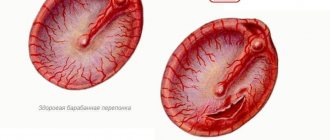
What is wax plug in the ear?
The cerumen plug itself is a collection of ear secretions produced by the sulfur glands of the ear canal, which leads to blockage of the ear canals.
But did you know that the presence of earwax is a normal physiological process? Moreover, sulfur protects the ear canal from dust and small particles; the fats in its composition prevent the ear from getting wet and do not allow pathogenic fungal microflora to multiply, thereby performing an antiseptic function.
As a rule, in a healthy person, sulfur is independently removed due to movements of the temporomandibular joint when talking or chewing. However, in some cases, sulfur accumulates in the ear canal, clogs it, forming a plug and, thus, often causes unpleasant sensations in a person.
Composition and functions of earwax
The main components of earwax are fats, cholesterol, unsaturated fatty acids and wax esters. Therefore, it does not dissolve in water, providing natural lubrication to the skin of the external auditory canal, as well as preventing it from drying out and protecting it from dust particles.
In addition, earwax contains sulfonamides (suppress the growth of pathogens), lysozyme (an enzyme that destroys the cell walls of bacteria) and immunoglobulins (cells of the immune system). Thanks to these components and the acidic reaction (pH = 4-6), earwax protects the external auditory canal from bacteria and fungi.
That is, the formation of earwax is a physiological process that is necessary for the protection and normal functioning of the hearing organ.
What is the self-cleaning mechanism of earwax?
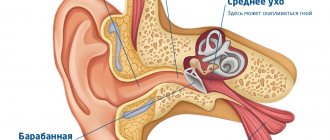
The external auditory canal contacts the inside of the temporomandibular joint. And thanks to his movements during talking or chewing, earwax moves outward from the eardrum.
In addition, the skin of the external auditory canal grows at a rate equal to the growth of nails. As it grows, it moves outward from the eardrum, pushing earwax toward the exit. That is, for example, wax attached to the eardrum will move outward on its own within 3-4 months.
Also in the skin of the external auditory canal there are cilia, which, making oscillatory movements, promote earwax from the inside out.
However, unfortunately, often when exposed to certain factors, the work of the sulfur and sebaceous glands, as well as the self-cleaning mechanism, is disrupted.
Causes of wax plug formation Improper hygienic care of the external auditory canal Excessively frequent and rough use of cotton swabs or cleaning the external auditory canal with improvised means (for example, pins or knitting needles) is the most common cause of wax plug formation.
As a result, the skin of the external auditory canal is injured, and the production of secretion by the sulfur glands is enhanced. Next, the earwax is pushed deeper into the eardrum, where it becomes compacted. Therefore, the process of its self-cleaning is disrupted.
In addition, during intensive cleaning, the cilia of the skin of the external auditory canal are damaged. Therefore, they cease to perform their function: moving the formed sulfur outward. It is noteworthy that often methods of improper hygienic care of the external auditory canal come from childhood. Because children, watching adults, adopt their methods of removing earwax. Anatomical features There is tortuosity or narrowness of the external auditory canal, therefore the process of self-cleaning of earwax is disrupted. Moreover, the anatomical features of the structure can be either congenital or acquired (for example, appear after an injury).
Tendency to increased secretion of earwax Occurs when there are disturbances in the metabolism of fats in the body, which lead to increased formation of cholesterol, which is part of earwax. As a result, it becomes more viscous, and therefore the process of self-cleaning from the external auditory canal is disrupted. Inflammatory and infectious diseases of the external auditory canal (for example, otitis ) Lead to increased secretion production by the sebaceous and sulfur glands, but it does not have time to be removed, so it accumulates. In addition, the lumen of the external auditory canal decreases due to inflammatory swelling of the skin. As a result, a mechanical obstacle is created in the path of self-cleaning of earwax. The qualitative composition of earwax also changes: the number of protective factors in it decreases (lysozyme, immunoglobulins and others). Therefore, the ear glands are secondarily affected by pathogens, and the course of the infectious-inflammatory disease is aggravated. Using hearing aids or regularly using headphones leads to injury to the skin of the external auditory canal (for example, abrasions), so the production of earwax increases. Subsequently, it is pushed inside the external auditory canal and compacted. In addition, conditions are created for the addition of a secondary infection and the development of inflammatory diseases in the outer ear. Excessive hair growth inside the external auditory canal leads to disruption of the process of self-cleaning of earwax. This cause most often occurs in elderly patients. Working in a dusty environment (for example, in a mill or in mines) Dust settles in the external auditory canal. As a result, the secretion production of the ear glands increases, and the functioning of the skin's cilia is disrupted. A foreign body in the lumen of the external auditory canal leads to increased secretion production by the ear glands (a natural protective reaction of the body), which does not have time to be removed. In addition, a mechanical obstacle is created in the way of self-purification of sulfur. Prolonged stay in a room with dry air (humidity up to 40%) leads to the drying out of the secretion of the external auditory canal, so a sulfur plug of solid consistency is formed. The older a person is, the higher his risk of developing wax plugs. Because with age, the self-cleaning mechanisms of earwax weaken, and its production by the glands increases. In addition, in older patients, the number of hairs in the external auditory canal tends to increase. Therefore, an additional obstacle is created in the way of self-purification of sulfur.
