Utrozhestan is the only hormonal drug based on plant-based progesterone. Without this hormone, the process of ovulation, conception and a healthy pregnancy are not possible, therefore, before a planned conception, an analysis is required to determine the level of this steroid compound.
The main indication for the use of this drug is a lack of the hormone progesterone in case of hormonal infertility, after a miscarriage caused by a decrease in the level of progesterone in the blood, as well as in case of an unreasonable decrease in the concentration of the hormone.
The level of progesterone changes depending on the day of the menstrual cycle, the highest concentration is observed in the second phase: it is then that laboratory tests should be carried out to determine its level in the blood, it is also important to take this fact into account when taking the drug.
How to take utrozhestan?
A specialist should draw up an exact treatment regimen based on test results, the individual characteristics of the woman’s body and other factors. So, if during pregnancy planning progesterone is not synthesized at all, vaginal use of utrozhestan in the form of suppositories is indicated, according to the following scheme:
- Days 13-14 of the menstrual cycle - 100 mg of the drug per day;
- 15-25 days - 2 times a day, 100 mg.
- from day 26 and if pregnancy occurs, it is necessary to increase the dosage by 100 mg every day, up to 800 mg.
It is very important not to cancel utrozhestan, which was taken when planning pregnancy, when it occurs, since this is fraught with spontaneous miscarriage. During pregnancy, you should continue to take the drug until the second trimester of pregnancy. It is better to use vaginal forms of the medicine, since capsules may not be completely absorbed during toxicosis. If progesterone levels are normal, then the daily dose should be 200-300 mg (divided into 2 doses).
Despite the fact that utrozhestan has a minimum of contraindications, is a fairly gentle drug and is prescribed during pregnancy, you should definitely consult with your doctor before using it.
Prepare for pregnancy with the specialists of our Center: you can take the necessary tests and receive recommendations from leading specialists in the field of obstetrics and gynecology at a time convenient for you.
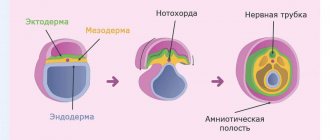
How does the embryo transfer into the uterine cavity occur?
At the clinic, you are taken to a special room - the embryo transfer room, which borders the embryology laboratory, where you sit on a gynecological chair. Using an ultrasound, the doctor measures the length of the cervical canal, examines the ovaries, fluid in the retrouterine space if the transfer occurs in a “fresh” cycle, and tells the embryologist the length of the cervical canal so that the embryologist places a mark on the catheter (in which the embryo will be placed). The doctor then uses a speculum to expose (expose) the cervix. Use a soft tampon to treat the mucous membrane of the cervix and vagina. How is the mucous membrane treated? Most often this is a neutral medium, for example, saline solution), treatment with nutrient media is allowed. After the mucous membrane of the cervix and vagina has been treated, the doctor tells the embryologist that he is ready for the transfer. The embryologist, under a binocular magnifying glass, draws the embryo into the catheter along with the nutrient medium. There is a sequence for recruiting the embryo into the catheter: medium-bubble-embryo-bubble-medium. Catheters that are used for embryo transfer are different: with a guide, with a soft tip, more rigid, curved and straight. In our clinic we use only imported catheters. Each doctor chooses the most suitable catheter for himself.
In America, some doctors prefer metal catheters, we prefer disposable plastic ones. All catheters are certified and tested for biological safety. The speed of embryo transfer is very important; the embryo does not like light and air.
The embryologist then hands the catheter to the doctor and says the name of the patient whose embryo he is transferring. This is important for patient identification.
The doctor inserts a catheter into the cervical canal and passes beyond the internal os, about 2 cm, and presses the plunger of the syringe to which the catheter is attached. Then the catheter is removed from the uterine cavity, while the syringe plunger is not released so that the embryo does not “suck” back into the catheter.
The catheter is passed into the hands of an embryologist, who checks under a magnifying glass whether the embryo remains in the catheter? If the transfer has occurred and there is no embryo left in the catheter, the doctor removes the gynecological speculum and uses ultrasound to check where the embryo is located in the uterine cavity. What does the doctor see?
On ultrasound in the uterine cavity we see bubbles that have a hyperechoic structure. We cannot see the embryo with our eyes because it is very small.
Specialists
Makatsaria Alexander Davidovich
Obstetrician-gynecologist, famous scientist, founder of clinical hemostasiology.
It will help you plan and maintain your pregnancy if you have had cases of fetal loss, thrombosis, obstetric complications or blood coagulation disorders. You can also contact your doctor for a transcript of hemostasis tests.
Akinshina Svetlana Vladimirovna
Obstetrician-gynecologist, hemostasiologist with an academic degree.
Pregnancy management S.V. Akinshina will help avoid severe complications: gestosis, placental insufficiency, fetal loss syndrome.
The doctor's expertise includes hemostasis disorders and immunological infertility.
Margiani Fatima Abdurashidovna
Doctor of Medical Sciences, qualified diagnostician of female infertility factors.
Provides competent support for late, multiple or problematic pregnancies. A consultation and examination with Fatima Abdurashidovna will help determine the cause of failure to conceive a child or recurrent miscarriage.
