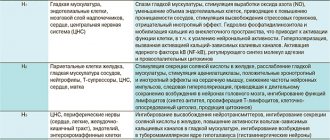
Non-drug therapy Drug therapy Advantages of a combination of phospholipids with glycyrrhizic acid Today, one of the primary tasks of hepatology is to provide medical care to patients with liver dysfunction of alcoholic, non-alcoholic, medicinal and toxic origin. The high medical and social significance of this problem is associated with the need for adequate treatment, which requires the use of drugs of various pharmacological groups and non-drug methods. Experts recommend the use of hepatoprotectors as pathogenetic therapy agents that have a positive effect on the structure and function of hepatocytes and increase their resistance to pathogenic factors. Essential phospholipids are among the most studied and safe drugs in this group.
Non-drug therapy for various liver diseases (ALD, NAFLD, LLD)
Non-drug treatment of liver diseases should be aimed at eliminating the pathogenic cause that served as the trigger for the development of the pathological process.
Calculate your BMI right now! Calculate
- Patients suffering from ALD are recommended to completely stop drinking alcohol and normalize their diet (increasing the consumption of protein-rich foods). Such actions help improve the functional state of the organ primarily responsible for ethanol metabolism, and significantly reduce the risk of developing fatty liver degeneration and fibrotic degeneration.
- Persons with symptoms of fatty liver disease of non-alcoholic origin are individually prescribed a special diet aimed at reducing body weight and providing for the complete exclusion of fatty foods from the diet. Constant monitoring of blood glucose levels is required, as well as a moderate increase in physical activity.
- In the event that signs of liver damage are associated with taking hepatotoxic drugs that cause structural and functional disorders of the organ, discontinuation of the drug is necessary (the decision to cancel can only be made by a doctor), taking into account the patient’s allergy and medication history. If treatment cannot be stopped, it is necessary to change the form and adjust the dose of the drug, as well as in parallel use a drug that has a hepatoprotective effect.
Drug therapy for various liver diseases
When treating liver diseases of a non-infectious nature, pathogenetic therapy is usually used to help restore damaged liver cells. According to experts, the most effective and safe drugs that help restore intracellular metabolism are essential phospholipids. Being integrated into the membranes of liver cells, they have a hepatoprotective and antifibrotic effect, reduce the deficiency in building materials, counteract the processes of peroxidation, and create conditions for the normal functioning of enzyme systems. Due to the ability of these drugs to reduce the production of collagen fibers, the processes of proliferation of connective tissue in the liver are significantly slowed down, which reduces the risk of developing cirrhosis.
Compound
Soy lecithin, medium chain triglycerides, shell (gelatin, glycerin (plasticizer), water, dyes (sugar color IV, titanium dioxide)), mono- and diglycerides of fatty acids (stabilizer), milk thistle extract, refined soybean oil, vitamin B2 (riboflavin) , vitamin B6 (pyridoxine hydrochloride), vitamin B1 (thiamine mononitrate), mixture of tocopherols (antioxidant)
Contents in 1 capsule
Vitamin B1 0.56 mg
Vitamin B2 0.7 mg
Vitamin B6 0.7 mg
Phospholipids 400 mg
Silymarin 22 mg
Benefits of combining phospholipids with glycyrrhizic acid
Despite the fact that essential phospholipids have a positive effect on the structure and function of the liver, they are not able to independently eliminate inflammation, which most often causes the development of the pathological process. Therefore, a good solution is their combination with glycyrrhizic acid, which enhances the effect of essential phospholipids and has a pronounced antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effect.
Experts recommend using Phosphogliv* as a basic therapy drug that helps normalize the morphofunctional state of the liver. This combined hepatoprotective agent, containing phospholipids and glycyrrhizic acid, reduces oxidative stress and inflammation, inhibits the formation of connective tissue, stimulates the restoration of liver cells, and reduces the risk of developing fibrosis and cirrhosis.
The influence of phospholipids on fertility.
