| Microscopic examination of urethral discharge | 619 rub. |
| PCR-12 complex (diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections) | RUB 3,975 |
| Instillation into the urethra (administration of medications), without the cost of medications | RUB 1,815 |
| Removal of a foreign body from urological organs | RUB 6,466 |
Urethritis is an inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane of the urethra (urethra) of infectious or non-infectious origin. Urethritis is a fairly common disease, its scale is steadily growing every year. Both men and women are susceptible to this disease. However, in the stronger sex, urethritis takes a more acute course, which is associated with the anatomical features of the male urinary system. A significant role in the development of this disease is occupied by unfavorable environmental factors, such as alcohol, smoking, certain medications, unbalanced and poor nutrition (deficiency of vitamins and proteins).
Causes of the disease
Among the causes of urethritis, a number of factors should be noted:
- Unprotected sex, frequent changes of sexual partners;
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- Hypothermia of the body;
- Reduced immune defense of the body;
- Traumatic damage to the genital organs;
- Cystitis and other inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary tract of non-venereal etiology;
- Entry of pathogenic microorganisms (bacteria, viruses) into the urethra.
Types of urethritis
Depending on the degree of intensity of the process and the duration of the disease, acute urethritis and chronic urethritis .
Acute urethritis is characterized by a bright onset and severity of all symptoms, the duration of the disease is up to 2 months.
Chronic urethritis (a disease lasting more than 2 months) is characterized by a prolonged course, mild symptoms and the development of complications.
Based on the nature of occurrence, the following types of urethritis are distinguished:
- primary (after sexual intercourse or medical manipulations in the groin area) and secondary urethritis (the appearance of infection from other organs of the genitourinary system);
- allergic urethritis (allergy to medications, shampoos, soap, condoms);
- chemical urethritis (reaction to drugs entering the urethra);
- mechanical urethritis (occurs due to mechanical damage to the urethra);
- infectious urethritis (caused by specific pathogens, such as chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, gardnerella, gonococcus, and nonspecific pathogens (streptococcus, staphylococcus, E. coli);
- non-infectious urethritis , occurs due to injuries to the urethra (due to the passage of a stone during urolithiasis, when using a bladder catheter), as well as due to narrowing of the urethra and congestion in the pelvis;
- nonspecific urethritis - purulent inflammation that is caused by streptococci, staphylococci and E. coli;
- specific infectious urethritis - appears as a result of a sexually transmitted infection.
According to pathological signs, the following types of urethritis can be distinguished:
- gonorrheal urethritis (the causative agent of the disease is gonococcus, infection through sexual intercourse with an infected person, through underwear, general hygiene and personal items - washcloths, towels, etc.);
- bacterial urethritis (the causative agent is a nonspecific bacterial flora, the disease can appear as a result of endoscopic manipulations, long-term use of a catheter);
- trichomonas urethritis (characterized by the presence of foamy, whitish discharge, itching, which, if untreated, quickly becomes chronic and becomes trichomonas prostatitis);
- candidal urethritis (the causative agent is a yeast fungus that affects the mucous surface of the urethra, appears after long-term use of antibacterial drugs, less often after contact with an infected partner);
- chlamydial urethritis (viral urethritis, affects the urethra, conjunctiva, vagina and cervix).
1 Diagnosis of urethritis in men
2 Diagnosis of urethritis in women
3 Diagnosis of urethritis
Symptoms of the disease
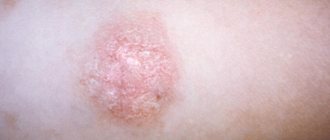
Acute urethritis is characterized by fairly strong symptoms. Patients complain of severe burning pain when urinating, increased urge and profuse purulent discharge, the nature of which depends on the individual characteristics of the pathogen. In men, redness and sticking of the sponges of the external opening of the urethra are noted.
If the disease takes a chronic course, then the symptoms of the disease are somewhat smoothed out. However, when exposed to certain provoking factors (ARVI, hypothermia, constant stress, alcohol consumption, poor diet), the patient again experiences symptoms of the inflammatory process.