Symptoms of wax plug
As a rule, sulfur plugs do not manifest themselves for a long time. Only when the lumen of the external auditory canal is almost completely blocked (70% or more) do signs of cerumen plug appear. Moreover, they can occur on either one or both sides, if wax plugs have formed in both ears. Ear congestion and , hearing loss Symptoms develop slowly due to the gradual accumulation of wax in the external auditory canal. Therefore, the patient usually does not pay any attention to the fact that he gradually becomes deaf and noise appears in the ears. Dry and irritating cough , nausea and dizziness, moderate pain and the echo of your own voice in the ear. Signs appear if the wax plug presses on the eardrum, irritating its nerve endings. With prolonged pressure from wax plugs, inflammation of the eardrum (myringitis) or the middle ear cavity (otitis media) sometimes develops. As a result, mild pain in the ear appears (with otitis media it intensifies during chewing or talking), body temperature may rise moderately, and small discharge (most often purulent) appears from the external auditory canal. On a note! Most often, the first signs of wax impaction appear upon contact with water (for example, after diving in a pool or taking a shower). Because it swells and partially pushes inward closer to the eardrum, blocking the lumen of the external auditory canal.
How to remove wax plug
There are several ways: using pharmaceutical drugs at home, as well as using hardware methods in a medical institution.
How to remove wax plug at home
Trying to remove large wax plugs at home yourself and in the presence of severe symptoms is useless, and not always harmless. Since you can accidentally get an infection, damage the eardrum or the skin of the external auditory canal. However, small wax plugs can be removed at home, using caution. Moreover, it is necessary to use pharmaceutical products (ear drops), and not hygienic cotton swabs.
Why can't you use cotton ear swabs?
Because with their help, earwax is compacted and pushed closer to the eardrum. That is, the sulfur plug, on the contrary, increases in size. In addition, such deep cleaning may cause injury to the skin of the external auditory canal and/or eardrum (perforation - loss of integrity). Drops for removing wax plugs - pharmaceutical products
They are used for the safe and painless removal of wax plugs at home, as well as to prevent its formation. In addition, ear drops are used as a preparatory step before an ENT doctor removes wax plugs. The most commonly used agents for cerumenolysis
| A drug | Release form | Mode of application |
| A-Cerumen | In 2 ml dropper bottles | To remove wax plug , 1 ml of solution (half of a dropper bottle) is instilled into the external auditory canal, and after one minute it is cleaned. The procedure is carried out twice a day for 3-4 days. To prevent the formation of wax plugs (for example, in patients using hearing aids), a solution of 1 ml is instilled into each ear canal twice a month. |
| Remo-Wax | In 10 ml bottles with a plastic dispenser | To remove wax plug, 10 to 20 drops of solution are instilled into the external auditory canal of the diseased ear, and after 20-60 minutes it is removed. The procedure is carried out daily for 3-4 days. To prevent the formation of sulfur plugs, the drug is used once every two weeks. |
When should you not use ear drops?
- In case of a defect (violation of integrity) of the eardrum.
- If the patient has chronic otitis or in the past he suffered purulent otitis.
- A-Cerumen is contraindicated for use in children under 2.5 years of age.
Can peroxide be used to remove earwax?
Yes, you can use 3% hydrogen peroxide. Whereas the use of a higher percentage of the solution is contraindicated, since it causes a chemical burn to the skin of the external auditory canal and eardrum. The mechanism of action of hydrogen peroxide When in contact with tissues, peroxide breaks down into molecular oxygen and water. In this case, oxygen oxidizes the tissue (in this case, the cerumen plug), forming foam, which mechanically cleanses the external auditory canal. Moreover, it should be remembered that hydrogen peroxide leads to swelling of the cerumen plug, so ear congestion and hearing loss intensify. However, after cleaning the external auditory canal, the symptoms disappear.
