March 22, 2011
The active ingredient in all alcoholic drinks is ethyl alcohol. You can use it as you wish, but you should not drink it.
The active ingredient in all alcoholic drinks is ethyl alcohol. Aka ethanol, aka C2H5OH. All the troubles of alcohol abusers are associated with it. However, it would be completely wrong to call ethanol evil - it is a sought-after and necessary substance, although not related to food products
. There are many ways to use it for its intended purpose, although ingesting it is not one of them. So how to use ethanol correctly?
Antiseptic
Medicine actively uses a variety of poisons in its arsenal. Ethanol – including. After all, bacteria die perfectly in ethyl alcohol. Therefore, before taking blood for analysis, the skin at the site of the future puncture is wiped with a cotton swab soaked in alcohol. Bacteria on the skin die, the alcohol evaporates - and here it is, a sterile finger or elbow is ready for blood collection. Alcohol is still sometimes used by surgeons on their hands before surgery, especially in the field. This means
that every time you order a cocktail, you are getting something that acts as a mixture of creosote and carbolic acid.
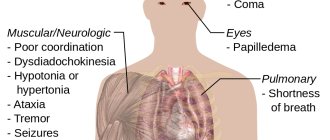
Symptoms of ethanol poisoning
Classification of alcohol effects:
- Effect of weak alcohol: smell of ethanol, mild behavioral disturbances with impaired functional and reaction levels, or slight impairment of coordination.
- Moderate effects of alcohol: ethanol odor, mild behavioral disturbances with impaired functional and reaction levels, or moderate problems with coordination.
- Significant influence of alcohol: significant behavioral disturbances with impaired function and level of reaction, significant difficulties with coordination and reduced ability to cooperate.
- Strong effects of alcohol: very low functional and reactionary levels, severe coordination problems and lack of ability to cooperate.
When should you drink?
There is one case when you need to drink ethanol for medical reasons. If a person drinks methyl alcohol, it is exposed to two enzymes in the body - alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase. As a result, poisonous formaldehyde and formic acid are formed, which kill people. In this case, ethanol is the only antidote. It binds to these enzymes better than methyl alcohol, and methyl alcohol leaves the body without causing much harm to it. In the face of poisoning, the negative effects of ethanol are less dangerous than the almost guaranteed death from methyl alcohol. This means
that ethyl alcohol acts as an emergency rescue remedy, and not as a habitually consumed product.
Consequences of drinking medical alcohol
Drinking medicinal 95% alcohol, like any other alcoholic drink, if abused, can lead to poisoning of the body, so you need to know moderation in everything. If you use it constantly, it is fraught with addiction and alcohol dependence.
When the body is intoxicated with a medical alcohol substance, there are general symptoms characteristic of poisoning with any alcohol. If poisoning occurs, the following happens:
- convulsions that are present with severe alcohol poisoning;
- dehydration of the body, since this substance, dissolving in the body’s water balance, absorbs the water resource into itself;
- vomiting and nausea, as the body fights intoxication and tries to remove toxins on its own;
- confused consciousness, partial memory loss, because alcohol deals the first blow to the blood vessels, their large accumulation in the brain gives such a reaction;
- loss of strength, apathy, fever.
Addiction and dependence on the use of medical alcohol occurs in the same way as with the use of any other alcoholic beverages, if you overdo it, so it is better to use it according to its name, only for medical purposes in accordance with the antiseptic effect.
Things to remember
So, ethanol is a very necessary and useful substance for humanity.
Cars can drive on it, it helps doctors and chemists make our lives better and safer. Just don't drink it. Tags:
- Alcohol
4 comments • To leave a comment you must be an authorized user
- MADic I support ZNo4kу! It’s sad that this is exactly how the majority thinks... It’s sad that a person who doesn’t drink is out of the ordinary... It’s sad that people can’t imagine a party or holiday without alcohol... And even more people are killed by stupid people who shout: “expensive alcohol is not harmful!” or “barely harmful!” Who issued a diploma to these PSEUDO doctors who claim that small amounts are not harmful!? Alcohol is one thing, no matter how cheap or expensive! All from the same barrel and containing ethanol. I advise everyone to watch “Zhdanov V.G. Alcohol, tobacco, drugs." It would take me five fingers to count my non-drinking acquaintances, but I think these people are worthy of respect. And a person who drinks is unhappy, poor, has no will and freedom. PS doctors are not delusional, alcohol is harmful!
