrowding, living in a polluted environment, poor condition of water supply and sewerage systems, and non-compliance with sanitary and hygienic rules. A predisposition to the disease has been identified in children under the age of 10 years, in people with malnutrition or dystrophy, congenital defects of the biliary tract, diseases of the stomach and intestines with a reduced level of acidity, as well as in those adhering to diets with too low a protein content.
Symptoms of giardiasis
In almost half of the cases, a person finds out that he is infected with Giardia only by examining his stool for Giardia cysts. In other words, the patient does not even suspect that he has giardiasis. In other cases, certain signs of the disease may be observed.
The acute period lasts for five days, but can sometimes last for a week. If an adult has an immunodeficiency, then the acute period of giardiasis is usually longer, and all of the listed symptoms are fully manifested. Sometimes in the acute phase symptoms of biliary dyskinesia occur. If in children with giardiasis the body temperature rises and symptoms of intoxication increase, then for adult patients such a clinical picture is not typical.
The acute stage of giardiasis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Nausea, lack of appetite, frequent belching.
- Bloating, flatulence, rumbling in the intestines, excessive gas production.
- Loss of body weight.
- Painful sensations occur in the area of the right hypochondrium and in the peri-umbilical zone. At the same time, every second patient reports pain in the navel area, and about 15% of people report pain in the right hypochondrium. Painful sensations are very often associated with food intake, so they are not associated with giardiasis.
- A bitter or sour taste appears in the mouth.
- Diarrhea may develop. In this case, bowel movements become more frequent and can occur from 3 to 5 times a day. If at the beginning of the acute period the stool is liquid and watery, then later it thickens and becomes greasy.
- Salivation increases.
- There is rapid fatigue and unexplained weakness.
- Performance deteriorates.
- Skin rashes appear.
- Avitaminosis. Its symptoms boil down to increased brittleness of nails, hair loss, peeling of the skin, etc.
After a week, giardiasis either goes away on its own or becomes chronic.
Clinical picture of helminthiasis
Symptoms of helminthiasis appear 2-4 weeks after the parasites enter the child’s body. In approximately 1/3 of patients, signs of parasitosis are mild, but the toxic effect of their waste products does not stop. The main manifestations of helminthiasis in children include:
- feverish condition;
- exudative rashes;
- swelling of the face;
- loose stools;
- lymphadenopathy;
- flatulence;
- stomach cramps;
- nervousness;
- insomnia;
- chronic fatigue.
Note: the development of complications associated with helminthiasis is facilitated by immunodeficiencies, vitamin deficiencies and mineral deficiency.
With massive invasions, damage to vital organs occurs, as evidenced by the development of myocarditis, pleuropneumonia, meningoencephalitis, etc. The degree of eosinophilia during helminthiasis depends on the immune status of the patient and the intensity of infection.
Chronic giardiasis
If Giardia parasitizes an adult for a long time, then signs of immunosuppression and symptoms of intoxication will be observed. At the same time, the lymph nodes periodically become inflamed, the tonsils become enlarged, and the body temperature rises to subfebrile levels.
Symptoms indicating a chronic form of giardiasis in adults:
- The patient continues to lose weight.
- Hair becomes thinner, becomes brittle, and loses its natural shine.
- The general well-being of a person suffers. Often headaches occur, excessive drowsiness and irritability appear. This condition leads to deterioration in working ability.
- Disorders of the digestive system. The patient's stool becomes unstable, frequent constipation is replaced by equally frequent diarrhea. Appetite remains reduced, and bloating and rumbling in the intestines are periodically disturbing.
- Skin rashes begin to bother the patient more and more often, even if the person did not suffer from allergies before. Dermatitis or urticaria may occur. Quincke's edema in adults against the background of giardiasis occurs extremely rarely; asthmatic bronchitis or bronchial asthma develops more often. The main features of allergies against the background of giardiasis are: long-term course, lack of response to taking antihistamines, frequent relapses.
- Skin color deteriorates and mild jaundice may develop. First of all, the neck, face, axillary folds, and abdomen acquire a jaundiced tint.
- Urticaria is especially difficult in adults against the background of giardiasis, disrupting the patient’s quality of life. Moreover, it occurs without any background errors in nutrition, without taking medications, etc. Very often, urticaria is accompanied by symptoms of blepharitis.
- Giardiasis is associated with xerosis in which the patient's heels peel, especially in the cold season.
- The mucous membrane of the oral cavity suffers. A person often develops aphthous stomatitis, jams appear in the corners of the mouth, and the border of the lips becomes inflamed.
