Gastroenteritis is a disease of the gastrointestinal tract, which is expressed by inflammatory processes in the intestines and stomach. Gastroenteritis can be either acute or become chronic.
Acute gastroenteritis
Acute gastroenteritis is an inflammation of the stomach or intestines, often caused by improper diet or the entry of various types of viruses and infectious agents into the intestinal tract.
Too much overeating or frequent dry meals, as well as an irregular diet can also cause inflammation of the stomach. Symptoms of the disease manifest themselves sharply, the pain is in the nature of contractions. The main symptoms of acute gastroenteritis are severe pain in the abdomen or in the navel area, nausea, vomiting, general weakness of the whole body, rapid heartbeat, pale skin, loss of appetite, and a feeling of dizziness.
In particularly severe cases, the patient may experience fainting. In acute gastroenteritis, a change in stool is observed - the discharge becomes mucus-like. When the disease manifests itself, another visual symptom is sharpening of facial features. If the first symptoms of acute gastroenteritis occur, the patient must be given first aid - rinse the stomach with warm water with the addition of potassium permanganate or with the addition of soda. After gastric lavage, it is necessary to consult a doctor and conduct a comprehensive examination of the gastrointestinal tract and identify the causative agent of gastroenteritis.
Causes of gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis is divided into several types depending on what caused the disease. Bacterial gastroenteritis - is provoked by intestinal pathogens, bacteria, salmonella or staphylococci, which enter the esophagus with poor-quality food or with a weakened immune system. Viral gastroenteritis - the causative agent is rotavirus - an intestinal viral bacterium.
Rotavirus exposure is caused by dirty hands, poor hygiene before and during meals, poor quality, unwashed food, poorly prepared food, or eating raw food such as seafood. Chronic gastroenteritis mainly appears as a consequence of untreated acute gastroenteritis, or against the background of cancer. Gastroenteritis can also be classified as an “occupational” disease.
Symptoms of gastroenteritis
The main symptoms of gastroenteritis are nausea, vomiting and changes in stool; in more severe cases of inflammation, stool may be accompanied by bloody discharge. Quite often the patient experiences fever, severe headaches, and abdominal pain, especially in the navel area. When viral gastroenteritis occurs, the patient experiences a strong increase in body temperature. Abdominal pain is accompanied by severe bloating.
The main symptoms of gastroenteritis manifest themselves within a day or two after infection. If a patient experiences severe dizziness and deep fainting, it is necessary to immediately seek help from a doctor, since such symptoms indicate advanced disease and the body’s inability to resist the disease. In particularly severe cases, body convulsions are observed.
Gastroenteritis in children
Gastroenteritis in children is a common disease, but in particularly severe and advanced cases it can cause death. Gastroenteritis in children can be a consequence of dysbiosis, previous influenza, or rotavirus entering the body. Symptoms of gastroenteritis in children are nausea when eating, bloating, colic, sleep disturbance, fever, diarrhea. When the first signs of gastroenteritis appear in a child, it is necessary to take measures to prevent dehydration - give as much water as possible to drink.
If vomiting does not stop within a day after the disease is detected, consult a doctor immediately. If gastroenteritis is detected, the child must adhere to a diet to normalize the functioning of the stomach. It includes unsweetened pureed vegetables or fruits, baked apples, boiled lean meat, lean soups, and fish. This diet is followed for a week, after which you can return to your usual diet. When treating gastroenteritis in children, it is necessary to exclude the consumption of dairy products for two weeks.
Treatment of gastroenteritis
When the first signs of the disease appear, the patient must refrain from eating food for several hours to normalize intestinal function. Drink as much fluid as possible - water or light juices without pulp. After the feeling of nausea disappears, you can eat some boiled rice, a cracker or a banana. Antibiotics are not used to treat gastroenteritis. If there is severe pain, it is necessary to lavage the stomach with a weak solution of potassium permanganate or soda.
The diet for gastroenteritis includes lean boiled fish and meat, lean soups, cereals, vegetables, and as much liquid as possible - water, juices. The patient is prohibited from consuming dairy products and fruits. The diet must be followed for 3-4 days, after which you return to your previous diet.
Over the course of three days (June 3-5, 2015), 7 citizens with a diagnosis of acute gastroenteritis turned to the emergency department of the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug “Gubkinsky City Hospital”, 6 more patients were delivered by emergency department staff; of which: 1 was hospitalized in the intensive care unit and anesthesiology department, 7 were hospitalized in the infectious diseases department in a state of moderate severity, the rest refused hospitalization. The age range of patients is from 12 years to 61 years. At this time, the condition of all patients is stable.
Diagnosis of gastroenteritis
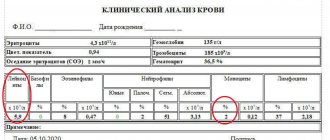
The first stages of diagnosis are studying the patient’s complaints and collecting anamnesis. To clarify the cause of the disease, the patient’s biological material is examined:
- blood;
- vomit;
- feces;
- urine.
An examination using instrumental methods is prescribed for chronic gastroenteritis. The patient will need to undergo an ultrasound of the peritoneum, which helps to clarify the condition of various organs of the gastrointestinal tract. To determine the acidity of gastric juice, intragastric pH-metry is performed. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy allows a detailed examination of the stomach and duodenum.
You have questions? Leave a request and we will call you back!
Principles of treatment
When the first signs of gastroenteritis appear, you must limit your food intake. To prevent dehydration, you should drink enough fluids. It is recommended to drink boiled water, rosehip decoction, saline solution, mineral water with an alkaline composition. The liquid should be taken in small portions (50 ml per dose), taking small sips. You can prepare formulations with pharmaceutical powders (Regidron, Oralit).
