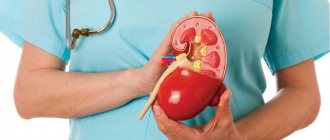
A kidney cyst is a round fluid formation in the body or capsule of the kidney. This formation always has a clearly defined connective tissue capsule and negative blood supply. The composition of the fluid in the cyst is primary urine.
Kidney cysts can be single (they are called “solitary cyst”) or multiple. Multiple kidney cysts are often misdiagnosed as polycystic kidney disease. However, these diseases differ significantly. Multiple kidney cysts do not seriously affect the filtration function of the kidney parenchyma. Cysts push aside the kidney parenchyma, but do not replace it. Whereas polycystic kidney disease is essentially the replacement of normal kidney parenchyma tissue with cysts.
Based on the nature of the cyst contents, they are classified into:
- serous - transparent liquid with a yellowish tint;
- purulent - pus accumulates in the cavity;
- hemorrhagic - containing blood admixtures.
Kidney cyst symptoms
The degree of kidney damage varies from negligible with small solitary cysts to total with polycystic kidney disease, often leading to severe renal failure and hemodialysis.
Is a cyst on the kidney dangerous?
Large cysts often cause pain in the kidney area due to compression of both the kidney itself and adjacent organs. One of the signs of a kidney cyst is erythrocyturia (the appearance of red blood cells in a urine test). Patients with large or multiple kidney cysts often develop secondary hypertension (high blood pressure).
Therefore, accurate diagnosis and, most importantly, timely treatment of kidney cysts allows you to prevent complications and achieve maximum results.
Classification of kidney cysts
Systematization of neoplasms is carried out taking into account various parameters: location, structure, content.
| Type of neoplasm | Characteristics |
| Based on location | |
| Renal sinus cysts | Localized in the area of the renal hilum or pelvis, there are two types:
|
| Subcapsular | Located under the kidney capsule. |
| Intraparenchymal renal cyst | Found in the tissues of the renal capsule or in the sinus area. |
| According to structural features | |
| Solitary | A cavity with one chamber filled with liquid, with a diameter ranging from a few millimeters to ten centimeters. Very common, detected in almost 80% of cases. |
| Polycystic | Multiple cysts of different shapes and diameters, often forming in the tissues of both kidneys. The initiating factor often lies in congenital anomalies of the MVS, which is why neoplasms are detected already in childhood. |
| Multilocular | Inside the cavity has dividing partitions. Passed on by inheritance. |
Kidney cysts classification
Depending on the structural features (according to computed tomography with intravenous enhancement) and the likelihood of tumor degeneration, kidney cysts are divided into 5 classes ( Bosniak classification of kidney cysts ).
| Class | 1 |
| Characteristics (according to MSCT data with intravenous contrast) | Thin-walled kidney cysts with homogeneous contents, the density corresponding to water and not accumulating contrast. |
| Treatment tactics | Does not require treatment or observation. It is advisable to have an ultrasound of the kidneys once a year. |
| Class | 2 |
| Characteristics (according to MSCT data with intravenous contrast) | The cysts contain single thin septa and small calcifications; Small areas of thickened and calcified wall or septum are allowed. Elements of the cyst do not accumulate contrast. |
| Treatment tactics | Does not require treatment or observation. It is advisable to have an ultrasound of the kidneys once a year. |
| Class | 2f |
| Characteristics (according to MSCT data with intravenous contrast) | The cysts contain multiple thin septa; Calcification and thickening of the cyst walls or septa are allowed. Cyst elements do not accumulate contrast |
| Treatment tactics | Ultrasound of the kidneys 1-2 times a year. |
| Class | 3 |
| Characteristics (according to MSCT data with intravenous contrast) | Renal cysts with unclear contours, uneven thickened walls or septa that accumulate contrast |
| Treatment tactics | Surgery. |
| Class | 4 |
| Characteristics (according to MSCT data with intravenous contrast) | Obviously malignant cysts that have all the characteristics of category 3, but with a soft tissue component that accumulates contrast |
| Treatment tactics | Surgery. |
As can be seen from the table, in most cases with kidney cysts, it is sufficient to monitor the size and structure of the cyst using an annual control ultrasound.
Our doctors
Khromov Danil Vladimirovich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
35 years of experience
Make an appointment
Mukhin Vitaly Borisovich
Urologist, Head of the Department of Urology, Candidate of Medical Sciences
34 years of experience
Make an appointment
Perepechay Dmitry Leonidovich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
40 years of experience
Make an appointment
Kochetov Sergey Anatolievich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
34 years of experience
Make an appointment
Treatment of kidney cysts or how to treat a kidney cyst
Since kidney cysts are not tissue formations, it is useless to treat them with medications. Thus, the only option left is surgical treatment of kidney cysts , the options for which are the following (listed in order of increasing complexity and radicality):
- puncture of a kidney cyst under ultrasound control with sclerosis of its wall;
- laparoscopic excision of the walls of a kidney cyst (renal cyst laparoscopy);
- laparoscopic resection of the affected area of the kidney;
Indications for surgical treatment of a kidney cyst are large size (more than 5-7 cm), rapid growth of the cyst, clinical manifestations caused by the cyst (pain in the kidney area, erythrocyturia, increased blood pressure). Also, cysts belonging to categories III and IV according to the Bosniak classification are subject to mandatory surgical treatment.
Puncture and sclerosis of a kidney cyst under ultrasound control is an ideal method for treating thin-walled single cysts.