When should you not use hydrogen peroxide?
- If there is a defect in the eardrum.
- If the patient has suffered from purulent otitis media in the past or is currently suffering from chronic otitis media. Hydrogen peroxide should be used with caution as it can burn the skin of the external auditory canal and/or eardrum. Therefore, if during the procedure there is a severe burning sensation and pain in the ear, stop it and be sure to consult an ENT doctor.
Do I need to rinse my ear to remove wax?
Washing out (irrigation) is the most common and effective way to remove wax plugs by an otolaryngologist. However, it is not recommended to remove wax plugs by rinsing yourself at home. Since there is a high probability of damage to the eardrum and/or skin of the external auditory canal.
How to rinse wax plug?
If the sulfur plug is soft, then washing is carried out without preliminary preparation. When the sulfur plug is dry, it is necessary to soften it first. For this purpose, half a pipette of 3% hydrogen peroxide is instilled into the external auditory canal of the diseased ear 5-6 times a day for 2-3 days. Or use cerumenolysis products according to the instructions. To rinse the external auditory canal, use water or any solution of external antiseptic (for example, furatsilin), which are heated to 37°C. There are instrumental (manual) and hardware methods for washing out wax plug:
- Using a Janet syringe, the capacity of which is 100-200 ml. During the procedure, the doctor delivers a high-pressure stream of water into the external auditory canal towards the eardrum. Due to this, particles of sulfur plug move away from the place of attachment. The water then flows into the tray through the outlet of the external auditory canal. However, Janet's syringe is capable of creating pressure up to 10 atmospheres. Whereas the eardrum can only withstand 2 atmospheres. Therefore, the success of the procedure largely depends on the professionalism of the doctor.
- An electronic irrigator is used (Propluse 4th generation) - a new technique that has found wide application. The effectiveness of the procedure is based on the pulsed nature of the jet supply, as well as the ability to regulate its pressure. This ensures complete, painless and safe removal of the wax plug.
When should you not rinse your ear to remove wax?
- Violation of the integrity of the eardrum (perforation) is the result of injury or infection.
- The presence of acute or chronic otitis media.
- Previous history of purulent otitis media.
Because in these cases, water entering the middle ear cavity can lead to an exacerbation of the chronic inflammatory process.
Prevention of wax plugs
It is important for everyone, but especially for people with an increased risk of wax accumulation in the external auditory canal. What do we have to do?
- Clean the pinna and the opening of the external auditory canal with a swab soaked in water, without penetrating the external auditory canal.
- To improve the natural removal of wax, take your earlobe in your hands and pull it down several times. It is recommended to carry out such “charging” daily in the morning.
- If necessary, use ear cotton swabs with a limiter, but do not be too overzealous. Because they clean the external auditory canal from earwax quite well, preventing deep penetration into it.
- If you have an increased risk of developing wax plugs (for example, using hearing aids or working in a dusty room), use cerumenolysis products (for example, Remo-Vax) for prevention.
- Maintain indoor air humidity at least 40% using humidifiers.
- Use earplugs when working in dusty areas.
- When swimming in a pool or open water, protect the external auditory canal from water: put a cap on your head or use protective equipment. There are special earplugs for swimming: wax-impregnated tampons, plugs that protect against water or with a water-repellent effect.
- If the anatomical structure of the external auditory canal is prone to the formation of cerumen, periodically visit an otolaryngologist and follow all his recommendations.
What should you avoid?
- You should not use hygienic cotton swabs that penetrate deep into the external auditory canal. Since the sulfur is pushed closer to the eardrum and compacted. In addition, there is a risk of injury to the eardrum if you are accidentally distracted by another event during the procedure. Young children especially suffer from this, because during cleaning they fidget or break out of their mother’s hands.
- Do not use matches, knitting needles, pins or other sharp objects to remove wax. Since there is a high risk of injury to the eardrum and skin of the external auditory canal.
- Avoid sudden changes in ambient temperature. For example, in the heat - moving from the street to a room where the air conditioner is running.
- Do not use earwax candles to remove wax plugs on your own and without consulting an ENT doctor, as you may harm yourself. For example, cause a burn to the eardrum or the skin of the external auditory canal, and if there is inflammation in the outer ear, aggravate the course of the disease.
