Galvus®
When using Galvus as monotherapy or in combination with other drugs, most adverse reactions were mild, temporary and did not require discontinuation of therapy. There was no correlation between the frequency of adverse reactions and age, gender, ethnicity, duration of use or dosage regimen.
The incidence of angioedema during therapy with Galvus was >1/10,000, <1/1000 (rare) and was similar to that in the control group. Most often, angioedema was observed when the drug was prescribed in combination with ACE inhibitors. In most cases, angioedema was of moderate severity and disappeared with continued vildagliptin therapy.
During therapy with Galvus, asymptomatic liver dysfunction (including hepatitis) was rarely observed. In most cases, these disorders and deviations of liver function tests from normal resolved independently without complications after discontinuation of drug therapy. When using Galvus at a dose of 50 mg 1 time/day or 2 times/day, the incidence of increased liver enzyme activity (ALT or AST ≥ 3xULN) was 0.2% or 0.3%, respectively (compared to 0.2% in the control group). Increases in liver enzyme activity were in most cases asymptomatic, did not progress, and were not accompanied by cholestatic changes or jaundice.
Determination of the frequency of adverse reactions: very often (≥1/10); often (≥1/100, <1/10), uncommon (≥1/1000, <1/100), rare (≥1/10,000, <1/1000), very rare (≤1/10,000), including individual messages.
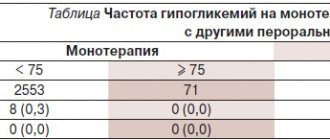
When using the drug Galvus as monotherapy
When using the drug Galvus at a dose of 50 mg 1 time / day or 2 times / day, the frequency of discontinuation of therapy due to the development of adverse reactions (0.2% or 0.1%, respectively) was not higher than that in the placebo group (0.6%) or the reference drug (0.5 %).
During monotherapy with Galvus at a dose of 50 mg 1 time/day or 2 times/day, the incidence of hypoglycemia without increasing the severity of the condition was 0.5% (2 out of 409 people) or 0.3% (4 out of 1082), which is comparable with the reference drug and placebo (0.2%). When using the drug Galvus as monotherapy, there was no increase in body weight of patients.
From the nervous system:
often - dizziness; infrequently - headache.
From the digestive system:
infrequently - constipation.
From the body as a whole:
infrequently - peripheral edema.
Long-term clinical studies of up to 2 years did not reveal any additional safety profile deviations or unexpected risks when using vildagliptin as monotherapy.
When using the drug Galvus at a dose of 50 mg 1 time / day or 2 times / day in combination with metformin
When using the drug Galvus at a dose of 50 mg/day in combination with metformin, the frequency of discontinuation of therapy due to the development of adverse reactions was 0.4%; In the groups vildagliptin (50 mg 2 times/day) + metformin and placebo + metformin, there were no cases of discontinuation of therapy due to the development of adverse reactions.
When using the drug Galvus at a dose of 50 mg 1 time / day or 2 times / day in combination with metformin, hypoglycemia was observed in 0.9% and 0.5% of cases, respectively; in the placebo + metformin group - 0.4%. There was no development of severe hypoglycemia in the Galvus group. Combination therapy with vildagliptin + metformin did not affect the body weight of patients.
From the nervous system:
often - tremor, dizziness, headache.
Long-term clinical studies of up to 2 years did not reveal any additional safety profile deviations or unexpected risks when using vildagliptin in combination with metformin.
When using the drug Galvus at a dose of 50 mg/day in combination with sulfonylurea derivatives
When using the drug Galvus at a dose of 50 mg/day in combination with glimepiride, the frequency of discontinuation of therapy due to the development of adverse reactions was 0.6% (compared to 0% in the glimepiride + placebo group).
The incidence of hypoglycemia in patients receiving Galvus at a dose of 50 mg/day along with glimepiride was 1.2% (compared to 0.6% in the placebo + glimepiride group). There was no development of severe hypoglycemia in the Galvus group.
When using the drug Galvus at the recommended dose (50 mg/day) in combination with glimepiride, there was no increase in patient weight.
From the nervous system:
often - tremor, dizziness, headache.
From the body as a whole:
often - asthenia.
When using the drug Galvus at a dose of 50 mg 1 time / day or 2 times / day in combination with thiazolidinedione derivatives
When using the drug Galvus at a dose of 50 mg/day in combination with pioglitazone, the frequency of discontinuation of therapy due to the development of adverse reactions was 0.7%; In the vildagliptin (50 mg 2 times/day) + pioglitazone and placebo + pioglitazone groups, there were no cases of discontinuation of therapy due to the development of adverse reactions.
When using the drug Galvus at a dose of 50 mg/day in combination with pioglitazone at a dose of 45 mg, hypoglycemia was not observed; in the group of vildagliptin (at a dose of 50 mg 2 times a day) + pioglitazone (at a dose of 45 mg), hypoglycemia was observed in 0.6% of cases, and in patients receiving placebo + pioglitazone at a dose of 45 mg, in 1.9% of cases. There was no development of severe hypoglycemia in the Galvus group. The mean increase in body weight compared to placebo in patients receiving Galvus 50 mg once a day or twice a day with pioglitazone was +0.1 kg or +1.3 kg, respectively.