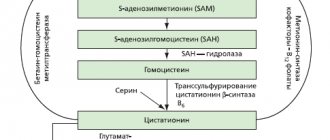
Chemical structure of phospholipidsFrom the point of view of a chemist, the concept of “phospholipids” implies a large group of substances that are similar in structure. In general, all phospholipids resemble molecules of neutral fats - triglycerides. Unlike triglycerides, phospholipid molecules contain fatty acid substituents at positions C1 and C2. And in position C3, instead of a fatty acid, it contains a phosphoric acid ester with various substituents. Typically, endogenous phospholipids contain in their molecule one saturated (at position C1) and one unsaturated (at position C2) fatty acids. Moreover, natural unsaturated fatty acids almost always have a cis configuration. The physicochemical and biological properties of phosphatidylcholines largely depend on the length of the hydrocarbon chain of the fatty acids included in its molecule, on the position and number of double bonds in them.
Phospholipids - a natural fertility factor
Many authors associate phospholipids with the concept of fertility. Phospholipids, as active components that affect human fertility and potency, are used in food supplements and some medications intended to treat insufficiency of the function of the sex glands and menopause in men.
It is probably no coincidence that the main sources of phospholipids, the most accessible to consumers and technologists, are bird eggs and soybeans. These sources of phospholipids are nothing more than components of reproductive organs in one case of an animal, and in another of plant origin. That is, they are by nature intended to be used as part of a “reserve” of nutrients, as building blocks necessary for effective reproduction in both the animal and plant kingdoms.
Historical reference. The most studied representative of phospholipids is the “phosphatidylcholine” fraction, also known as “lecithin”. The first mention of lecithin in scientific literature dates back to 1850, when the French chemist M. Gobley first proposed calling the phosphorus-containing lipid fraction divided by him from egg yolk and brain (1846), the term “lecithin”, which takes its originated from a Greek word meaning “egg yolk” (J Pharm Chim, Paris 1850; 17: 401). Initially, the term “lecithin” was used to designate all phosphorus-containing lipids. However, at present this term in the scientific literature is used to designate only one group of phospholipids - phosphatidylcholines.
Phosphatidylcholine
Phosphatidylcholine (PC) is the most prominent representative of phospholipids. It is believed, for example, that in the liver 70-80% of all phospholipids are PC (V. Abramchenko, 2001). This is one of the richest human organs in phospholipids. In other tissues, FX also dominates. Phospholipids of the brain, kidneys and human sperm contain 29.2, 37.9 and about 30% PC, respectively (A. Kotyk, K. Janacek, 1980; J. Alvarez, B. Storey, 1995).
PC and other phospholipids are contained in the cellular and subcellular membranes of all living organisms, providing their structural and functional features. To obtain phospholipids of animal origin, eggs are used - a very expensive source. PC and other phospholipids are also obtained from plant sources, which are oil seeds: sunflower, corn, soybeans, peanuts, etc. The most accessible and popular plant source of high-quality and highly effective (in terms of fatty acid composition) PC is currently soybean. It is soybean PC that is most often used for food and medical purposes.
"Essential" phospholipids
The phospholipid fraction from soybeans was first isolated by Eikermann in 1939. A distinctive feature of the soybean PC fraction he isolated, which differs favorably from PCs of other, for example, animal (from eggs) origin, is the presence of two polypeptides in the molecule saturated, “essential”, i.e. . fatty acids essential for the human body - linoleic and linolenic. In this regard, the isolated fraction from soybeans was called EPL substance, which stands for essential phospholipids. EPL substance is a highly purified fraction of FX, containing mainly linoleic acid in positions C1 and C2, i.e. the main active ingredient of the EPL substance is 1,2-dilinoleoylphosphatidylcholine (K. Oette et al., 1995; V. Abramchenko, 2001).