Petreykov Evgeniy Rafailovich
If you are planning a pregnancy, IVF, or have a history of fetal failure in the first trimester, contact Dr. Petreikov.
A gynecologist of the highest category, Candidate of Sciences, will help determine the risk and cause of obstetric complications, and also prescribe supportive treatment for a genetic predisposition to thrombosis.
On what day of embryo development can the transfer take place?
Transfer is allowed from days 2 to 6 of embryo development. The timing of the transfer is agreed upon with the embryologist; it depends on the quantity and quality of the embryos transferred. In our country, it is regulated to transfer no more than 2 embryos in order to prevent the development of multiple pregnancies. If a woman has poor quality embryos or many unsuccessful attempts, then the patient’s consent to transfer more than 2 embryos into the uterine cavity is filled out. SET selective transfer of 1 embryo is now the preferred method, especially if the embryo has undergone genetic typing. Transfer of the best SET embryo is legal in Sweden.
Utrozhestan® (Utrogectan®)
Utrozhestan® should not be used for contraception.
The drug should not be taken with food, since food intake increases the bioavailability of progesterone.
The drug Utrozhestan® should be taken with caution in patients with diseases and conditions that may be aggravated by fluid retention (arterial hypertension, cardiovascular disease, chronic renal failure, epilepsy, migraine, bronchial asthma); in patients with diabetes mellitus; liver dysfunction of mild to moderate severity; photosensitivity.
Patients with a history of depression should be monitored, and if severe depression develops, the drug should be discontinued.
Utrozhestan® contains soy lecithin, which can cause hypersensitivity reactions (urticaria and anaphylactic shock).
Patients with concomitant cardiovascular diseases or a history of them should also be periodically observed by a doctor.
The use of Utrozhestan® after the first trimester of pregnancy may cause the development of cholestasis.
During long-term treatment with progesterone, regular medical examinations (including liver function tests) are necessary; Treatment should be discontinued if abnormal liver function tests or cholestatic jaundice occur.
When using progesterone, it is possible to reduce glucose tolerance and increase the need for insulin and other hypoglycemic drugs in patients with diabetes mellitus.
If amenorrhea occurs during treatment, pregnancy must be excluded.
If the course of treatment begins too early in the menstrual cycle, especially before the 15th day of the cycle, shortening of the cycle and/or acyclic bleeding is possible. In case of acyclic bleeding, the drug should not be used until the cause is determined, including a histological examination of the endometrium.
If there is a history of chloasma or a tendency to develop it, patients are advised to avoid UV irradiation.
More than 50% of spontaneous abortions in early pregnancy are caused by genetic disorders. In addition, the cause of spontaneous abortions in early pregnancy can be infectious processes and mechanical damage. The use of the drug Utrozhestan® in these cases can only lead to a delay in rejection and evacuation of a non-viable fertilized egg. The use of the drug Utrozhestan® to prevent threatened abortion is justified only in cases of progesterone deficiency.
When conducting MHT with estrogens during perimenopause, it is recommended to use the drug Utrozhestan® for at least 12 days of the menstrual cycle.
With a continuous MHT regimen in postmenopause, it is recommended to use the drug from the first day of taking estrogen.
When conducting MHT, the risk of developing venous thromboembolism (deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism), the risk of developing ischemic stroke, and coronary heart disease increases.
Due to the risk of developing thromboembolic complications, the use of the drug should be discontinued if: visual disturbances such as loss of vision, exophthalmos, double vision, vascular lesions of the retina occur; migraine; venous thromboembolism or thrombotic complications, regardless of their location.
If there is a history of thrombophlebitis, the patient should be closely monitored.
When using Utrozhestan® with estrogen-containing drugs, you must refer to the instructions for their use regarding the risks of venous thromboembolism.
The results of the Women Health Initiative Study (WHI) clinical study indicate a slight increase in the risk of breast cancer with long-term, more than 5 years, combined use of estrogen-containing drugs with synthetic gestagens. It is unknown whether there is an increased risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women when undergoing MHT with estrogen-containing drugs in combination with progesterone.
The WHI study also found an increased risk of dementia when starting MHT after age 65 years.
Before starting MHT and regularly during it, a woman should be examined to identify contraindications to its implementation. If clinically indicated, a breast examination and gynecological examination should be performed.
The use of progesterone may affect the results of some laboratory tests, including liver and thyroid function tests; coagulation parameters; pregnanediol concentration.
What complications can occur during embryo transfer?
- the doctor cannot pass through the cervical canal due to bends, adhesions, etc. – in this case, the embryo is transferred to a more rigid catheter with a guide and the transfer is carried out;
- the embryo after transfer is found in the catheter - it is collected again and the embryo is transferred again.
The patient cannot relax and asks to be given anesthesia - this happens extremely rarely, since the procedure is painless.
Do I need to use vaginal suppositories (with progesterone) before the transfer? Yes, morning suppositories (balls) must be administered in the morning.
