1.General information
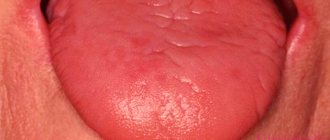
The apt, albeit somewhat frivolous name “geographic tongue” refers to the inflammatory-dystrophic process in the mucous membrane of the tongue, also known as “wandering glossitis”, “migratory oral erythema”, “exfoliative glossitis” (formulation in ICD-10), “desquamative glossitis”, etc. Exfoliative in translation means “flaky”, desquamative means “deprived of scales”, glossitis is inflammation of the tongue. Peeling of the epithelium in combination with inflammation and dystrophic changes together form red and white patterns on the tongue, which in many cases really resemble a fragment of a geographical map.
In different historical periods in medicine, there were different views on the essence and pathogenesis of desquamative glossitis (the term and concept were introduced into the medical paradigm in 1831), and the discussion continues to this day. Thus, some authors consider this process to be neurodegenerative, others to be purely inflammatory, and others generally consider it as a non-pathological variant of the norm.
The prevalence of “geographic language” varies significantly depending on the age, gender, and clinical composition of the studied samples; in terms of the general population, it is estimated at 2-5% of the population. There is a slight predominance of women, children and adolescents.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Classification of glossitis and their characteristics
Based on external manifestations, there are 3 groups:
- Catarrhal
The inflammatory process affects only the superficial layers of the tongue. Characterized by redness, swelling and plaque formation. The main reason is a fungal disease of the oral cavity (candidiasis) or a burn of a muscle organ. In rare cases, catarrhal glossitis is a consequence of advanced stomatitis or vitamin deficiency.
- Purulent
The most severe form. The pathological process spreads deeper, causing pain and severe swelling. Sores with purulent contents form on the surface of the tongue. The disease is accompanied by high fever and intoxication. Treatment by a specialist is required.
- Ulcerative
With this type, multiple ulcers form on the surface of the tongue, which can bleed. The person experiences severe pain, which leads to a decrease in appetite. Speech disturbances are possible due to swelling and hypertrophy. Provoking factors are inflammatory diseases of the gums and oral cavity.
There is also a form of glossitis called folded. This is a congenital disease, the clinical manifestations of which are folds on the surface of the tongue. Treatment is not required, as this form does not cause pain or discomfort. In some cases, aesthetic correction is possible.
As a secondary disease, glossitis can be a sign of various diseases of the internal organs. In this regard, the following forms are distinguished:
- Desquamative or “geographic tongue” - the external surface of the tongue with this form is similar to a geographical map, that is, lines, grooves, and bright red spots are observed. It occurs in pregnant women due to changes in hormonal levels, as well as in people suffering from chronic gastrointestinal pathologies. A desquamated tongue is often a symptom of parasitic diseases or liver dysfunction.
- Villous - the main symptom is the proliferation of filiform papillae on the surface of the muscular organ. Subsequently, they become like villi. This form occurs with candidiasis or frequent injuries to the tongue. Taking certain medications and smoking can also cause villous glossitis.
- Gunterovskaya is a sign of B12 deficiency and folate deficiency anemia. The surface of the tongue is smoothed and appears shiny. The color is bright red, the papillae atrophy.
- Rhomboid (median) - characterized by thickening of the epithelium with the formation of diamond-shaped pathological areas. Has a chronic course. People with gastritis or low acidity in the stomach suffer from this form. There are flat, tubercular and warty glossitis.
The most dangerous form is considered interstitial, as it acts as a precancerous condition. Without treatment, the cells of the tongue affected by glossitis become malignant, which leads to cancer formation. Also, such glossitis is a characteristic sign of syphilis.
2. Reasons
There is no single point of view regarding the etiopathogenesis of inflammatory desquamation of the tongue; the issue continues to be studied and discussed. According to the most reasoned hypotheses, the cause may be infections (both bacterial and viral), hereditary predisposition, diseases of the liver, pancreas, gastrointestinal tract (primarily gastritis, gastroduodenitis, peptic ulcer and intestinal malabsorption syndrome), endocrine and metabolic disorders, exudative diathesis in children, autoimmune diseases, helminthiasis.
Visit our Gastroenterology page
Prevention
To prevent the development of such a disease, you need to follow some simple preventive rules:
- Promptly treat all diseases that provoke the development of pathology.
- Do not abuse alcoholic beverages, tobacco products, sweet foods and sugar, and strong coffee.