In case of insufficient effectiveness of rehydration or a sharp deterioration in health, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor. The tactics for further treatment of gastroenteritis will be determined by its form and degree of dehydration.
Patients are prescribed:
- Antibiotics.
- Antiviral agents.
- Antiemetic drugs.
- Enzyme medications.
- Adsorbents.
- Antidiarrheal medications.
- Probiotics.
- Vitamin complexes.
In case of severe intoxication syndrome, the patient is hospitalized. In this case, therapy is supplemented with intravenous administration of medicinal solutions. After the acute phase subsides, physiotherapy is performed. The most effective treatments for gastroenteritis are paraffin applications and inductothermy. During the entire treatment course, the patient must follow a special diet (tables No. 4, No. 2). To fully recover, you must adhere to a diet for several weeks after recovery.
With timely treatment, a favorable prognosis remains. Most patients make a complete recovery.
Clinical manifestations of the disease
The incubation period lasts from several hours to three days. The severity of symptoms depends on the cause of the disease. General manifestations:
- weakness, general malaise;
- headache;
- nausea, flatulence;
- cramping abdominal pain, heaviness in the stomach;
- elevated temperature;
- vomiting, diarrhea.
The course of bacterial gastroenteritis is more severe than the form caused by a virus.
In acute gastroenteritis, special attention should be paid to dehydration of the body, which increases very quickly as a result of uncontrollable vomiting and diarrhea. Dehydration is manifested by confusion, convulsions, severe weakness, tachycardia and decreased blood pressure. The skin becomes dry and its elasticity decreases. There is a decrease in urine output, up to anuria. Treatment of acute infectious gastroenteritis should primarily be aimed at restoring the body’s water and electrolyte balance and eliminating the pathogen.
Symptoms of gastroenteritis in children
In childhood, bacterial and viral gastroenteritis is very severe. The disease is especially dangerous for infants, since in the presence of dehydration, irreversible processes occur in the baby’s body.
The first symptoms of acute gastroenteritis occur a few hours after infection. The clinic depends on the age of the child, the state of immunity and the type of pathogen. Symptoms of the initial stage:
- stomach pain, flatulence;
- general weakness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- headache;
- diarrhea.
As the disease develops, the initial manifestations intensify with increased temperature, decreased blood pressure and bradycardia.
How to treat childhood gastroenteritis? Broad-spectrum antibiotics and antimicrobial agents are used. In addition, the use of antiemetics, enterosorbents, antispasmodics, and enzymes is indicated.
Foodborne illnesses
A typical example of gastroenterocolitis is food poisoning. This is a group of diseases that occur when microbial agents and (or) their toxins enter the body along with food. The disease typically has an acute onset, a rapid course, symptoms of general intoxication and damage to the digestive organs. The cause of foodborne toxic infections can be a variety of bacteria: salmonella, shigella, escherichia, streptococci, spore anaerobes, spore aerobes, halophilic vibrios, staphylococcal enterotoxins types A, B, C, D, E.
Source of infection
- a sick person or a bacteria carrier, as well as sick animals and bacteria-shedding animals. Microbes get on food products, mainly those that are not cooked. For example, staphylococci can multiply in milk and dairy products and release specific toxins. At the same time, the appearance and smell of the product is no different from the usual one. Often the disease can be associated with the consumption of cakes and pastries with milk or butter cream, cottage cheese. Other bacteria more often contaminate meat pates, canned fish in oil, vegetable dishes, and salads. The disease can occur in both sporadic cases and outbreaks. The incidence is recorded throughout the year, but increases slightly in warm weather.
Prevention
It is not difficult to protect yourself or your child from developing the disease. It is enough to adhere to the basic rules of prevention:
- Maintaining hygiene. Wash your hands thoroughly after going to the toilet and before eating.
- High-quality dishwashing. In public places it is better to use disposable or individual devices.
- Strictly adhere to the technology of preparing dishes from eggs, fish, meat.
- Drinking boiled or bottled water.
- Compliance with storage conditions and terms of perishable products.
- Limiting fast food consumption.
If you are traveling to a country with poor public hygiene standards where there is a risk of water contamination, such as some countries in Africa or Asia, avoid the following foods and drinks:
- tap water;
- fruit juices (sold from a stall on the street);
- ice cream or ice cubes;
- shellfish;
- eggs;
- salads;
- raw and undercooked meat;
- peeled fruits;
- mayonnaise;
- sauces.
Before you travel, it is advisable for you to have all traveler's vaccinations recommended for the country you are traveling to.
Classification
Acute gastroenteritis is distinguished:
- Nutritional (caused by overeating with the intake of large amounts of spicy or too rough food, seasonings that irritate the mucous membrane, strong alcoholic drinks).
- Infectious and viral origin (cholera, typhoid fever, salmonellosis, sometimes influenza, etc. occur with the clinical picture of severe gastroenteritis).
- Allergic (with idiosyncrasy to certain foods - strawberries, eggs, crabs, etc. or with an allergic reaction to medications - iodine, bromine preparations, some sulfonamides, antibiotics, etc.).
- Toxic (in case of poisoning with arsenic compounds, sublimate and other poisons; poisoning with mushrooms - toadstool, fly agarics, false honey mushrooms, other toxic substances of a non-bacterial nature that may be contained in food products - stone fruits, some fish products - burbot liver, pike, mackerel caviar etc.).