Composition and release form
| Effervescent tablets | 1 table |
| magnesium lactate | 200 mg |
| magnesium carbonate | 100 mg |
| pyridoxine hydrochloride (vitamin B6) | 2 mg |
| cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) | 0.001 mg |
| folic acid | 0.2 mg |
| excipients: sodium bicarbonate (sodium bicarbonate); lemon acid; sodium saccharinate; sorbitol; polyethylene glycol (macrogol); flavor additive |
in a pencil case 10 or 12 pcs.; in a cardboard pack or in an envelope pack with a device for hanging 1 pencil case.
Buy Magnesium plus effervescent tablets No. 10 in pharmacies
Instructions for use Magnesium plus tab. thorn. No. 10
Dosage forms: effervescent tablets
Synonyms There are no synonyms. Group Magnesium-based products International nonproprietary name No INN. Manufacturers Natur Product (France)
Description of the drug
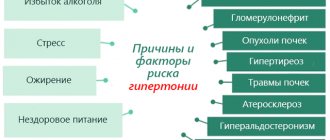
Magnesium Plus Magnesium Plus is a vitamin-like metabolic preparation based on magnesium. It is used for magnesium deficiency in the body, sleep disturbances, irritability, anxiety, and asthenic syndrome. A decrease in magnesium content in the blood is observed with uncontrollable vomiting, diarrhea, thyrotoxicosis, hyperfunction of the parathyroid glands, chronic alcoholism, primary aldosteronism, renal acidosis, liver cirrhosis, epilepsy, eclampsia and pancreatitis.
Latin name: MAGNESIUM PLUS / MAGNESIUM PLUS.
Composition and release form: Magnesium plus effervescent tablets, 10 pcs. packaged. 1 tablet Magnesium Plus contains: magnesium carbonate 100 mg, magnesium lactate 200 mg, pyridoxine (vitamin B6) 2 mg, cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) 1 mcg, folic acid 200 mcg.
Pharmacological action: Magnesium plus is a vitamin-like metabolic drug based on magnesium. 1 tablet of Magnesium Plus contains 15% of the daily requirement for magnesium and 100% of the daily requirement of vitamins B6, B12 and folic acid. Magnesium is one of the most important bioelements necessary for the normal functioning of the body. The human body contains about 20 g of magnesium. The magnesium content in cells is 3-10 times higher than its content in extracellular fluids. The daily human need for magnesium is about 300 mg. Magnesium activates many enzymes, regulating the reactions of phosphorus metabolism, glycolysis, metabolism of lipid proteins, and nucleic acids. In most reactions in which ATP is involved, the true substrate is the ATP-Magnesium complex. Magnesium is necessary for the normal functioning of nerve and muscle tissue; reduces the excitability of nerve cells and neuromuscular transmission. For example, Magnesium sulfate is prescribed as an anticonvulsant and sedative. With a low magnesium content in the blood plasma, disturbances in neuromuscular transmission, tetany, the formation of trophic ulcers, pathological calcification of tissues and other phenomena characteristic of hypercalcemia, but occurring against the background of normal calcium levels in the body, may occur. An increase in the concentration of magnesium in the blood plasma has a sedative and sometimes narcotic effect. Vitamins B6, B12 and folic acid are involved in the regulation of nervous system metabolism and complement the effect of magnesium.
Indications: magnesium deficiency in the body; sleep disorders; irritability; anxiety; asthenic syndrome. A decrease in magnesium content in the blood is observed with uncontrollable vomiting, diarrhea, thyrotoxicosis, hyperfunction of the parathyroid glands, chronic alcoholism, primary aldosteronism, renal acidosis, liver cirrhosis, epilepsy, eclampsia and pancreatitis.
Directions for use and dosage: Magnesium plus is taken orally, 1 tablet in the morning or afternoon, dissolved in 1 glass of water. Children aged 4-12 years: 1/2 tablet.
Contraindications : hypersensitivity; severe renal failure; depression of the respiratory center; hypothyroidism; diabetic ketoacidosis; children up to 3 years old.
Side effects: Possible allergic reactions, diarrhea, abdominal pain.
Storage conditions: In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Shelf life : 3 years.
Pharmacodynamics
Magnesium is a vital element. Plays an important role in the activity of the nervous system, participates in the regulation of the transmission of nerve impulses and in muscle contraction, in most metabolic reactions, promotes the production and consumption of energy, and plays an important physiological role in maintaining ion balance.
