The spleen is a small organ that is located in the abdominal cavity, just to the left of the rib cage. It plays a very important role in the human body. This is the organ of the body's immune response to infection.
The spleen is where immunoglobulins are made, which fight disease. It also cleanses the blood of red blood cells and platelets that are already outdated or have abnormalities. Additionally, it is responsible for hematopoiesis. And, of course, this is one of the main organs in the human body, which is responsible for the deposition of blood.
The normal size of the spleen is 10-13 cm in length and 8-9 in width. Thickness up to 5 cm, and weight about 200 grams.
In 3-4% of thin people, doctors can palpate the spleen even when its size is normal. ( https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/hematology-and-oncology/spleen-disorders/splenomegaly )
Like any organ, the spleen actively reacts to various changes in the body. And one of the responses to irritants is an increase in the size of the spleen.
Splenomegaly is an increase in size greater than 300 grams and length greater than 20 centimeters. In turn, an increase in the organ by more than 20 cm and 1000 grams indicates massive splenomegaly
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430907/
Reasons for increasing size
The most common causes of splenomegaly are:
— Oncohematological diseases. Blood cancer cells cause infiltration of the spleen and, as a result, its enlargement;
— Acute and chronic infectious diseases (syphilis, mononucleosis, tuberculosis, cytomegalovirus, malaria) in the body lead to an increase in the activity of the immune function of the spleen and, with a long process, its size increases.
— Autoimmune processes in the body (rheumatoid arthritis, amyloidosis, lupus)
— Liver diseases increase pressure in blood vessels, which leads to an enlarged spleen;
— Stagnation of blood in the spleen (venous thrombosis, heart failure, portal hypertension)
- Sequestration of the spleen. These are conditions in which increased destruction of platelets occurs in the spleen.
— Local process. (Cysts, cancerous tumors, abscesses);
The exact cause of an enlarged spleen is difficult to determine. This process requires a full medical examination.
Symptoms of splenomegaly
In most cases, the patient does not feel specific symptoms. Most often, this is accompanied by a large symptom complex of a certain disease, which causes an enlargement of the spleen. The following may indicate a malfunction of the spleen:
* Constant fatigue, malaise, drowsiness, pale skin, which is caused by anemia;
* Frequent infectious diseases as a result of impaired immune function of the spleen;
* Pain in the left hypochondrium;
* Feeling of overeating, even after eating a small amount of food.
And the last, most obvious symptom is a noticeable visual enlargement of the spleen. It happens quite rarely, and means a critical increase in the organ.
Quite often, asymptomatic splenomegaly is diagnosed during routine examinations. In this case, there is a high probability of detecting the primary disease that provoked the growth of the spleen in the early stages and providing effective treatment.
Symptoms
Severe pain behind the stomach, in the area of the left hypochondrium, indicates a pathology of the spleen. Discomfort may extend to the shoulder blade area. Similar manifestations occur due to various cracks and wounds, ruptures of the spleen. If the problem is accompanied by hemorrhage into the abdominal cavity, the patient may experience an attack of shock. In this case, symptoms are observed:
- nausea and vomiting
- tremor
- paleness of the skin
- thirst
- lowering blood pressure
- anemia
- difficulty breathing
A protruding lump in the left side may indicate an enlarged spleen. At the same time, a person’s skin turns pale, especially on the face. When moving or straining, the pain in the left hypochondrium intensifies, and discomfort occurs in the navel. These manifestations are accompanied by excessive fatigue, decreased immunity, and damage to the lymph nodes.
Symptoms of an enlarged spleen:
- decrease in hemoglobin
- decreased immunity
- ulcers on the upper and lower extremities, as well as in the mouth
- increased heart rate
- frequent bleeding
- increase in temperature indicators
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach
If you experience such symptoms, you should seek medical help.
Diagnosis of splenomegaly
When you come to the doctor with certain symptoms, first of all, he begins to collect your complaints, medical history, etc. Then he begins an objective examination, during which he palpates and percusses the abdomen in the projection of the spleen. The doctor assesses by palpation the size of the spleen, its sensitivity and the tension of the abdominal muscles above the spleen.
Palpation and percussion of the abdomen are quite sensitive methods. The probability of successfully determining splenomegaly is about 60-80% (which is confirmed by ultrasound data).
(https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/hematology-and-oncology/spleen-disorders/splenomegaly)
After this, he directs the patient to undergo tests:
- General blood analysis;
- Blood chemistry;
— Liver tests;
The doctor also prescribes laboratory tests for a specific disease that could cause splenomegaly:
— Oncohematological tests;
— Blood test for immunoglobulins for a specific infection;
Additionally, the patient undergoes instrumental diagnostic methods;
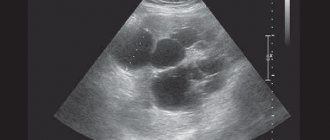
* Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
* CT;
* MRI;
They allow you to visualize the spleen, calculate its exact size and wall thickness. Diagnose a neoplasm or cyst as the cause of a large organ size.
Classification, stages
“Spleen cancer” is not quite the correct term. Strictly speaking, cancer refers to tumors that originate from epithelial tissue. In the spleen, malignant neoplasms develop from other types of tissue. Their classifications have changed over time and differ among different authors. Currently, doctors are often guided by the L. Morgenstern classification, developed in 1985. In accordance with it, all malignant tumors of the organ are divided into three large groups: vascular, lymphoid and non-lymphoid:
| Examples of vascular tumors |
|
| Examples of lymphoid tumors |
|
| Examples of non-lymphoid tumors |
|
Lymphomas most often occur in the spleen. However, primary organ damage is a rare occurrence. It is known that in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma the spleen is involved in 50–80% of cases, and this often occurs in Hodgkin's disease.
