August 16, 2020
Dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin that can occur due to a variety of irritants: allergens, aggressive chemicals, fungi, and adverse weather factors. Chronic inflammation of the skin also occurs with psoriasis, but in this case the condition is distinguished as a separate disease, and dermatitis is a collective concept, a syndrome that may not relate to any specific disease, occurring periodically.
What are the varieties?
Dermatitis has a complex classification. Depending on the nature of the skin disease, there are:
Simple contact
Occurs with direct physical irritation. Factors that provoke the occurrence of dermatitis are skin friction, pressure, temperature effects, alkalis, acids, poisonous plants. Surely, many have encountered this type of skin irritation. Yes, yes, we are talking about burns, frostbite, chafing, and rashes from detergent.
Contact
Symptoms appear almost immediately after contact, the area of skin damage corresponds to the area of contact with the irritant. With minor exposure, dermatitis manifests itself as mild redness and itching; acute cases may be accompanied by the appearance of blisters filled with liquid and swelling of the skin.
Allergic
This is a hyperreaction of the body to contact with certain substances. Allergic dermatitis, like all forms of allergies, manifests itself in individuals predisposed to it.
Causes of allergic type development
Unlike simple contact, allergic does not develop immediately, but after several contacts with the allergen. An allergic reaction must form; several weeks may pass from the moment of the first interaction.
Manifestation of allergic dermatitis
With the allergic type, the area of the affected skin area may be larger than the immediate site of contact with the irritant. As the disease worsens, the skin becomes bright red with pronounced swelling, weeping blisters appear, which open and erosion develops in their place. As the inflammation heals, scales and crusts form - these may be symptoms of incipient eczema.
Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp
Irritation appears in the area of greatest accumulation of sebaceous glands - in the scalp, on the ears, and less often on the face (on the wings of the nose). Often the initial form of the disease is dandruff in the hair.
The cause is the Malassezia fungus, which is present on the skin of most people. But its excessive reproduction leads to increased peeling, and as a result, seborrhea develops.
One form of the disease is perioral cutaneous dermatitis - irritation appears near the mouth.
Preparations for external use
Dermatitis on the hands is often accompanied by itching, which gets worse at night. Many patients complain of waking up in the middle of the night and being unable to fall back to sleep. In such cases, it is recommended to wear cotton gloves before going to bed and take a light herbal sleeping pill.
Acute inflammatory process is relieved with glucocorticoid ointments or creams. Depending on the severity of the lesion, the use of drugs of weak or moderate effect is prescribed. If skin lesions spread and affect not only the skin of the hands, but also other parts of the body, the use of strong hormonal drugs is necessary. Since dermatitis on the hands is accompanied by swelling and burning, patients are often prescribed creams. Due to their structure, they have a cooling effect, which helps reduce swelling, and a rapid antipruritic effect. Weak hormones include hydrocortisone, and moderate hormones include prednisolone, fluocortolone, and prednicarbate. Glucocorticoid creams are used for a limited amount of time, usually no longer than a week.
Relieving acute inflammation is only the first step of therapy. The chronic stage is also characterized by itching (albeit not as intense) and, most importantly, dry skin. Dryness provokes peeling and cracks that interfere with the healing of the skin. To normalize metabolic processes in the skin, including water balance, it is necessary to resort to additional hydration. The greatest effect comes from applying creams after hygiene procedures. Under the influence of warm (but not hot) water, the epidermis softens, and the crusts dissolve and come off.
However, it is worth noting that washing your hands with soap will most likely lead to a negative result, since alkali dries out the skin and, once it gets into the wounds, causes tingling and exudate. Delicate care is provided by special medicinal and cosmetic care products for inflamed skin. Thus, “Losterin” body gel, which can also be used as hand soap, does not contain surfactants, fragrances or dyes. And 4 types of vegetable oils in its composition, deresined naphthalan and Japanese sophora extract provide both cleansing, bactericidal effect, and moisturizing of the skin. In the acute period, it is recommended to cleanse the skin of the hands with micellar water and clean soft wipes.
