Causes of pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is caused by a bacterial infection. Inflammation is often caused by the simultaneous activity of microorganisms of various types, activated against the background of predisposing factors.
The infection can enter the kidney in an ascending way - through the ureter, for example, from the bladder (in this case, pyelonephritis is a complication of cystitis) or from the genitals, which is especially typical for women: a woman’s urethra (urethra) is short, which facilitates the entry of infection. That is why pyelonephritis at the age of 18-30 years occurs in women more often than in men.
Another route of penetration is through the flow of lymph or blood. The infection can be transferred with blood even from distant foci of inflammation (for example, with tonsillitis, furunculosis, wound suppuration).
Factors contributing to the development of pyelonephritis
In most cases, the development of pyelonephritis requires the influence of local predisposing factors, including:
- violation of the outflow of urine from the kidney;
- impaired blood flow in the kidney;
- diseases of nearby organs (primarily the intestines);
- systemic diseases (diabetes mellitus, etc.).
Among these factors, the most significant is the disruption of urine outflow. Stagnation of urine creates an environment favorable for the growth of bacteria, therefore, if the outflow of urine from the kidney is impaired, pyelonephritis is an expected disease.
Impaired urine flow may result from:
- prostatitis or prostatic hyperplasia (prostate adenoma). Similar diseases are observed in many men over the age of 30, and the higher the age, the more likely the disease;
- urolithiasis;
- pregnancy (the growth of the uterus leads to compression of the ureter. Hormonal changes also affect).
What are risk factors?
There are a number of extrasexual factors that increase the risk of developing acute pyelonephritis:
- Congenital or acquired anomaly, pathology of the structure of the kidneys and other organs of the urinary system.
- AIDS virus.
- Urolithiasis disease.
- Diabetes. With increased sugar content in the urine, pathogenic microorganisms will multiply.
- Age.
- The spinal cord and peritoneal organs are injured.
- Surgery or other medical intervention on the urinary system.
- Bacterial chronic disease, the presence of an infectious focus in the body.
The occurrence of acute pyelonephritis in a man may be associated with prostate disease and an increase in its size.
Symptoms of pyelonephritis
There are acute and chronic pyelonephritis.
Symptoms of acute pyelonephritis
Acute pyelonephritis begins suddenly. The main symptoms are as follows:
- high temperature (39-40° C);
- profuse sweat;
- chills;
- general weakness;
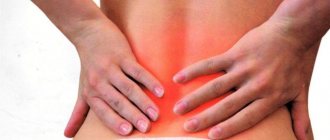
- pain concentrated in the lumbar region (with unilateral pyelonephritis - on one side). The pain is dull in nature, but can be very severe.
Pyelonephritis often occurs against the background of obstructed urine outflow, but problems with urination are not a symptom of this disease.
Symptoms of chronic pyelonephritis
If during treatment the severity of the symptoms was relieved, but the inflammation did not completely stop, pyelonephritis becomes chronic. Often chronic pyelonephritis develops without a preceding acute process.
Chronic pyelonephritis manifests itself as a dull aching pain in the lumbar region, especially in cold and damp weather. There may be periods of exacerbation during which the severity of symptoms returns again.
Often chronic pyelonephritis occurs secretly. A moderately elevated body temperature (37-37.5° C) may persist, the cause of which remains unknown for a long time. Often, chronic pyelonephritis is accidentally discovered during a medical examination, caused by completely different patient complaints.
If chronic pyelonephritis is not detected in time and left untreated, it leads to the development of chronic renal failure, which in the early stages manifests itself as an increased number of nighttime urinations (two or more per night).
Signs of the disease in women
Women are most susceptible to developing pyelonephritis. Symptoms of the disease may vary depending on its form. As a rule, signs of acute pyelonephritis in a woman are:
- Change in the color and odor of urine. The fluid may become cloudy and contain bloody or purulent inclusions.
- Increased body temperature above 38 degrees. In some cases, there is a sharp change in indicators.
- Burning sensation when urinating, frequent visits to the toilet.
- Nausea, accompanied by vomiting, chills.
- Having a headache.
- Painful sensations when tapping with the edge of the palm in the kidney area.
Methods for diagnosing pyelonephritis
The implicit nature of chronic pyelonephritis contributes to its prevalence (in the chronic form, pyelonephritis is much more common than in the acute form).
Meanwhile, pyelonephritis, including chronic one, is a serious disease that cannot be left without treatment. Each exacerbation of pyelonephritis involves more and more new areas of kidney tissue in inflammation. As a result of inflammation, the tissue dies and a scar appears in this place. The more such scars, the less normally functioning tissue remains. The kidney shrinks and stops working.
Diagnosis of pyelonephritis is carried out using laboratory and instrumental methods.