Phospholipids and fertility
As an active ingredient, EPL is included in the widely known preparations Essentiale (Germany). These preparations are distinguished by the high quality of purification of the active substance - FX in the form of an EPL substance. Thus, the concentration of PC in relation to the amount of phospholipids in the drug Essentiale Forte (according to the journal Pharmateka, 2001; 7:29) is more than 95%. For comparison: the so-called “raw” lecithin contains 50-60% mixed phospholipids (of which 20-30% PC). Granulated or powdered (after preliminary defatting), the so-called “pure” commercial lecithin contains 25-30% PC. Thus, the technology makes it possible to purify PC not only from neutral lipids, but also from “minor” components (phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylserine, etc.). The EPL substance of this company in Essentiale preparations has been successfully used for several decades in Russia and the countries of the former USSR. They are included in reference manuals and textbooks on pharmacology, popular reference and information publications and are rightly regarded as the “gold standard” of comparisons for new drugs autoprotectors with antioxidant properties.
Phospholipids: participation in vital processes
To date, a huge number of facts have been accumulated showing the high biological activity of PC and other phospholipids in maintaining the integrity of cell membrane systems (os especially hepatocytes), processes of differentiation, proliferation and regeneration of biological membranes. The participation of PC and other phospholipids has been proven in the regulation of the work of membrane receptors and enzymes, in the regulation of metabolic processes both inside and outside the cell, including those shown in influence on immune reactions. They, being structural elements of lipoproteins, and also participating in the process of blood clotting, affect hemodynamics and cholesterol levels in the blood (T. Mach, 2000; V. Abramchenko, 2 001).
All of the above is only part of the unique functional activity of PC and other phospholipids that has been studied to date. The breadth of biological activity of phospholipids is explained by the peculiarities of their chemical structure: diphilicity, the presence of charged groups (bipolar charge of PC) in the hydrophilic part of the molecule, the presence of biologically available phosphorus, polyunsaturated fatty acids and the active component choline (PC).
The wide range of studied bioactivity of PC and other phospholipids is naturally confirmed by the wide range of their therapeutic use. They are recommended to be used to treat liver diseases, reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases, improve memory and learning ability, to increase physical endurance, for normal analysis of the processes of reproduction and development of the human body (J. David, 1996). The interest of researchers in the therapeutic effect of the most pharmacologically active “essential” phospholipids on the reproduction process (and in particular on functional sex diseases in men) is confirmed by the work of N. Kiriakova et al. (1998).
Fertility - Risk Factors
The ability to reproduce or fertility is a complex phenomenon and depends on a very large number of factors. This includes both external (lifestyle, nutrition, smoking, alcohol, toxins, poisons, heavy metals, etc.) and internal: physical and structural changes in internal organs, infectious diseases and inflammatory processes, genetic problems, metabolic disorders and so on. All exo- and endogenous factors influence both female and male fertility. Moreover, most of them are characterized by both a direct effect on gametogenesis and fertilization, and an indirect effect - through the organs and systems of the human body. Thus, many diseases can affect fertility both directly and indirectly. For example, diabetes affects fertility in three ways: through vascular, neurological and metabolic changes. Liver cirrhosis, for example in men, can lead to endocrine diseases: hypogonadism, gynecomastia and testicular atrophy. Chronic kidney diseases can cause endocrine disorders: hypogonadism and hyperprolactinemia (S. Yen and R. Jaffe, 1991). With a disease of the adrenal glands - adrenogenital syndrome, a violation of spermatogenesis is observed. Neurological diseases can affect sexual activity (R. Martin-du Pan, F. Campana, 1993). Some medications, such as cytotoxics, tranquilizers, antidepressants, and some antihypertensive drugs, can reduce the number of sperm and worsen their quality, causing the phenomenon of impotence (L. Speroff et al., 1989; D. Labby, 1982).
From the above it follows that in addition to the direct effect on the reproductive organs and germ cells, in order to increase reproductive function it is necessary to carry out an indirect effect on reproductive functions, normalizing (along with others) metabolic, vascular, and neurological disorders in the body.
Phosphatidylcholine and reproductive function
Due to its indispensability as the main building block of biomembranes of cellular and subcellular structures, FX takes part in a huge number of biochemical and physiological processes at all levels of organization of the human body and, naturally, has a direct impact on the normal functioning of both somatic and very important , sex cells.