Otorhinolaryngologist L.V. Ledova.
So what causes wax plugs to form?
- The very first and most common cause of earwax in the ear is the use of cotton swabs for ear hygiene. Many people, using cotton swabs irrationally, push and compact earwax further, which provokes the formation of a plug. You can clean out wax only at the entrance to the ear canal, otherwise inserting sticks and turundas can damage the skin, injure the eardrum, and disrupt the natural process of self-cleaning.
- Too much sulfur can be produced due to overactive sulfur glands. The auricle does not have time to clean itself and wax quickly accumulates. Increased secretion of the sebaceous glands can be a consequence of high cholesterol levels in the blood, as well as diseases such as eczema, atopic dermatitis, chronic otitis media and external otitis.
- Large amounts of wax can be produced as a result of overzealous ear care. Of course, you need to wash your ears, but an excessive desire for cleanliness, when the patient cleans his ears with cotton swabs every day until they shine, leads to skin irritation, and very often to an increase in sulfur formation.
- If the anatomical ear canal is tortuous and narrow, then accumulation and compaction of wax into the ear plug is also possible. This is not a pathology when the ears are prone to the accumulation of wax, however, more attention should be paid to the hygiene of such ears.
- It is not common, but it happens that patients' earwax has increased viscosity. In addition, rapid hair growth in the ear canal, headphones, hearing aids, very dusty conditions, and dry indoor air can also cause wax plugs in the ears.
How to remove a plug from your ear
- rinse with water. Water is drawn into a special syringe and the stream is directed into the ear canal. Water pressure flushes wax out of the ear. It does not hurt. Sometimes multiple treatments are required;
- pull out with tweezers. Only an otolaryngologist removes the plug in this way. He has special devices: tweezers or a hook. With the help of them, he carefully removes the sulfur. The method is used for damaged membrane;
- drop drops. There are drops that dissolve sulfur. They are buried in the ear and wait until the substance takes effect. This takes a few minutes. After which the person tilts his head and the sulfur along with the drops flows out. You can instill it at home or at the doctor's office. The method is suitable for small children, as it is difficult for them to sit still for a long time;
- remove with heat. A person lies with his ear on a heating pad. The water in it should not be hot. Otherwise you might get burned. The heat softens the wax and leaves the ear. If you don’t have a heating pad, you can take a plastic bottle with warm liquid;
- blow out your ear. Take a deep breath and hold the air. Pinch your nose, cover your mouth and exhale sharply. Air will enter the ear canal through the Eustachian tube and push the plug towards the exit;
- use ear candles. Pharmacies sell candles to remove wax. They contain beeswax and propolis. The procedure can be carried out at home, but very carefully. An assistant will be needed. Insert the candle into your ear and light it. While the candle burns, a vacuum is created in the ear, which will push the wax out.
Regardless of the removal method, be prepared for a side effect - temporary hearing loss. Any intervention causes swelling. Because of it, the ear canal narrows and the person hears worse.
The main symptoms of wax plug
Often, the patient may not realize that there are wax plugs in the ears, because they do not present any particular discomfort. However, symptoms such as tinnitus, autophony (resonance of one's own voice), a feeling of fullness and, finally, severe hearing loss signal the formation of earwax.
Often, when water gets into the ear, the wax mass swells and completely blocks the ear canal. If the formed plug is located near the eardrum, irritation of the nerve endings occurs and the patient may feel nausea, dizziness and headache.
It is also worth remembering that due to prolonged irritation of the eardrum, inflammatory processes may develop in the middle ear, where our hearing aid is located.
When should you see a doctor?
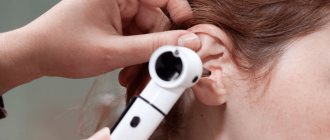
If a person notices any of these symptoms, he needs to visit a doctor. An experienced otolaryngologist will examine the patient using an otoscope to determine if a problem exists.
How to get wax plug? Your doctor may be able to remove the wax yourself using a device called a curette. In some cases, the specialist will prescribe wax softening medications or drops suitable for use at home to soften the wax before removing it. You don’t need to buy special medications yourself - this can make your health worse.
When should you see a doctor?
If a person notices any of these symptoms, he needs to visit a doctor. An experienced otolaryngologist will examine the patient using an otoscope to determine if a problem exists.
How to get wax plug? Your doctor may be able to remove the wax yourself using a device called a curette. In some cases, the specialist will prescribe wax softening medications or drops suitable for use at home to soften the wax before removing it. You don’t need to buy special medications yourself - this can make your health worse.
