Otolaryngologist for adults and children
Zubkov
Aleksey Aleksandrovich
20 years of experience
Otorhinolaryngologist of the first category, member of the European Rhinologic Society
Make an appointment
Many people wonder: what is sphenoiditis in adults? In fact, this is an insidious disease that can lead to serious consequences. Sphenoiditis is an inflammatory process in the mucous layers of the sphenoid sinus. Basically, the clinical picture of sphenoiditis boils down to headaches, increased body temperature, problems with the sense of smell, blurred vision, purulent and catarrhal discharge. If symptoms of sphenoiditis occur in adults, it is necessary to undergo an urgent examination. Therapy is reduced to drug treatment, and if necessary, surgery for sphenoiditis is possible. In general, this disease is considered quite rare in the practice of otolaryngology. It occurs in only 3% of cases.
Symptoms and signs
Symptoms and treatment of sphenoiditis in adults are interrelated. Clinical manifestations of the disease are unspecific. The main symptoms of this disease are as follows:
- headaches, and they are felt in the center of the head and spread to the temples and eyes;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- discharge from the nasal cavity;
- problems with smell;
- blurred vision;
- loss of appetite, sleep problems, dizziness, weakness and general malaise.
The initial form of the disease is catarrhal sphenoiditis. In this case, the discharge from the nasal cavity will be transparent. Subsequently, the discharge becomes purulent, which is why this form is called purulent sphenoiditis.
As for the localization of inflammatory processes, the disease can develop on different sides (left-sided and right-sided sphenoiditis) or on both sides symmetrically (bilateral sphenoiditis).
Depending on the intensity and nature of the inflammatory processes, acute and chronic sphenoiditis are distinguished. In the first case, symptoms are clearly expressed for about 3 weeks. The disease develops against the background of an acute form of respiratory tract disease caused by a bacterial or viral infection. Chronic sphenoiditis is characterized by periods of remission and exacerbation. This problem develops against the backdrop of a lack of timely treatment or incorrect treatment tactics, which causes chronic inflammatory processes.
What symptoms does sphenoiditis cause?
- Acute headache, especially when bending over.
- With sphenoiditis, the pain is often not localized, but diffuse and is felt in the occipital region, orbit, crown, and temples.
- Fever, flesh up to high numbers (39 oC).
- Nasal congestion does not occur in all cases.
- Accumulation of secretions and mucus in the nasopharynx (often purulent).
- Sensation of unpleasant odor and taste.
Sphenoiditis is often combined with sinusitis and frontal sinusitis. Single localization is quite rare.
Routes of infection
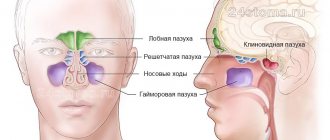
The sphenoid sinuses belong to the group of paranasal sinuses, but they are deeper than the others. The name comes from the fact that they are located deep in the sphenoid bone. Inflammatory processes in this place occur due to the fact that respiratory infections penetrate there through the cells of the ethmoid labyrinth from other sinuses. Most often they come from the frontal or maxillary. The infection can also spread from the pharynx, the nasal cavity itself. Very often, the infection spreads from the tonsils of the nasopharynx.
Sphenoiditis is a consequence of influenza, scarlet fever, sore throat or even ordinary rhinitis; it usually develops as a complication of these diseases. If there are no such diseases, then in other cases the risk of developing sphenoiditis is extremely small, since the infection penetrates into the sphenoid sinuses, causing inflammatory processes of low intensity, after which they quickly pass. So you can only get infected with sphenoiditis from people who have a sore throat, flu, scarlet fever or a common cold, but at the same time the person must also develop similar diseases, and then develop a complication in the form of sphenoiditis.
Forecast
With timely medical or surgical treatment, the patient suffering from sphenoiditis recovers. Relapses are rare.
