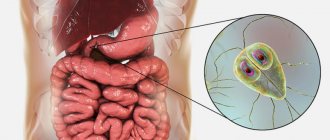
A genus of bacteria belonging to the opportunistic microflora. Almost all people, including infants, are carriers of various streptococci. Normally, microbial activity suppresses the immune system. When its protection is weakened or a large infectious dose is received from the outside, streptococcal infections develop: inflammatory diseases that affect the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, tissues of internal organs, teeth or membranes of the brain. Streptococci are very resistant to environmental factors and are capable of developing resistance to antibacterial drugs.
general information
Streptodermia refers to a pathology caused by streptococci. If we talk about the external manifestations of the disease, blisters and purulent rashes that itch appear on the skin.
Streptoderma in children can occur in two different forms: acute and chronic. Acute is characterized by pronounced symptoms, and chronic - by periodicity.
According to the degree of damage, the disease is classified into superficial, deep and intertriginous. Each form has a specific feature.
Symptoms
If streptoderma occurs, what is the treatment? Before we know the treatment options, let's find out the symptoms. The disease in children occurs in extremely severe forms:
- temperature up to 39C,
- poisoning,
- large lymph nodes.
The texture of the skin may vary depending on the form of the pathology:
- Superficial. Initially, red spots form on the skin. After a couple of days they turn into blisters with a certain liquid inside. The blisters grow up to two cm in diameter, after which they rupture. Yellow crusts form in this area. After this, the skin in this area heals, and the pathology develops further.
- Dry streptoderma . This form usually occurs in boys. Light and pink spots up to 5 cm in diameter form on the skin. They are found everywhere on the body. After they disappear, scars may remain.
- Streptococcal infection. The pathology extends specifically to the corners of the lips; it is encountered when there is a deficiency of vitamin B. Small cracks form on the skin, causing discomfort. After some time, they form into pustules that become crusty. The child has difficulty consuming food, as it causes pain.
- Felon. In a situation where streptococcus spreads to the area around the nails, panaritium develops. Oddly enough, this disease is more often encountered by children at an early age who bite their nails.
- Streptococcal diaper rash. This form of pathology is typical for breastfed children. Blisters form in the folds of the skin.
Understanding how streptoderma begins to develop in children, treatment which requires timely contact with a dermatologist and the implementation of therapeutic actions, not a minute can be lost. If you constantly put off going to the doctor, the pathology can develop into a chronic form, and it will be almost impossible to achieve a final cure.
streptoderma, treatment
Causes
The causative agent of streptoderma, the photo of which you will find below, is group A streptococcus. However, it is worth noting that infection can only develop in a situation where certain factors are present:
- skin damage,
- lack of following basic hygiene rules,
- weak immune system,
- disruption of the endocrine system,
- dermatological diseases,
- depressive mood
- vitamin deficiency,
- constant washing of the skin, which leads to damage to the protective layer,
- strong influence of different temperature ranges,
- poisoning,
- circulatory disorders.
What are streptococci
The genus Streptococcus comprises a variety of gram-positive microorganisms that can reproduce under anaerobic conditions. The bacteria are spherical in shape, their shells are extremely resistant to environmental aggression. In dried samples of biological materials, streptococci remain viable for more than a year. They die when boiled; chemical disinfectants kill them within 20 minutes. For this reason, superficial antiseptic treatment is often not enough.
The source of spread of streptococci is carriers: infected or sick people. The infection is found in high concentrations on the surface of the mucous membranes, in liquid secretions: pus, exudate, saliva. Germs are transmitted from person to person through airborne droplets from sneezing or coughing. Unlike viruses, streptococci spread over a relatively short distance from the source: within a radius of no more than three meters. The high resistance of bacteria in the external environment also determines the nutritional route of infection: through dirty hands, food. Streptococci persist for a long time in milk, meat and seafood, which are a breeding ground for this group of infections.
When multiplying in the human body, streptococci provoke intense inflammatory reactions:
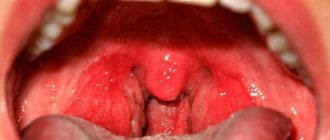
- Group A microbes more often affect the mucous membranes of the nose, oral cavity, larynx, bronchi and lungs, hearing aid, skin, and become causative agents of sinusitis, tonsillitis, caries, sore throat, pneumonia, dermatitis, erysipelas, scarlet fever, complications of wounds and burns;
- Group B streptococci usually provoke inflammation of the tissues of the urinary system, joint structures, connective tissue, cause cystitis, adrexitis, infectious nephritis, rheumatic processes, postpartum complications in women; these microbes can be transmitted through sexual contact.
