Fibrosis is a medical term that means scarring, so pulmonary fibrosis is the formation of scarring in the lungs. With fibrosis, the elasticity and extensibility of the lung tissue decreases, and the passage of oxygen and carbon dioxide through the wall of the alveoli (pulmonary vesicles in which the inhaled air comes into contact with the blood) becomes difficult. Fibrosis can be:
- one-sided;
- bilateral;
- focal (a small area of the lung is affected)4
- total (applies to the entire lung).
This is a chronic disease that leads to irreversible processes. It is very difficult to treat; therapy is aimed at alleviating the condition. This pathology is more common among men. Fibrosis is found more often in people over 60 years of age.
What is fibrosis
Fibrosis is the process of proliferation of connective tissue as a result of an inflammatory process. There are two types of fibrosis:
- controlled, when wound healing occurs after tissue damage and tissue growth helps the skin create the necessary supporting framework;
- uncontrolled when bumps and scars form as a result of infection in the wound. The causes of infection can be either a simple scratch or an incision during surgery.
Photos before and after thread lifting. Photo from the website of D.R. Grishkyan. There are contraindications, specialist consultation is required
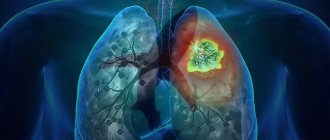
CT diagnostic method for detecting pulmonary fibrosis
Fibrosis is the proliferation of connective tissue with the appearance of scars due to disruption of the healing mechanisms of the wound surface.
When healing does not proceed properly, scarring can occur, causing the organ to fail to function fully.
Accordingly, pulmonary fibrosis is scarring of the lung tissue. The number of cells capable of saturating the blood with oxygen decreases. Consequently, respiratory efficiency decreases - respiratory failure develops, leading to intoxication, first during exercise, as the disease worsens - at rest, and then even during sleep. Scar tissue in the lungs not only has reduced functional properties, but also serves as an excellent environment for the development of associated infections, for example, bacterial (pneumococcal or staphylococcal) pneumonia.
Pulmonary fibrosis is the outcome of tissue inflammation during interstitial (that is, damage to the intercellular connective tissue) lung disease. The reasons for the development of such a disease may include lung injuries, high environmental pollution, smoking, inhalation of drugs, mold, organic, asbestos, quartz and coal dust, infectious, autoimmune, viral diseases and their complications - bronchitis, tuberculosis, pneumonia, COVID- 19 and much more.
Until recently, pneumofibrosis was synonymous with interstitial diseases themselves, but, fortunately, it was found that not all variants of such lung diseases are fibrosing.
The most complex and practically untreatable is primary or idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis - a rapidly progressive fibrosing disease of the lungs, the cause of which is unknown.
Symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis
Pulmonary fibrosis is characterized by symptoms of shortness of breath and dry cough (rarely productive - with sputum) during physical activity, persistent pain in the chest area, fatigue due to difficulty breathing, weight loss without changing the diet. When auscultating the lungs (listening with a phonendoscope), early (in the inhalation phase) inspiratory wheezing is detected, that is, respiratory wheezing, most often localized in the lower posterior zones of the lungs.
Fibrosis can develop in one lung or in two at the same time. Focal and total forms of fibrosis are also possible. In the total form, surgical intervention is often required, since most of the lungs are affected. In the focal form, changes are local in nature.
CT diagnosis of pulmonary fibrosis
The gold standard for diagnosing pulmonary fibrosis is high-resolution computed tomography. CT diagnostics of pulmonary fibrosis allows one to reliably identify the degree of lung damage and determine the localization of scar tissue. This diagnostic method is recognized as one of the most sensitive non-invasive methods for detecting pulmonary fibrosis. Thus, comparative studies conducted already in 1990 showed that pulmonary fibrosis using high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) was detected in 91% of cases and only in 39% using chest radiography.
In the presence of pulmonary fibrosis in a serious stage, a CT scan shows a pattern (a term adopted to denote pathological signs in medicine) of the so-called “honeycomb” lung - this condition is visible on scans as cysts of the same type, located in several rows, containing air, in the affected parts of one or both lungs. In the early stages of pulmonary fibrosis, a similar picture is not observed, so it was necessary to search for signs on CT that would allow identifying the disease at its onset. One of these signs was the presence of a “frosted glass” pattern in the images—foci of slight compaction of the lung tissue. Also, specific signs of fibrosis in a patient can be detected by performing a CT scan of the lungs with functional tests. Thus, one of the signs—subpleural enhancement of the peripheral pulmonary interstitium—was previously considered a sign of the absence of pathology. Such changes are almost impossible to track using other hardware diagnostic methods.
