Right hypochondrium area
If we talk about localization, we should clarify which place in the human body is called the “right hypochondrium.” For this there is a classic definition from topographic anatomy - the area of the anterior abdominal wall that has:
- the upper border is the right dome of the diaphragm at the level of the V rib;
- lower - the inner edge of the costal arch;
- in the center - a conventional vertical line passing through the lowest edge of the rib;
- on the right side - the vertical connection of the XII rib and the right iliac crest of the pelvic bone.
As you can see, the anatomical definition is quite complex. In fact, we refer to the hypochondrium as everything that is located in the area of the right lower ribs and under them, starting from the spine (from the back) to the sternum joint.
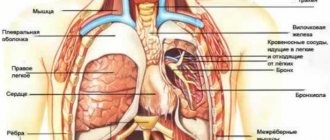
The projection of the right hypochondrium includes internal organs:
- liver and gall bladder;
- bend of the ascending and transverse colon;
- upper pole of the right kidney with the adrenal gland;
- the peritoneal side of the dome of the diaphragm, separating the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity.
Conditions for pain
The causes of pain in the right hypochondrium consist of the structure of the walls of the internal organs and the characteristics of their innervation. For the diseased organ, the following conditions must be met:
- in dense parenchymal organs - swelling, increase in size and stretching or destruction of the capsule that has pain receptors;
- for the intestine and gallbladder - spasm or stretching of the muscle layer, inflammation in the submucosa (the mucosa itself has no pain points), violation of the integrity of the wall.
An equally important feature of the abdominal viscera is the general innervation from some parts of the spinal cord, so pain under the right lower ribs may reflect local pathology in the stomach, pancreas, duodenum, and inferior vena cava.
Diagnostics
The primary examination is carried out by a gastroenterologist or a highly specialized hepatologist. During the physical examination, bladder symptoms, liver size, signs of peritoneal irritation and local tension in the abdominal muscles are assessed. If necessary, a consultation with an infectious disease specialist, gynecologist, or oncologist surgeon is scheduled. The diagnostic plan includes:
- Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary zone.
An ultrasound examination visualizes the gallbladder, measures the thickness of its wall, and identifies stones in the cavity. To confirm the diagnosis of dyskinesia of the gallbladder, a test with a choleretic breakfast is performed. An examination of the liver is necessary to study the structure of the parenchyma and find individual hyperechoic foci. - ERCP.
The study is indicated to assess the condition of the bile and pancreatic ducts and duodenal mucosa. Cholangiopancreatography allows you to take samples of material from pathologically changed lesions to examine them under a microscope for signs of cellular atypia. - Duodenal sounding.
The method is used to determine the contractile function of the gallbladder. Then portions of bile are subjected to microscopic and bacteriological examination. Analysis of the biochemical composition of bile is necessary when diagnosing cholelithiasis. - X-ray methods.
CT scan of the abdominal cavity is a highly informative method that helps to detect benign and malignant tumors of the hepatobiliary zone and parasitic cysts. The structural and functional features of the liver can be studied by scintigraphy. - Additional methods.
To determine the degree of fibrosis, rapid and non-invasive elastography is performed. For unspecified forms of hepatitis and neoplasms, a biopsy of the liver tissue is performed, followed by histological analysis.
Of the laboratory methods, a biochemical blood test with liver tests, which looks at the level of bilirubin, cytolysis enzymes, cholesterol and alkaline phosphatase, is of diagnostic value. To diagnose parasitic diseases, feces are analyzed for helminth eggs. To exclude the viral nature of pain in the right hypochondrium, serological tests are done for hepatitis A, B, C.
Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary zone
Can pain occur in a healthy person?
Pain in the right hypochondrium in the front can occur for physiological reasons and not be accompanied by pathology. During physical activity (usually running, push-ups), an untrained person may experience stabbing pain on the right side under the ribs.
This is explained by a decrease in tone and stretching of the biliary tract under the influence of the release of an additional portion of adrenaline, an increase in blood supply to the liver with stretching of the capsule, and spastic contraction of the diaphragm muscles during inspiration due to untrained breathing.
