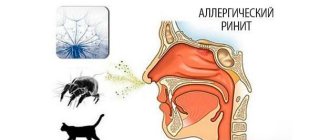
Increasingly, people are seeking help with complaints of nasal congestion, persistent runny nose, and impaired nasal breathing. Attempts to treat yourself, purchasing at the pharmacy those not prescribed by a doctor and therefore not the fact that suitable medications, often lead not to improvement, but, on the contrary, to an even greater deterioration of the condition. The symptoms listed above most likely indicate the development of a disease called medicinal vasomotor rhinitis or drug runny nose .
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of the disease medicinal (vasomotor) rhinitis or drug runny nose appear at the microscopic and macroscopic levels.
Symptoms of the disease at the microscopic level:
- the presence of a multilayer non-keratinizing integument;
- loss of epithelial cilia;
- enlargement (hyperplasia) of glands with increased secretion;
- increasing capillary permeability.
Macroscopic symptoms:
- nasal breathing is difficult, which occurs due to an increase in the volume of the nasal turbinates, which often leads to impaired sensitivity of receptors, in particular the sense of smell;
- mucous clear discharge from the nose;
- the appearance of burning and itching in the sinuses;
- sleep disturbance;
- the appearance of snoring.
The protective function of the body decreases, which affects the general condition of the patient, blood pressure rises, and tachycardia appears.
Tonsilgon N as an anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory drug for acute ENT pathology
The article substantiates the use of immunomodulators in the treatment of infectious respiratory diseases and the prevention of their relapses in pediatric practice. It has been shown that one of the most effective and safe drugs for children is the herbal medicine Tonzilgon N, due to its complex antiseptic, immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory and antiviral effects. Data from our own study in children with acute catarrhal nasopharyngitis of mild and moderate severity are presented, confirming the effectiveness of the drug Tonsilgon N when added to symptomatic therapy in relieving the main symptoms of viral infection in children and reducing the number of complications. The study also demonstrated the effectiveness of the drug in the prevention of ARVI in frequently ill children aged 3–6 years, which resulted in a 3-fold reduction in the frequency of ARVI episodes.
Table. Pharmacological effects of the active components of the drug Tonsilgon N
Frequent acute respiratory diseases (ARI) occupy a leading place in the structure of morbidity among children. More than 80% of the child population annually consults doctors with various forms of acute respiratory infections. Acute forms of respiratory diseases lead to structural changes in the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, disruption of the body's adaptive defense mechanisms and the formation of early chronic pathology of the ENT organs, bronchopulmonary system, as well as other somatic diseases. On average, each child, depending on age, suffers from 2-3 to 5-6 episodes of acute respiratory infections per year. Among children attending preschool institutions, a significant portion (60%) are often ill children. Moreover, in a third of cases, not only frequent and repeated diseases are observed, but also a long-term (more than 2 weeks) ongoing respiratory infection. In such children, acute respiratory infections are severe, with complications in the form of adenoiditis, sinusitis, tracheobronchitis, and otitis. These clinical features of respiratory diseases in frequently ill children are associated with the imperfection of their specific immune defense and with the weakening of the nonspecific resistance of the growing organism [1, 2].
Among the etiological factors of acute respiratory infections in frequently ill children, the leading role is played by viral infection (up to 90%): influenza A viruses (serotypes 1, 2), parainfluenza (serotypes 1, 2), respiratory syncytial viruses, adenoviruses (serotypes 1–4), rhinoviruses, enteroviruses. Bacterial infections account for only a quarter of respiratory diseases in this group of children, and the causative agents are pneumococcus, staphylococcus, group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus, and Haemophilus influenzae [2]. In adolescents with recurrent diseases, ENT pathology is diagnosed 3 times more often, allergic diseases (bronchial asthma, atopic dermatitis, drug allergies) 2 times more often, and chronic pathology of the digestive organs 6 times more often. With an increase in the frequency of episodes of respiratory infections, a decrease in the anti-adhesive activity of saliva is observed [3].
It is known that various types of immune response disorders are accompanied by the sequential appearance of signs of immunodeficiency, allergic, autoimmune and oncological pathologies. Infections, injuries, chronic physiological and mental stress cause a state of secondary immunodeficiency in weakened patients. This is facilitated by the deterioration of the environmental situation and the unreasonable prescription of antibiotics, leading to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains of microorganisms. All these factors lead to an increase in the incidence of upper respiratory tract diseases, which, in turn, lead to an even greater decrease in immunity [4, 5]. Treatment and prevention of such conditions is impossible without increasing the body's own defenses. Infections of the ENT organs with insufficient function of the immune system take a chronic course, the body's response is insufficient to completely suppress the pathogens [6].