Magnesium deficiency manifests itself in the form of neuromuscular disorders (muscle weakness, tremors, spasms, convulsions), mental disorders (insomnia, irritability, anxiety), heart rhythm disturbances (extrasystole, tachycardia) and gastrointestinal tract activity (pain, diarrhea, cramps, bloating intestines). Vitamin B6 plays an important role in metabolism, helps maintain the structure and function of bones, teeth, and gums; influences erythropoiesis, promotes the normal functioning of the nervous system and complements the effect of magnesium.
Vitamin B12 and folic acid are involved in many enzymatic reactions.
Magnesium Plus tablets spike No. 10
Compound
Active ingredients: magnesium lactate 200 mg, magnesium carbonate 100 mg, pyridoxine hydrochloride 2 mg, folic acid 0.2 mg, cyanocobalamin 0.1% 1 mg (which corresponds to the content of cyanocobalamin 0.001 mg).
Excipients: sodium bicarbonate - 800 mg, citric acid - 1300 mg, sodium saccharinate dihydrate - 10 mg, sorbitol - 966.8 mg, macrogol - 40 mg, lime flavor - 80 mg.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption of magnesium in the gastrointestinal tract is no more than 50% of the dose taken. In the body, 99% of magnesium is found inside cells. Approximately 2/3 of intracellular magnesium is distributed in bone tissue, and 1/3 is in smooth and striated muscle tissue. Excreted in urine. Glomerular filtration is 70% of plasma filtration, tubular reabsorption is 95-97%. At least 1/3 of the administered dose of magnesium is excreted in the urine.
Pyridoxine hydrochloride is absorbed rapidly throughout the small intestine, with larger amounts absorbed in the jejunum. Metabolized in the liver to form pharmacologically active metabolites (pyridoxal phosphate and pyridoxaminophosphate). Pyridoxal phosphate is 90% bound to plasma proteins. Penetrates well into all tissues; accumulates mainly in the liver, less - in muscles and the central nervous system. Penetrates the placenta and is secreted into breast milk. T1/2 - 15-20 days. It is excreted by the kidneys (with intravenous administration - with bile 2%), as well as during hemodialysis. About 8-10% of the drug is excreted unchanged in the urine.
Folic acid is well and completely absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, mainly in the upper parts of the duodenum. Intensively binds to plasma proteins. Penetrates through the blood-brain barrier, the placenta and into breast milk. The time to reach maximum concentration is 60 minutes. Deposited and metabolized in the liver to form tetrahydrofolic acid (in the presence of ascorbic acid under the action of dihydrofolate reductase). It is excreted by the kidneys, mainly in the form of metabolites.
Cyanocobalamin is absorbed in the small (partly large) intestine, combining with intrinsic factor and becoming protected from intestinal microflora. In the blood, cyanocobalamin combines with transcobalamins I and II, with which it is transported to tissues. Cyanocobalamin is deposited mainly in the liver and is excreted from the liver with bile into the intestine, from where it is reabsorbed. Eliminated from the body by the kidneys. After oral administration of up to 2 mg, 30-97% is absorbed; absorption of the drug (depending on the internal absorption factor) after administration at a dose of more than 2 mg is noticeably reduced. Communication with plasma proteins - 90%. Cmax after oral administration is achieved within 6-14 hours. T1/2 in the liver is 500 days. Excreted with normal renal function - 7-10% by the kidneys, about 50% - with feces; with reduced renal function - 0-7% by the kidneys, 70-100% - by feces. Penetrates through the placental barrier into breast milk.
Indications for use
Prevention of magnesium deficiency and related conditions:
- neuromuscular disorders (muscle weakness, tremors, spasms, convulsions);
- mental disorders (insomnia, irritability, anxiety);
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract (pain, cramps, bloating).
Contraindications
- severe renal failure (creatinine clearance<30 ml/min);
- children under 6 years of age;
- hypersensitivity to the components of the combination.
Carefully:
Moderate renal failure (since there is a risk of developing hypermagnesemia).
Directions for use and doses
Inside.
Adults and children over 12 years old: 1-2 tablets.
Children from 6 to 12 years: 1/2 tablet.
Take in the morning, after dissolving in a glass of water.
Storage conditions
At a temperature not higher than 25 °C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Best before date
3 years. Do not use after the expiration date.
special instructions
In cases of concomitant calcium deficiency, magnesium deficiency must be corrected before supplemental calcium is administered.
With frequent use of laxatives, alcohol, increased physical and mental stress, the need for magnesium increases.