The development of streptococcal infections is facilitated by various systemic pathologies and tissue damage. Including: diabetes mellitus, malignant tumors, immunodeficiency, postoperative conditions, hypovitaminosis, open wounds.
Therapy
Streptoderma has occurred ? Even in cases where the initial examination was carried out by a pediatrician, only a dermatologist can select therapy. Doctors in this field have an understanding of drugs with a narrow scope of action.
The first step is to limit the child’s diet. The course of treatment also involves avoiding water procedures, which can cause the spread of the disease. Healthy areas of the skin should be washed with a solution of chamomile, and damaged areas should not be touched at all.
The sick person needs to choose the right wardrobe, from which items of clothing made from synthetics and wool must be removed.
Doctors advise popping blisters that form on the skin with a disinfected needle, after which the abscess should be drained twice a day. Healthy areas of the skin are washed with a boron solution.
If crusts appear on the skin, they should be treated with antibacterial gels or ointments.
In more complex situations, many other medications may be prescribed:
- antibiotics for streptoderma of the tetracycline or chloramphenicol series,
- means that prevent the occurrence of an allergic reaction,
- means aimed at improving the body's immune system,
- vitamin preparations,
- antipyretic.
The set of medications must be discussed with the doctor. With the right treatment, the symptoms disappear within a week, but after the severe form is eliminated, scars may remain. This is what streptoderma looks like .
what does streptoderma look like?
Diagnostic methods
To diagnose streptoderma, the doctor does not limit himself to examination and history taking, since external signs of the disease can easily be confused with other skin infections. To obtain accurate data, the patient is prescribed:
- microscopic examination;
- bacterial culture is the most informative research method, which allows not only to detect the causative agent of infection, but also to establish its pathogenicity, and also to check how sensitive it is to antibiotics.
Both tests are prescribed only if the patient has not used antibiotics or other medications. The patient may need to consult an endocrinologist if he has diabetes or is suspected of having this disease.
Causes of complications and re-infection
The reason for re-infection may be incorrect therapy when, for example, if you have primary criteria for improvement, you decide to stop therapy. The most important thing is to remember that you need to unquestioningly follow the advice and instructions of your doctor.
streptoderma complications
What can streptoderma be confused with?
Pyoderma
With pyoderma, the sebaceous and sweat glands are damaged. The rash appears in certain areas of the skin - parts of the body, scalp.
Herpetic rash
Herpes is characterized by the presence of blisters with constant inflammatory processes. They burst and provoke development.
Thrush or candidiasis
Candidiasis is characterized by erythematous papules or reddened, wet plaques. In the pathology under consideration, the lesion, as a rule, occurs in the mucous membranes or fold areas.
Manifestations of allergies
An allergic rash continues to occur as long as the influence is the causative agent of the allergy.
Types of disease
- Streptococcal impetigo. The most common standard form of the disease. A characteristic rash forms on the face, arms and legs. This form is also the most limited, since the pathogen does not move beyond the upper layer of the skin, which has certain protective mechanisms. The appearance of the integument does not change, only individual blisters with liquid appear on the reddened areas. Initially, the patient will experience itching, after which the blisters become darker, which helps the blister to crust over. The duration of this process reaches one week. However, it is worth remembering that if the rash resolves, bacteria are further transferred to healthy areas of the integument, which has its negative consequences for the sick person.
- Bullous impetigo. The rashes are located on the arms and legs and had a fairly impressive diameter. Once the blisters open, these areas of skin develop ulcers that can spread quickly.
- Streptococcal diaper rash. Most of the patients are young children and overweight people. The location of the rash is under the mammary glands, in the axillary folds, intergluteal or inguinal-femoral folds. If you are overweight, the abdominal area is affected.
- Ringworm common. Appears in the form of bright pink rashes. The place of appearance is the face. The rash may become smaller due to exposure to direct sunlight. Those areas of the skin that are affected will not take on a tan like before.
- Streptococcal infection is characterized by the formation of blisters in the corners of the mouth. After the blisters disappear, a crack appears in their place, which in a matter of minutes becomes covered with a yellow crust. It also happens that children tear off the crust, but it forms again.
- Streptococcal ecthyma is the most complex form of the disease. The disease is accompanied by the appearance of characteristic lesions and scars on the arms and legs. In case of development of ecthyma, as a rule, there is a deterioration in health.
Therapy and drugs
Throughout the spread of the disease, basic hygiene rules should be observed: in the first days, it is forbidden to take baths and wet impetigo, and it is forbidden to comb the affected areas.
