- Standard of care
Acute tonsillitis, or tonsillitis, is a widespread acute infectious and inflammatory disease in which the lymphoid formations of the pharyngeal ring, mainly the palatine tonsils, are affected. The problem of treating the disease still remains relevant, as the frequency of complications with angina increases every year.
The importance of prescribing adequate treatment for sore throat is associated with a high likelihood of complications
The following forms of tonsillitis are distinguished:
- catarrhal;
- lacunar;
- follicular;
- combined.
Also, angina can be primary and secondary.
Code for acute tonsillitis according to ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision):
- J0 Streptococcal tonsillitis;
- J8 Acute tonsillitis caused by other specified pathogens.
Symptoms
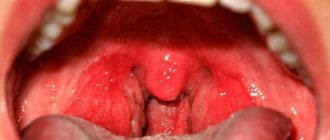
Lacunar tonsillitis appears quickly. The obvious and most common symptom is a severe sore throat that gets worse when swallowing.
In addition to a sore throat, lacunar tonsillitis presents symptoms such as:
- Increase in temperature.
- Pain in the head.
- Pain in muscles and joints.
- General weakness of the body.
- Redness on the cheeks.
- Fever, chills in the body.
Complications
Inadequate treatment of follicular tonsillitis can lead to purulent complications.
The first place in frequency is paratonsillar abscess - the formation of an abscess in the soft tissues surrounding the tonsil. With this disease, fever persists for a long time, and opening the mouth is so painful that the patient even refuses to take fluids. Surgery is often required. Purulent lymphadenitis and other pathological processes associated with the spread of bacterial infection and the need for surgical drainage of a purulent focus also occur.
3-5 weeks after an acute streptococcal infection, signs of delayed infectious and allergic complications may appear. Possible damage to the myocardium and valve apparatus, which is accompanied by pain in the heart, rhythm disturbances, and shortness of breath. There is swelling of the joints, pain when moving, and a feeling of stiffness.
The development of glomerulonephritis is possible - kidney damage with decreased diuresis, fluid retention, and arterial hypertension. These conditions require consultation with specialists - a cardiorheumatologist and a nephrologist, respectively.
Follicular tonsillitis
Causes
Lacunar tonsillitis is caused by bacteria (staphylococcus, streptococcus) or viruses, fungi and is an infectious disease. This type of sore throat is transmitted through the air from a sick person to a healthy one. The development of the disease may also continue due to:
- Hypothermia of the body.
- Allergic reactions.
- Chronic diseases of organs and systems.
- Experiences, stress.
- Lack of normal, full sleep.
- Deterioration of immunity.
- Poor, poor quality food.
- Diseases of the ENT organs.
- Advanced dental diseases.
Etiological factors
Follicular tonsillitis in children and adults can be caused by various microbial pathogens:
- viruses: adeno-, rhino-, boca-, metapneumoviruses, Epstein-Barr, parainfluenza, etc.;
- bacteria: beta-hemolytic streptococcus of group A (less often - other serogroups), Staphylococcus aureus, Pfeiffer bacillus, Moraxella, pneumococcus, corynebacteria, Neisseria, etc.,
- fungal agents.
What is important is a decrease in the overall resistance of the body against the background of overwork, hypothermia, malnutrition, and advanced chronic diseases.
While viral tonsillitis is more common in children, bacterial pathogens predominate among adults. Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus is of greatest clinical importance. It causes about 35% of all tonsillitis in children and up to 80% in adults. It is this microorganism that “triggers” autoimmune long-term complications of the disease - acute rheumatic fever, rheumatic heart disease, glomerulonephritis, arthritis.
Diagnostics
When a patient comes to an otolaryngologist with the first signs of lacunar tonsillitis, the doctor begins an examination. During it, the specialist notices general redness in the throat, as well as enlargement of the tonsils and palate due to swelling. Plaque can be seen inside the tonsils, in their lacunae. Lymph nodes with sore throat increase in size and are easy to feel. They also hurt when touched. After the examination, the doctor sends the patient for tests, which include:
- General analysis.
- A smear from the tonsils to identify the bacteria that caused lacunar tonsillitis.
- Analysis for C-active protein in the blood.
Treatment of acute tonsillitis
Only the doctor decides how to treat this or that form of sore throat. Clinical guidelines are used for this purpose.
Standard of care
In most cases, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis.
Most often, sore throat is treated at home.
If the patient's condition is severe, there are purulent complications or concomitant diseases with a likelihood of decompensation, hospitalization in a hospital is required.
For bacterial tonsillitis, systemic antibacterial therapy is prescribed.
Symptomatic systemic treatment is indicated for relief of fever or pain.
Local therapy is used to reduce the severity of inflammatory phenomena.
