Ear pain is one of the most difficult to endure; it is difficult to endure even for an adult with a high pain threshold. It occurs suddenly and knocks the patient out of the usual rhythm of life for a long time.
More often, acute pain is caused by an ear disease such as otitis media. When an ENT doctor gives you this diagnosis, you need to understand that an inflammatory process is developing in the organ of hearing, and the nature of the course of the disease and the possibility of developing complications depend on how quickly treatment is started. Complicated course of the disease in adults and children can lead to serious consequences, including deafness.
Unfortunately, this is a very common disease. It most often occurs in children under seven years of age, but adults are also susceptible to this inflammation. How does the disease manifest itself in an adult? What recommendations exist for treating the disease? What consequences may occur if you do not receive competent and effective treatment on time? Let's figure it out.
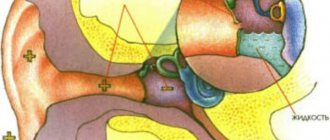
Hearing organ: structure.
To understand how the disease manifests itself in humans and to understand what processes occur, let’s turn to the structure of our hearing organ. The ear, in our usual understanding, is only the visible part of the hearing organ, so to speak, the tip of the iceberg. This visible part is called the outer ear. It includes the auricle and external auditory canal. Its main function is to catch sounds from the outside and direct them further.
Then comes the middle section, represented by the eardrum, the tympanic cavity with three auditory ossicles and the auditory (Eustachian) tube. Here the incoming sound signal is amplified many times. It is in this department that most inflammation originates.
Next, the sound enters the internal section, which is called the “cochlea”. Here it is converted into microelectric impulses and sent to the brain.
The organ of hearing is a very complex system with well-established operation. Exposure to unfavorable factors can easily disrupt the activity of this well-coordinated mechanism, so taking care of ear health is our direct responsibility.
What are the types of the disease?
The hearing organ consists of three areas; accordingly, inflammation is divided according to its location.
The outer section rarely becomes the target of any inflammation. More often, external otitis develops due to boils, eczema, and acne. Drafts and hypothermia can also become a provoking factor. In this case, we are talking about a point form of the disease. When a large area of the ear is affected, we talk about diffuse inflammation. External inflammations are relatively easy because they are visible to the naked eye, immediately manifest themselves and are quickly diagnosed. But there is a danger that the infection will get into the inner parts of the ear, so therapy must be carried out in a timely manner to prevent complications.
Otitis media is more common in adults. With this type of disease, the components of the tympanic cavity become inflamed. There are many variations of this diagnosis, and if middle ear inflammation is not given timely attention, the risk of serious and even dangerous complications is extremely high.
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
For adults, the greatest danger is inflammation of the inner ear (labyrinthitis). It does not manifest itself as an independent disease. More often it occurs as a complication. Such otitis is accompanied by complications, as a result of which hearing can completely disappear. A distinctive feature of this form of the disease is that the person does not experience pain, but experiences severe dizziness and hearing problems.
Diagnostics
In typical cases, the diagnosis of acute otitis media is not difficult and is based on the results of an analysis of complaints, anamnestic information and an objective examination. The use of endoscopes and microscopes makes it possible to make a diagnosis at stages when changes in the eardrum are barely noticeable during normal examination. If complications are suspected, additional tests are prescribed - audiometry, radiography or computed tomography of the temporal bones, a blood test to assess inflammatory changes.
Classification of the disease according to the nature of its course.
There are many classifications of diagnosis. We will dwell on a few in more detail.
Based on duration, the disease is divided into three forms: acute, subacute and chronic. The acute form lasts no more than three weeks. If the disease does not go away within three months, then we are dealing with a subacute variation of the disease. Chronic inflammation is characterized by sluggish symptoms that prevent an adult from leading a full lifestyle for more than six months in a row.
Based on the type of causative agent of the disease, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- bacterial - when the cause of infection is bacteria;
- viral - provoked by viruses;
- fungal - the causative agents are fungi;
- allergic - manifests itself against the background of the action of allergens;
- traumatic - due to damage to the hearing organ (more often occurs when improperly manipulating a cotton swab when cleaning the ears or a pressure drop during diving or air travel).
There is an exudative type of disease, when fluid is released from the ear cavity, catarrhal (no discharge, but severe swelling is present) and purulent. Purulent otitis is accompanied by discharge from the organ of hearing and is fraught with complications.