At the moment, the accuracy of CT diagnostic methods is increasing due to the introduction of new research protocols and careful study of the results of numerous studies. In this case, the leading role in the diagnostic process is given to the radiologist, who interprets visible changes as pulmonary fibrosis or its absence. Finding early radiation signs of fibrosing lung disease is key to timely initiation of antifibrotic therapy.
Also, when a diagnosis is made, multislice CT is used to assess the rate of disease progression, identify favorable and unfavorable types of fibrotic changes, the success of treatment and the correct selection of therapeutic drugs.
Formation of fibrosis after threads
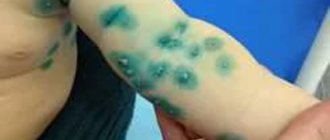
After thread lifting, scar tissue forms in the tissues - this is a normal process, as a result of which collagen is released and a supporting frame is formed. But sometimes, instead of the planned result, collagen can grow around the thread in separate fibers, which leads to solid fibrous cords. This appears at 3-4 weeks. Once they are detected, it is necessary to begin immediate treatment, which will be selected by your doctor.
“Threads promote fibrosis!” Is this so?Clinic of Plastic Surgery Grishkyan David RubenovichJune 4
Pulmonary fibrosis: symptoms, treatment and prevention
Zinovenkova Elena Alekseevna
Head of the Department of Occupational Pathology, General Practitioner (family doctor), General Practitioner, Pulmonologist
Pulmonary fibrosis
is the process of formation of fibrous (scar) tissue in the lungs, which leads to respiratory dysfunction. With fibrosis, the elasticity and extensibility of the lung tissue decreases, and the passage of oxygen and carbon dioxide through the wall of the alveoli (pulmonary vesicles in which the inhaled air comes into contact with the blood) becomes difficult.
Causes of the disease
Lung fibrosis can occur due to the development of inflammation in the alveoli of the interstitial lung tissue. As a result, this causes scarring and further tissue growth.
The main reasons for the formation include: • Hereditary factor - the first and main reason • Smoking • Staying in a polluted area or in an industrial area, hazardous production • Complication of diseases such as diabetes, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis • Complication of lung diseases - such as alveolitis, sarcoidosis, asbestosis, tuberculosis • Prolonged inhalation of particles of organic substances or minerals • Chemical intoxication • Radioactive radiation in the chest area
Types of pulmonary fibrosis
• Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis – when it is impossible to determine the disease that caused it • Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis – when the cause of the disease can be found
Forms
Fibrosis can be unilateral or bilateral, focal (a small area of the lung is affected) and total (spreads to the entire lung).
• fibrosis (pneumofibrosis)
– moderate stringy proliferation of connective tissue, alternating with unchanged lung tissue;
• sclerosis (pneumosclerosis)
– gross replacement of areas of lung tissue with connective tissue with compaction of the lungs;
• cirrhosis of the lungs
– complete replacement of the lung tissue with connective tissue with damage to the bronchi and blood vessels of the lung.
Due to development, they distinguish:
• fibrosis as a consequence of dust-induced lung diseases (silicosis is an occupational lung disease that develops after prolonged inhalation of silicate dust; asbestosis is an occupational lung disease that occurs after prolonged inhalation of asbestos dust); • drug-induced fibrosis (develops against the background of long-term use of drugs for the treatment of arrhythmia, chemotherapy drugs (for the treatment of tumors)); • fibrosis in connective tissue diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus); • fibrosis of an infectious nature (after pneumonia or pulmonary tuberculosis); • idiopathic (primary) fibrosis (occurs for no apparent reason).
Symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis
• The leading symptom is shortness of breath - first during physical activity, and as the disease progresses, at rest. • Cough (dry or with a small amount of sputum). • Paleness, cyanosis (blueness) of the skin. • If the process lasts for a long time – a change in the shape of the fingers (thickening of the fingers, convexity of the nail plate). • With a long course of the process and a large volume of damage, signs of heart failure (the so-called “pulmonary heart”) develop: increased shortness of breath, palpitations, swelling in the legs, swelling and pulsation of the neck veins, chest pain. • Weakness, increased fatigue, inability to perform heavy physical activity.
