Introduction
Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori
still remains quite high, despite actively carried out eradication therapy.
According to N.V. Zakharova et al., H. pylori
in St. Petersburg is 50% of the total population [1].
On the other hand, eradication of H. pylori
leads to histological remission of chronic gastritis, interrupts the chain of events in the Correa cascade by reducing the activity of the inflammatory process and reducing the severity of atrophy and metaplasia of the gastric mucosa, established histologically in accordance with the OLGA classification (Operative Link for Gastritis Assessment ) or OLGA-IM (OLGA-intestinal metaplasia).
According to M. Kodama et al., the severity of atrophy and intestinal metaplasia decreases significantly 10 years after eradication [2]. A meta-analysis of 16 studies by YJ Kong et al. revealed a significant decrease in the severity of atrophy of the gastric mucosa in the antrum and body of the stomach, as well as intestinal metaplasia in the antrum [3]. Consequently, eradication of H. pylori
has not only a direct effect on reducing and eliminating the inflammatory process in the gastric mucosa, healing the ulcer and preventing the development of relapses and repeated bleeding (both with peptic ulcer disease and with the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs against the background of the presence of
H. pylori
), the development of histological remission in the early stages of gastric maltoma, but also leads to good long-term results - a decrease in the severity of atrophy and intestinal metaplasia and ultimately to a decrease in the incidence of cancer of the distal stomach.
This makes it clear how important adequate eradication of H. pylori
is in clinical practice.
According to a Cochrane review, eradication of H. pylori
reduces the incidence of gastric cancer by 34% [4].
Meta-analysis data by YC Lee et al. prove the high effectiveness of H. pylori
in preventing the development of gastric cancer [5].
In Russia, evidence of a decrease in the incidence of cancer of the distal stomach [6, 7] associated with the eradication of H. pylori
.
The enormous importance of H. pylori
is reflected in numerous provisions and recommendations adopted in recent years by medical communities [8–20].
The need to eradicate H. pylori
in all patients infected with this pathogen is consistent with the Kyoto consensus on Helicobacter pylori gastritis, Maastricht V and Houston consensuses [8, 10, 20]. Realities of the 21st century are such that there has been a significant decrease in the effectiveness of previously used anti-Helicobacter regimens, including in Russia. Predictors of low effectiveness of anti-Helicobacter therapy are various factors, the main ones of which are recognized: pathogen resistance, insufficient acid-suppressive effect, low compliance.
Methods for increasing the effectiveness of anti-Helicobacter therapy:
Targeted therapy taking into account bacterial resistance and genotypic polymorphism of CYP2C19, individualized anti-Helicobacter therapy taking into account the characteristics of micro- and macroorganisms.
Increasing the duration, frequency of administration or dose of components of the anti-Helicobacter regimen.
Use of double doses of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). The use of new, stronger acid-suppressive drugs (K-competitive proton pump blockers - vonoprazan), control of acid production during the anti-Helicobacter regimen and maintaining it at a certain level.
The use of 3 antibacterial drugs simultaneously and the use of new antibacterial drugs, the use of natural antibiotics (pyloricidin A, B and C), natural antimicrobial peptides (cathelicidins and defensins), benzimidazole derivatives, polycyclic components.
Combination of anti-Helicobacter therapy and sanitation of the oral cavity (elimination of gingivitis, periodontitis, etc.).
Effect on H. pylori
(acetylcysteine, proteinase complex,
quorum sensing
, silver nanoparticles, nanoemulsions, lactoferrin, etc.), adjuvant use of probiotics, prebiotics or metabiotics.
Inclusion of rebamipide, pyridodiazepines, and sulfonamides into the treatment regimen.
Herbal medicine (ginger rhizome extract, red and chili pepper (capsaicin), broccoli (sulforaphane), red ginseng extract, green tea, St. John's wort, cloves), grapes, cranberry juice, curcumin, concentrated honey solution, red wine (resveratrol), vitamin supplements (vitamins C and E).
The use of special gastric drug delivery systems (gastro retentive drug delivery sestems - GRDDS), micro- and nanoparticles of various drugs.
It can be assumed that increasing the duration of the Pilobact AM-based anti-Helicobacter regimen from 7 to 14 days, increasing the dose of omeprazole from 40 mg/day to 80 mg/day and including bismuth in the colloidal subcitrate with the adjuvant use of a prebiotic complex will lead to a significant increase in H2 pylori
without increasing the number of adverse events.