Exercising after a heavy meal makes the condition worse because the liver feels pressure from a full stomach.
In women, colic in the hypochondrium on the right is caused by an increase in estrogen and a drop in progesterone in the period before menstruation. Hormonal imbalance affects the tone of the gallbladder and tract, causing stagnation and overdistension, therefore, short-term colic is possible.
Hormonal contraceptives work in a similar way; their use is also accompanied by a violation of the outflow of bile. In the third trimester of pregnancy, physical activity is accompanied by moderate pain in the hypochondrium or a feeling of heaviness. Symptoms stop after delivery.
After load
Unpleasant sensations in the form of nagging or stabbing pain occur after physical exertion in people with hepatitis, cirrhosis, or congestive liver. After shaking or physical exertion, an attack of calculous cholecystitis may occur. Also, periodic pain during exercise appears in patients with myositis, intercostal neuralgia, osteochondrosis, rib fractures, and vena cava thrombosis.
Pathological causes of pain
Diseases of the organs located in the right hypochondrium are accompanied by pain of various shades, irradiating to other parts of the abdomen, to the lower back and chest. Doctors should know the symptoms of pain in the right hypochondrium, since differential diagnosis is based on them.
With limited localization, the pain syndrome has accompanying symptoms and differs in different diseases.
Liver diseases, including hepatitis of various natures, alcoholic hepatosis, cirrhosis, parasitic diseases (echinococcosis, trichinosis), abscesses, liver cancer or metastatic node from the stomach, lungs, colon, breast.
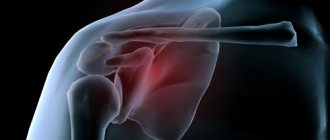
Heart pathology (coronary disease, widespread infarction, cardiopathy, inflammatory diseases of the membranes, defects) - weakness of the right ventricle occurs. This means that the muscle loses its ability to pump blood in the required volume. Circulatory failure is accompanied by stagnation of blood below the vena cava.
Cardiac cirrhosis of the liver is formed, which causes constant pain in the right hypochondrium
Thrombosis at the level of the inferior vena cava should be kept in mind in case of acute, sudden pain. In the gallbladder and ducts, inflammation, dyskinesia, and precipitation of salts with the formation of stones are possible. There are chronic calculous and acalculous cholecystitis, cholangitis, cholelithiasis. Tumors are rarely detected.
Diseases of the right kidney are very diverse. Inflammation (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis) can occur on one side for a long time, the second kidney takes on the functions of both. The kidneys suffer from abscess formation, tuberculosis, echinococcosis, the tissue structure is disrupted by hydronephrosis, polycystic disease.
Urolithiasis contributes to blockage of the pelvis or ureter with a stone, further stagnation of urine provokes inflammation. Tumors from the renal parenchyma, as well as frequent metastasis from cancer of other localizations, are accompanied by severe constant pain. Pheochromocytoma and other types of malignant neoplasms develop in the right adrenal gland.
Among the diseases of the colon, irritable bowel syndrome, colitis caused by infection, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, tumors, diverticulosis, and intestinal obstruction should be highlighted.
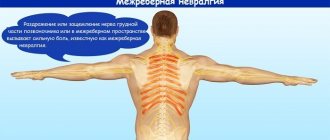
In the border tissues of the diaphragm and ribs, damage is possible due to fractures of the lower ribs, intercostal neuralgia, diaphragmatitis and tumors, herpes zoster caused by the herpes virus.
Abdominal pain radiates to the upper right region and hypochondrium due to perforation of a duodenal ulcer, pancreatitis, appendicitis, traumatic injury to the kidney and liver.
Patients describe pain differently. The type of pain is taken into account in the differential diagnosis.
Such patients are urgently taken to the nearest surgical department and examined by emergency specialists
Prevention
Preventive measures to prevent pain in the right hypochondrium boil down to following the following recommendations:
- taking medications only as prescribed by a doctor;
- avoidance of stressful situations;
- compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- healthy and active lifestyle;
- rejection of bad habits;
- proper and nutritious nutrition;
- use of barrier contraceptives during sexual intercourse, refusal of casual relationships.