Urethritis - symptoms and treatment
The recommendations of the Center for Disease Control (CDC) and the European Association of Urology are currently the most authoritative and regularly updated clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of urogenital tract infections [7][8].
Symptoms of urethritis may be similar to those of other diseases of the genitourinary system, so it is very important to carry out a differential diagnosis. A correctly and carefully collected anamnesis, patient complaints, laboratory and instrumental diagnostics help with this [3].
Initially, a standard examination and history taking . During the conversation, the doctor must find out what exactly is troubling the patient, when the first symptoms appeared, whether there has been unprotected sexual intercourse recently, whether treatment for STIs was previously prescribed, and whether there are chronic diseases.
After this, a gynecological examination in women to exclude inflammatory diseases of the genital area; in the absence of the latter, an examination by a urologist is performed. The doctor evaluates the condition of the urethra and identifies the presence of discharge (purulent or mucous). At the same time, the skin of the perineum and external genitalia are examined for the presence of hyperemia (redness), plaque and rashes. To confirm the diagnosis of dystopia of the external urethral meatus, all patients undergo a digital examination of the vagina. It allows us to identify urethro-hymenal adhesions, leading to intravaginal displacement and gaping of the external urethral opening during sexual intercourse, which contributes to re-infection of the lower urinary tract and mechanical trauma to the external urethral opening [9].
After examination, urethral smears are taken from both for microscopy and bacteriological examination in order to identify the causative agent of the disease [10]. They also examine a general urine test, as well as a Nechiporenko urine test for the presence of leukocytes, bacteria and salt crystals.
Carrying out a 3-glass urine sample allows you to indirectly determine the level of prevalence of the inflammatory process. The number of leukocytes in the field of view is assessed:
- in the first portion - corresponds to urethritis;
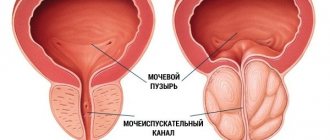
- in the second portion - cystitis, prostatitis (in men);
- in the third portion - inflammation of the upper urinary tract (pyelonephritis).
Bacteriological examination (culture) of discharge from the urethra allows us to identify pathogenic and opportunistic microflora, its titer (concentration) and sensitivity to antibiotics. The diagnostically significant titer in women is 10x4, in men - 10x3 CFU/ml.
Serological method - determination of antibodies (immunoglobulins of class G, M and A) in the patient’s venous blood to the most common pathogens of urethritis. Used as an auxiliary method.
PCR is a technique for studying discharge from the urethra, blood or urine, as well as other biological fluids using a polymerase chain reaction, in order to detect certain pathogens in them.
The advantage of the method is its high sensitivity. The chance of a false negative is negligible, and the chance of a false positive is less than 1%.
There are specially developed diagnostic complexes [11]. These include the “Androflor” studies in men and “Femoflor” in women, which include the most complete and comprehensive etiological diagnosis of acute and chronic diseases and assessment of the microbiocenosis of the urogenital tract.
Along with laboratory tests, specific studies such as urethrocystoscopy or urethrography . In the first case, a cystoscope is inserted into the urethra, with the help of which the mucous membrane of the urethra and bladder is visualized. With urethrography, diagnosis is carried out using a radiopaque substance and taking a series of images to assess the patency and presence of pathological processes in the urethra.
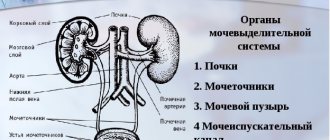
an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs and upper urinary tract (bladder, uterus, appendages, prostate and seminal vesicles, kidneys) is performed
Diagnosis of the disease
The final diagnosis is based on complaints, medical history and life of the patient, examination of the external and internal genital organs, as well as laboratory research methods (general urine analysis and biochemical blood test). To accurately identify the causative agent of this disease, bacteriological and bacterioscopic diagnostics of smears taken from the urethra are required. The specific features of the microorganism and its sensitivity to various groups of antibacterial agents used in urological practice are determined.