All of the above served as the basis for studying the effectiveness of modified Pilobact AM-based therapy (MPAMOT) for the eradication of H. pylori
.
The introduction of a prebiotic complex into the anti-Helicobacter regimen can also increase the effectiveness of treatment [22–30]. The prebiotic complex selectively stimulates the growth and/or activity of a limited number of microbiota bacteria; prebiotics are resistant to the digestive process in the upper gastrointestinal tract, are fermented by intestinal microbiota, and have a proven synergistic effect on the intestinal microflora [22]. Prebiotics are well tolerated, act throughout the colon, have an anti-infective effect (due to the synthesis of propionate), and are highly effective [23–27]. The effect of the prebiotic does not depend on the viability of the culture, while its own microflora is maintained and not colonized by foreign ones. Probiotics create a positive effect in dysbiosis, but not always and not as expected [28]. Every second person who uses a probiotic exhibits antagonistic properties towards host microorganisms; biocompatibility - 15% [29].
Purpose of the study:
determine the effectiveness of MPAMOT in patients infected with
H. pylori
.
To achieve the intended goal, the following tasks are set:
Assess the eradication rates of H. pylori
in all patients included in the study.
Assess the eradication rates of H. pylori
in all patients undergoing treatment.
Assess the incidence of adverse events among all patients included in the study (intention to treat - ITT) and all patients undergoing treatment ( per protocol
- PP).
To compare MPAMOT with standard 7-day Pilobact AM-based therapy (SPAMOT) and targeted anti-Helicobacter therapy.
To assess the frequency of adverse events (diarrhea, nausea, abdominal discomfort, taste changes) with MPAMOT and SPAMOT.
Contraindications
Pilobact is not prescribed for porphyria , breastfeeding, chronic diseases of the hepatic system, intolerance to active components (omeprazole, tinidazole, clarithromycin, for Pilobact AM - amoxicillin), during pregnancy, severe renal, liver failure, when taking ethanol (the risk of developing disulfiram-like disorders increases). reactions), children under twelve years of age.
Material and methods
A two-center controlled multifactorial study was conducted according to a specially developed protocol in accordance with GCP (Good Clinical Practice) standards. All patients signed informed consent. In the 1st study group (n=201), there were 90 men and 111 women. Age ranged from 18 to 87 years (mean age 47.9±6.9 years). Average height - 168.3±9.5 cm. Body weight - 73.2±11.7 kg. Among the patients, 177 were with H. pylori
- induced chronic gastroduodenitis, 19 - with peptic ulcer, with ulcer localization in the duodenal bulb, 5 - with gastric ulcer.
Patients of the 1st group received a 14-day MPAMOT - the drug Pilobact AM (in accordance with the instructions for this complex drug), which includes omeprazole 20 mg, amoxicillin 1000 mg and clarithromycin 500 mg, 2 times / day and additionally omeprazole 20 mg 2 times a day 30–45 minutes before breakfast and dinner, colloidal bismuth subcitrate (CBS) 240 mg 2 times a day 40–60 minutes after breakfast and dinner for 14 days and a prebiotic complex 5.0 × 2 times. /day 28 days. In group 2 (n=15), patients received SPAMOT - omeprazole 20 mg twice a day, amoxicillin 1000 mg and clarithromycin 500 mg twice a day for 7 days. The compared groups did not have statistically significant differences in age, gender and other criteria, including nosological forms, frequency and severity of symptoms before treatment, which could have affected the results of the study. The rationale for the 14-day course was based on data from a Cochrane meta-analysis assessing the effectiveness of the anti-Helicobacter regimen depending on its duration [31]. H. pylori
eradication rates [32, 33]. A prebiotic complex with fructooligosaccharides, gum arabic, and lactitol was introduced into the anti-Helicobacter regimen.
Diagnosis of H. pylori
carried out using a rapid urease test (Biochit), histologically, and eradication of
H. pylori
after 1 month.
after the end of all medications - by determining the H. pylori
in the stool and a carbon-labeled urease breath test, which corresponded to provisions 20, 21 and 27 of the Houston Consensus on the diagnosis of
H. pylori
in the USA. The fact of eradication was established only if the results of both validated tests were negative.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
It contains three active components - omeprazole, tinidazole and clarithromycin. The drug has antiulcer and antimicrobial effects. Under the influence of omeprazole, the secretion and acidity of hydrochloric acid decreases (due to the inhibition of a special enzyme located in the membranes of parental cells in the gastric mucosa), and the level of stimulated and basal secretion . Oral administration of omeprazole inhibits the secretion of gastric juice after an hour, the effect persists throughout the day. A 97% reduction in gastric acidity is achieved by repeated administration of 20 mg of omeprazole during the day.