Regular medical examination (once a year) will allow you to prevent or promptly detect any health problems and receive the necessary treatment.
Characteristics of pain
Next, we consider the options for pain and their characteristics against the background of diseases.
The pain is sharp
Acute pain in the right hypochondrium occurs suddenly and is included in the concept of “acute abdomen.” The issue of surgical treatment is being decided. Sharp pain in the hypochondrium on the right is caused by the following conditions.
Injuries and ruptures of the liver, kidney, intestines. Increasing hematomas due to internal bleeding add dull pressing pain, accompanied by shock, dizziness, and signs of anemia in blood tests.
Acute cholecystitis, pancreatitis, appendicitis with an abnormal location at the beginning of the attack cause nausea and vomiting, fever, pain radiates to the side, back, shoulder blade. It begins to pulsate if the inflammation turns purulent. In this case, urgent measures are necessary since the condition indicates rupture of the organ in the near future and the spread of pus throughout the peritoneum.
Intestinal perforation is caused by ulcerative lesions of the entire depth of the wall. Characterized by cutting pain. Occurs when an ulcer perforates (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, duodenal ulcer), or diverticula rupture.
Intestinal obstruction develops gradually, usually the acute condition is preceded by a period of constipation and aching pain. Abdominal bloating in the upper sections, vomiting, and gas retention are added.
When the bile ducts are completely blocked by a stone, muscle contraction occurs. On the other hand, stagnation of bile causes enlargement and inflammation of the gallbladder. Therefore, an acute attack alternates with dull arching pain in the right hypochondrium.
Thrombosis of arteries and veins, thromboembolism of feeding vessels lead to oxygen starvation (ischemia), then to tissue necrosis. The pain is very intense, painful shock is possible. Renal colic, caused by the movement of a stone along the right ureter, radiates upward to the hypochondrium, into the back and groin organs. The pain is acute, unbearable, excruciating.
Intense pain in the right hypochondrium on the side is characteristic of acute pyelonephritis. It is accompanied by pain and frequent urination, fever with chills.
Sudden compressive pain accompanies acute myocardial infarction in the abdominal form
A fracture of the right ribs causes shooting pain, which intensifies with inhalation and movement. A patient with intercostal neuralgia and herpes zoster feels similarly.
You can find out more about the causes of pain when breathing in this article.
The pain is dull
Dull pain in the right hypochondrium is described by patients as “something aching, preventing you from lying on your right side, bursting.” They are tolerated by patients, although they can vary in intensity. With moderate pain, some patients do not want to see a doctor.
This type of pain syndrome is characteristic of long-term chronic inflammation, the initial stage of a neoplasm, and is observed:
- for chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis;
- parasitic liver diseases;
- chronic cholecystitis and pyelonephritis without exacerbation;
- colitis without ulceration of the wall;
- colon diverticula;
- gradually growing hydronephrosis;
- metastases from other organs.
Feeling of "heaviness"
Patients with heart failure indicate constant heaviness in the right hypochondrium caused by blood stagnation. At the same time, swelling is observed in the feet and legs, and an enlargement of the abdomen (ascites) due to the leakage of plasma into the abdominal cavity.
With significant enlargement of the organ, a nagging pain appears. Similar symptoms occur with hepatitis, fatty hepatosis, biliary dyskinesia (hypomotor type), chronic cholecystitis without exacerbation.
What causes pain?
All organs located in the right hypochondrium “do not like” spicy and fatty foods, fried foods, smoked foods, and pickles. These foods make digestion work harder.
Unsuitable food provokes hidden forms of diseases and causes malfunction of the digestive system.
The nature of the pain is characterized by dullness, spasm (cramping, stabbing), the presence of nausea, accompanied by bloating, and stool disturbances. You can learn more about pain in the right hypochondrium after eating in this article.
Physical activity activates calculous processes in the gallbladder and kidneys. A special role is given to shaking in transport, running, and jumping. The movement of stones is caused, which means an attack of renal colic, cholelithiasis.
At the same time, the filling of the liver with blood is activated, and the aching pain in the hypochondrium on the right intensifies after performing hard work or sports training. Loads provoke exacerbation of intercostal neuralgia, osteochondrosis, myositis. Promote thromboembolic complications of blood vessels.