- Isolated damage to the palms and feet is possible, when the skin begins to peel off from the tips of the phalanges. The fingers resemble those of an old man. This process, as a rule, does not reach the palms.
- Chronic giardiasis is characterized by keratosis pilaris with the appearance of pinpoint swellings on the skin. The skin of the shoulders is predominantly affected. It becomes covered with a rough crust or white round plaques, prone to increased peeling.
Another indirect sign of giardiasis in adults is intolerance to whole cow's milk, since these parasites infect enterocytes responsible for the hydrolysis of carbohydrate components of food. This also explains the increased gas formation in the intestines.
Treatment of helminthiasis
The principles of deworming are determined by the type of parasite that caused the development of the disease. The main goal of treatment and preventive measures is to reduce the number of helminthic infestations in the intestines and strengthen nonspecific immunity. The following groups of medications can be used to kill worms:
- anti-nematodes – “Vermox”, “Mintezol”;
- anticestoid - Praziquantel, Phenasan;
- anti-trematodes - “Khloksil”, “Azinox”.
Many of the above medications can cause side effects such as anemia and intestinal bleeding. To prevent deterioration of well-being during therapy, it is advisable to use Neopagen, Methyluracil, Ursosan, Colespitol.
Diagnostics
Necessary diagnostic methods for suspected giardiasis:
- Morphological examination of a biopsy taken during endoscopy.
- PCR diagnostics of stool to detect pathogen antigens in the studied biomaterial.
- Duodenal sounding with microscopic analysis of the contents. It also confirms the presence of Giardia in duodenal juice.
- Immunodiffusion is a new, more specific method of immune diagnostics compared to ELISA, based on the study of the precipitation reaction and allowing the detection of antibodies to the pathogen.
- Enzyme immunoassay blood test - laboratory isolation of specific IgM class antibodies to Giardia from blood serum.
- Immunoelectrophoresis is a combined method that combines immunoprecipitation and electrophoresis. The antigenic composition of the biomaterial is being studied.
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay ELISA. Used in the diagnosis of giardiasis and other infections.
- Protozoological examination of feces. When examining native or Lugol-stained smears from freshly excreted feces under a microscope, trophozoites and Giardia cysts are detected. For reliability, multiple tests are required, carried out from 2 to 7 times with an interval between tests of 1–2 days.
An infectious disease specialist is involved in the diagnosis and treatment of giardiasis. Recognition of this protozoal invasion is difficult due to the variety of clinical manifestations and their nonspecificity. The diagnosis requires mandatory laboratory confirmation.
How to treat giardiasis?
For acute forms of giardiasis in adults, a one-stage treatment regimen with a course of antiparasitic therapy can be used.
- The drug of choice is metronidazole for a course of treatment of 5-7 days. Adults are prescribed 250 mg, children - 15 mg/kg/day. in 3 doses every 8 hours (without chewing, during or after meals, or washed down with milk).
- Another dosage regimen for adults: 2.0 g in one dose for 3 days or 0.5 g / day. within 10 days. According to a clinical and pharmacological article, specific dosages are recommended for the treatment of giardiasis: for adults - 500 mg 2 times a day for 5-7 days, for children 3-5 years old - 250 mg / day, 5-8 years old - 375 mg / day, over 8 years - 500 mg / day. in 2 doses, course of treatment is 5 days.
- It should be borne in mind that at the moment the use of metronidazole and other nitroimidazole derivatives, as well as furazolidone, is losing its relevance due to the emergence of a large number of parasite strains resistant to them.
It is not advisable to begin treatment of chronic giardiasis with the use of antiparasitic drugs, as this can lead to toxic-allergic complications and exacerbation of the clinical symptoms of the disease. Therefore, treatment in such cases should be carried out in three stages:
- The first stage is the elimination of toxicosis, improvement of intestinal enzymatic activity, correction of the immunological status. Depending on the severity of the symptoms of the disease, stage 1 is carried out over 1-2 weeks and includes: a diet that is aimed at creating conditions that worsen the reproduction of Giardia (porridge, dried fruits, vegetables, vegetable oil); limiting carbohydrate intake; taking choleretic drugs; administration of enterosorbents; enzyme therapy (based on the results of the coprogram); antihistamines.
- The second stage is antiparasitic therapy with drugs that affect protozoa: trichopolum (metronidazole), furazolidone, tiberal (ornidazole). Taking antihistamines and enterosorbents continues throughout the entire antigiardiasis therapy.