How to maintain pregnancy after IVF
Pregnancy after IVF often occurs with complications. This happens because women with diseases of the endocrine system and reproductive system resort to in vitro fertilization. They often experience miscarriage, toxicosis and other problems that put pregnancy at risk. To prevent this and maintain pregnancy after IVF, you need to be observed in a clinic that has the necessary equipment and qualified specialists working with IVF mothers.
Hormonal disorders during pregnancy after IVF
These problems are caused by the introduction of large doses of hormones during the preparation for IVF, if hormonal stimulation of the ovaries was carried out. For many women, this is a necessity and the only opportunity to become pregnant, since stimulation of the ovaries leads to the maturation of several follicles at once. At the same time, the concentration of estrogen in the blood increases sharply. Hormonal imbalance can cause disturbances in vascular permeability and accumulation of fluid in the lungs and abdominal cavity. Excess moisture prevents a woman from breathing, causes nausea, vomiting and loss of appetite.
Another possible consequence of HS is a slow increase in hCG levels (human chorionic gonadotropin), which is called the “pregnancy hormone”. This hormone should:
- preserve the corpus luteum;
- prepare the woman’s immune system for the upcoming pregnancy;
- stimulate fetal development
With a lack of hCG, fetal growth slows down, which leads to miscarriage and fading of pregnancy.
In this case, pregnancy support after IVF When observed in a specialized clinic, doctors will be able to correct hormonal levels in time, remove swelling and eliminate the threat of miscarriage.
Infectious and inflammatory processes
Women who become pregnant after IVF often suffer from chronic inflammation of the genital organs, which leads to the impossibility of natural conception. Although women are treated as much as possible during the period of preparation for pregnancy, the disease often worsens again. All this affects the functioning of the immune system and reduces the production of hormones responsible for the normal course of pregnancy.
A woman develops a bloody “spot,” indicating a threat of miscarriage. Under these conditions, it is not easy for the fetus to stay in the uterus, so medical support for pregnancy after IVF is required. Medical supervision helps eliminate dangerous inflammatory processes, maintaining pregnancy after IVF.
Maternal problems
IVF is mainly used by women aged 30 years and older. A large percentage of them have various diseases of internal organs (kidneys, heart, liver, gall bladder) and metabolic disorders. All these “sores” are prone to exacerbation during pregnancy, which negatively affects the intrauterine development of the child.
Women who already have health problems may develop gestational diabetes, caused by the pancreas not working properly. The level of glucose in the blood rises, which causes oxygen starvation of the fetus. This complication occurs more often if a woman is carrying twins, which often happens after artificial insemination. If the problems that arise are not treated in time, the pregnancy can be lost. To do this, women, being observed in the clinic after IVF, regularly donate blood for biochemistry and sugar.
Fetoplacental insufficiency
This condition occurs as a result of malformation and or insufficiency of the placenta. Since women who become pregnant after IVF often have problems in the sexual sphere, fetoplacental disorders are not uncommon.
As a result, the fetus suffers, which receives few nutrients and oxygen, which can lead to miscarriage or the birth of a sick child. Periodic Doppler testing, which shows the state of the feto-placental blood flow, can help with this condition. If a pathology is suspected, supporting pregnancy after IVF involves prescribing medications that improve blood circulation in the placenta and help the pregnancy proceed properly.
Multiple pregnancy
During IVF, a woman is often implanted with several embryos at once. If they all take root, a multiple pregnancy occurs. Sometimes twins develop from one egg, as in a normal pregnancy; a woman gives birth to identical twins. Many people consider twins or triplets to be an excellent result after IVF, forgetting that several babies are harder to bear and easier to lose.
Sometimes nature itself regulates the process, and extra embryos stop developing, but often all implanted eggs grow equally. It is possible, of course, to reduce (remove) excess embryos, but parents rarely agree to this.
In women pregnant with twins, toxicosis occurs more often and is more severe. The uterus, growing much faster, puts pressure on the legs, causing them to swell. Pressure on the diaphragm in recent months interferes with the mother’s ability to breathe properly. In the later stages of pregnancy with twins or triplets, an increase in blood pressure is more often observed, which can lead to convulsive syndrome (eclampsia) and premature birth. Since twins are already born with low weight, this can lead to extreme prematurity and death of newborns.
Overstretching of the uterus and increased stress on the body cause:
- bleeding;
- oxygen starvation of the fruits;
- anemia caused by a high load on the mother’s hematopoietic system;
- feto-fetal transfusion syndrome, when one fetus takes more nutrients, inhibiting the development of the second;
- thrombosis of placental vessels. During multiple pregnancies, one or both “baby places” are located incorrectly, which causes premature placental abruption;
- oblique, transverse or pelvic location in the uterus of one or all babies
A woman who has developed a multiple pregnancy as a result of IVF needs special observation and strict control, so she often undergoes an ultrasound to find out how the children are developing.
The condition of babies carried by IVF mothers is monitored using ultrasound and Doppler. Competent doctors working at the Life Line clinic will provide full support for pregnancy after IVF and will help you successfully endure multiple pregnancies and give birth to healthy children. The conscious attitude of a woman and the supervision of experienced specialists allows us to save the majority of pregnancies that occur after IVF.