The prospects for treating upper respiratory tract pathology and preventing its relapses are currently largely associated with the use of immunomodulatory drugs. There are many different immunomodulators: thymus preparations, microbial agents, interferon preparations and others. The herbal drug Tonsilgon N () deserves attention, having successfully proven itself in the pharmaceutical market not only as an effective antiseptic, but also as a safe and effective herbal immunomodulator, the properties of which have been confirmed in clinical studies. Thanks to the concept of phytoniring, it was possible to create a herbal preparation with impeccably reproducible properties, quality, composition and clearly defined pharmacological effects, comparable to synthetic drugs. To ensure the quality of the initial plant raw materials, selection and careful selection of seed material is carried out - breeding the “ideal plant”. The company's main plantations are located on the island. Mallorca (Spain). Control and standardization of soil composition, irrigation water, harvesting time and methods ensure the high quality of grown plants. In order to prevent the loss of biologically active substances during the processing of raw materials, the company has developed a new gentle method for obtaining extracts without “temperature stress”. Low-temperature vacuum extraction in a closed cycle avoids oxidation and destruction of active substances, as well as loss of volatile components. Control of product purity and quality is carried out at all production stages - from raw materials to the finished product [7].
Tonsilgon N (produced since 1933 in Germany) has antiseptic, immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, antiviral effects. The drug is available in the form of a hydroalcoholic extract, as well as in the form of dragees containing plant materials. The properties of Tonsilgon N are due to the biologically active substances of medicinal plants included in the preparation (table) [8].
Tonsilgon N is taken orally: during acute illnesses, 2 tablets or 25 drops are prescribed 5-6 times a day; children from 1 to 5 years old - 1 drop per 1 kg of weight 5-6 times a day; children from 5 to 10 years old – 15 drops 5-6 times a day; children from 10 to 16 years old - 20 drops or 1 tablet 5-6 times a day. The alcohol content in the solution is 19 vol.%. Due to its composition and actions, Tonsilgon N is indicated for acute and chronic diseases of the upper respiratory tract, tonsillitis, viral infections, and reduced resistance to infections. The immunocorrective activity of the drug was proven in in vivo studies on mice with immunodeficiency provoked by the administration of cyclophosphamide [9]. Ten years of experience in using this herbal medicine for the treatment of children from infancy to 17 years at the Research Institute of Pediatrics and Pediatric Surgery of the Russian Federal Health Service has proven its effectiveness in treating tonsillitis, pharyngitis, and laryngitis [10]. Timely administration of the drug helped prevent the spread of infection to the lower respiratory tract. Prescribing the herbal medicine Tonzilgon N to children in the first days of acute respiratory infections can significantly reduce the incidence of complications, and in the event of bacterial complications, its administration increases the effectiveness of antibacterial therapy [11]. The safety of the drug in patients with allergies has been proven [12], but caution must be exercised in case of hypersensitivity to nuts and plants of the Asteraceae family [13].
The results of a clinical study confirmed the effectiveness of the drug for the prevention of influenza and ARVI in schoolchildren: the incidence decreased by 3.6 times, the proportion of severe forms of the disease decreased from 48 to 12.5%, which turned out to be better than with the use of cycloferon, the homeopathic drug AGRI, and vaccination with Grippol [14]. It has been demonstrated that taking Tonsilgon increases the phagocytic activity of macrophages, the levels of sIgA and lysozyme in saliva, and the production of alpha and gamma interferons in the blood [2].
For tonsillitis and pharyngitis, Tonsilgon N is used 5–6 times a day; it accelerates the recovery process and shortens the duration of the disease; for chronic tonsillitis, it can be used as basic therapy to prevent relapses 3 times a day for 4–6 weeks [15]. For the treatment of young children - up to 2.5 years - there is practically no real alternative to Tonsilgon N for local treatment of the inflammatory process in the pharynx.
Purpose of the study
Studying the effectiveness of the drug Tonzilgon N as a means of treating and preventing acute respiratory viral infections in children was the goal of our study. To achieve this goal, the following tasks were solved:
1. To assess the dynamics of symptoms and the frequency of complications of ARVI in children when treated with Tonzilgon N as part of complex therapy.
2. To determine the frequency of ARVI episodes in frequently ill children before and after prophylactic administration of the drug Tonsilgon N.
Material and methods
Treatment with the drug Tonzilgon N (in drops) was carried out in 20 children with acute catarrhal nasopharyngitis of mild and moderate severity. The age of the patients varied from 3 to 14 years, the ratio of boys to girls was 3:2. The drug was prescribed in an age-specific dosage when the first signs of ARVI appeared. The control group consisted of 18 children of the same age diagnosed with ARVI who did not receive Tonsilgon N. In both groups, symptomatic therapy was used (vasoconstrictor nasal drops, antipyretics). The effectiveness of treatment was assessed using a sensory-visual-analog scale, where the doctor assessed the severity of symptoms (redness of the throat, fever, runny nose, cough, sore throat) on the 1st, 3rd and 7th days of illness.
Prevention of ARVI was carried out in 15 frequently ill children aged 3 to 6 years (11 boys, 4 girls) with the drug Tonzilgon N (drops and tablets) in an age-appropriate dosage 2 times a day for 1 month. The incidence of ARVI patients during the previous and subsequent 6 months was compared.
Statistical processing of the results was carried out using standard methods.
results
ARVI symptoms before treatment for each patient were assessed at 25 points (5 points each – cough, runny nose, sore throat, low-grade fever, hyperemia of the mucous membranes of the nose and pharynx).