After water procedures, the skin is carefully blotted (do not wipe!) with a towel and moisturizer is applied. For hand skin dermatitis, creams containing vegetable oils and panthenol are useful, which create a thin fatty film on the surface of the skin and do not allow the liquid to evaporate. Vegetable oils can be applied to the skin in the form of lotions, or they can be included in creams. Traditionally, olive, flaxseed, sea buckthorn, sunflower oil, avocado and jojoba oils are used in dermatology. In addition, products with the addition of plant extracts and vitamins are needed. These components provide nutrition to skin cells and accelerate regeneration. Preparations containing tar, naphthalan, salicylic acid, and zinc help relieve skin itching.
The restoration of epithelial cells is facilitated by preparations with propolis. This natural remedy has desensitizing, anti-inflammatory and regenerative properties due to its composition. Propolis contains flavonoids, aromatic and fatty acids, free amino acids, proteins, alcohols, minerals, sugars, vitamins, steroids, and many microelements. However, ointments, sprays and creams with propolis can be prescribed only to those people who are not allergic to honey and pollen. In other cases, the product may cause a severe allergic reaction.
In most cases, chronic dermatitis on the hands can be treated with external herbal medicine. It can be combined with hygienic procedures. For example, after an evening shower, it is useful to take hand baths with extracts or infusions of pine needles, chamomile flowers, oak bark, calendula, birch buds, string, burdock root, plantain leaves, poplar buds, and lungwort. After a 10-minute bath, the skin of the hands is also dried with a towel and moisturizer is applied.
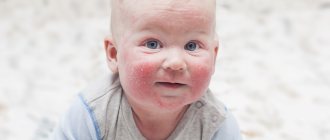
Atopic dermatitis
Serious chronic disease. It is of an allergic nature: irritation occurs to substances that can penetrate both through contact and through the lungs and stomach. The atopic type often develops in childhood and often remains with a person for life, turning into a chronic form.
Due to the fact that dermatitis is a general name for skin diseases, symptoms and external manifestations of the disease are of great importance in diagnosis.
Sorbents and preparations for normalizing flora
An integral element of the treatment of atopic dermatitis is the normalization of intestinal functions. Often it is gastrointestinal pathologies that cause atopic dermatitis. Such drugs are prescribed in the acute period of the disease for one week. At the end of the course of treatment of dermatitis with sorbents, drugs are recommended that normalize the flora and restore the protective properties of the intestines:
- smectin - protects the intestinal mucosa and absorbs toxic substances;
- lignin - removes harmful microorganisms and toxins from the intestines, has a detoxification effect and increases local immunity;
- bifidumbacterin - increases nonspecific immunity and normalizes intestinal microflora;
- hilak forte - restores the intestinal mucosa, increases its protective properties and regulates the balance of intestinal flora.
Itchy skin dermatitis
Chronic inflammation of the skin, which is characterized by inflammation, itching, burning. Itchy skin is the body's reaction to irritation of nerve endings, accompanied by scratching of the skin and general increased nervousness.
Itchy dermatitis can spread throughout the body (atopic and allergic dermatitis, allergies to animal hair, pollen, etc.) and be localized - on moving parts of the body, on open areas of the skin.
Sanitary standards
Particular attention is paid to observing the rules for putting things in order in the room in which a person prone to dermatitis lives. Prevention of the disease involves systematic cleaning of the house: wet cleaning should be done every day, and general cleaning should be done once a week. In this case, it is advisable not to use conventional vacuum cleaners, since mites can penetrate through the filters and then spread throughout the apartment.
It is best to clean with special vacuum cleaners with air filters. When cleaning, it is advisable not to use products containing a lot of chlorine or strong fragrances. Since mold is considered one of the most common allergens, surfaces in the bathroom and kitchen should be wiped dry and treated with special products once a month.