Description
A drug that replenishes magnesium deficiency in the body.
Dosage form
Effervescent tablets are round, flat-cylindrical, with a beveled edge, white or white with a slightly yellowish-greenish tint, with a dividing strip on one side, with a slight specific odor.
Use in children
Contraindicated for children under 6 years of age. Children from 6 to 12 years old - 1/2 tablet.
Action
Magnesium is a vital element. Plays an important role in the activity of the nervous system, participates in the regulation of the transmission of nerve impulses and in muscle contraction, in most metabolic reactions, promotes the production and consumption of energy, and plays an important physiological role in maintaining ion balance.
Magnesium deficiency manifests itself in the form of neuromuscular disorders (insomnia, irritability, anxiety), heart rhythm disturbances (extrasystole, tachycardia) and gastrointestinal tract activity (pain, diarrhea, cramps, bloating).
Vitamin B6 plays an important role in metabolism, contributes to the normal functioning of the nervous system and complements the effect of magnesium.
Vitamin B12 and folic acid are involved in many enzymatic reactions.
Side effects
Possible: allergic reactions, dyspeptic disorders (diarrhea, abdominal pain).
When used in high doses: hypermagnesemia may develop.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
During pregnancy and lactation, the drug can be used with caution and according to indications, since at this time the need for magnesium increases significantly. If its content is not balanced, it can lead to serious complications, including miscarriage.
Magnesium passes into breast milk, so use of the drug should be avoided during breastfeeding.
Interaction
Phosphates and calcium salts reduce the absorption of magnesium in the gastrointestinal tract.
Magnesium preparations reduce the absorption of tetracycline; It is recommended to wait 3 hours before using this combination.
Vitamin B6 inhibits the activity of levodopa.
Overdose
Symptoms of overdose: drop in blood pressure, nausea, vomiting, slowed reflexes, respiratory depression, coma, cardiac arrest and cardiac paralysis, anuria.
Treatment: rehydration, forced diuresis. In case of renal failure, hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis is necessary.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
The drug does not affect the ability to drive vehicles or operate potentially dangerous machinery.
Magnesium plus
Magnesium absorption
in the gastrointestinal tract is no more than 50% of the dose taken. In the body, 99% of magnesium is found inside cells. Approximately 2/3 of intracellular magnesium is distributed in bone tissue, and 1/3 is in smooth and striated muscle tissue. Excreted in urine. Glomerular filtration is 70% of plasma filtration, tubular reabsorption is 95-97%. At least 1/3 of the administered dose of magnesium is excreted in the urine.
Pyridoxine hydrochloride
Absorbed quickly throughout the small intestine, larger amounts are absorbed in the jejunum. Metabolized in the liver to form pharmacologically active metabolites (pyridoxal phosphate and pyridoxaminophosphate). Pyridoxal phosphate binds to plasma proteins by 90%. Penetrates well into all tissues; accumulates mainly in the liver, less - in muscles and the central nervous system. Penetrates the placenta and is secreted into breast milk. T1/2 - 15-20 days. It is excreted by the kidneys (with intravenous administration - with bile 2%), as well as during hemodialysis. About 8-10% of the drug is excreted unchanged in the urine.
Folic acid
is well and completely absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, mainly in the upper parts of the duodenum. Intensively binds to plasma proteins. Penetrates through the blood-brain barrier, the placenta and into breast milk. The time to reach maximum concentration is 60 minutes. Deposited and metabolized in the liver to form tetrahydrofolic acid (in the presence of ascorbic acid under the action of dihydrofolate reductase). It is excreted by the kidneys, mainly in the form of metabolites.
Cyanocobalamin
absorbed in the small (partly large) intestine, combining with internal factor, becoming protected from intestinal microflora. In the blood, Cyanocobalamin combines with transcobalamins I and II, with which it is transported to tissues. Cyanocobalamin is deposited mainly in the liver and is excreted from the liver with bile into the intestine, from where it is reabsorbed. Eliminated from the body by the kidneys. After oral administration of up to 2 mg, 30-97% is absorbed; absorption of the drug (depending on the internal absorption factor) after administration at a dose of more than 2 mg is noticeably reduced. Communication with plasma proteins - 90%. Cmax after oral administration is achieved within 6-14 hours. T1/2 in the liver is 500 days. Excreted with normal renal function - 7-10% by the kidneys, about 50% - with feces; with reduced renal function - 0-7% by the kidneys, 70-100% - by feces. Penetrates through the placental barrier into breast milk.