The medicine belongs to the subgroup of H1-histamine receptor blockers. Diphenhydramine has a sedative and hypnotic spectrum of action and is not a narcotic. Taking the medication in large dosages or together with alcoholic beverages can cause hallucinations. Diphenhydramine is addictive.
Indications for use
Diphenhydramine is indicated for:
- hives;
- itchy dermatoses;
- vasomotor rhinitis;
- allergic conjunctivitis;
- serum sickness;
- kinetosis;
- chorea.
The medication is also indicated to prevent the progression of allergic reactions during blood transfusion, in the complex therapy of bronchial asthma, gastritis, and gastric ulcers. Diphenhydramine is also effective in treating sleep problems, colds, and extensive injuries to the dermis and soft tissues. It is actively used for local anesthesia in patients who suffer from allergic reactions to other anesthetic medications.
Features of the composition and pharmacological action of Diphenhydramine
The drug is prepared in tablets and solution for intramuscular or intravenous injection. The main active ingredient of Diphenhydramine is diphenhydramine hydrochloride. Each tablet contains 50 mg of the active ingredient, an additional substance in the solution is purified water.
The medication causes local anesthesia; when consuming the pills, a temporary sensation of loss of sensitivity of the oral mucosa appears. Diphenhydramine has antispasmodic, antiemetic and hypnotic effects. The drug is ineffective in the allergic form of bronchospasm and bronchial asthma.
Contraindications and special instructions
Diphenhydramine is contraindicated for:
- stenosing gastric ulcer;
- lactation;
- bearing a child;
- excessive sensitivity to the components in the composition;
- angle-closure glaucoma;
- bladder neck stenosis;
- pyloroduodenal obstruction;
- benign enlargement of the prostate gland.
Carry out therapy with special attention in case of lung pathologies, in case of increased intraocular pressure, in case of vascular and heart diseases, and in old age. It is not recommended to use the medication for people who drive a vehicle or need increased concentration.
An alcoholic cannot take the drug. Mixing diphenhydramine with alcohol leads to narcotic intoxication.
Indications for Diphenhydramine therapy and contraindications
The instructions recommend the use of the medicine for patients:
- with nettle fever, hay fever, vasomotor rhinitis;
- itchy dermatoses, acute iridocyclitis, conjunctivitis of allergic etiology;
- Quincke's edema, capillary toxicosis, reaction to vaccination;
- allergies caused by taking medications or blood transfusions;
- problems with sleep, colds;
- burns, violations of the integrity of the dermis or soft tissues;
- parkinsonism, chorea, Meniere's syndrome;
- air or sea sickness.
Diphenhydramine is prescribed for local anesthesia - in case of intolerance to other painkillers. The medication is included in the complex treatment of anaphylaxis, radiation sickness, and gastrointestinal ulcers.
The drug is contraindicated:
- in case of individual intolerance to the component composition;
- angle-closure glaucoma, enlargement (by weight and volume) of the prostate;
- stenosing gastrointestinal ulcer;
- Marion's disease;
- chronic inflammation of the respiratory tract;
- pyloroduodenal obstruction.
The medicine is not used for pregnant and lactating women, newborns and premature infants.
Side effects
Uncontrolled use of the drug and overdose provoke adverse reactions. The most common disorders are:
- nausea, vomiting, problems with stool, dry mouth, numbness of the mucous membrane, loss of appetite;
- allergic reactions;
- disruption of the heart, changes in the condition of blood vessels, anemia, tachycardia;
- dryness and congestion of the nasal passages, difficulty breathing;
- fatigue, drowsiness, lack of coordination of movements;
- cramps, weakness, headaches.
Patients may also experience increased sweating.
In case of an overdose, overexcitation or an overly depressed state, dilated pupils of depression, and redness of the face occur. After taking the remedy, gastric lavage is necessary to combat negative reactions.
Attention! In particularly severe cases, confusion may occur.
Adverse reactions
The abstract indicates the development of non-standard effects during Diphenhydramine therapy:
- a state of general weakness and fatigue, drowsiness;
- decreased concentration, cephalgia with dizziness;
- problems with coordination of movements, unreasonable anxiety;
- increased irritability, nervousness, euphoria;
- insomnia, involuntary muscle tremors;
- neuritis, convulsive syndrome with partial loss of sensitivity;
- decreased visual acuity, diplopia, extraneous noise in the ears.
With local damage to the brain, the drug in any dosage can cause an attack of epilepsy. The medication provokes the appearance of:
- decreased blood pressure, tachycardia, hemolytic anemia;
- dryness of the mucous membranes of the mouth, anorexia, dyspeptic disorders;
- frequent or difficult urination, delayed urine output, early menstruation;
- nasal congestion, breathing problems;
- increased thickness of secretions in the bronchi, a feeling of tightness in the chest;
- nettle fever, anaphylaxis, skin rashes.
Diphenhydramine increases the activity of the sweat glands, causing fever with chills and photosensitivity.
Benefits and harms of use
Reviews from patients who suffer from insomnia indicate that the product helps with the problem. It guarantees a quick fall asleep and sound sleep until the morning. The drug is also effective against infectious diseases.
Despite the large number of advantages, there are also disadvantages. The disadvantages include:
- addictive;
- toxic, so it can provoke hallucinations;
- provokes headaches and poor health in the morning;
- inability to control emotions, inhibition.
A doctor's consultation is required.
Features of interaction and application
Taking the drug together with tranquilizers, alcoholic beverages, sleeping pills or sedatives leads to central nervous system depression. Combination with MAO inhibitors causes activation and prolongation of anticholinergic effects.