Infectious dermatitis
The main causes of this disease are infections in non-healing wounds on the skin. The infectious type develops in patients with chickenpox, atopic dermatitis, or another disease if the infection gets into the rash that accompanies these diseases (often by scratching). Also, skin irritation may appear after operations and injuries due to infection with staphylococcus, streptococcus, etc.
The course of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of pustules without clear boundaries on the surface of the skin or purulent inflammation under the skin.
Providing a hypoallergenic environment
It must be remembered that exacerbation of atopic dermatitis can be triggered by inhaling dust containing mites. In the house, sources of dust include mattresses, blankets, pillows, carpets, carpets, upholstered furniture and curtains. Patients with atopic dermatitis are recommended to sleep on pillows and mattresses with synthetic filling, since fluff and wool are considered a favorable breeding ground for mites. They also belong to epidermal allergens. Bed linen must be changed at least twice a week (in this case, it must be boiled once a week). All sleep accessories that cannot be washed must be treated with special preparations.
It is advisable that the house have a minimum number of carpets, which must be treated with special agents that destroy ticks. It is recommended to replace all curtains and curtains with blinds made of polymer materials. During the flowering period, windows can be sealed, since plant pollen can aggravate the course of dermatitis. Areas of increased dust accumulation also include figurines, books, and souvenirs, which are best removed from the room or placed in cabinets.
Red dermatitis, also known as lichen planus
This is a chronic itchy skin disease, which is accompanied by the appearance of pink-red-violet rashes, merging into large plaques, up to 10 cm in size, with the formation of garlands and rings.
Locations: the lateral part of the body, the inner surface of the arms in places of flexion, mucous membranes of the mouth and genitals.
There are several forms of damage to the skin and mucous membranes. Manifestations of the disease are very diverse: papules, spots, erosions, blisters, etc.
Exclusion of nonspecific factors
Prevention of the disease also involves the exclusion of all nonspecific factors that are not allergens, but can aggravate the course of the disease. Triggers that need to be addressed to prevent the disease include:
- Stress aggravates the course of the disease. It has been proven that during times of strong experiences and emotional discomfort, itching and rashes on the skin become more intense. This is why a quarter of atopics begin to develop psychological disorders over time. To combat stress, doctors recommend playing sports, getting proper rest, engaging in various hobbies, and using techniques that help relax muscles.
- Excessive exercise - sweating increases during intense exercise. In combination with tight clothing, this process increases the itching of the skin. Atopics should not give up sports altogether, but it is still advisable to reduce physical activity.
- Climatic influences - temperature changes have a negative impact on the course of the disease, as they can aggravate it. It has been proven that exacerbation occurs during the cold season, so it is advisable to use protective creams in autumn and winter. In the warm season, atopics need to protect their skin from exposure to direct ultraviolet rays. In the room where an atopic person lives, a comfortable microclimate must always be maintained: the air temperature should not exceed 23 degrees, and the humidity should not exceed 60%.
- Diseases of other body systems aggravate the course of the pathology, so it is extremely important to detect and treat them in a timely manner. Diseases that can provoke or aggravate the course of atopic dermatitis include weak immunity, dysfunction of the endocrine and nervous systems, gastrointestinal diseases (hepatitis, cholecystitis, gastritis), ENT diseases.
Attention!
This article is posted for informational purposes only and under no circumstances constitutes scientific material or medical advice and should not serve as a substitute for an in-person consultation with a professional physician.
For diagnostics, diagnosis and treatment, contact qualified doctors! Number of reads: 8206 Date of publication: 08/01/2018
Dermatologists - search service and appointment with dermatologists in Moscow
How to distinguish psoriasis from seborrheic dermatitis?
Diseases are often confused. Although both diseases share common features, they also have many differences. Common characteristics include a chronic type of disease and an undulating course, the presence of rashes, itching, and peeling of the skin. What is the difference between psoriasis and dermatitis?