When Galvus was added at a dose of 50 mg once a day or twice a day to pioglitazone at a dose of 45 mg/day, the incidence of peripheral edema was 8.2% and 7%, respectively (compared to 2.5% with pioglitazone monotherapy). However, when prescribing initial combination therapy with vildagliptin at a dose of 50 mg 1 time / day or 2 times / day together with pioglitazone at a dose of 45 mg / day, peripheral edema was observed in 3.5% or 6.1% of patients, respectively (compared to 9.3% with pioglitazone monotherapy at a dose of 30 mg/day).
From the cardiovascular system:
often - peripheral edema.
From the body as a whole:
often - weight gain.
When using the drug Galvus at a dose of 50 mg 2 times a day in combination with insulin
When the drug was prescribed in combination with insulin (in combination with metformin or without metformin), the rate of discontinuation of therapy due to the development of side effects was 0.3% in the group of patients receiving vildagliptin; in the group receiving placebo, there was no discontinuation of therapy.
When prescribing the drug in combination with insulin (in combination with metformin or without metformin), there was no increase in the risk of hypoglycemia compared with the combination of placebo + insulin (14% in the vildagliptin group and 16.4% in the placebo group). Two patients in the vildagliptin group and 6 patients in the placebo group developed severe hypoglycemia.
At the time of completion of the study, the drug had no effect on average body weight (body weight increased by 0.6 kg compared to baseline in the vildagliptin group, and no changes were noted in the placebo group).
Adverse reactions in patients receiving vildagliptin 50 mg 2 times a day in combination with insulin (with or without metformin)
From the nervous system:
often - headache, chills.
From the digestive system:
often - nausea, gastroesophageal reflux; infrequently - diarrhea, flatulence.
From the side of metabolism:
often - hypoglycemia.
When using the drug Galvus
in
combination with sulfonylureas and metformin
There were no cases of drug withdrawal associated with adverse reactions in the combination therapy group with vildagliptin, metformin and glimepiride. In the combination therapy group with placebo, metformin and glimepiride, the incidence of adverse reactions was 0.6%.
Hypoglycemia was observed in both groups (5.1% in the combination therapy group of vildagliptin, metformin and glimepiride and 1.9% in the combination therapy group of placebo, metformin and glimepiride). There was one episode of severe hypoglycemia in the vildagliptin group.
At the time of completion of the study, no significant effect on body weight was detected (+0.6 kg in the vildagliptin group and -0.1 kg in the placebo group).
Adverse reactions in patients receiving vildagliptin at a dose of 50 mg 2 times a day in combination with metformin and sulfonylureas
From the nervous system:
often - dizziness, tremor.
From the side of metabolism:
often - hypoglycemia.
From the skin and subcutaneous fat
: often - hyperhidrosis.
From the body as a whole:
often - fatigue.
Post-marketing studies
During post-marketing studies, the following adverse reactions were identified: rarely - hepatitis (reversible upon cessation of therapy); frequency unknown - urticaria, pancreatitis, local peeling of the skin or blistering.
Vildagliptinum
Hypoglycemic agent. Vildagliptin is a representative of the class of stimulants of the islet apparatus of the pancreas, selectively inhibits the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4. Rapid and complete inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 activity (>90%) causes an increase in both basal and meal-stimulated secretion of glucagon-like peptide type 1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide from the intestine into the systemic circulation throughout the day.
By increasing the levels of glucagon-like peptide type 1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, vildagliptin causes an increase in the sensitivity of pancreatic beta cells to glucose, which leads to improved glucose-dependent insulin secretion. When using vildagliptin at a dose of 50-100 mg per day in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, an improvement in the function of pancreatic beta cells is noted. The degree of improvement in beta cell function depends on the degree of initial damage; Thus, in individuals who do not have diabetes mellitus (with normal plasma glucose levels), vildagliptin does not stimulate insulin secretion and does not reduce glucose levels.
By increasing levels of endogenous glucagon-like peptide type 1, vildagliptin increases alpha cell sensitivity to glucose, resulting in improved glucose-dependent regulation of glucagon secretion. Reducing the level of excess glucagon during meals, in turn, causes a decrease in insulin resistance.
An increase in the insulin/glucagon ratio during hyperglycemia, caused by increased levels of glucagon-like peptide type 1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, causes a decrease in hepatic glucose production both during the prandial period and after meals, which leads to a decrease in plasma glucose levels.
In addition, with the use of vildagliptin, a decrease in plasma lipid levels is observed, but this effect is not associated with its effect on glucagon-like peptide type 1 or glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and improvement in pancreatic beta-cell function.
It is known that an increase in the level of glucagon-like peptide type 1 can lead to a slowdown in gastric emptying, but no such effect is observed with the use of vildagliptin.