How to clean a healthy person's ears
The ability of the ears to clean themselves does not mean that you can forget about hygiene. Quite the opposite: minimal and regular ear cleaning is necessary. The best way to proceed is as follows:
- When showering or washing your hair, rinse your ears and the area around your ears. At the same time, you should not stick your fingers into the ear canal, since your task is only to soften the wax as much as possible.
- Thoroughly wipe the inside of the ear with a towel or piece of cotton wool, removing any remaining dirt from all folds.
- Wrap your index finger in a cotton pad and use it to remove any remaining wax from the ear canal without pushing your finger deep inside.
Why shouldn't you use cotton swabs? They penetrate too deeply, even if it seems to you that you are in complete control of the process. In this case, the risk is not even that you can injure your eardrum, although such a danger should not be excluded. The thing is that you gradually push a small amount of sulfur inside. Every month more and more of it accumulates, it gets compacted and turns into a dense plug that must be removed.
Independent ear toilet
As noted above, ears do not require special cleaning. According to the American Academy of Otolaryngology, wax removal should only be done when plugs form and unpleasant symptoms occur.
Sulfur removal sequence:
- Drops to soften sulfur or a solution of hydrogen peroxide (3%) are taken into a warm pipette.
- Lie on your side and carefully pour/drip the solution into your ear.
- Leave for 5-7 minutes.
- Press a napkin to your ear and tilt your head.
- Use a small bulb to rinse the ear canal with warm water (~37°C), pulling the earlobe up and out.
- Blot the ear with a napkin to remove any remaining water.
The procedure can only be performed on a healthy ear, and very carefully. Perforation of the eardrum and inflammation are contraindications for getting rid of wax on your own. A doctor will help identify the pathology: depending on the symptoms, he will conduct an additional examination.
To avoid injury or other complications, it is best to carry out cleaning in a medical facility. At the clinic, the otolaryngologist will perform irrigation - washing the ear canal with a stream of water under pressure. Doctors use a special syringe or electronic irrigator with pressure control, directing the stream at different angles. In the case of dense wax, the doctor will examine the ear canal using a mirror to ensure that the ear is completely clean. If irrigation is contraindicated, the ENT doctor removes the sulfur plug using special instruments (probe, otoscope and others).
For detailed advice on the procedure, please contact otolaryngologists at the President-Med medical centers
How to clear wax from ears?
Is it painful to remove wax plug? There is no sharp pain, there may be some discomfort. If you are prone to wax, the best way to remove excess wax and clean your ears is to use a soft cloth. In some cases, as prescribed by a doctor, you can use softening solutions - mineral oil, glycerin, peroxide solutions, hydrogen peroxide.
If the wax plug is not softened with solutions, the doctor can use rinsing - using a syringe to rinse the ear canal with saline solution or water. Rinsing is done after using the drops - this enhances the effect.
Note: Irrigation is contraindicated for people with ruptured eardrums. If you suspect a ruptured ear tube or other injury, you should consult a doctor immediately. Making decisions on your own often makes the situation worse.
How to prevent problems with sulfur production?
To prevent disruption of wax production, do not insert anything into your ears to clean them. Use cotton swabs to clean the outer surface. If you often have wax plugs, then you need to remove it with the help of a specialist at least once a year. Talk to your doctor about which methods to prevent excess wax production may work best for you.
Why do some people experience wax plugs? Every body produces earwax, but in varying amounts, which depend on a person's genetics.
How to remove wax from ears? Due to the special structure of the ear, removing wax from it is not difficult. Jaw movements move the ear canal and help push wax out. For people whose ear canals are smaller than standard or have a large curve, cleaning with a Q-tip can cause injury.
How to clear wax from ears?
Is it painful to remove wax plug? There is no sharp pain, there may be some discomfort. If you are prone to wax, the best way to remove excess wax and clean your ears is to use a soft cloth. In some cases, as prescribed by a doctor, you can use softening solutions - mineral oil, glycerin, peroxide solutions, hydrogen peroxide.
If the wax plug is not softened with solutions, the doctor can use rinsing - using a syringe to rinse the ear canal with saline solution or water. Rinsing is done after using the drops - this enhances the effect.
Note: Irrigation is contraindicated for people with ruptured eardrums. If you suspect a ruptured ear tube or other injury, you should consult a doctor immediately. Making decisions on your own often makes the situation worse.