- Prerequisites for development. If psoriasis appears under the influence of autoimmune, endocrine, and genetic disorders, then seborrheic dermatitis is caused by increased activity of the sebaceous glands and yeast-like fungi.
- Symptoms. Despite the fact that in both cases the skin is covered with scales, their structure and appearance are different. When oily yellow crusts appear, we are talking about seborrheic dermatitis, and when dry gray, white or silvery scales form, psoriasis can be diagnosed.
- Localization. Psoriasis can affect almost all areas of the skin, and seborrheic dermatitis is localized mainly on the scalp, neck and face.
If you experience skin rashes that could be a sign of both dermatitis and psoriasis, be sure to consult a dermatologist. Usually, a qualified doctor can determine what it is by the external manifestations of the disease. If mixed symptoms occur, the dermatologist will write a referral for additional examinations.
Causes of dermatitis in children and adults
The disease is caused by various external and internal causes of dermatitis:
- atopic dermatitis is associated with a complex of factors - dry skin, genetic changes, immune dysfunction, bacterial contamination of the skin, environmental conditions;
- contact dermatitis is the result of direct exposure to one of many irritants - poisonous plants, nickel, cleaning products, preservatives, perfumes, etc.;
- Seborrheic dermatitis is caused by fungal parasitism in the sebaceous secretions of the skin.
Risk factors for the disease:
- Age. The disease can occur at any age, but allergic dermatitis usually begins in infancy.
- Hereditary predisposition. Atopic skin inflammation in a child is more likely if one or both of his parents have allergic diseases.
- Allergic diseases and asthma. People with these conditions are more likely to develop atopic skin lesions.
- Profession. The risk of contact dermatitis increases when working with metals, solvents, cleaning products, and medications.
Accompanying illnesses. The risk of seborrhea is increased by heart failure, Parkinson's disease, and HIV infection.
Reasons for appearance
The main factors that can trigger the appearance of one or another form of dermatitis have already been listed. All inflammation and irritation of skin diseases are the result of remote or provoked causes.
- Remote ones include genetic predisposition or acquired individual predisposition. The latter occurs, for example, due to allergies or a previous infectious disease.
Related causes that trigger the development of dermatitis are various conditions to which the body reacts with skin irritation. These include stress, contact with chemicals, reaction to climate, and hormonal changes in the body.
Regardless of what resulted from the onset of the disease, remember: dermatitis must be treated immediately before it becomes protracted and chronic.
Etiology and pathogenesis
The main role in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis is played by hereditary determinism, that is, heredity. It is a number of hereditary mutations in genes that lead to disruption of the skin barrier and defects of the immune system. The patient also has hypersensitivity to allergens, an increased number of inflammatory mediators and a number of pathogenic microorganisms such as Staphylococcus aureus and Malassezia furfur.
The pathological reaction of the body, which provokes atopic dermatitis, occurs as a result of the interaction of three factors:
- skin barrier dysfunction;
- disturbances in the functioning of the immune system;
- influence of environmental factors.
In addition to the factors described, skin barrier dysfunction can be affected by:
- Reduced levels of ceramides (lipids), which protect the skin from aggressive environmental influences.
- An increase in proteolytic enzymes - substances that are responsible for the speed of cell reaction to external stimuli.
- Exposure to proteases from house dust mites or Staphylococcus aureus.
Violation of the protective barrier leads to high skin permeability to allergens and toxins. As a result of their penetration into tissues, a pathological immune response occurs. It comes from Th2 (T helper cell type 2), a special type of cell that enhances the adaptive immune response. They activate B lymphocytes that produce immunoglobulin E (IgE), which results in an allergic reaction.
During an immune response, characteristic itching and rash appear on the skin. Constant scratching stimulates the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, which in turn cause chronic inflammation. As a result, the epidermis intensively absorbs allergens, which provokes microbial colonization of the skin.
