- Causes
- Symptoms of vasomotor rhinitis
- Kinds
- Diagnosis of vasomotor rhinitis
- Treatment of vasomotor rhinitis
- Therapy at home
- Folk remedies for vasomotor rhinitis
- Pharmacotherapy
- Treatment of vasomotor rhinitis in pregnant women
- Surgical treatment of vasomotor rhinitis
- Possible complications
- Prevention
Under the influence of unfavorable external and internal factors, the vessels of the nasal wall become prone to hyperreactivity and expansion.
Chronic inflammation develops - vasomotor rhinitis. It is not associated with an allergic reaction. Vasomotor does not include cases of rhinitis caused by occupational factors, salicylate intolerance, the atrophic variant of the pathology and cases of the disease that are not associated with allergies, but are accompanied by the appearance of immunocompetent cells (eosinophils, mast cells, neutrophilic leukocytes) in the nasal mucus. Vasomotor rhinitis occurs in almost 10% of the population. A quarter of these patients suffer from persistent symptoms of the disease, and in half of the patients, signs of pathology are moderately or significantly expressed. Women get sick 2 times more often than men, the average age of patients is 40 years. However, allergic rhinitis occurs 3 times more often than vasomotor rhinitis.
Very often, vasomotor rhinitis occurs with long-term use of decongestants, as well as during every 3rd pregnancy. This disease occurs in both children and the elderly. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a doctor in time and begin proper treatment of vasomotor rhinitis in adults or children in order to avoid subsequent complications.
Causes
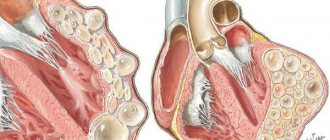
Vasomotor rhinitis primarily affects the inferior turbinates. They humidify and warm the air, but against the background of the disease, this function is disrupted, and the vessels of the mucous membrane do not react correctly to environmental conditions. Constant congestion develops - the main symptom of vasomotor rhinitis. Violation of vascular regulation is associated with an imbalance of the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for vascular tone.
External and internal factors cause such an imbalance. Environmental conditions include:
- temperature too low or high;
- rapid change in atmospheric pressure;
- air pollution from smoke, substances with a strong odor, the effects of spicy foods, alcohol, nicotine and tar from cigarette smoke, cocaine use;
- respiratory diseases of a viral nature.
Internal factors that can provoke autonomic imbalance:
- stress and strong emotions;
- physical and sexual stress;
- hormonal diseases: ovarian dysfunction (puberty, pregnancy, menstruation), hypothyroidism, excess growth hormone (acromegaly and gigantism);
- pathological reflux (reflux of contents) from the stomach into the esophagus, from the stomach into the pharynx and from the pharynx into the larynx;
- deformation of the nasal septum;
- decreased patency of the upper respiratory tract (adenoids in children).
There may be a hereditary predisposition to the occurrence of the disease.
Rhinitis caused by medications has 2 options. The first of them is associated with long-term use of vasoconstrictor drops, as a result of which vascular receptors lose sensitivity to internal vasoconstrictor factors and chronically dilate.
The second variant of drug-induced vasomotor rhinitis occurs with long-term use of medications that affect the general tone of the autonomic nervous system. These are many drugs for hypertension (ACE inhibitors, alpha and beta blockers, methyldopa, calcium antagonists), antipsychotics, anticonvulsants, oral contraceptives, drugs for regulating potency (sildenafil).
Quite often, rhinitis develops in pregnant women and goes away after childbirth. The reasons for this phenomenon are being studied by doctors. It is believed that hormonal imbalance, stress, and an increase in the volume of blood circulating in the body are important.
Types of disease
The disease occurs in two forms - neurovegetative and allergic. The first occurs when the nervous mechanisms responsible for the tone of blood vessels are disrupted. In this case, any irritant that gets on the mucous membrane can cause illness. The allergic form occurs when allergens come into contact with the surface of the mucosa. This form of the disease manifests itself as a response of the immune system to interaction with an irritant, in contrast to the neurovegetative form.