General urine analysis
A general urine test will reveal the presence of an inflammatory process. Pyelonephritis is characterized by an increase in the number of leukocytes, as well as the presence of bacteria (normally, bacteria should not be detected in the urine). The presence of protein and glucose is also likely. However, a general urine test cannot confirm the diagnosis of pyelonephritis, as similar results can be obtained for other diseases.
More information about the diagnostic method
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko
If pyelonephritis is suspected, a urine test according to Nechiporenko is performed. With pyelonephritis, one should expect an increased number of leukocytes and erythrocytes, as well as the presence of casts (normally they are absent).
More information about the diagnostic method
Ultrasound of the kidneys and adrenal glands
Kidney ultrasound can diagnose pyelonephritis. Using ultrasound, the size of the kidney can be determined (the affected kidney decreases in size), deformations of the collecting system and kidney stones can be detected.
More information about the diagnostic method
Excretory urography
Urography can also be used to diagnose pyelonephritis. Compared to kidney ultrasound, it has a number of advantages, in particular, it will show the condition of not only the kidneys but also the urinary tract. If a tumor and stone are present, urography will make it possible to assess how they affect the outflow of urine.
More information about the diagnostic method
Computed tomography (CT)
Computed tomography of the kidneys is used when data from other studies already performed is insufficient. In particular, it is used for differential diagnosis - if necessary, to distinguish one disease from another.
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
What are the stages of the disease?
The clinical course of acute pyelonephritis has several stages. Each of them develops in accordance with the pathomorphological changes occurring in the kidneys.
At the initial stage of pathological development, serous inflammation occurs. This stage is characterized by a slight increase in kidney tension and perivascular infiltration. If a specialist is contacted in a timely manner, the patient is prescribed conservative therapy, with the help of which the inflammatory process is replicated. The patient makes a full recovery. If there is no treatment at the initial stage, the disease will progress, and purulent-destructive kidney damage will subsequently occur.
The next stage is called apostematous pyelonephritis. This is an inflammatory disease when pustular formations are formed, localized in the renal cortex. If there is no adequate therapy, such pustules will merge and form a large purulent focus. It is called a kidney carbuncle. When this condition develops, the risk of kidney abscess formation increases. Purulent contents can spill into the perinephric tissue. If treatment is started in a timely manner, the infiltration lesion heals, scars are formed, which consist of connective tissues.
Treatment methods for pyelonephritis
Treatment of pyelonephritis should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor, who will establish this diagnosis through research, prescribe a course of treatment, and monitor the progress of recovery. It is very important not only to treat pyelonephritis itself, but also to eliminate the causes that led to the development of the disease.
For treatment of pyelonephritis in Moscow, you can contact Family Doctor JSC. Treatment of the disease is carried out by urologists.
Doctors at Family Doctor are highly qualified and have extensive experience in treating pyelonephritis in children and adults, which allows them to implement an individual approach that takes into account the characteristics of each specific case of the disease.
Drug treatment
Treatment of pyelonephritis is carried out using antibacterial therapy and anti-inflammatory drugs. To strengthen the immune system, immunomodulators and multivitamins are used. For chronic pyelonephritis, diuretics and drugs that improve renal blood flow are also prescribed.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Use of Fitolysin® paste in complex therapy of urinary tract infections
For cystitis, urethritis, exacerbation of chronic pyelonephritis, treatment should be comprehensive. Together with the antibiotic, Fitolysin® paste can be prescribed to prepare an oral suspension (hereinafter referred to as Fitolysin®), which, according to the instructions, is used for the complex treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urinary system.6
The drug has a natural composition, which includes a condensed extract of a mixture of plant raw materials (9 components), 4 essential oils and auxiliary components6.
Fitolysin® paste is intended for the preparation of an oral suspension. In this form, the active components are better absorbed into the blood and delivered directly to the site of inflammation.2,6 The convenient release form significantly simplifies the dosage and use of the drug.
The herbal preparation has antispasmodic, diuretic, and anti-inflammatory effects. According to the instructions, Fitolysin® paste should be taken 3-4 times a day, dissolving 1 teaspoon of the composition in half a glass of sweet warm water. The course of treatment lasts from 2 weeks to 1.5 months (can be extended if necessary).6
What complications can there be?
With improper treatment or its absence, complications may develop. The pathology is especially dangerous for pregnant women and people with diabetes. The pathology is amenable to therapeutic treatment. Untimely or incorrect treatment contributes to the development of complications, in some cases leading to the death of the patient.
One of the complications of the disease is sepsis. If left untreated, pathogenic bacteria multiply rapidly. Once the limit is reached, microorganisms enter the bloodstream. Thus, the infection spreads throughout the body. The complication in some cases ends in the death of the patient.
In addition to sepsis, other complications may develop, such as kidney abscess, emphysematous pyelonephritis, kidney carbuncle, etc.