If the inflammatory process occurs in the right ear, we talk about right-sided inflammation, if in the left ear, we talk about left-sided inflammation. The most difficult course is for bilateral ear lesions.
What is acute otitis media?
The human ear is a complex system. It is conventionally divided into three important sections: the outer, middle and inner ear.
Any part of the hearing organ can become inflamed. Accordingly, external, middle and internal otitis are distinguished. In eighty percent of cases we are dealing with the manifestation of acute otitis media.
Acute otitis media affects people of all ages. But most often children get sick.
Medical statistics show that by the time they reach first grade, almost every child experiences this disease at least once. What can trigger the disease?
There are many factors that provoke the disease:
- previous inflammation of the ENT organs;
- ear damage;
- foreign objects entering the ear;
- frequent entry of water into the ear canal;
- improper ear cleaning;
- hypothermia;
- weak immunity;
- allergic reactions;
- features of the anatomical structure of the hearing organ in children (in childhood, the auditory tube is shorter, so infections from the nasopharynx are easier to get into the tympanic cavity of the ear).
Depending on the type of pathogen, bacterial, viral and fungal forms of inflammation are distinguished.
The acute form of the disease, as the name implies, begins rapidly and proceeds with vivid symptoms.
What causes the disease?
If there is inflammation in the ear, then it must contain pathogenic microorganisms - bacteria, viruses or fungi. The following causes of otitis media in adults can be identified:
- Inflammation of the outer ear most often results from the ingress of water from polluted reservoirs containing pathogens;
- if the skin of the hearing organ is damaged, infection can enter the bloodstream through wounds or scratches and cause inflammation;
- the disease can act as a complication after an untreated cold;
- when some disease is already occurring in a chronic form in the human body, then this constant source of infection can easily activate the inflammatory process;
- excessive zeal when cleaning ears; Earwax is a natural barrier that prevents bacteria from entering the ears, and there is no need to try to remove it every day;
- poor hygiene: never use someone else’s headphones or earplugs, they may contain pathogens;
- a foreign body in the ear can cause illness (for example, an insect caught in it).
As you can see, there are quite a few sources of infection. In order to correctly diagnose the disease and treat it, it is necessary to distinguish between the symptoms of otitis media.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
Prevention
It is very important to take care of your hearing and if any difficulties arise, be sure to go to the doctor. But, if you want to avoid ear-related diseases, you must follow the standard rules:
- to avoid otitis media, wear a hood or hat if it is raining or cold outside;
- Do not use paper clips, pencils, or matches to clean your ears and remove wax. Otherwise, the self-cleaning process becomes more difficult, the plug becomes denser, and sulfur production increases. There is also a possibility of damage to the membrane and ear canal;
- do you work with loud music? Use earplugs or headphones that can isolate sound. Then an adult’s ear will not hurt;
- You should not ignore diseases of the throat and nasopharynx, which become acute or chronic. After all, such a disease can go further, as a result of which the right ear may hurt;
- Visit your otolaryngologist regularly for preventive examinations. If any changes occur in the ears, he will definitely notice it.
How does the disease usually manifest?
Manifestations of the diagnosis depend on the location of the inflammatory process.
Signs of otitis externa are: redness of the skin of the auricle, itching, pain that can “radiate” to the jaw, to the temples when a person eats or speaks, possible hearing loss, and the appearance of tinnitus. As a rule, after measures are taken, for example, to treat ear boils, the pain goes away. With this form of the disease, discharge from the external auditory canal almost always occurs.
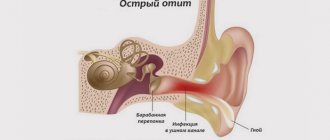
Inflammation of the midsection: in adults, the disease occurs in acute and chronic forms. The main symptom of the acute form is a sudden “shooting” pain in the ear, which is very difficult for an adult to tolerate. Possible fever and hearing loss.
In case of acute purulent inflammation, an accumulation of pus is added to the above listed signs. If a spontaneous rupture of the eardrum occurs, the pus comes out, and after this the patient experiences relief, the temperature begins to subside. If there is no rupture, the ENT doctor can make an incision himself to release the purulent masses.
Without timely effective therapy, the subacute form of the disease or its acute form takes a chronic course: chronic otitis media manifests itself. A chronic disease does not have clearly defined symptoms. Chronic processes are more characterized by a constant feeling of congestion, tinnitus, and hearing loss.