I hope that this publication will help both patients and specialists in the diagnosis and proper treatment of acute or chronic sphenoiditis. If you suffer from a similar disease, you can contact the author. See CONTACTS section
Sincerely, ENT surgeon, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Head of the surgical ENT department of the clinic for diseases of the ear, nose and throat, First Moscow State Medical University named after I.M. Sechenova Petr Aleksandrovich Kochetkov
[email protected] 8-962-957-11-22 8-495-978-65-07
| Use of materials from the website of Dr. Kochetkov P.A. on other Internet resources is allowed if there is an active hyperlink to the site. Any other use of materials without the written consent of the author is prohibited! |
Risk factors
In order for an infection to develop and lead to sphenoiditis, the action of predisposing factors is necessary:
- weakened immune system, which can be caused by severe physical or mental exhaustion, vitamin deficiency, hypothermia, somatic diseases, endocrine pathologies, as well as the rehabilitation period after surgery;
- allergic form of rhinitis;
- frequent colds;
- the presence of foci with chronic infections in the oral cavity or nasopharynx;
- developmental abnormalities (they can be congenital or acquired);
- smoking;
- poor environmental situation;
- harmful working conditions;
- gradually increasing resistance to antibiotics in various microorganisms that cause diseases;
- severe specific diseases (tuberculosis, syphilis, etc.), which lead to the deformation or destruction of the sphenoidal (sphenoid) bone).
These factors increase the risk of developing sphenoiditis. Because of them, the infection penetrates the mucous layers of the sphenoid sinuses and leads to inflammatory processes.
Causes of sphenoiditis
Sphenoiditis develops as a result of damage to the mucous membrane by bacteria, viruses or fungal infection. In fact, any acute respiratory infection or flu causes inflammation in all paranasal sinuses, not excluding the sphenoid. However, such conditions usually pass quickly. For the development of bacterial sphenoiditis, certain conditions or predisposing factors are required.
The main ones are: - Narrowness or complete absence of the outlet of the sphenoid sinus (ostium) - The presence of a cyst or polyp in the sphenoid sinus blocking the anastomosis - Severe curvature of the nasal septum in its posterior-superior section, which also contributes to insufficient patency of the sinus anastomosis. — Foreign bodies entering the sinus during a sharp inhalation, which occurs when the sinus has a very large anastomosis. - Additional bays or septa in the sphenoid sinus - Small and narrow size of the sphenoid sinus. — Tumors of the sphenoid sinus More often in practice, specialists are faced with a combination of one or more of the described causes of sphenoiditis. Their elimination in the vast majority of cases of sphenoiditis leads to recovery.
Complications
Sphenoiditis can cause the following consequences:
- damage to the nerves in the cranial region, including the optic nerve, which can lead to loss of vision (partial or complete);
- transfer of infection to the cranial cavity;
- transfer of infection to other paranasal sinuses;
- infection of the eye sockets.
Since the sphenoid sinus is located next to many important structures, inflammatory processes in it can lead to serious complications.
Diagnostics
Due to the deep location of the sphenoid sinuses, the diagnosis of sphenoiditis is quite difficult. This disease is more difficult to recognize than sinusitis in other sinuses.
If, when sinusitis or frontal sinusitis is suspected, radiography is usually performed, then in case of sphenoiditis, this traditional option is considered uninformative. This is due to the fact that there are a sufficient number of structures nearby that are in the path of X-rays, so the images do not provide enough data for diagnosis. Because of this, it is preferable to conduct magnetic resonance or computed tomography, and on equipment with high accuracy and resolution. Endoscopic diagnosis is also used. But first of all, the otolaryngologist examines the patient (otolaryngoscopy, rhinoscopic examination, and pharyngoscopy are performed), and also studies the medical history and listens to complaints.