- The third stage is increasing the body's defenses and creating conditions that prevent the proliferation of Giardia in the intestines and gall bladder. For this, a diet is prescribed that improves intestinal motility (cereal porridges, vegetable and fruit purees, baked apples, fresh fruits and vegetables, dairy products). To correct the immune response, herbal adaptogens and multivitamin complexes are prescribed. To eliminate intestinal dysbiosis and fermentopathy, probiotics, prebiotics, and enzyme preparations are prescribed. The third stage takes on average 2-3 weeks.
To reduce the toxic effect of Giardia decomposition products under the influence of etiotropic treatment in children over 5 years of age, it is recommended to use Demyanov tubes with mineral water, 25-30% solution of magnesium sulfate, sorbitol, and xylitol 1-2 times a week. This measure prevents the absorption of toxic products and weakens the manifestations of the Yarisch-Herxheimer reaction. Along with specific treatment, the patient is prescribed plenty of fluids and diet. If the syndrome of maldigestion and malabsorption is detected, enzyme therapy is prescribed; if intestinal dysbiosis is detected, appropriate correction is carried out.
Treatment of giardiasis in adults
Treatment of Giardia in adults is carried out by an infectious disease specialist.
Before deciding on therapy, the doctor must take into account such aspects as:
- The severity of the symptoms of the disease;
- Duration of presence of Giardia in the intestines;
- Presence of concomitant diseases.
It is equally important to try to determine the source of the invasion in order to prevent reinfection. Treatment should not be started by taking antiprotozoal drugs, as this will exacerbate the symptoms of the disease and may provoke a reactive response from the body.
Therefore, treatment of Giardia in adults is carried out in stages:
- Preparatory stage before treatment of giardiasis. At the preparatory stage, it is necessary to try to mechanically remove the maximum amount of Giardia from the intestines, as well as remove intoxication from the body. During this time, the patient must adhere to a dietary diet.
To do this, the patient must follow the following recommendations:
- Completely exclude sweets and carbohydrates from the menu, which are quickly absorbed;
- Eat foods rich in fiber;
- Eat protein foods;
- Avoid whole milk and limit fat intake;
- Eat according to a schedule, switch to fractional meals (5-6 times a day);
- Drink more fluids, giving preference to sour fruit drinks and choleretic decoctions.
- The use of antiparasitic drugs against Giardia. The second stage of antiparasitic therapy takes 5-10 days. All medications are prescribed by the attending physician, since almost all drugs have contraindications and side effects.
How to treat Giardia in adults - list of medications:
- Metronidazole (Trichopol) - dosage in adults is 0.4 g three times a day, vomiting, nausea, headache, sleep disturbances are possible.
- Albendazole - 0.4 g once for 5 days, possible development of liver failure, nausea and vomiting, hyperthermia.
- Fazizhin – one tablet 4 times a day for 2 days.
- Macmiror - 15 mg per kg of body weight, taken twice a day after meals for a week, possible manifestations of diarrhea, gastralgia, skin rash, nausea and bitterness in the mouth.
- Furazolidone is rarely used, since the drug is ineffective against modern strains of parasites.
- Flamin - 1/3 or 1/2 tablet three times a day, the course of treatment is designed for 10 days.
- Macmiror – used from 2 years of age at 15 mg per kg of child’s body weight, no more than 0.4 g in total. The course of treatment with 2 doses takes from 7 to 10 days.
- Intetrix - recommended for children from one year old, the therapeutic dose is ?-1-1? capsules three times a day.
- Restoration of the body after treatment of giardiasis. The final stage of treatment is aimed at increasing the patient’s immunity and normalizing the intestinal microflora. To do this, he is prescribed vitamin and mineral complexes, intestinal bacteria, and enzyme preparations.
Supplementing the diet is the intake of enterosorbents, choleretic drugs, antihistamines and digestive enzymes. In this way, conditions will be created in the intestines that are unfavorable for the proliferation of parasites and the rate of their division will be significantly reduced.
Drugs and dosages for the treatment of children are selected with special care, trying to minimize the toxic effect of drugs.
How to treat Giardia in children - medications:
Simultaneously with taking antiparasitic drugs, both adults and children take a course of antihistamines, enzymes and sorbents.
As a rule, the prognosis for giardiasis in adults is quite favorable. If the patient strictly follows all the doctor’s instructions, recovery is observed in 92-95% of cases. However, reinfection cannot be ruled out, so the patient should remain under clinical observation for another 3-6 months. During this time, it must be examined at least 2 times.