When the internal part is inflamed, the general symptoms include dizziness, nausea, and vomiting. You need to see a doctor immediately! If proper therapy is not carried out, the prognosis, alas, is disappointing.
Otitis in adults.
Treatment of ear diseases is the specialty of an otolaryngologist. The methods of work depend on the type of inflammation. Drug therapy should be carried out under the supervision of an ENT doctor, and should begin in the early stages of the disease.
Otitis media is treated according to the following scheme:
- Reducing pain. In this case, symptoms of otitis media are relieved with the help of painkillers (for example, Nurofen), special ear drops (Otipax, Otinum) or a Tsitovich compress (a gauze turunda is soaked in the drug and placed in the external auditory canal for several hours).
- To relieve swelling of the Eustachian tube, adults are prescribed one of the vasoconstrictor drugs for the nose (Nazivin, Tizin and others).
- If the disease is of an allergic nature, it is necessary to take antihistamines (Suprastin, Claritin and others);
- Antibacterial therapy is indicated for the presence of bacteria in the middle ear. The right to choose an antibiotic and duration of therapy remains with the ENT doctor.
- If the cause of infection is viruses, you will be prescribed antiviral drugs, if fungi, antimycotic drugs.
- If you have an elevated body temperature, hesitate to use antipyretic drugs.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures are also effective.
Treatment of chronic otitis in adults.
Chronic inflammation of the ear canal is diagnosed if the disease does not stop for more than a month. The chronic development of inflammation is divided into three types:
- Purulent chronic otitis (divided into mesotympanitis and epitympanitis). With mesotympanitis, chronic inflammation affects only the tympanic cavity; with epitympanitis, the bone is also involved.
- Chronic exudative otitis - this chronic form of the disease is characterized by the concentration of secreted exudate in the tympanic cavity for a long time, since the eardrum is not perforated.
- Chronic adhesive otitis - this chronic form is characterized by soldering together of the auditory ossicles and eardrum - this greatly reduces hearing.
Therapy for chronic purulent otitis includes a complex of therapeutic measures with medications.
If the patient has a ruptured eardrum, it is necessary to avoid contact of the ear with water by covering it with a cotton pad.
A chronic disease in the acute stage is treated with conservative methods, which include rinsing the ear with an otolaryngologist, using antibacterial drops (attempts to prescribe medications for yourself or adjust the therapy prescribed by a doctor are unacceptable! The cost of incorrect manipulations in this case is your hearing!).
If it is not possible to cure chronic otitis media with medications, adult patients will be offered surgery, the essence of which is to restore the integrity of the eardrum and prevent further inflammation and infection, thereby stopping chronic inflammatory processes in adults.
Exudative otitis media in chronic form is treated with shunting: a Teflon tube, hollow inside, is inserted into the tympanic cavity through an incision in the eardrum, through which liquid is removed and a medicinal solution is placed.
It is also possible to cure chronic inflammation in adults with adhesive inflammation through surgery.
It is very important, when starting to treat a disease, to eliminate foci of chronic inflammation in the nasal cavity and nasopharynx.
Treatment in our clinic.
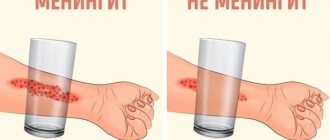
Dear friends! Please do not forget that if you do not seek help in a timely manner, you will advance the disease and may cause the inflammatory process to become chronic. If the problem of chronic or acute otitis is not addressed in time, serious complications may occur (for example, brain abscess, meningitis or encephalitis).
Our profile is the treatment of ENT diseases, and otitis media is one of them. Our clinic is known for its proprietary treatment methods. We work with the most modern equipment, and our doctors are graduates of the best medical universities in the country with extensive experience.
Please come to us! We will help you effectively cope with your problem and will definitely tell you what measures should be taken to prevent otitis media in order to avoid unpleasant symptoms in the future.
We will always be happy to help you! You are welcome!
What complications can otitis media lead to?
- chronic otitis - constant or recurrent symptoms in the form of ear pain, suppuration, swelling, congestion and ringing in the ears
- hearing loss - impaired hearing acuity
- loss of coordination of movements, frequent dizziness and nausea
- transfer of inflammation to other parts of the body - jaw or salivary glands (quite dangerous and can lead to disability)
- complex intracranial pathologies that can be fatal - meningitis, brain abscess, encephalitis, hydrocephalus
- paresis of the facial nerve (paralysis of part of facial expressions)