Increased caution during therapy with Diphenhydramine is required for hyperthyroidism, increased IOP, and cardiovascular pathologies. Physician supervision is necessary for elderly patients. The medicine is not recommended for patients whose work requires constant concentration: when driving a car or operating complex moving mechanisms.
During therapy it is necessary to avoid drinking alcohol.
Instructions for use and dosage
Diphenhydramine tablets taken orally 30 or 50 mg per day 1 to 3 times a day. Duration of therapy is from 10 to 15 days. The maximum single dosage for adults is 100 mg, daily dosage is 250 mg. Take half an hour before bedtime.
Doctors do not recommend taking Diphenhydramine for children under 7 months. The need to take the drug depends on the disease, the characteristics of the baby’s body, and his age. For sleep problems, children are given milder sleeping pills and sedatives. Children aged 2 to 6 years old receive 12.5 or 50 mg every 4-6 hours, from 6 to 12 years old they receive 25 or 50 mg 3-4 times a day. If a liquid form is used, inject slowly 20 or 50 mg. For intravenous administration, dilute in 9% sodium chloride solution.
Diphenhydramine is contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding. If there is an urgent need, it is used only as prescribed by a doctor.
Attention! Diphenhydramine is contraindicated in the first and second trimesters. The drug is not prescribed during feeding, as there is a possibility of complications developing in the baby.
Patients over 65 years of age are not recommended to use Diphenhydramine for sleep. There is a risk of accommodation disturbance, dizziness, urinary retention, memory loss, and constipation. A doctor's consultation is required.
Nuances of dosages from the instructions
The tablets are intended for oral administration. Doses depend on age and current pathology6
- for adults – from 30 to 50 mg, up to three times a day, therapy lasts two weeks;
- combat insomnia - in a similar volume before bedtime;
- warnings of seasickness or air sickness - in the same amount, half an hour before the trip;
- children from 6 to 12 years old - from 15 to 30 mg per procedure.
The maximum daily dose cannot exceed 250 mg, a single dose - 100 mg.
Accidentally exceeding the recommended amount of Diphenhydramine contributes to the development of an overdose. Intoxication is manifested by dryness of the oral mucosa, redness of the face, persistent mydriasis, and impaired clarity of consciousness. In children, excitement or depression of the central nervous system and convulsive syndrome may occur. A complex overdose can lead to death. Treatment of poisoning consists of gastric lavage, taking sorbents, supportive and symptomatic therapy, with constant monitoring of blood pressure and breathing.
Customer Reviews
Customer reviews indicate a high effect from taking it.
Anna, 20 years old
“I study at the university, so I have to stay up long during the session and go to bed late. Overwork and tension negatively affect your general condition. For insomnia, I took the drug before bed. The regime has returned to normal, aggression and irritability have passed.”
Sergey, 28 years old
“Diphenhydramine is an inexpensive drug that very quickly normalizes sleep. I work in security, so I have to work both day and night shifts. The mode is down. The product helps you fall asleep quickly and not wake up at night.”
DIMEDROL. Dimedrolum.Properties. White fine-crystalline powder with a bitter taste. Hygroscopic, easily soluble in water. Aqueous solutions are sterilized at 100°C for 30 minutes.
Release form. Available in powder, tablets of 0.025 and 0.05 g and in ampoules of 1 ml of 1% solution.
Store according to list B, in standard packaging, in a place protected from light.
Action and application.
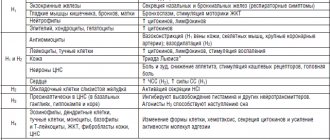
Diphenhydramine reduces the body's response to histamine, relieves the spasm of smooth muscles caused by the latter, reduces capillary permeability, prevents the development of tissue edema caused by histamine, weakens the hypotensive effect of histamine, prevents and weakens the course of allergic reactions. Diphenhydramine, like other antihistamines, blocks the biochemical systems in the tissues affected by histamine and modifies its effect. When administered for prophylactic purposes, diphenhydramine attaches to cell receptors before histamine, and when used for therapeutic purposes, it replaces histamine on cell receptors - it exhibits a competitive effect.
Diphenhydramine has a local anesthetic effect, relaxes smooth muscles, blocks H-cholinergic receptors of the autonomic nodes, increases the excitability of the peripheral cholinergic and adrenoreactive systems of the body, exhibits sedative, moderate hypnotic and antiemetic effects. Its effect begins in 15-30 minutes and lasts 4-6 hours.
Used to relieve allergic reactions, treat urticaria, serum sickness, drug anaphylaxis, pruritic dermatitis, prevent and treat motion sickness in animals, allergic conjunctivitis and rhinitis. Prescribed for asthma in cows, anaphylactic shock, atony and tympanic rumen, retained placenta, metritis, postpartum paresis of cows. For atony and tympany of the rumen, this therapy is useful at the onset of the disease in animals receiving protein-rich food.
Diphenhydramine is sometimes used for polyarthritis, articular and muscular rheumatism (the ointment is rubbed in or injected intradermally). Used to treat anaphylactic shock in cattle caused by sensitization during the administration of biological products, to reduce reactions during blood transfusions and blood-substituting fluids, during radiation sickness, as a sedative in combination with sleeping pills. It is often used in dogs for dermatitis (itching, erythema, eczema, etc.), gastric dilatation, and drug-induced anaphylaxis.
Prescribed orally, intramuscularly, intravenously and locally 1-2 times a day for several (7-12) days. For instillation into the eye, use a 0.5% solution (preferably a 2% solution of boric acid) 1-3 drops 2-3 times a day.
doses :
horses 0.1-0.5 g, cattle 0.3-0.6 g, dogs 0.02-0.04 g;
orally
1.5-2 times more than subcutaneously.