- Take enough vitamins to avoid vitamin deficiency.
- Perform hygiene .
- Treat caries in a timely manner.
There are separate preventive measures for children:
Caring for baby teeth – timely treatment and removal of baby teeth. If a child complains of dry mouth, rinse with herbs such as sage, St. John's wort or chamomile.
Brushing your teeth should be done only with toothpastes, since the powders contain mint oil and menthol, which are bad for the oral mucosa in children.
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
The first manifestations are usually small, up to several millimeters, light gray lesions. Then such an area from the center turns red and swells somewhat, beginning to protrude above the surface and become covered with red papillary dots. The shape of desquamation foci can be very different, from round to arched. The alternation of inflamed, exfoliated and keratinized areas (usually they are multiple) forms a bizarre picture that can change quite quickly. The process is usually localized on the upper and lateral surfaces of the tongue, sometimes spreading to the lower areas.
In rare cases, desquamative glossitis causes subjective discomfort at the level of sensations - usually a burning or tingling sensation, less often pain when eating. In most cases, the disease is asymptomatic, for years or even decades; A recurrent (recurrent) type of course with long-term remissions is often noted.
To establish a diagnosis, an examination, collection of complaints (if any) and anamnesis are usually sufficient. However, given the importance of desquamative glossitis as a possible indicator of serious diseases, a multifaceted laboratory study is indicated (they begin with the appointment of general clinical and biochemical tests).
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Why does the disease occur?
The culprits of inflammation on the mucous membrane of the tongue are pathogenic microorganisms (viruses, bacteria) that the local immune system cannot cope with. Most often, glossitis is caused by the herpes virus. It can remain in a latent (sleeping) state for many years after infection and not bother a person in any way. But when immunity decreases, it becomes more active and begins to multiply.
Other possible reasons:
- thermal or chemical burns;
- allergic reaction to toothpaste,
- drinking tongue-burning drinks;
- frequent mechanical injuries from the edges of decayed teeth or sharp edges of fillings, biting the tongue;
- abuse of spicy foods;
- excessive passion for mouth fresheners, rinses with aggressive composition.
People over 50 years of age, smokers, and lovers of caramel and lollipops are at risk. The oral cavity is an ideal place for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, therefore, ignoring hygiene and chronic dental pathologies also cause inflammatory processes in the tongue area.
In most cases, glossitis acts as a symptom of disorders of the digestive system, dysbacteriosis and autoimmune diseases.
4.Treatment
In cases of asymptomatic disease, if there are no signs of underlying somatic diseases, therapy is not required and is not prescribed. The exception is the mandatory sanitation of problematic teeth and oral cavity, as well as normalization of the diet - which, however, is indicated for absolutely all people.
If there are symptoms of a particular disease that may be the cause or basis for the development of desquamative glossitis, the patient is referred to a specialist of the appropriate profile, where he receives etiopathogenetic treatment.
Geographic language
HomeAbout Dentco Medical Center and DentistryPublicationsArticles on DentistryGeographical language
Geographical language, it’s hard to imagine in your head what it might look like. But people who are faced with such a problem are not laughing at all.
Desquamative glossitis is a tongue disease in which the tongue changes color in areas, forming spots.
The spots can be of different sizes and may change their position throughout the course of the disease. The language becomes like a map hence the “nickname” of the disease is geographic language.
Desquamation is essentially the peeling or peeling of the epithelium. The patient does not experience discomfort with this illness.
It can last from several days to several months. In some cases, a person may experience a burning sensation when eating food.
This type of glossitis is not considered a disease, but can be a harbinger of serious diseases and negative processes in the body. Although its phenomenon has not been fully studied.
Geographic tongue can occur with the following diseases:
- Avitaminosis
- Gastrointestinal diseases
- Dysfunction of the oral mucosa
- Puberty (in children)
- Skin disease
- Hereditary predisposition
Glossitis can also occur in women during pregnancy or menopause, in children under three years of age during teething, and in the rest of the age group of children with helminthic infestation.
In rare cases, a person may discover glossitis, most likely this will happen during a dental examination. In extreme cases, the patient may complain of tingling and numbness of the tongue. As mentioned above, desquamative glossitis is not a disease and, accordingly, it cannot be treated.
If you suddenly find such a nuisance, you should take some measures:
- To begin with, exclude foods of high and low temperatures, spicy and salty foods from your diet. Adults should give up alcohol and cigarettes.