Due to their unique properties, it is PC and other phospholipids that have the ability to both directly influence germ cells and indirectly increase reproductive function, for example, through the normalization of metabolic and including lipid disorders in the body. Phosphatidyl choline is able to directly influence the processes of gametogenesis: the formation of differentiated germ cells or gametes (from the Greek gametes - spouse). PC is involved in the construction of cell membranes of both male and female germ cells: for example, human sperm contains about 30% (J. Alvarez, B. Storey, 1995). In a healthy male body, during the process of fertilization, about 108 germ cells are released simultaneously with a concentration in the seminal fluid of at least 2-107 cells/ml (WHO, 1987). Their number is directly proportional to the fertility of the male body. In addition, PC and other phospholipids (including lecithin crystals) contained in seminal plasma provide its quantitative and qualitative characteristics, including favorable conditions for the existence and functioning of sperm. Naturally, a sufficiently nutritious diet is required, the presence of “essential” components in the diet in order to ensure normal reproductive function. For example, it is believed that PC deficiency, which can affect choline levels, can lead to the development of infertility (S. Zeisel, 1994).
The positive correlation of the total amount of phospholipids in sperm with fertility is confirmed in the work of S. Cerolini et al. (1997). In an experiment on model biological objects, it was established that a lack of PC in food leads to a decrease in the number of eggs formed and a slight decrease in their size (J. van Herrewege, 1975).
The formation of a sufficient number of germ cells makes a significant, but not overwhelming contribution to ensuring reproductive function. Their quality has a significant influence: morphological features, viability and ability to fertilize, mobility. All these properties are provided during the long-term maturation of germ cells. Thus, an egg matures on average in 28 days, and the formation of a sperm in humans lasts approximately 72 days. During this entire period, a strictly defined sequence of changes occurs in the qualitative and quantitative composition of the inner and outer layers of the lipid membrane of cells, including with the participation of PC (A. Rana et al., 1993; P. Martinez, A. Morros, 1996).
In the membrane, phospholipids form a double layer, in which the hydrophobic fatty acid chains of the outer and inner layers are directed into the membrane, i.e. its surface acquires hydrophilic properties, which makes it possible for membrane proteins to attach and even enter into the lipid bilayer, ensuring the functional activity of germ and somatic cells.
Disruption of the phospholipid bilayer of sperm membranes can lead to changes in cell morphology, viability and motility, leading to loss of fertility. In this regard, the protective and regenerative role of PC, which has been well studied to date, is relevant. Phosphatidylcholine maintains the predominantly lamellar configuration of the membrane, which explains the significant contribution of PC to its stability. A large amount of experimental material has shown the positive effect of “essential” phospholipids (EPL substance of Essentiale preparations) on toxic, allergic, metabolic and other damage to cell membranes (for example, hepatocytes). In this case, the incorporation of exogenous phospholipids into damaged membranes is observed within 1-2 days, which is decisive in restoring morphology and functions (V. Abramchenko, 2001). The regenerating effect of EPL also extends to other types of cells: for example, their high restorative activity has been demonstrated using the example of chemical damage to the membranes of bacterial cells (A. Fruchart et al., 1977).
PC eliminates damage to the cell membrane and restores functions in sperm. Thus, phosphatidylcholines showed significant activity in protecting and restoring the membranes of male germ cells when they are destroyed by cold shock, which makes it possible to recommend PC as a cryoprotector during sperm cryopreservation (P. Quinn, 1980; A. Simpson et al., 1987; J. Graham and R. Foote, 1987). It is believed that the quality of sperm is more important than their quantity. Quality often refers to the concept of “mobility”. Recent studies have shown that PC is required for sperm to achieve normal motility (J. Infante, V. Huszagh, 1985; G. Haidl et al., 1993).
The participation of PC has also been shown in the process of fertilization itself. Thus, when moving towards the egg, the structure of the lipids of the sperm cell membrane undergoes important sequential changes - “capacitation” (the process of increasing fertilizing ability: from the Latin capacitas - ability) and then - the activation phenomenon, or acrosomal reaction.