Treatment of the disease
There is no specific effective treatment for pulmonary fibrosis. Among the main recommendations are the following: • eliminate exposure to damaging factors (occupational hazards); • limited areas of pneumosclerosis that do not manifest themselves clinically do not require therapy; • oxygen therapy (oxygen inhalation using special devices); • surgical treatment: it is possible to remove a functionally defective limited lesion; in the case of total fibrosis (spreading to the entire lung) - a lung transplant.
Today, in the field of medicine, various drugs are being developed that help reduce such scars. Also, some of them, for various types of fibrosis, are able to reduce processes that contribute to tissue scarring. These drugs include corticosteroids, which can suppress the immune system. By suppressing the immune system, lung inflammation and subsequent tissue scarring in the lungs are reduced. In addition, corticosteroids can be taken in combination with anti-inflammatory and other drugs.
Complications and consequences
• Chronic respiratory failure (lack of oxygen to the body). • Pulmonary hypertension. • Chronic cor pulmonale. • Attachment of a secondary infection (with the development of pneumonia).
Prevention of pulmonary fibrosis
• Use of personal protective equipment when working with occupational hazards, compliance with safety regulations. • Timely treatment of inflammatory lung diseases (pneumonia; tuberculosis). • To give up smoking. • When taking drugs that can lead to the development of pulmonary fibrosis (some antiarrhythmic drugs), periodic preventive monitoring of the condition of the lungs.
General practitioner (family doctor), therapist Zinovenkova Elena Alekseevna
Reasons for the formation of uncontrolled fibrosis:
1. Medical error or poor quality material. This consequence can be eliminated by removing the thread.
2. Wound infection during the rehabilitation period. In this case, antibacterial drugs prescribed by the doctor will help.
3. Formation of hematomas. In this case, the doctor pumps out excess accumulated fluid with a syringe.
Photos before and after thread lifting. Photo from the website of D.R. Grishkyan. There are contraindications, specialist consultation is required
Causes
Pulmonary fibrosis can be caused by various reasons, including:
- chronic inflammatory processes in the lungs (for example, sarcoidosis or Wegener's granulomatosis);
- infections, the influence of environmental factors (asbestos, silicon, exposure to certain gases);
- exposure to ionizing gases (for example, radiation therapy used to treat breast tumors);
- chronic autoimmune diseases (lupus, rheumatoid arthritis);
- taking certain medications.
In allergic pneumonia, pulmonary fibrosis can develop as a consequence of an increased immune response to organic dust or chemicals that enter the lungs during inhalation. Some people may develop fibrosis without any specific cause. In this case, as a rule, they talk about idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, which is not amenable to therapeutic treatment, while with other types of fibrosis (for example, interstitial pneumonia), the patient’s condition improves with properly selected treatment.
Why does fibrosis form after fillers?
After injections, compactions are observed in the first days. This is because the drug has not yet been distributed. But, if the lump appears in the form of a lump and lasts for more than a week, then you need to contact your surgeon.
Causes of fibrosis:
- rejection of a foreign substance.
- vascular damage;
- incorrect technique for administering the drug;
- violation of sanitary standards, etc.
Photos before and after thread lifting.
Photo from the website of D.R. Grishkyan. There are contraindications, specialist consultation is required. You can see more before and after photos in the photo gallery
Fibrosis after fillers: what is the danger? David Rubenovich Grishkyan Plastic Surgery Clinic May 8
Diagnosis and treatment
To diagnose pulmonary fibrosis, a pulmonologist performs the following tests and studies: general blood test; chest x-ray; computed tomography of the lungs, magnetic resonance imaging of the lungs; lung biopsy; breath tests. Treatment of pulmonary fibrosis is determined by a qualified specialist depending on the characteristics of the disease in a particular person. Glucocorticoids, cytostatics and immunosuppressants are used for severe forms of fibrosis. Lungs affected by fibrosis often become a favorable environment for the attachment of pathogenic microflora and the development of inflammation. To prevent this, antibacterial drugs are prescribed; oxygen inhalation and cardiac glycosides will be useful. For debilitating cough and shortness of breath, bronchodilators are prescribed. Drug treatment of pulmonary fibrosis should be supported by therapeutic breathing exercises, while large physical activities are contraindicated for the patient. It is also necessary to exclude exposure to fibrosis-provoking factors on the body.