- Since glossitis is an inflammatory disease, it is not a bad idea to rinse your mouth with decoctions of chamomile, St. John's wort or sage.
- If unpleasant sensations do not allow you to live in peace, apply vitamin A (in the form of oil) or rosehip oil to the oral mucosa.
- Oral hygiene during the period of geographic tongue must be observed impeccably. If your tongue has deep grooves, brush it gently, otherwise bacteria may grow, causing further inflammation.
The appearance of glossitis is a sign that you need to be examined. Visit a gastroenterologist, dentist and endocrinologist. Perhaps this is a consequence of a deeper problem.
Be healthy!
What is glossitis?
Glossitis (from the Greek glossa (tongue) + suffix –itis) is an inflammation of the tongue. The reasons for its occurrence are different. Glossitis can develop as a result of a viral or bacterial infection, or as a result of another disease in the body. In addition, there are some other factors that provoke the development of the disease. These include mechanical, chemical and thermal damage to the oral cavity; nicotine; food that is too spicy or too hot; alcohol; caramel; some components present in toothpastes.
Glossitis has the following forms:
- folded
- diamond-shaped median
- desquamative
- hairy black
- Gunter's
- interstitial
According to the duration of the inflammatory process, acute and chronic glossitis are distinguished. The acute form of glossitis manifests itself as inflammation of the tongue, a change in its structure or color. Symptoms of the chronic form are more varied, but in most cases the disease is diagnosed by the presence or absence of papillomas - fungal growths on the tissues of the tongue. There are cases when the cause of the disease can be identified only after comprehensive medical research. True, this happens quite rarely and, as a rule, is associated with the presence of congenital, hereditary diseases.
Manifestations of tongue glossitis in children
In children, glossitis usually occurs at an early age - from 1 to 5 years. The causes of this pathological process have not yet been fully studied and can be very diverse: from infection to poor heredity. Externally, glossitis in children is manifested by the appearance of spots on the tongue, which slightly swells and itches. Itching and a burning sensation are the most unpleasant signs of glossitis, since a small child begins to scratch the tongue, thereby contributing to the appearance of microcracks with their subsequent infection. However, the disease does not pose a threat to the child’s life. The famous pediatrician Komarovsky does not recommend panicking about this and self-medicating by giving the baby serious medications. As a rule, multivitamins and a gentle regimen will have a positive effect within a week.
Features of glossitis during pregnancy
The causes of glossitis of the tongue in pregnant women are due to the fact that the immune defense weakens to allow the fetus to develop, which means that the body during this period becomes practically defenseless in the face of various bacteria and viruses. The second risk factor is a lack of vitamins and minerals obtained from food.
According to statistics, most often pregnant women experience a picture of desquamative and Gunter's glossitis. Symptoms that should alert you during pregnancy include:
- Profuse drooling. During the period of bearing a child, a woman already secretes a larger amount of saliva than usual, but a sharp increase may indicate the onset of glossitis.
- "Lacquered Tongue" A specific symptom that indicates the development of B12 deficiency anemia.
- Color change. White spots on the surface of the tongue alternate with spots of rich red color.
- Refusal of food. Acute glossitis in pregnant women is characterized by severe pain in the tongue during chewing and speaking, which, among other things, affects appetite.
As for the treatment of glossitis in pregnant women, the safety of the fetus comes first. Therefore, all therapy is exclusively local in nature (sprays, rinses), eliminating the penetration of the drug through the placenta. It is recommended to adjust your diet in such a way as to remove any foods that irritate your tongue.
Attention!
In order to avoid complications that can negatively affect the health of the fetus, treatment of glossitis during pregnancy must be carried out under the supervision of an obstetrician-gynecologist monitoring the woman.
Our team of doctors
Maxillofacial surgeon, Implantologist
Bocharov Maxim Viktorovich
Experience: 11 years
Dental surgeon, Implantologist
Chernov Dmitry Anatolievich
Experience: 29 years
Orthopedist, Neuromuscular dentist
Stepanov Andrey Vasilievich
Experience: 22 years
Endodontist, Therapist
Skalet Yana Alexandrovna
Experience: 22 years
Orthopedic dentist
Tsoi Sergey Konstantinovich
Experience: 19 years
Endodontist, Therapist
Akhmeeva Elena Petrovna
Experience: 22 years
Dentist-orthodontist
Enikeeva Anna Stanislavovna
Experience: 3 years