Allergic rhinitis can be seasonal (for example, during the flowering period) and year-round, which manifests itself throughout the year (for example, on the hair of pets).
According to the nature of the disease, acute, subacute and chronic diseases are distinguished. The symptoms of the acute form are most intense.
According to the nature of the manifestation of symptoms of the disease in adult patients, there is a vasomotor form (characterized by swelling), a hypersecretory form, which occurs with abundant mucus discharge from the nasal passages, and a combined form (there is both swelling and increased secretion production).
Symptoms of vasomotor rhinitis
The main signs of vasomotor rhinitis:
- difficult nasal breathing, permanent or temporary, occurring either on one side or the opposite, especially when lying on one side and turning over;
- moderate nasal discharge;
- discharge running down the back of the throat.
Some patients have a clear connection between the appearance of symptoms of the pathology and the intake of food, alcohol, and exposure to the cold. In other patients, no obvious triggering factors can be detected.
Depending on the prevailing symptoms, patients with rhinitis can be divided into groups with “wet” and “dry”, stuffy nose.
Sneezing, itching, severe runny nose, and lacrimation are more common with the allergic variant of the pathology, but can also be observed with the vasomotor variant, but much less frequently.
With the medicinal option, the main complaint is dependence on vasoconstrictor drops and sprays.
When examining a patient, the doctor may notice signs of an imbalance in the autonomic nervous system:
- pallor or cyanosis, coldness of the extremities;
- increased sweating;
- a tendency to decrease body temperature, blood pressure and slow heart rate;
- drowsiness, irritability, hypochondriacal disorders.
During rhinoscopy, the inferior turbinates of the nose are enlarged, their surface is reddened, with a bluish tint, or pale. Sometimes hemorrhages are visible.
Kinds
The classification of vasomotor rhinitis is based on its causes and mechanisms of development. The following types of disease are distinguished:
- medicinal (caused by decongestants or oral medications);
- hormonal (during pregnancy, puberty, diseases of the endocrine system);
- reflex (food, cold and others);
- psychogenic (associated with emotional stress);
- idiopathic (unexplained nature);
- mixed.
Treatment with modern methods
Vasomotor rhinitis requires an integrated approach to treatment. Simultaneous medication, physiotherapeutic treatment, and general strengthening procedures will help cope with the disease.
Complex treatment should be aimed at strengthening the vascular system of the nasal cavity, regulating blood circulation, relieving swelling, eliminating factors that lead to dysfunction of the mucous membrane, and increasing immunity.
Along with the use of vasodilating drugs, physiotherapeutic treatment is used: electrophoresis, ultrasound irradiation, laser irradiation. This treatment normalizes the functioning of the nervous system, enhances lymphatic drainage, increases blood circulation, relieves inflammation and swelling of the mucous membrane, and has a regenerating effect.
Traveling to nature, regular walks in the fresh air, visiting a swimming pool, bathhouse, and sanatorium-resort treatment have a beneficial effect on the course of treatment of the disease.
Surgical intervention is indicated in case of ineffectiveness of therapeutic complex treatment.
Diagnosis of vasomotor rhinitis
The diagnosis of vasomotor rhinitis is established by exclusion. The only sign that allows us to speak with confidence about this disease is dependence on decongestants.
This pathology is defined as non-infectious non-allergic inflammation. Therefore, first of all, it is necessary to exclude chronic rhinosinusitis. This disease is usually caused by bacteria. It is accompanied by mucous or purulent discharge at the mouths of the paranasal sinuses, headache, signs of intoxication, periods of exacerbation and remission. To exclude chronic rhinosinusitis, an X-ray examination or computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses is prescribed.
To exclude allergic rhinitis, skin tests with allergens (dust, pollen, animal hair, mold and others) or determination of antibodies to these allergens (specific IgE) in the blood are carried out.