Our services
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Ultrasound of the kidneys and adrenal glands | 2 700 |
| Urography intravenous | 6 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Cyst in the kidney what to do
The procedure is simple, effective and safe, performed under local anesthesia and requires only minimal observation in the hospital for 24 hours.
Puncture of a cyst involves inserting a thin needle into its cavity under ultrasound control, aspirating the contents (emptying the cyst) and introducing a sclerosing agent, which causes gluing of the cyst walls and prevents re-accumulation of fluid (cyst recurrence).
For recurrent kidney cysts, as well as for multi-chamber or thick-walled cysts (when puncture and sclerotherapy under ultrasound guidance are ineffective), we perform laparoscopic excision of the walls of the kidney cyst (renal cyst laparoscopy) . This operation is performed under general anesthesia through three small punctures in the abdomen.
The advantage of laparoscopic renal cyst excision (renal cyst laparoscopy) is the absence of recurrence. The hospitalization period for this operation is from 3 to 5 days.
If the cyst is suspicious for malignancy (malignancy), then it is often necessary to perform laparoscopic resection of the kidney (or even laparoscopic nephrectomy, that is, removal of the kidney).
By contacting me with a problem such as kidney cysts, you can be sure of correct and timely diagnosis and adequate treatment, including modern high-tech minimally invasive procedures.
Laparoscopic treatment methods
In the hospital of the Scientific and Practical Surgery Center, patients with kidney cysts undergo operations using the latest high technologies. Modern laparoscopic methods are also used. They are used to remove tumors of any size, regardless of where they are located.
This is a radical surgical intervention that involves excision of the cyst and transfer of tissue for histological examination. However, this is a minimally invasive procedure, after which only 3 5 mm incisions are left on the body.
The operation is absolutely safe, since the doctor sees all the subtle anatomical structures on the monitor. When performing laparoscopic interventions, the Scientific and Practical Surgery Center uses innovative surgical equipment. For example, doctors have ultrasonic scissors at their disposal, which allow them to perform bloodless operations.
Specialists carefully monitor the patient’s condition, preventing all possible complications. To prevent relapses, argon-enhanced plasma produced in the USA can be used. If doctors note the proximity of the vessels, they will prescribe hemostatic agents from leading European manufacturers to the patient. To prevent the occurrence of adhesions and thrombosis, the clinic’s specialists use:
- synthetic absorbable suture materials
- anti-adhesion barriers
- high quality compression jersey.
The patient can get out of bed the very next day after laparoscopic surgery. On the second day, doctors allow him to eat. On the third day, the patient can already go home. Return to active life and work is allowed 10-14 days after surgery. But in the future, a person must be observed by a urologist, as well as regularly undergo ultrasound and CT scans.
Diagnostics
- Survey and excretory urography
- Ultrasound, Dopplerography
- CT (computed tomography)
- Diagnostic puncture and cystography
X-ray methods: It is not possible to establish an accurate diagnosis of a simple renal cyst only on the basis of survey and excretory urography. With the help of excretory urography, it is possible to identify the “sickle” symptom or the “open mouth” symptom, which are characterized by the spreading of the kidney calyces without their “amputation”.
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) reveals a simple renal cyst as an echo-negative formation of a round or oval shape, with clear, even, continuous contours and thin walls. Ultrasound allows for dynamic observation and use as a screening test. Dopplerography is a method that allows you to study the blood supply to the kidney. This diagnostic method is especially important for the combination of kidney cysts and arterial hypertension.
Computed tomography (CT) in some cases cannot provide 100% confidence in the accuracy of the diagnosis, especially with parapelvic cysts and tumors in the cyst. This somewhat reduces its diagnostic value. The CT scanning criteria for cystic renal lesions are similar to those used in echography: sharp, thin, distinct, smooth walls and edges; round or oval shape; homogeneous content. Density ranges from -10 to +20 HU, similar to that of water, and no enhancement should occur after intravenous injection of contrast medium.
Percutaneous puncture cystography is currently not the main diagnostic method, but can be used in the process of percutaneous puncture treatment of a simple cyst to clarify the location of the cyst and determine its relationship with the pyelocaliceal system.
Diagnosis of a kidney cyst at the Yusupov Hospital
A preliminary examination before starting treatment at the Yusupov Hospital, as a rule, takes no more than two to three days. First of all, patients are recommended to visit a nephrologist or urologist who collects anamnesis. In accordance with the results of the initial examination, an individual diagnostic program is selected for each patient using modern methods to determine the condition and functionality of the kidneys, identify the exact location of the cystic formation, its type and category. For this purpose, specialists at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe the following studies:
- computed tomography (CT);
- kidney ultrasound (ultrasound);
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- nephroscintigraphy;
- biochemical blood tests;
- angiography;
- cyst biopsy;
- general blood and urine tests.
Causes and consequences of kidney cysts
Kidney cysts are a pathology that can develop under the influence of various causes. Polycystic disease occurs under the influence of teratogenic factors on the fetus during intrauterine development. Kidney injuries are often accompanied by rupture of the renal parenchyma and hematoma, which eventually turns into a cyst. With prostate adenoma in men, blockage of the urinary tract by kidney stones, urine stagnation occurs, the renal pelvis dilates, and cystic cavities form.
When urine stagnates in the kidney, infection occurs and acute and chronic pyelonephritis develops. As the inflammatory process progresses, pus may form in the kidneys and urosepsis may develop. If the cyst ruptures, fluid spills into the perinephric space, causing paranephritis. When the contents of the cyst leak into the abdominal cavity, peritonitis develops. Large cysts disrupt the outflow of urine with the formation of hydronephrosis.