Therapy for this disease is aimed at destroying the pathogen and strengthening the protective functions of the immune system. As a complex treatment, antibacterial drugs of the category of cephalosporins, macrolides and penicillins are prescribed. If you have bullous streptoderma, you should stop taking medications. As an immunocorrective treatment, the drugs “Likopida”, “Amiksin” and their analogues are effective. Treatment with drugs for . Restoration of microflora in the intestines occurs with the help of probiotics and prebiotics. Appropriate antihistamines will help get rid of scabies.
Means that increase the body’s resistance to infections in the form of solutions - “Eleutherococcus”, “Echinacea”, “Leuzea”, etc.
Sets of vitamin nutrients should also be taken in accordance with the instructions.
Local treatment includes antiseptic drugs that prevent the spread of putrefactive bacteria. Such medications include various alcohols, brilliant green, as well as their analogues - “Fukartsin”, “Chlorhexidine”, “Miramistin”, “Rivanol” or the cauterizing agent “Resorcinol”.
The use of a huge number of zinc-based pastes, preparations and ointments for streptoderma in children with intense scabies.
Diagnosis and treatment of streptococcal infections
Specific diagnosis of pathogens requires bacteriological analysis of scrapings of mucous membranes, samples of saliva, urine, sputum, purulent discharge and other biomaterials. In addition, blood testing for antibodies to streptococci is often necessary. Laboratory tests determine the type of pathogen within 20–30 minutes.
In addition to etiological tests for various pathologies, diagnosis of the general condition of organ damage is required: examination by an otolaryngologist, ultrasound, fluorography and some others.
Treatment tactics are selected taking into account the identified disorders and resistance of microbes to medications. Therapy is carried out by doctors of various profiles: gynecologists, therapists, pulmonologists, dermatologists. To suppress the activity of infectious microflora, patients are prescribed a course of antibiotics. Azithromycin, Erythromycin, and fluoroquinolone drugs are effective against streptococci: Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin. It is important to purchase and use medications as prescribed by a doctor. Self-indulgence in this matter leads to the development of superinfections. Therapy is also supplemented with immunomodulatory agents.
Sanitary measures, hardening, and the use of antiseptics help prevent the development of streptococcal diseases.
Preventive measures and prognosis
Due to the high risk of infection, sick children should keep their distance for some time and not contact other people. Quarantine is provided for up to 10 days. For the entire period of therapy, it is necessary to follow the rules of hygiene.
To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to disinfect the child’s personal belongings. Sick children should have a proper diet rich in nutrients. To improve the quality of the immune system, certain measures should be taken.
streptoderma treatment
As a rule, streptoderma ICD 10 in children is cured without any problems. Exacerbation of the disease and re-infection are observed mainly in children from disadvantaged families or in children with weak immunity. With timely treatment, symptoms disappear within one week. If you do not attach any importance to this, the disease can develop into a more severe form. In the worst case, the disease can lead to blood poisoning. For streptoderma, treatment with ointments and antibacterial agents is mandatory.
Signs of infection
Common symptoms of streptococcal infections:
- increased local or general body temperature;
- itching, burning, dryness in the larynx;
- swelling and redness of the tonsils, the formation of a yellow or grayish coating on the mucous membranes;
- nasal congestion followed by thick greenish or yellow discharge;
- sharp pain and congestion of the ear canal, serous discharge mixed with pus.
Most people have a natural high tendency to become infected with streptococci. When one or another type of infection is transmitted, the so-called entrance gates become inflamed. Laryngitis, pharyngitis, sore throat, and otitis occur. When microbes spread from foci of infection, the lower respiratory tract, brain, kidneys, intestines and other organs are affected. Secondary infections include processes involving autoimmune mechanisms: rheumatoid arthritis, streptococcal vasculitis, glomerulonephritis.
Streptococci are common causes of toxic and necrotic complications, including severe fever, abscesses and sepsis.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of infection, you should follow the following rules:
- follow the rules of hygiene,
- disinfect damage to the skin,
- strengthen the name system with useful substances,
- do not carry out frequent water procedures, as this may pose a certain danger for the child,
- In case of primary symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Streptoderma on the face can be treated, but only if you consult a doctor in a timely manner. The earlier therapy was carried out, the easier it is to exclude complications and transition to the chronic stage. You can undergo a full examination in a clinical clinic.
Can it be treated at home?
- First of all, it is necessary to establish the nature of pyoderma. In other words, identify the causative agent of the disease and determine its sensitivity to antibiotics. After a course of antibacterial therapy (local use of antibacterial drugs in most cases is ineffective) against the background of normal multivitamin-mineral support (taking vitamins), such diseases usually go away. But pyoderma, as a rule, develops against the background of reduced immunological resistance or is provoked by diseases of the internal organs: stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas. Therefore, an in-depth examination is necessary.
to the begining