The following diagnostic methods are less common:
- endonasal provocation test with methacholine (performed to exclude non-allergic rhinitis with eosinophilic syndrome);
- electrophoretic analysis of nasal secretions;
- rhinomanometry and acoustic rhinometry to assess the effectiveness of the treatment.
It should be borne in mind that allergic rhinitis is not immediately accompanied by characteristic changes, and in about a quarter of patients with initially negative allergy tests, they become positive after 3 years. This forces us to reconsider the diagnosis and is often observed in pediatric practice.
Vasomotor rhinitis should not be a diagnosis made at the first visit to an ENT doctor. Additional studies listed above are needed. You may need to consult other specialists - an allergist, neurologist, endocrinologist, gynecologist, gastroenterologist.
Pathogenesis
The pathophysiological mechanisms of development of this disease are not fully understood. Vasomotor rhinitis does not have a clearly defined cause: viruses, infections or allergies. Often, this pathology appears due to the fact that a person has impaired regulation mechanisms of the nerves responsible for the connection between the nasal mucosa and the central nervous system (sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves). The parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for the secretion of mucus, and the sympathetic nervous system is responsible for normal vascular tone. If an imbalance appears between the mediators that transmit nerve impulses, then vascular permeability and the volume of mucus produced automatically increases. As a result, a person develops symptoms of rhinitis.
Treatment of vasomotor rhinitis
Treatment of vasomotor rhinitis in adults and children should be carried out taking into account the triggering factors of the disease, both external and internal, and their elimination.
Therapy at home
If symptoms are determined to be related to certain conditions (alcohol use, stress, etc.), lifestyle changes must be made to avoid such situations. It is important to influence the function of the autonomic nervous system through regular exercise and hardening.
Folk remedies for vasomotor rhinitis
Popular folk recipes for vasomotor rhinitis:
- instillation of beet juice, Kalanchoe, birch sap, menthol oil into the nose;
- lubricating the mucous membrane with ointments based on petroleum jelly and walnut or calendula leaves;
- rinsing the nasal cavity with a solution of honey;
- acupressure in the area of the bridge of the nose and at the upper edge of the wings of the nose;
- breathing exercises, including slow inhalation through one nostril and even slower exhalation through the other; The exercise must be repeated 10 times for at least a month.
Pharmacotherapy
Several groups of drugs are used to treat vasomotor rhinitis in adults:
- local H1 receptor blockers (azelastine, levocabastine) for nasal discharge, sneezing, congestion;
- intranasal glucocorticoid drugs when congestion predominates;
- local stabilizers of mast cell membranes with the predominance of sneezing and congestion in children over 2 years of age;
- local M-anticholinergic agents (ipratropium bromide) with a predominance of strong nasal discharge;
- peptidergic neuron blockers (capsaicin);
- botulinum toxin A.
The first choice drugs are glucocorticoids for intranasal use - Avamis and Beclomethasone sprays, Benacap drops, Dezrinit, Nazarel, Nasonex, Nasobek, Nosephrine, Rinoclenil, Tafen-Nasal and Flixonase sprays.
For the treatment of vasomotor rhinitis in children over 6 years of age, budesonide nasal spray is used, 1 to 2 doses 1 to 2 times a day for 3 months. The exact dosage should be selected by the doctor in accordance with the age of the child. Before using the hormonal spray, it is recommended to rinse your nose with saline solution.
Budesonide is also recommended for the treatment of drug-induced rhinitis; the course of treatment is at least 2 months. If ineffective, short-term use of prednisolone tablets is possible. If these measures do not allow the patient to wean off decongestants, surgery is the only option.
Treatment of vasomotor rhinitis in pregnant women
Provoking factors, active and passive smoking, and manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux are eliminated.
The most effective and safe method of therapy in this group of patients is nasal rinsing with saline solution, irrigation with sea water, breathing exercises and occasional use of decongestants.