The second component of the drug Pilobact is clarithromycin , a semi-synthetic derivative of erythromycin A, an antibiotic of the macrolide , which acts on Helicobacter pylori , anaerobic microorganisms, gram-negative and gram-positive flora.
The third component of the drug Pilobact is tinidazole ; acts on Giardia, amoebas, Trichomonas , Helicobacter pylori, causative agents of anaerobic infections, and has an antiprotozoal effect.
Pilobact AM additionally contains amoxicillin (an antibiotic). Pilobact NEO is used for triple Helicobacter pylori therapy.
special instructions
Tinidazole may cause urine to turn dark.
Throughout the entire course of antiulcer therapy, complete abstinence from drinking alcoholic beverages is required due to the risk of developing disulfiram-like reactions .
In case of chronic pathology of the hepatic system, periodic monitoring of the level of liver enzymes is mandatory.
Before starting therapy, the attending physician must exclude the presence of malignant neoplasms (taking omeprazole may mask the clinical manifestations of cancer).
Pilobact, instructions for use (Method and dosage)
The medicine is taken orally.
Each blister contains 2 capsules of omeprazole at a dose of 20 mg, 2 tablets of tinidazole at a dose of 500 mg and 2 tablets of clarithromycin at a dose of 250 mg.
Each blister is designed for 1 day of antiulcer therapy. According to the instructions, you need to take 1 capsule of omeprazole, 1 tablet of tinidazole and 1 tablet of clarithromycin in the morning (the capsule and tablets are located in the orange part of the blister), repeat the procedure in the evening (the capsule and tablets are located in the blue part of the blister).
Each package contains 7 blisters, designed for a weekly course of antiulcer therapy.
After completion of treatment, it is recommended to take omeprazole at a dose of 20 mg per day for three weeks.
Interaction
Clarithromycin, which is part of the drug Pilobact, can cause an increase in the level of theophylline and terfenadine in the blood (a prolongation of the QT interval is recorded on the ECG).
An enhanced effect of the drug is observed with simultaneous therapy with oral forms of anticoagulants .
When treated with digoxin, astemizole, phenytoin, carbamazepine, cisapride , pimozide, valproate, Lovastatin , disopyramide, cyclosporine , an increase in the concentration of the above drugs is observed.
Omeprazole can reduce the rate of metabolic processes when taking diazepam and phenytoin.
Pilobact reduces the absorption of iron salts (reducing acid production in the stomach), ampicillin, ketoconazole .
Pilobact price, where to buy
The price of Pilobact is approximately 1250 rubles per set.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
ZdravCity
- Pilobact combination set n42 (6 pcs x 7 blister)SUN Pharmaceutikal Industries Ltd.
RUB 1,232 order - Pilobact am combination set n56 (8 pcs x 7 strips) SUN Pharmaceutikal Industries Ltd.
RUB 1,271 order
- Pilobact AM set of tablets and capsules No. 7 Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
RUB 1,272 order
- Pilobact set of tablets and capsules No. 7 Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
1270 rub. order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Pilobact combined set (set No. 7)Ranbaxy
RUB 1,048 order
- Pilobact combiner AM (set No. 7)Ranbaxy
RUB 1,086 order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Pilobact NEO N42 set of tablets Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd, India
464 UAH.order
PaniPharmacy
- Pilobact neo tablets Pilobact Neo comb. table No. 42 India, SUN
476 UAH. order
show more
Side effects
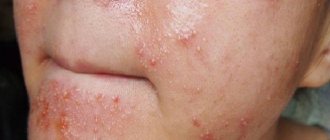
Omeprazole, which is part of Pilobact, can cause headaches, increased gas formation, diarrhea, weakness, dizziness, epigastric pain, constipation, nausea, thrombocytopenia, increased levels of liver enzymes, eosinocytopenia , neutropenia, leukopenia, skin rashes.
Tinidazole can cause cholestatic jaundice , gastralgia, nausea, headache, allergic reaction in the form of itching and rash, pseudomembranous enterocolitis , diarrhea, vomiting, and the development of secondary resistance of microbial flora. Side effects of tinidazole: skin itching, vomiting, leukopenia, unpleasant taste in the mouth, appetite disturbances, headaches, urticaria.