- ZNo4ka Comments from the outside look like teenagers in the toilet are measuring their dicks, sorry. Everyone realized that you are smart. As accustomed as we are to looking at the surface, people look at the root of “drinking is BAD.” The man wanted to convey this to you, and not to cause rapid brain movement and convulsive recall of chemistry lessons. And as for wine, it costs more than 10 euros... Well, damn it. Even if the whiskey costs a million, it won’t make alcohol water. Drinking is bad for you, friends. Let's live healthy.
- sgapich I’ll add one more case of medical use of ethyl alcohol. In case of pulmonary edema, the victim is given 10-15 minutes to breathe in ethyl alcohol vapor.
- DragonCat Solid seliger in the comments... Yes, a strange site.
 However, the articles also smack of it. Apparently, this is still a site for children of “young 20-year-old Russia”, which has nothing in common with my Motherland, Russia.
However, the articles also smack of it. Apparently, this is still a site for children of “young 20-year-old Russia”, which has nothing in common with my Motherland, Russia.
Clinical classification of alcohol withdrawal
Depending on the degree of intoxication, the patient’s condition is characterized by corresponding symptoms.
1. Mild degree of poisoning - anxiety, restlessness, depression, insomnia .
2. Moderate degree of poisoning - manifests itself after 24-36 hours. More pronounced psychological symptoms and increased adrenergic activity: tremor, sweating, headache, nausea, mild tachycardia, hyperventilation, systolic hypertension.
3. Severe - significant anxiety, incoming hallucinations or illusions. Severe autonomic hyperactivity with tremor, nausea and vomiting. The general condition is clearly weakened.
4. Complex condition - delirium tremens or somatic complications, such as generalized convulsions , hyperthermia or severe tachycardia and hypertension.
Only 5% of alcohol withdrawal patients progress to delirium tremens. The boundaries between the phases are smooth and begin to appear gradually.
Secondary psychiatric conditions: Suicidal ideation or substance abuse are also more common among alcoholics than the rest of the population.
Properties
Rubbing alcohol is a liquid:
- volatile (evaporates well);
- transparent:
- having no color;
- having a specific smell and “sharp” taste;
- with a lower density than water;
- with weak acidic properties - like acids, the compound can interact with alkali metals, as well as aluminum, magnesium and their hydrides (substances that contain hydrogen).
The compound dissolves well many organic compounds, as well as some inorganic salt complexes. There is so-called absolute ethanol with a concentration of 100%. In medicine, a rectified product is used, the concentration of which is 95.57% (labels are marked “96%).
An important property for pharmacological use is the ability to be diluted with water in different quantities and ratios. Thanks to this, medical alcohol of the required concentration is obtained, which allows it to be used both internally (as part of alcohol tinctures) and externally. When mixing, an interesting effect is observed - a smaller volume of liquid is formed. The “loss” is about 3%. This is considered an indication of pure substance. Another characteristic phenomenon is spontaneous slight heating during the mixing process.
The substance is classified as a fire hazard because it is highly flammable. Therefore, it and the liquids in which it is included should be used with precautions. At 400 degrees Celsius, spontaneous combustion occurs. You should also remember that a mixture of alcohol vapor and air is explosive.
Scope of application
Medical alcohol has found its greatest use as an antiseptic. It has long been known that many drugs contain harmful substances and poisons that are neutralized under the influence of ethanol. To prevent infection, in hospitals the blood collection site is treated with alcohol, which evaporates after a short time, leaving a completely sterile area of skin. It is also widely used in pharmaceuticals, where it serves as the basis for the preparation of various medicinal tinctures. Can be used in other medical areas.
As a result, food and medical alcohol, despite similar manufacturing technology (and in some cases the same raw materials), have different degrees of purification and different areas of application.
There is a huge variety of alcohols used both in everyday life and in production. Most of them are dangerous to life and health. The most common ones taken as alcohol include ethanol, methanol and various medicinal alcohol solutions.
Synthetic route of production
Currently, the production of alcohol by fermentation of natural food raw materials is gradually beginning to fade into the background. Some ethyl alcohol is already produced through synthetic hydration of ethylene or hydrolysis of plant materials. After receiving the substance, it is analyzed and purified. Next, part of the alcohol is used for medical purposes, the other part is sent for the production of alcoholic beverages. The remaining, most “dirty” part of the alcohol belongs to the “technical” classification and is used for industrial needs.