Of the glucocorticoids in pregnant women, only budesonide is the most studied and therefore considered safer. It is prescribed for existing allergic rhinitis, complicated by the addition of a vasomotor variant of the pathology.
Surgical treatment of vasomotor rhinitis
At the beginning of treatment, the only surgical procedure that should be performed in patients with vasomotor rhinitis is the correction of possible deformation of the nasal septum. Only if drug treatment is ineffective within a year can other interventions be considered.
Any operation for vasomotor rhinitis only facilitates nasal breathing. It has very little effect on symptoms such as nasal discharge, itching, sneezing, and decreased sense of smell.
For vasomotor rhinitis, the following interventions can be performed:
- displacement of the nasal concha;
- removal of part of the bone and soft tissue under the mucous membrane;
- plastic techniques;
- superficial or submucosal interventions.
It is preferable to use the operations of the last group: vasotomy, electrocoagulation, ultrasonic disintegration, laser intervention, shaver or radiofrequency reduction, cryosurgical method. The choice of intervention method is determined individually for each patient. The intervention can be supplemented by partial denervation of the vessels of the mucous membrane.
Surgical treatment of vasomotor rhinitis is also carried out in children. It is often combined with adenoid removal, correction of the nasal septum and other interventions.
The result of any operation for vasomotor rhinitis may be unstable. Sometimes repeated intervention is required.
Questions and answers
Do people with vasomotor rhinitis join the army?
If a diagnosis is made, this is not a reason for removal from service. They are drafted into the army with it, and if during service the soldier has an exacerbation, he can undergo treatment locally.
How to get rid of vasomotor rhinitis forever?
As a rule, this disease cannot be eliminated forever with a 100% guarantee. But it is possible to achieve stable remission and, if you follow doctors’ recommendations, not return to it for a very long time.
How dangerous?
Since difficult breathing can affect any other body system, the danger cannot be considered small. Of course, this is not a fatal disease, but if vasomotor rhinitis is not treated, the quality of life will be significantly reduced.
Possible complications
With a long course, vasomotor rhinitis can be accompanied by complications:
- constant nasal congestion, causing sleep disturbances and impairing work ability;
- persistent deterioration of sense of smell;
- development of chronic rhinosinusitis, frequent colds;
- formation of polyps or atrophy of the mucous membrane.
Read also
Smell from the mouth
Strong bad breath, also called halitosis, probably causes a feeling of embarrassment in everyone, and if the disease persists for a long time, even anxiety and depression.
It’s no surprise that the shelves… Read more
Hearing loss
Hearing loss is an impairment in the perception of environmental sounds. This disorder occurs in most cases gradually, patients do not immediately understand what is happening and therefore not always in a timely manner...
More details
Tubootitis
What is tubootitis Tubootitis is an inflammation, also called eustachitis, salpingotitis or tubotympanitis, which occurs in the area of the Eustachian tube, causing a decrease in the lumen of the ear canal. How…
More details
Naphthyzine addiction
In our age of availability of medicines, everyone knows about nasal drops, they have used naphthyzine at least once in their life and have heard about naphthyzine addiction. Some are even so afraid of her that they deliberately...
More details
Ear congestion
Sometimes people take the health of their hearing organs lightly and begin to take action only in case of severe discomfort, ignoring such a problem as ear congestion. So that you don’t have to overcome it in the future...
More details
Prevention
Considering the possible provoking factors of the disease, its prevention requires the following actions:
- avoid constant stay in rooms with polluted air, use respirators if necessary;
- get vaccinated against the flu, try not to get sick during cold season;
- correct hormonal imbalances in a timely manner;
- carry out treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease and other pathological refluxes;
- When the first symptoms of ENT pathology appear, immediately contact an otolaryngologist.
At the NIKIO center, ENT doctors with extensive experience and high qualifications conduct consultations. The clinic is well equipped and has all the capabilities for timely diagnosis and necessary treatment of vasomotor rhinitis in adults and children. We invite all people suffering from this disease to our medical center.