Additional drug therapy
To influence pathogenic intestinal microflora, Enterol (1-2 capsules or a packet of powder 2 times a day for a week) or Intetrix (4 capsules per day for four days) is usually prescribed. To combat dysbiosis, probiotics are used (Narine, Linex, Bio-Gaia, Bifiform, etc.). For liver damage, hepatoprotectors (Gepabene, Karsil) and choleretic agents (Allohol) are indicated. Also, to improve the functioning of the gallbladder, you can use drugs such as Hofitol or Holosas. By the way, these drugs slightly increase urination, which promotes the rapid elimination of toxins.
If the results of the coprogram indicate an enzymatic deficiency, then Mezim, Festal, Creon or Pancreatin are prescribed. Even in the absence of clinical symptoms of an allergic reaction, antihistamines are necessary. These are Erius, Claritin, Telfast, Cetrin. 1 – 2 tablets per day is enough. Sometimes you may feel drowsy after using these medications. That is why it is recommended to take them in the afternoon before bed.
Acute and chronic giardiasis most often occurs in people with weakened immune systems. Therefore, after the end of antiparasitic therapy, it is necessary to identify the cause of disturbances in the functioning of the immune system. In some cases, additional drug support with immunomodulators (Polyoxidonium, Lykopid) is necessary.
Nutrition rules
The diet for giardiasis in adults at the first, preparatory stage, is based on products that slow down the reproduction of giardia. It is recommended to limit the consumption of carbohydrates (flour dishes and sweets) to a minimum and give preference to protein foods and foods high in fiber. During this period, the patient needs to consume:
- Dried fruits;
- Fresh and boiled vegetables;
- Lean meat;
- Various cereals;
- Vegetable oil.
At the third, recovery stage, the daily menu is based on products that improve intestinal motility. The diet includes:
- Fermented milk products (kefir, yogurt, cottage cheese);
- Boiled lean meat and lean fish;
- Porridge (oatmeal, buckwheat, pearl barley);
- Fruit and vegetable purees;
- Fresh fruits and vegetables (cabbage, carrots, apples, pears);
- Berries (cranberries, lingonberries);
- Baked apples;
- Greenery.
Bread, flour, confectionery and sweets, whole milk, and pasta should be completely excluded from the diet. It is recommended to avoid sausages, canned meats and animal fats. From cereals you can eat rice, buckwheat, pearl barley.
The patient must adhere to an increased drinking regime in order to quickly cleanse the body of toxins. It is useful to drink sour fruit drinks from cranberries, lingonberries, green tea with lemon, fresh juices (carrot, beetroot, birch).
Folk recipes
We bring to your attention several common recipes for traditional treatment of giardiasis that help remove giardia from the body:
- prepare a decoction of burnet (6 grams of herb per glass of water, boil for 10 minutes), which is taken once a day before meals. Dosage – 100 ml;
- 100 ml of beet juice are mixed in equal proportions with carrot juice, cognac and honey. The mixture is thoroughly mixed and taken three times a day half an hour before meals;
- Take green walnuts, cut them into several pieces and pour in 1 liter of vodka. The tincture reaches its condition in a dry, dark place within two weeks. The medicine is taken three times a day, one teaspoon.
Prevention of giardiasis
Preventive measures are divided into measures aimed at suppressing the source of infection and breaking the mechanism of transmission of parasites from carriers to healthy people.
- Measures aimed at the source of infection mean identifying carriers and patients with giardiasis with their subsequent treatment. Protozoological examination is recommended to be carried out among service personnel of children's institutions, employees of food and similar food enterprises, and children.
- To break the mechanism of transmission of parasites, it is necessary to ensure organized collection of household and agricultural wastewater with their further purification. It is necessary to protect soils and water bodies from contamination by potentially invasive wastes. This group of measures includes measures to control the quality of drinking water.
- In addition to public prevention of parasitic diseases, it is important to observe personal hygiene, food storage rules and food preparation technology. When using water from natural sources, it must first be boiled. Fresh fruits and vegetables must be washed with running water before consumption.
Compliance with preventive measures reduces the risk of contracting giardiasis, as well as infectious and parasitic diseases of other etiologies.
Prevention of Giardia in adults
Prevention of Giardia in adults comes down to the following measures:
- Timely detection of cases of invasion with subsequent high-quality treatment of patients with giardiasis.
- Following strict hygiene rules with regular hand washing.
- Use boiled or bottled water for drinking.
- Preventing fecal matter from entering the environment.
- Compliance with sanitary and hygienic measures in food and water supply institutions.
- Regular examination of people at risk for giardiasis.
- Conducting sanitary education work among the population by local authorities.
There is no vaccine for giardiasis, and the immunity that is developed after an illness is not very stable. Therefore, the risk of reinvasion remains high.