On the third day from the onset of the disease, in 15 children (75%) of the main group, sore throat and cough were relieved, and body temperature returned to normal. In the control group, at the same time, a runny nose, cough, low-grade fever, sore throat and hyperemia of the mucous membrane of the nose and pharynx persisted in 15 children (80%).
After a week, only 3 people in the main group had symptoms of the disease: mucous discharge from the nose - in 2 children (with a history of allergic rhinitis), low-grade fever and cough - in 1 child (bronchitis was diagnosed, antibacterial therapy was prescribed). On the 7th day of the disease, ARVI symptoms persisted in 8 people in the control group, 6 of them were diagnosed with sinusitis, 2 with bronchitis. The dynamics of ARVI symptoms (in points) is shown in the figure.
Tonsilgon N was used prophylactically for a month in frequently ill children. After taking the drug over the next 6 months, 2.1 cases of ARVI were registered per patient. One child had a complication in the form of sinusitis. Before taking the drug, the observed children were sick every month; the number of ARVI cases per child averaged 6.1 during the study period. The diseases lasted a long time, complications such as otitis (in 2 children), sinusitis (in 6 people) were observed, which required the prescription of antibiotics. We did not observe any allergic reactions when using the drug Tonzilgon N in any case.
conclusions
The herbal preparation Tonzilgon N allows you to effectively relieve the main symptoms of a viral infection in children (most quickly - sore throat and cough), and reduces the number of complications. Prophylactic use of Tonsilgon N in frequently ill children reduces the frequency of ARVI episodes by 3 times (p
Treatment with modern methods
Vasomotor rhinitis requires an integrated approach to treatment. Simultaneous medication, physiotherapeutic treatment, and general strengthening procedures will help cope with the disease.
Complex treatment should be aimed at strengthening the vascular system of the nasal cavity, regulating blood circulation, relieving swelling, eliminating factors that lead to dysfunction of the mucous membrane, and increasing immunity.
Along with the use of vasodilating drugs, physiotherapeutic treatment is used: electrophoresis, ultrasound irradiation, laser irradiation. This treatment normalizes the functioning of the nervous system, enhances lymphatic drainage, increases blood circulation, relieves inflammation and swelling of the mucous membrane, and has a regenerating effect.
Traveling to nature, regular walks in the fresh air, visiting a swimming pool, bathhouse, and sanatorium-resort treatment have a beneficial effect on the course of treatment of the disease.
Surgical intervention is indicated in case of ineffectiveness of therapeutic complex treatment.
The main action of Tonsilgon
The instructions for the drug describe in detail its pharmacological effect on the body. The medicine is made from medicinal plants, represented by:
- medicinal dandelion herbs, yarrow, horsetail;
- oak bark;
- chamomile flowers;
- marshmallow roots.
Biologically active substances included in Tonsilgon:
- essential oils, polysaccharides;
- glycosides, flavonoids;
- carotenoids, pectin;
- saponins, vitamin and mineral elements.
The complex of herbal ingredients suppresses the activity of viruses, reduces the level of inflammation, and has an immunomodulatory effect. Due to the components, allergy symptoms disappear, cough stops, swelling of the mucous membranes in the respiratory tract decreases, and breathing becomes easier. The medicine has antioxidant properties.
Conservative pharmacological treatment
Pharmacological treatment is still considered the main method. The most effective is rinsing the nasal cavity with solutions with antiseptic properties: anti-inflammatory, saline, furatsilin solution. Their action is aimed at reducing swelling, relieving inflammation, and cleansing the mucous membrane of irritants. Drug treatment involves the use of medications.
- Vasoconstrictors . Once in the nasal cavity, they act on the vascular receptors, narrowing them, which leads to a decrease in swelling of the mucous membrane. For the treatment of drug-induced rhinitis, it is recommended to use drops of a new generation: Nazivin, Xymelin, Tizin, Nazol. They have a mild effect on the mucous membrane and are indicated for long-term use.
- Glucocorticosteroids (GCs) . These include Nazarel, Nasonex, Avmis, Flexonase. These drugs, along with powerful anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effects, reduce the sensitivity of the mucous membrane to irritants, reduce the permeability of the mucous membrane and the production of mucus. GCs, having a local effect, are well tolerated and are recommended for long-term use for up to 30 days.
- Antihistamines . They prevent the production of histamine, which is involved in all allergic reactions. Claritin, Zertec, Teridine, Telfast are new generation drugs. Helps reduce mucus production, reduce swelling, suppress allergic reactions without affecting the nervous system.
Surgical treatment. Radio wave sparing vasotomy
In case of ineffectiveness of pharmacological treatment, with advanced forms of rhinitis, surgical intervention is resorted to. It is also indicated during pregnancy to protect the fetus from the negative effects of medications. Laser destruction, shaver vasotomy, classical vasotomy are aimed at removing or destroying the plexus of blood vessels in the submucosal layer. The duration of the operations is about 15 minutes. Such operations can restore nasal breathing, completely eliminating vasomotor rhinitis.
The most gentle are radio wave vasotomy of the submucosal and laser vasotomy. It effectively affects the vessels, simultaneously cauterizing them, as a result of which the postoperative period is shorter and passes without complications.