Prevention
Preventive measures are the best way to avoid illness. Prevention includes:
- maintaining personal hygiene;
- use of barrier methods of protection during sexual intercourse;
- active lifestyle – physical activity;
- avoiding hypothermia.
It is also very important to undergo regular scheduled examinations by a gynecologist and urologist. The specialists of the Desir clinic offer comprehensive medical care: our highly qualified doctors will conduct high-quality diagnostics and prescribe the necessary effective treatment. Our doctors are always there to protect the health of their patients. Choose the right specialist, make an appointment at a time convenient for you.
Drug therapy
The basis of drug treatment, first of all, is the regular use of strong antibacterial drugs (macrolides, penicillins, cephalosporins, etc.). The course of antibacterial therapy is carried out for quite a long time. In addition, in some cases, the use of products from the nitrofuran group is recommended. The selection of drugs is carried out individually for each patient, based on the nature and severity of his disease, as well as age and concomitant pathology.
Also, for the treatment of urethritis, local therapy is recommended - injection of antiseptic solutions (furatsilin or miramistin) directly into the urethra.
Nutrition
A proper diet is one of the components of a complete treatment. It includes meals containing a balanced amount of fats, carbohydrates and proteins. Products should not cause irritation to the urethra. This means that salty, spicy, smoked dishes are prohibited.
Alcohol can also trigger an exacerbation of the disease. You will have to completely stop drinking alcohol and limit smoking as much as possible.
Instilled nutrition in the treatment of pathology:
- consumption of products of natural origin;
- breakfast and lunch can be hearty, and dinner can be light;
- The norm of fluid consumption is at least 2 liters per day.
It is very important not to put stress on the kidneys, so products should not contain preservatives.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Physiotherapy is a fairly effective and popular method of treatment, which uses physical factors such as a magnetic field, currents, ultrasound, laser, ultraviolet and infrared radiation, etc. Diathermy, hot baths, electrophoresis of antibiotics also have a significant anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect.
Laser therapy
Laser therapy is one of the most popular methods of light therapy. When the body is exposed to laser radiation of 10 mW, blood microcirculation processes are activated, thereby improving tissue trophism. During the session, non-invasive irradiation of the outer part of the urethra is performed: in men, the back surface of the penis is irradiated, and in women, the external opening of the urethra is irradiated. To obtain the desired effect, you must complete a course consisting of 5-6 procedures.
Thermotherapy
Thermotherapy is a method of physiotherapeutic effects on organs using high temperatures. The temperature is constantly at a level of at least 45°C. To achieve this temperature, various types of energy are used. For example, with microwave thermotherapy, the temperature instantly rises to 100° C. The time of the thermotherapy session is determined individually. On average it is about 5-30 minutes. One course of treatment requires 8-10 sessions.
Diet
When prescribing therapy, the doctor gives recommendations on permitted and prohibited foods. It is prohibited to eat:
- herbs, spices;
- foods high in acid;
- broths and meat decoctions;
- conservation;
- radishes, garlic, horseradish;
- strong tea and coffee-containing drinks.
Allowed and required foods include vegetables and fruits. Antimicrobial and antibacterial properties have:
- pumpkin;
- zucchini;
- celery;
- parsley and asparagus;
- honey.
These products are good for making purees and casseroles or eating raw. You can include low-fat fish, poultry, and veal in your diet. To ensure normal bowel function, you need to eat fermented milk products every day.
Consequences and complications of the disease if left untreated
The following complications of urethritis are observed in men:
- the disease takes a chronic course;
- inflammation of the prostate gland;
- inflammation of the testicle;
- inflammation of the seminal vesicles;
- balanitis;
- balanoposthitis;
- urethral stricture.
In women, the negative consequences of urethritis can be:
- cystitis;
- inhibition of vaginal microflora;
- other inflammatory diseases of the urinary system.