Diagnosis of sphenoiditis at the Yauza Clinical Hospital
The hospital's otorhinolaryngologists carry out a comprehensive diagnosis of the disease using the following examination methods:
- bacteriological examination of pathological discharge from the nasal cavity and affected sinuses;
- rhinoscopy (at the initial examination);
- radiography;
- computed tomography of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses using Philips digital equipment, which increases the accuracy of diagnosis, allows you to obtain layer-by-layer images in different planes, and correctly plan ENT operations;
- endoscopic examination of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx.
Endoscopy allows you to detect the disease at the earliest stage of development without surgical intervention. The technique is applicable for children, since it is absolutely non-traumatic and is performed under local anesthesia. The doctor inserts a thin endoscope tube with a camera through the nose and observes the condition of the nasopharynx in an enlarged image on the monitor.
Methods for diagnosing inflammation of the sphenoid sinus used in hospitals make it possible to determine:
- individual characteristics of the structure of the nasal septum and sinuses;
- condition of the mucous membrane;
- volume and localization of inflammation;
- swelling, nature and volume of pathological discharge in the lumen of the sinus.
Multifaceted diagnostics allows you to accurately establish a diagnosis and develop a conservative or surgical treatment plan with a sustainable therapeutic effect.
Treatment
Treatment of sphenoiditis is aimed at reducing swelling of the mucous layers of the nasopharynx and sphenoidal sinus, accelerating the outflow of pathological masses, and also destroying pathogenic microflora. Therapy is selected depending on the severity of the disease. This may include the following measures:
- antibacterial therapy. It is the main method of treatment, as it is of decisive importance. Typically, antibiotics with a wide spectrum of effects are used, for example, the doctor prescribes drugs containing penicillin or cephalosporin components. If necessary, material is taken from the sinus and bacteriological culture is performed in order to further study the sensitivity of the pathogenic microflora to the selected medications. In the future, depending on the results of such a study, therapy is adjusted - the doctor may prescribe other drugs. But antibiotics will not help if the disease is caused by fungi or viruses. In this case, antiviral and antimycotic agents are prescribed;
- symptomatic therapy. The doctor prescribes vasoconstrictors that reduce swelling of the sinuses. In addition, painkillers, antipyretics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. If intoxication is pronounced, then infusion therapy is carried out with the administration of drugs through a vein. Additionally, the doctor prescribes probiotics to prevent the consequences of long-term use of antibiotics;
- surgery for sphenoiditis. A sphenotomy is performed. It is prescribed when it is not possible to restore normal patency in the sphenoid sinus.
The doctor chooses a treatment method depending on the patient’s condition, the course of the disease, and complications that have arisen.
How to treat
If there is purulent discharge, antibiotics are 100% required, which must only be prescribed by a doctor. “As a rule, it is better to treat sphenoiditis in a hospital setting. But this may be at the discretion of the doctor. If a specialist has enough experience and the necessary equipment, then he can observe the patient on an outpatient basis, however, the person will have to go to the doctor every day,” says Vladimir Zaitsev.
Article on the topic
Encephalitis, meningitis, loss of vision. The most dangerous complications of measles
Prevention
The most important thing in preventing sphenoiditis is strengthening the immune system. It is because of weakened immunity that sphenoiditis develops - the body simply cannot fight pathogenic microflora and infections. To strengthen the body's defenses, it is necessary to develop resistance to stress. It is also important to follow a daily routine, eat right, and lead a healthy lifestyle. Hardening will also be beneficial, but it must be carried out strictly according to the rules.
How to make an appointment with the specialists of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg)
You can make an appointment with the specialists of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg) on the website - the interactive form allows you to select a doctor by specialization or search for an employee of any department by name and surname. Each doctor’s schedule contains information about visiting days and hours available for patient visits.
Clinic administrators are ready to accept requests for an appointment or call a doctor at home by calling +7 (495) 775-73-60.
Convenient location on the territory of the central administrative district of Moscow (CAO) - 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, building 10 - allows you to quickly reach the clinic from the Mayakovskaya, Novoslobodskaya, Tverskaya, Chekhovskaya and Belorusskaya metro stations .