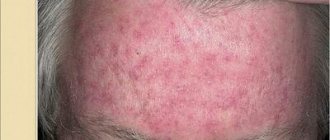
Dermatitis on the skin of the body
A dermatologist can diagnose the disease. Contact him if you notice the first symptoms.
Symptoms
Typical manifestations of skin disease:
- redness
- itching
- combs
- pustules
- peeling skin
Allergic dermatitis can be accompanied by a prolonged runny nose, paroxysmal cough, nasal congestion and sneezing. Acute dermatitis is usually characterized by the formation of subcutaneous blisters filled with colorless liquid. With wet dermatitis, redness and deep cracks form on the skin, from which pus or lymph oozes. Dry dermatitis is characterized by flaking and a feeling of tightness of the skin. Since it is possible to cure your skin, you should never give up, no matter what the symptoms of the disease are!
Antihistamines
For atopic dermatitis, antihistamines are also indicated, which have an antiallergic effect on the body. These drugs effectively block the release of histamine, thereby eliminating swelling, redness and reducing severe itching. Drugs are prescribed in the form of tablets, less often - in the form of injections. Antihistamines include drugs such as loratadine, clemastine, suprastin and others. Fenistil gel has also proven its effectiveness, which successfully blocks P1 receptors, which prevents the release of histamine:
- clemastine - eliminates swelling and itching;
- suprastin - taking this drug blocks histamine receptors and prevents its release;
- loratadine - eases the allergic process and eliminates redness;
- ketotifen - blocks the release of mediators, thereby eliminating their effects.
Treatment is real!
How to treat allergic dermatitis is an individual question. Sometimes it is enough to eliminate the irritating substance, sometimes drug therapy is necessary.
Treatment of any type of dermatitis, even such a complex form as chronic itching, begins with determining the source of such a reaction. Often you just need to stop contact with the irritating substance, and the reaction on the skin will gradually go away on its own. In more complex cases, therapy with antihistamines is necessary.
Treatment at home is only possible for mild skin lesions and a known cause. If you have any suspicions or doubts, you should contact a professional.
The answer to the question “How to cure dermatitis?” should be added a little: treatment of dermatitis should be accompanied by maintaining a healthy lifestyle. After all, irritation on the skin can occur with general weakening of the body. Therefore, it is necessary to switch to a diet of natural hypoallergenic products, maintain hygiene of the affected areas, and limit the use of decorative cosmetics that do not allow the skin to breathe.
An important aspect is the impact on the symptoms of the disease in order to relieve itching, eliminate the feeling of dryness and tightness of the skin - this is usually what worries patients the most, preventing them from leading a full lifestyle.
Sedatives
Many patients diagnosed with atopic dermatitis complain of severe and even painful itching. This condition sooner or later leads to emotional and mental disorders. Therefore, for successful treatment it is extremely important to normalize the patient’s emotional background in order to prevent exacerbation of the disease. To eliminate tension and stress, the patient is prescribed sedatives - herbal remedies (tincture of passionflower or motherwort) and tranquilizers (tofisopam, alprazolam):
- tofisopam - taking 3-6 tablets of this drug helps relieve tension and has a stress-protective effect;
- bellataminal - has a calming effect on the body and relieves excitability;
- persen - has a hypnotic effect;
- atarax - taking 2 tablets of the drug per day promotes a mild hypnotic and sedative effect;
- amitriptyline - normalizes the emotional background and eliminates severe overstrain;
- diazepam - relieves anxiety and nervous tension.
Ointment "La-Cri" - a reliable assistant
To care for affected skin, either alone or in combination with ongoing therapy, we recommend using La Cree cream. This is a non-hormonal product that does not contain dyes or fragrances, and therefore is suitable even for newborns, nursing and pregnant women.
The natural composition of the cream is selected in such a way as to simultaneously solve all the problems of irritated skin. The product perfectly relieves redness and itching, promotes rapid regeneration of damaged skin, nourishes and softens even very dry and flaky skin.