Features of therapy
Sore throat of viral etiology does not require the use of antibiotics. In this case, the doctor prescribes antiviral drugs, immunomodulating agents and local treatment.
Rational antibacterial therapy for sore throat caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus is completely justified, since the number of complications of this pathology is increasing every year.
The drugs of choice for the treatment of acute forms of tonsillitis are penicillins and first generation cephalosporins.
Rational antibacterial therapy for sore throat caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus is completely justified, since the number of complications of this pathology is increasing every year.
Antibiotics of the penicillin group:
- Amoxicillin + clavulanic acid;
- Benzathine Penicillin;
- Phenoxymethylpenicillin.
Among cephalosporins, Cefadroxil is often prescribed. In case of exacerbation of a chronic process, second generation cephalosporins (Cefuroxime) are used.
In case of intolerance to these groups of antibiotics (beta-lactams), macrolides are indicated:
- Spiramycin;
- Azithromycin;
- Roxithromycin;
- Clarithromycin;
- Josamycin.
Reserve drugs in the treatment of streptococcal tonsillitis are lincosamides (Lincomycin, Clindamycin).
The required dosage and duration of treatment with antibacterial agents is determined by the attending physician. Penicillins and cephalosporins are prescribed for an average of 10 days.
You should not stop taking the antibiotic prematurely when your condition improves and symptoms stop. A spontaneous increase in the duration of treatment is also not recommended. This can lead to the development of resistance of pathogenic flora to antibacterial agents.
To reduce body temperature and reduce sore throat, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are recommended:
- Paracetamol;
- Ibuprofen.
A nebulizer or steam inhaler can be used for local treatment
Local therapy in the form of rinses, inhalations, tablets and lozenges has an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect.
The most widely used antiseptics and local non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are:
- benzalkonium chloride (Benatex);
- hexethidine (Hexoral);
- dichlorobenzyl alcohol + amylmetacresol (Strepsils, Suprima-ENT);
- chlorhexidine bigluconate (Chlorhexidine);
- iodine preparations;
- octenidine + phenoxyethanol (MestaMidin-sens);
- Miramistin (Miramistin);
- biclotymol (Hexasprey);
- flurbiprofen (Strepsils Intensive);
- benzydamine hydrochloride (Tantum Verde).
The lacunae of the palatine tonsils are washed with an antiseptic solution and lubricated with 1% Lugol's solution.
Treatment
After identifying the causative agent of a sore throat, the doctor will prescribe the patient special medications that will help kill the bacteria. The patient will also need rest and bed rest. To reduce discomfort and get rid of discomfort, doctors advise taking:
- Drugs that lower body temperature and relieve fever.
- Antihistamines.
- Vitamin complexes to improve immunity.
- Medicines to fight viruses.
- Immunomodulators.
The patient should also drink warm drinks and liquids, gargle with antiseptics, and inhale when possible. Often patients are sent for a further course of treatment - physiotherapy. It quickly gives effect and includes ten treatment procedures.
Treatment of follicular sore throat
The need for hospitalization for acute tonsillitis is determined by the severity of the general condition. As a rule, follicular purulent tonsillitis is treated at home. Until the end of the fever, it is recommended to observe bed rest, then gentle rest, i.e. the patient should stay at home and avoid physical activity. A sufficient amount of liquid (warm teas, fruit drinks, juices) helps relieve fever and eliminate bacterial toxins. You need to eat according to your appetite - do not force yourself to eat, but give preference to light, low-fat dishes.
Etiotropic treatment is of key importance - the prescription of drugs that suppress the pathogen. For bacterial infections, antibiotics are indicated for follicular angina - protected penicillins, cephalosporins of the 1st-2nd generation, in case of intolerance to beta-lactam antibiotics - macrolides or lincosamides. For a fungal pathological process, antifungal drugs are indicated - fluconazole, ketoconazole, etc. Herpetic tonsillitis requires the prescription of acyclovir. It is critical to maintain the full course of etiotropic therapy, and not stop taking medications when the first relief occurs. An incomplete course contributes to the formation of microflora that is resistant to medications - more aggressive and difficult to treat.
To eliminate the immunopathological process, the use of antihistamines is indicated. During the period of fever, antipyretic therapy (ibuprofen, paracetamol or nimesulide in appropriate dosages) is recommended.
Local treatment to reduce pain in the throat is prescribed in the form of sprays or gargles. It is necessary to keep in mind the risk of aspiration when resolving tablets and laryngospasm when using the spray in young children. Mechanical removal of plaque is contraindicated.
During the period of convalescence, physical therapy is possible as prescribed by the attending physician.
Avoid complications
There are often cases when a patient is careless about his health and decides that “it will go away on its own” or, conversely, tries to try all the advice of traditional medicine on himself. This is the other extreme of negligent attitude towards one’s health. Catarrhal tonsillitis, although it is one of the mildest forms of acute tonsillitis, but in the absence of proper treatment, severe complications can develop, which will be quite difficult to treat.