In the “inactive” state, male germ cells are characterized by a stable state of the membrane, supported by the asymmetry of the composition of its phospholipid layers. Asymmetry of phospholipid composition is a universal phenomenon, characteristic of almost all cells (A. Schroit and R. Zwaal, 1991), which occurs due to the activity of ATP and the sulfhydryl-dependent lipid pump (A. Schroit and R. Zwaal, 1991; P. Devaux, 1992). During the activation process, the symmetry of the local portion of the sperm membrane (acrosome) is restored, which promotes fusion with the egg. Currently, a number of studies have shown the inducing effect of PC on the acrosomal reaction (J. Graham, R. Foote, 1987; A. Davis, R. Foote, 1987; M. Diaz Fontdevila, 1988; C. Holden, A. Trounson, 1992 ; N. Cross, 1994).
Along with the direct effect on gametogenesis and the process of fertilization, PC can also influence fertility indirectly, for example, through the normalization of metabolic disorders in the body. Thus, the effect of lipid metabolism disorders on the menstrual and reproductive functions of women is known. Menstrual irregularities and infertility are observed in 15 and 10% of obese women, respectively, and are accompanied by hyposecretion of the gonads (M. Shekhtman et al., 2001). Hypogonadism and testicular atrophy in men can be a consequence of liver cirrhosis (S. Yen and R. Jaffe, 1991). Normalizing liver function, its enzyme system, and lipid metabolism through the use of Essentiale drugs, which have proven themselves in this area, can help restore hormonal changes and, consequently, reproductive function.
PCs are for the cells of the reproductive organs a source of ready-made “building” blocks of their lipid membranes, as well as such biologically active substances as phosphorus, choline and essential “essential” fatty acids (J. David et al., 1996; I. Mozgov, 1979) .
It is a known fact that sexual motivation, which indirectly affects fertility, may be based on a psychogenic mechanism, and neurological diseases can affect sexual activity (R. Martin-du Pan, F. Campana, 1993; A. Gregoire, J. Pryor, 1993). PC and other phospholipids take part in the normalization of the central nervous system as structural blocks of nerve cell membranes and, indirectly, by participating in the cycle of synthesis of the mediator acetylcholine (J. David et al., 1996).
Recent studies have shown that choline-containing phospholipids promote the process of implantation of a fertilized egg (C. Morin et al., 1992), improve conditions for maturation and development of the fetus, and facilitate childbirth (J. Johnston, 1992). As one of the drugs that provides favorable conditions for pregnancy and the treatment of certain complications (toxicosis of pregnancy, fetal hypoxia during gestosis), the well-known drug Essentiale is used (V. Abramchenko, 2001).
Conclusion
Presented in the article is some, far from complete, information about the positive effect of phosphatidylcholine on fertility, about its participation in the processes of functioning of the sexual sphere as male and female organisms show that FX, apparently, is advisable to use for prevention, and in some cases for complex treatment of infertility. It is believed that the lack of FX is very easy to compensate for with food. Indeed, phosphatidylcholine can be found in a wide variety of foods. However, an interesting fact is that natural sources rich in it (meat, eggs, etc.) also contain a significant amount of such important (and for some people not harmless) substances as cholest erin and fat. The desire to exclude fatty, cholesterol-rich foods from your diet can lead to a lack of PC and other phospholipids. A vegetarian diet does not make it possible to compensate for the deficiency, since vegetables and fruits do not contain any significant amounts of phospholipids. The solution, apparently, is to take highly purified phosphatidylcholine-containing drugs, especially those containing “essential” phospholipids, for example, Essentiale forte N.
S.A.
Skatkov, Moscow
An ophthalmologist shows the patient the letters: “SKLMAZHGF” - Read this line - I can’t - What about this one? - I can’t either. The doctor is surprised: - Don’t you see such huge letters? - Of course, I see. But I can't read the word.



![Table 1. Comparison of the results of treatment with Tribestan for men with oligoasthenozoospermia [7] with mod.](https://irknotary.ru/wp-content/uploads/tablica-1-sravnenie-rezultatov-lecheniya-tribestanom-muzhchin-s-oligoastenozoospermiej-7-330x140.jpg)