As an auxiliary product, you can use the non-greasy emulsion “La-Cri”, which provides gentle care for the skin, moisturizing it and protecting it from drying out. Treatment of dermatitis on the face will be faster with La-Cri washing gel, which gently cleanses delicate skin without clogging pores.
Experts' opinion
The conducted clinical study proves the high efficiency, safety and tolerability of products for daily skin care of children with mild and moderate forms of atopic dermatitis and during remission, accompanied by a decrease in the quality of life of patients. As a result of therapy, a decrease in the activity of the inflammatory process, a decrease in dryness, itching and flaking was noted.
The products are recommended by the St. Petersburg branch of the Union of Pediatricians of Russia.
It has been empirically proven that La Cree emulsion moisturizes and nourishes the skin, relieves itching and irritation, and also soothes and restores the skin.
How does the immune system normally work?
The concept of atopic dermatitis reflects the immunological mechanism of pathology development. It is based on the body’s ability to produce an excess amount of antibodies in response to incoming allergens. Antibodies combine with the allergen, which provokes a more pronounced allergic reaction than should be normal.
Let's figure out how the immune system should work normally. It’s worth starting with the fact that the system is represented by several organs (thymus, lymph nodes) and immunocompetent cells. Their main task is to protect the body from foreign elements: viruses, bacteria, fungi and allergens. This is accomplished through the development of protective reactions that are provided by certain cells. That is, the immune system recognizes foreign elements, destroys them and forms immunological memory.
Two types of cells help to perform such functions - B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes (killers, suppressors and helpers). Each type of cell has its own role in the operation of the system. Thus, B lymphocytes recognize foreign elements and form memory cells. T-killers are necessary to destroy foreign elements, T-helpers are involved in strengthening the immune response in response to the penetration of pathogenic agents. Suppressor T cells regulate the strength of the immune response by controlling the number of helper and killer cells.
The key to proper functioning of the immune system is a certain ratio of immunocompetent cells. With any quantitative disturbances, the immune reaction becomes pronounced, which is what happens during atopic dermatitis.
To prevent repeated exposure to the pathogen, the immune system forms a memory. It is synthesized by certain antibodies, or immunoglobulins, that form on the surface of B lymphocytes. Antibodies are proteins that have high specificity for antigens. As a result of their connection with antigens, an immune response is triggered in the body.
Several types of antibodies may be present in the body - immunoglobulins A, M, G and E. Each of them has its own function. For example, immunoglobulins A are responsible for protecting the respiratory tract. Immunoglobulins M and G are components of humoral immunity and arise as a result of the penetration of bacteria and viruses. Also, immunoglobulins G appear some time after the disease and can remain in the body for up to several years.
Immunoglobulins E arise as a response to the penetration of allergens. They are the ones who trigger an allergic reaction, which is accompanied by the release of various biological substances (for example, histamine). Under the influence of these substances, a person develops characteristic allergy symptoms: redness, itching, swelling.
Normally, the body contains very little immunoglobulin E, since these cells quickly disintegrate. However, as a result of a genetic mutation, some people have very high levels of these immunoglobulins, which increases the risk of developing atopic dermatitis on the face and body.
When it first encounters a foreign element, the immune system synthesizes certain antibodies. They help protect the body from re-infection for a certain period of time. During an allergic reaction, the process occurs differently. Upon contact with an allergen, a sufficient amount of antibodies is produced, which will subsequently bind to the allergen. Upon repeated contact, an antigen-antibody complex appears. An allergen acts as an antigen. An antibody is a protein produced by the body.
The antigen-antibody complex triggers a whole chain of immunoallergic reactions. With a large amount of immunoglobulin E, a pronounced and prolonged allergy appears. Simultaneously with the allergic reaction, a number of biologically active substances are released. It is these substances that trigger pathological processes that lead to the appearance of typical allergy symptoms. If the amount of immunoglobulins remains high, then the allergic reaction does not disappear, which indicates the development of atopy.