If biliary dyskinesia is caused by muscle hypotonia, then physical activity improves the passage of bile. Patients note the elimination of pain. Let us consider the features of pain syndrome using the example of various pathologies.
Pain caused by liver pathology
The right lobe of the liver is located in the hypochondrium, the left one goes into the epigastrium. The pain is caused by overstretching of the capsule. This mechanism is suitable both for swelling of the parenchyma during inflammation, and for volumetric processes (abscess, hydatid cyst, neoplasm).
Signs of liver disease
Hepatitis is a large group of inflammation of the liver parenchyma of various etiologies. For reasons, there are viral infectious, alcoholic, toxic, autoimmune. The pain is dull, arching in nature.
In the clinical course, intoxication of the body comes first: nausea, lack of appetite, vomiting, severe weakness. Violation of the metabolism of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, the exchange of bile pigments causes yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes. The feces become grayish, the urine darkens.
With cirrhosis of the liver, inflammation gradually passes into the stage of scarring. Dense nodes that do not contain hepatocytes are formed. Fatty hepatosis ends in the same way with alcoholic illness. Characterized by persistent aching pain at the beginning of the disease, when the liver is still enlarged. Then the size of the organ decreases. Liver failure develops.
Echinococcal cyst - manifests itself when larvae of the Echinococcus parasite enter the body. It is most often localized in the right lobe. As it grows, it compresses the liver and bile ducts and stretches the capsule.
In 12% of patients it causes suppuration with the formation of a liver abscess. Abscess formation is indicated by throbbing pain in the right hypochondrium. Clinically detected by intense, constant pain in the right hypochondrium of a dull and aching nature. Irradiates to the right shoulder, scapula.
Typically worsening when lying on the left side, against the background of movements and deep breathing. The pain decreases if you lie on your right side, curled up. Upon examination, doctors reveal severe pain when pressing on the lower right ribs.
Hepatocellular carcinoma is no different from cirrhosis in terms of pain and symptoms. Diagnosis is made based on tissue biopsy.
Liver abscesses with superficial localization break through the capsule and spread into the subdiaphragmatic space
Pain due to congestive heart failure
Heart failure causes a significant enlargement of the liver, swelling of the feet and legs, trophic ulcers, and ascites. The pain is of the nature of a feeling of heaviness in the hypochondrium on the right. It is possible to find out the patient’s previous history and previous diseases of the heart muscle.
In the abdominal form of myocardial infarction, the pain is distinguished by a pressing and burning intense attack (“stab of a knife”). They radiate to the right shoulder blade, behind the sternum. Most typical for infarction of the posterior wall of the left ventricle. Possible drop in blood pressure, arrhythmia, shortness of breath.
How does your gallbladder hurt?
The gallbladder and ducts are hollow organs. This means that pain in them can occur during stretching (impaired bile outflow) or spastic contraction. Dyskinesia is called hypotonic and hypertonic, respectively.
In its pure form, it is possible in childhood, in nervous, emotional people. Often accompanied by inflammation (cholecystitis and cholangitis). Increased tone causes spasm when the stone moves, which is manifested by an attack of hepatic colic. They radiate to the back, right shoulder blade.
Chronic cholecystitis occurs before exacerbation with dull, aching pain, but during the acute stage it is accompanied by sharp cutting sensations. Possible vomiting of bile, yellowing of the sclera, bloating, bitterness in the mouth in the morning.
Pain in the right side not associated with internal organs
Abdominal pain with depression
. Depression is accompanied by increased anxiety and increased levels of norepinephrine and cortisol. They cause spasms of smooth muscles, including the intestines. The person experiences symptoms characteristic of indigestion. Moreover, this is not associated with eating low-quality food. Abdominal pain cannot be relieved by medications because it is psychosomatic in nature.
A severe and persistent cough also causes abdominal pain
. This is due to the increased load on the abdominals, which not everyone has trained and strong. Often coughing, the patient strains the muscles, they stretch and put pressure on the diaphragm, causing a dull pain. It goes away on its own after the cough is cured.