When vildagliptin was used in 5795 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus for 12 to 52 weeks as monotherapy or in combination with metformin, sulfonylurea derivatives, thiazolidinedione, or insulin, a significant long-term decrease in the concentration of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and blood glucose was observed on an empty stomach.
Buy Galvus tablets 50 mg No. 28 in pharmacies
Galvus Buy Galvus in pharmacies DOSAGE FORMS tablets 50mg
MANUFACTURERS Novartis Pharma Stein AG (Switzerland)
GROUP Hypoglycemic agents - dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors
COMPOSITION Active substance: Vildagliptin.
INTERNATIONAL NON-PROPENTED NAME Vildagliptin
SYNONYMS Hemofer prolongatum, PMS-iron sulfate, Tardiferon, Ferro-gradumet, Ferrogradumet
PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTION Hypoglycemic drug, selective inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4). Rapid and complete inhibition of DPP-4 activity causes an increase in both basal and meal-stimulated secretion of glucagon-like peptide type 1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) from the intestine into the systemic circulation throughout the day. By increasing the levels of GLP-1 and GIP, vildagliptin causes an increase in the sensitivity of pancreatic beta cells to glucose, which leads to an improvement in glucose-dependent insulin secretion. Vildagliptin improves pancreatic beta cell function. By increasing endogenous GLP-1 levels, vildagliptin increases alpha cell sensitivity to glucose, resulting in improved glucose-dependent regulation of glucagon secretion. Reducing the level of excess glucagon during meals causes a decrease in insulin resistance. An increase in the insulin/glucagon ratio against the background of hyperglycemia, caused by an increase in the levels of GLP-1 and GIP, causes a decrease in glucose production by the liver both during the prandial period and after a meal, which leads to a decrease in plasma glucose levels. Vildagliptin is rapidly absorbed when taken orally. After oral administration on an empty stomach, maximum concentration is achieved after 1 hour 45 minutes. Plasma protein binding is low. Most of vildagliptin is excreted by the kidneys (85%) and a small part through the intestines (15%). The half-life is approximately 3 hours.
INDICATIONS FOR USE Diabetes mellitus type 2: 1. As monotherapy in combination with diet therapy and exercise. 2. As part of two-component combination therapy with metformin, sulfonylurea derivatives, thiazolidinedione or insulin in case of ineffectiveness of diet therapy, exercise and monotherapy of these drugs.
CONTRAINDICATIONS Hypersensitivity to vildagliptin and other components of the drug, children under 18 years of age, severe hepatic or liver failure, galactose intolerance, lactase deficiency, glucose-galactose malabsorption, pregnancy, breastfeeding. The drug should not be used in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus or for the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis.
SIDE EFFECTS: Liver dysfunction, including hepatitis, has rarely been reported during treatment with Galvus. In most cases, these disorders and deviations from the norm in liver function indicators resolved independently without complications after discontinuation of drug therapy. Monotherapy with Galvus: From the central nervous system: often dizziness, sometimes headache. From the digestive system: sometimes constipation. From the body as a whole: sometimes peripheral edema. In combination with metformin: From the central and peripheral nervous system: frequent tremor, dizziness, headache. In combination with thiazolidinedione derivatives: From the cardiovascular system: often peripheral edema. From the body as a whole: often - increase in body weight. In combination with insulin: From the central nervous system: often - headache. From the digestive system: frequent nausea, flatulence, gastroesophageal reflux disease. Metabolic and nutritional disorders: often hypoglycemia.
INTERACTIONS The drug has a low potential for drug interactions. No clinically significant interaction of Vildagliptin with drugs most commonly used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (glibenclamide, pioglitazone, metformin) or those with a narrow therapeutic range (amlodipine, digoxin, ramipril, simvastatin, valsartan, warfarin) has been established.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Galvus is taken orally, regardless of food intake. The dosage regimen of the drug is selected individually depending on the effectiveness and tolerability. The recommended dose of the drug when used as monotherapy or as part of two-component combination therapy with metformin, thiazolidinedione or insulin is 50 mg or 100 mg per day. In patients with more severe type 2 diabetes mellitus receiving insulin treatment, Galvus is recommended to be used at a dose of 100 mg per day.
OVERDOSE Symptoms: paresthesia, fever, edema, transistor increase in the concentration of lipase, creatine phosphokinase, alanine aminotransferase, C-reactive protein, myoglobin. All symptoms disappear after stopping the drug. Removal of the drug from the body by dialysis is unlikely, but the main hydrolytic metabolite of vildagliptin (LAY151) can be removed from the body by hemodialysis.
SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS Before treatment, as well as during treatment, it is necessary to determine biochemical indicators of liver function. If jaundice or other signs of liver dysfunction develop while using Galvus, treatment should be discontinued. If dizziness develops during treatment with the drug, you should not drive or operate machinery.
STORAGE CONDITIONS: In a dry place at a temperature not exceeding 30°C.