How to care for skin with dermatitis?
Helping herbs
Many plants have an amazing property - when absorbed into the skin, they reduce inflammation and normalize its structure. Therefore, a common remedy for the treatment of dermatitis is herbal compresses, wraps, and herbal ointments for dermatitis.
You can use a single plant or herbal mixtures that contain several herbs.
- Grind the celandine and squeeze the juice out of the resulting mass. Dilute the juice with boiled water in a ratio of 1 to 2. Use the solution for compresses: soak gauze in it and apply to the affected skin for 10-15 minutes.
- 1 tbsp. Pour 100 ml of boiling water over a spoonful of dry crushed string and leave until a dark brown solution is obtained. Moisten gauze or bandage in the prepared concentrate and apply it to the irritated skin until completely dry (not with weeping dermatitis, otherwise the bandage may dry to the skin). The procedure can be carried out 3 times a day.
Recipe with tar soap
The healing properties of tar have been known for a very long time. This thick oily liquid has a positive effect on the condition of the skin. Birch tar has an anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect, improves blood circulation and stimulates skin regeneration.
You can find tar soap on sale and use it to wash skin affected by dermatitis, or prepare soap according to a folk recipe.
- Mix 100 g of crushed and melted baby soap with 2 tbsp. spoons of any oil, add 2 tbsp. fly in the ointment and 100 ml of water. Mix the resulting mixture until smooth.
Glucocorticosteroids
The most commonly used drugs from the group of glucocorticosteroids include the following:
- afloderm - can have an antipruritic and anti-inflammatory effect, reduce swelling caused by inflammation, and constrict blood vessels;
- hydrocortisone - reduces pronounced redness of the skin, and also inhibits the development of edema at the site of inflammation and the manifestation of an allergic reaction;
- elocom - has a strong antipruritic effect and eliminates swelling;
- dermovate - immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory effects.
Chatterbox
Prepare a semi-alcohol solution: to do this, dilute 40 ml of alcohol with the same volume of water. Add 2 ml of 2% lidocaine or novocaine to the resulting solution - this will help relieve the painful symptom.
Add 30 g of dry white clay and the same amount of powdered zinc. Mix thoroughly until smooth.
The finished mash is applied to the affected skin, previously cleaned with an antiseptic, in a thin layer, the mixture is left on the skin for 20 minutes. There is no need to apply a bandage on top; excess talker can be carefully removed, and the remaining part on the skin forms a protective film.
Remember! Do not self-medicate, consult a doctor!
Cutaneous dermatitis is a general name for skin disorders caused by various irritants. All irritants can be divided into 2 large groups: those that cause irritation upon direct contact and those that affect the body when they get inside.
Sources:
- Molochkova Yulia Vladimirovna, Dermatology. Brief reference book, publishing house: GEOTAR-Media, 2017
- Baumann Leslie, Cosmetic Dermatology. Principles and practice, publishing house: MEDpress-inform, 2016
- Ratner Desiri, Avram M.R., Avram M.M., Procedures in Dermatology. Clinical cosmetology, Publishing house: GEOTAR-Media, 2019
- Sukolin Gennady Ivanovich, Clinical dermatology. A short guide to the diagnosis and treatment of dermatoses, publishing house: Notabene, 2017
Photos of dermatitis
Personal hygiene
A person prone to atopic dermatitis must comply with a list of personal hygiene requirements that will help him prevent exacerbation of the disease. First of all, you need to give up all cosmetics that contain alcohol. Particular attention should be paid to bathing: give preference to the shower, swim for no more than 20 minutes in warm water with a temperature no higher than 36 degrees, do not visit public bathing places (especially swimming pools). People prone to dermatitis are advised to wear underwear made from natural materials and loose clothing that does not fit tightly to the body.