Content:
- Total information
- Methods of obtaining
- Properties
- Application in medicine
- Negative influence
Since medical alcohol began to be used in medicine, a new era has begun. It is used as a component of medications for oral administration, as well as an antiseptic and aseptic agent. Modern analogues of this substance have been invented, but it continues to remain indispensable.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Effects of ethanol:
· Provides delay of impulse conduction in the central nervous system.
· Arterial hypotension.
· Hypoglycemia due to inhibited gluconeogenesis.
· Increased diuresis.
In most healthy people, ethanol is eliminated from the blood at a rate of about 0.15-0.20 ppm per hour, while in alcoholics this figure is much lower.
Predisposing factors:
· Poor nutritional status.
· Young age.
· Gender. Women have a lower volume of distribution and lower first pass metabolism because they have less alcohol dehydrogenase.
· Poisoning with a mixture of substances. The risk of serious poisoning, in particular respiratory depression, is significantly increased by concomitant medications.
Ethyl or methyl?
- Ethanol (ethyl) is used in various sectors of life. It is found in most alcoholic beverages and is the safest for consumption. Often needed in medicine as a disinfectant. It is sold in pharmacies only by prescription. It is often used for preparing tinctures and even in soap making.
- Methanol (methyl) is a poison for humans, it affects the liver, kidneys, lungs and eyes in an accelerated manner, and depression of the nervous system occurs instantly. However, it can also be consumed in small doses, but you cannot buy it in pharmacies. It is used for production purposes only. It CANNOT be used!
In order to distinguish these alcohols from each other, the following experiments are carried out. Cut a slice of potato and place it in a glass of liquid for a couple of hours. The color of potatoes in ethanol does not change, but upon contact with methanol the potatoes turn pink.
For a faster test, use a hot copper wire dipped in an alcohol composition. Ethanol will not emit a strong, unpleasant odor, unlike methanol. Or, they set fire to cotton wool soaked in alcohol. Ethyl alcohol burns with a green flame, methyl alcohol has a blue flame.
Such precautions can save lives, because the maximum permissible dosages of these alcohols differ greatly due to the toxicity of methanol.
Signs of intoxication
Ethyl alcohol poisoning is also not uncommon - this can be stated with complete confidence. How many people died from drinking this chemical liquid - only God knows. Drinking ethyl concentrate without moderation is tantamount to suicide. The lethal dose is different for each person, so there is no clearly limited framework for how much to drink.
Some people can consume 100 grams, others can handle half a liter. This statement is especially true for alcoholics of the second stage, in whom the degree of tolerance to alcohol, during the formation of the disease, has developed into a stable form.
Therefore, such concepts as percentage content, lethal dose or how much to drink so as not to die - for these people these formulations are considered vague.
Below are the symptoms when ethyl alcohol poisoning is pronounced. Intoxication occurs:
- excessive sweating, increased sweating;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- dilated pupils;
- redness of skin texture.
Other symptoms: slurred speech, decreased attention, inability to stand on your own. All these signs indicate that there is an excessive amount of ethanol in the human body.
The ethyl content is exceeded, which can lead to death. First aid is as follows: call an ambulance and protect the patient from alcohol, do not let him drink any more alcohol.
You can try to wash out his stomach, give him medications (activated carbon), and take him to fresh air.
Subsequent forecast
- The lethal dose is difficult to determine due to large individual differences, but most sources indicate around 5 g/kg.
- Chronic alcoholics usually tolerate greater increases in alcohol levels before poisoning occurs. However, patients with decreased general condition, liver function, and cardiomyopathy tolerate less ethanol.
- Death can occur at concentrations in the range of 3-7 g/kg.
The influence of alcohol is a contributing factor in a large number of accidents. For example, in the United States, ethanol is responsible for 3% of all deaths. The cost of alcohol consumption and drug addiction in 1983 was estimated at $117 billion. About 61% of the costs were related to lost earnings, and 13% went to medical care.
Complications
The influence of alcohol increases the risk of an accident and is a key element for injury. Against the background of an ethanol overdose, the following consequences and complications can be observed:
· Trauma in general and damage to the central nervous system.
· Half of suicides and suicide attempts.
· Milder withdrawal symptoms (most often, treatment is rarely required).
· Delirium tremens (withdrawal syndrome).
· Hypothermia. Ethanol dulls sensations and a person may not feel the cold. Ethanol also inhibits central thermoregulation and can itself lead to cooling, for example, through peripheral vasodilation.
· Liver damage (acute toxic hepatitis).
· Acute pancreatitis.
· Fatal poisoning due to interaction with other drugs.