The most common vascular malignant tumor in the spleen is angiosarcoma. However, it is a very rare disease - it affects 1-3 people in ten million. Angiosarcoma originates from the tissues of the vascular wall, is highly aggressive, and quickly metastasizes.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Why is splenomegaly dangerous?
Splenomegaly is a rather dangerous condition. Since, due to an increase in the size of the organ, it causes anatomical defects and physiological disruptions in the functioning of the spleen.
This leads to certain complications:
* Infectious diseases. The synthesis of lymphocytes is disrupted, which reduces the effectiveness of the immune system;
* Bleeding and anemia. Due to its large size, the spleen begins to actively capture and utilize platelets and red blood cells, which ultimately leads to bleeding;
And one of the most dangerous complications is splenic rupture. When the spleen enlarges, the wall of its capsule becomes thinner and even a slight blow to its area can lead to rupture. This is a very dangerous condition, since bleeding from the spleen is quite difficult to stop. Therefore it has to be completely removed.
Preventive measures
- Priority to a healthy lifestyle.
- Limit alcohol consumption.
- Physical activity, but not heavy. Running (two hours after eating) and frequent walks in the fresh air are very useful.
- Check your body frequently for infections.
- Strengthen immunity.
- Protect yourself from all kinds of injuries, blows to the abdominal area, and falls.
- Get a blood test every six months.
Life without a spleen
It is possible to live without a spleen. But it is important to remember that the main function of the organ is to protect the entire body from infections and pathogens.
If an organ is missing for any reason, its functions are performed by the bone marrow and liver. The purification of blood from infection is disrupted.
There is a high probability of thrombosis, because platelets are no longer excreted from the human body. In this case, there is a need to take medications and constantly monitor the doctor.
If the spleen has been removed, the likelihood of contracting viral infections increases significantly, and children are especially susceptible to this.
Splenomegaly in children
Because the size of the spleen varies widely depending on age and genetics. Therefore, the modern concept of splenomegaly is not applicable to children.
However, in adults, no predominant prevalence based on ethnicity, gender or age was reported.
(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430907/)
One of the main reasons for an enlarged children's spleen remains infectious and oncohematological diseases.
Prevention
It is now known that there is a connection between the development of malignant neoplasms of the spleen and infections such as hepatitis C, HIV infection, and infection caused by the T-cell lymphoma virus. It is recommended to follow recommendations that help prevent infection:
- Use condoms.
- If you decide to get a piercing or tattoo, choose a reliable salon.
- Do not inject with used needles.
A high fat diet and excess weight are two other risk factors for developing non-Hodgkin lymphoma. You need to eat a healthy diet and maintain a normal weight.
| More information about treatment at Euroonco: | |
| Oncologist-hematologist | 10500 rub. |
| Chemotherapy appointment | 6900 rub. |
| Emergency oncology care | from 12100 rub. |
| Palliative care in Moscow | from 44300 per day |
| Radiologist consultation | 10500 rub. |
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Treatment of splenomegaly
The main goal in the treatment of splenomegaly is to remove the cause of the development of this condition and prevent complications.
So, for infectious diseases, antibiotics or antiviral drugs are used.
If an oncohematological process develops, chemotherapy and radiotherapy are prescribed to help fight the tumor.
If the size of the spleen has reached a critical level, this can lead to serious disruption of its function and the functioning of the whole organism, which will be life-threatening. Such a patient undergoes a splenectomy - removal of the spleen. Sometimes this is the only way to save the patient.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you have pain in the spleen, you should consult your family doctor or general practitioner. In the future, the patient will need the help of highly specialized doctors - a gastroenterologist or surgeon. Treatment of spleen diseases is carried out under the supervision of a specialist. In advanced cases, surgical removal of the organ is recommended. This procedure will not affect the patient’s performance in the future. Drug therapy for pain in the spleen is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease, relieving pain, and stabilizing the functions of the organ.
As prescribed by a doctor, the following can be used:
- allergy remedies
- anti-inflammatory and/or painkillers
- antibiotics
- vitamin and mineral complexes to strengthen the immune system
- antitumor or antituberculosis drugs, etc.
Treatment of spleen diseases should be carried out under the supervision of a physician. Traditional medicine can be used as supportive medications (after consultation with a specialist).
Removal of the spleen and its consequences
The spleen is an organ without which you can function. Therefore, when this organ is removed, its functions are taken over by other organs, such as the liver. Splenectomy, that is, partial or complete removal of the spleen, is recommended in the following cases: extensive trauma or rupture of the spleen, splenic coabscess, splenic cancer, hematological diseases - polycythemia vera, leukemia, chronic immune thrombocytopenia.
Removing the spleen increases the chances of recovery and survival from certain diseases and post-traumatic conditions.
Most often, the operation is performed laparoscopically, which is less invasive than classical surgical methods.
Complications associated with the procedure occur in less than 10% of cases and mainly include infection and excessive bleeding. There are very few deaths - about 0.2%. Additional long-term complications and side effects may occur after the procedure.
People living without a spleen have a weakened immune system, especially when infected with enveloping bacteria. Recovery from a splenectomy can take up to several weeks and exercise should be avoided during this time. Patients are advised to get vaccinated against pneumococci every 5 years and monitor their health. Removing the spleen can cause the platelet count to increase, which in turn creates a risk of blood clots and clogged blood vessels.