If tonsillitis is not treated, you may encounter diseases such as chronic tonsillitis (a chronic form of inflammation), rheumatoid arthritis, peritonsillar abscess, myocarditis, kidney disease (glomerulonephritis), laryngeal edema, and even sepsis.
Pregnant women need to pay special attention to their health: the inflammatory process that spreads beyond the palatine tonsils can lead to tonsil intoxication and the threat of miscarriage! Therefore, treatment of catarrhal tonsillitis in adults should be carried out on time and always under the supervision of an ENT doctor.
Symptoms of catarrhal tonsillitis in children
Most often, catarrhal tonsillitis occurs in children from six months to three years. Children tolerate the disease worse than adults. Sometimes parents mistake the symptoms of this disease for ARVI, and therefore do not attempt treatment in a timely manner.
In children under three years of age, the temperature rises to 38°C, less often above 39°C. In this case, medical attention is required. In addition, the child complains of dry mouth, weakness, headache and dizziness, and increased salivation. Sore throat is accompanied by meningism and convulsions.
The severity of symptoms is observed during the first three days.
When there is a risk of getting sick
Like any similar infection, the disease is transmitted by airborne droplets. The main cause of catarrhal sore throat is the causative bacteria: staphylococci, streptococci and rhinoviruses. In addition to these bacteria, our oral cavity is inhabited by many microorganisms that are in a passive state and do not cause harm if the person is healthy. They wait for the right moment, and as soon as the body’s defenses weaken under certain conditions, microorganisms begin to become active, and as a result, inflammation of the tonsils and pharynx occurs.
The inflammatory process covers the palatine tonsils, or tonsils, as they are commonly called. The tonsils are affected superficially; in the catarrhal form there is no purulent plaque and pus in the lacunae of the tonsils. Despite the fact that catarrhal tonsillitis is the simplest form of tonsillitis, in the absence of proper treatment, it can develop into another, more severe form of the disease.
Factors that provoke the development of the disease include:
- weak immunity;
- the presence of a permanent source of infection in the body (for example, with chronic sinusitis or dental caries);
- unfavorable environmental conditions, gas pollution;
- bad habits, especially smoking;
- unbalanced diet, eating “on the run”;
- stress.
As doctors note, in order for pathogenic microorganisms to have a chance to survive and become more active, it is necessary that the body’s defenses weaken. In other words, for a healthy person, with a strong immune system, who eats well, avoids the negative influence of stressful situations, and does not abuse bad habits, the risk of getting sick is greatly reduced.
Expert opinion
As an ENT specialist, I want to say that catarrhal tonsillitis is a very common disease with an increase in incidence in the autumn-winter period. Due to the decrease in air temperature and the spread of respiratory infections, the number of sick children is increasing. However, the pathology responds well to conservative treatment. The main thing is not to ignore the signs of the disease and seek help from a specialist as early as possible. Self-treatment risks progression of the disease and the development of dangerous complications.
Complications of catarrhal tonsillitis
It is extremely important to treat catarrhal sore throat under the supervision of an experienced ENT doctor, since improper independent treatment leads to negative consequences - the pathology penetrates deeper into the throat, covering all elements of the pharyngeal ring, including lacunae and follicles, flowing into a chronic purulent form. In addition, if inflammation penetrates beyond the palatine tonsils and attacks the nasopharyngeal tissues, then inflammation of the adenoids occurs.
In children, catarrhal tonsillitis is dangerous due to false croup. Due to inflammation of the larynx, the subglottic area of the larynx may swell, which can lead to airway stenosis. If there is no improvement in the condition within four days, the temperature persists, spots appear on the tonsils, the voice begins to wheeze, and swallowing causes unbearable pain, then you need to visit the doctor again to adjust the treatment plan.
If the treatment tactics are chosen correctly, the disease is easily treatable and the risk of complications is low.
At the ENT CLINIC in Chertanovo, experienced ENT doctors prescribe treatment that is effective for both children and adults. Doctors will collect anamnesis, carefully examine the throat, conduct diagnostics, and only based on the tests will prescribe effective medications. The clinic also has the opportunity to conduct highly effective physiotherapeutic treatment methods to prevent the development of complications and quickly rehabilitate the patient after an illness.
Causes
The pathogen enters the body, covering the tissue of the palatine tonsils. Gradually, microbes spread through the bloodstream, causing the development of intoxication. Local immunity is immediately activated by producing a large number of leukocytes. Blood rushes to the tonsils, causing them to become red and swollen.
The main route of penetration of the pathogen is airborne. Children become infected through shared toys and close bodily contact. The infection begins to spread when the body is weakened and hypothermic. Adults become infected through droplets of saliva or household items.