Coronary heart disease, or IHD, occurs when there is poor blood supply to the heart muscle, resulting in damage to the myocardium. The pathology is widespread and is one of the main causes of death and disability in the world. The Alpha Health Center clinic in Moscow deals with the diagnosis and treatment of coronary heart disease, including chronic heart disease (HIHD). Equipping with modern equipment allows us to accurately determine the patient’s health status and prescribe the correct therapy.
Types of cardiac ischemia
- Angina (stable and unstable) is chest pain caused by a lack of oxygen supply to the myocardium.
- Myocardial infarction (primary, repeated) - partial or complete blockage of the artery through which blood flows to the heart.
- Post-infarction cardiosclerosis is the presence of parts of the heart that died during a heart attack and which were replaced by connective tissue.
- Heart failure is a violation of the pumping function of the heart, as a result of which the body does not receive sufficient oxygen supply.
- Sudden arrhythmic death is the death of a person within an hour after the onset of acute manifestations of the disease.
general description
Coronary heart disease (CHD) is the leading cause of death worldwide.
According to experts, in 2030 more than 23 million people will die from CVDs. Coronary heart disease (CHD) is a disease caused by insufficient supply of the heart (myocardium) with oxygen and nutrients, which occurs due to impaired blood supply to the myocardium due to damage to the coronary arteries. The clinical manifestations of IHD are varied: from acute manifestations in the form of myocardial infarction or sudden cardiac death to long-term chronic diseases - angina pectoris (recurrent chest pain), post-infarction cardiosclerosis, chronic heart failure.
Causes of ischemia
Impaired supply to the heart muscle occurs due to:
- significant narrowing of the lumen of the arteries;
- spasms and damage to the coronary arteries;
- problems with microcirculation;
- changes in blood clotting.
The main cause of coronary heart disease is atherosclerosis, which develops due to the accumulation of cholesterol in the arteries. Plaques form on the walls, which grow and block the passage. Further, cracks and ruptures appear on the plaques, which leads to thrombus formation. As a result, the lumen narrows by 95%, the condition is accompanied by fatigue even at rest and is considered critical.
The main risk factors for developing coronary heart disease:
- male gender;
- age - adults over 40 years old;
- genetic predisposition;
- heavy smoking for more than 5 years;
- high cholesterol;
- unhealthy diet, obesity;
- diabetes;
- low mobility;
- long-term stress.
Possible factors for the occurrence of coronary heart disease include:
- problems with sleep patterns (breathing apnea);
- congenital arterial pathologies;
- coronary artery stenosis;
- elevated blood lipid levels;
- exceeding the norm of amino acids responsible for metabolism;
- chronic kidney diseases.
Measures to prevent cardiovascular pathology
To avoid developing heart disease, you need to stop smoking and reduce your alcohol consumption.
Severe stress is also one of the predisposing factors to the occurrence of IHD. It is impossible to remove stress from life, but you can react to it correctly: humans are evolutionarily designed in such a way that muscle work is necessary after any stress. If you are worried or upset, then you need to squat, jog, or walk – the muscles should get tired. In case of severe anxiety, you may need to use sedatives, for the selection of which you need to consult a doctor.
Regular exercise with moderate physical activity is useful for the prevention of ischemia. You also need to monitor your weight and blood pressure. All persons over 40 years of age must be examined annually - take a biochemical blood test to check the level of cholesterol in the blood, and do an ECG.
Symptoms
The main symptom of coronary heart disease is pressing pain behind the chest or in the heart area. It can radiate to the lower jaw, left shoulder, hand, back and neck. During the acute form, a heart attack or pre-infarction condition develops. In chronic ischemic heart disease, pain is felt during physical activity, and pain tolerance decreases over time.
Main features:
- burning, suffocating pain in the heart area;
- heaviness in the chest;
- feeling of uneven heart rate, heart palpitations;
- dyspnea;
- weakness, dizziness, fainting;
- sweating;
- nausea;
- soreness after physical activity;
- duration from 30 seconds to 15 minutes;
- high efficiency of nitroglycerin.
Fatigue sometimes goes away completely after stopping physical activity. If the patient has unstable angina or myocardial infarction, then there may be no complaints about the heart after exercise. On the contrary, they appear during rest and last a long time - up to several hours. Depending on the form of the pathology, a certain discomfort prevails.
If the described signs of coronary heart disease are detected, you must make an appointment with a cardiologist. If acute pain does not go away for more than 10 minutes, you should call an ambulance.
In this case, progressive ischemic heart disease can develop over several years. In some patients, there are no signs or symptoms are vague. To avoid severe complications and not to trigger the disease, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination regularly, especially in adulthood.
Coronary heart disease (CHD)
Stroke
Diabetes
5231 08 February
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Coronary heart disease (CHD): causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
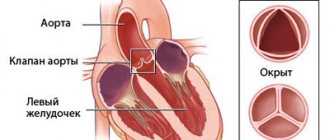
Definition _
Coronary heart disease (CHD) is an acute (transient) or chronic (stable) damage to the heart muscle (myocardium) caused by a decrease or cessation of blood flow through the coronary arteries.
Causes of coronary heart disease
Myocardial ischemia occurs when the myocardial demand for oxygen exceeds the ability to deliver it through the bloodstream through the coronary arteries. Normally, the coronary arteries have a reserve for expansion, providing a fivefold increase in coronary blood flow, and, as a result, oxygen delivery to the heart muscle. A discrepancy between oxygen delivery and muscle demand can occur under the influence of various factors.
In 95% of cases, the cause of coronary heart disease is a decrease in its blood supply (insufficient oxygen supply) through the coronary arteries due to atherosclerotic narrowing of the lumen of the vessel.
The course of the disease is determined by the presence and further growth of an atherosclerotic plaque, which can block the vessel completely or partially. When blood pressure increases, the sclerotic endothelium of the vessel is easily damaged, blood penetrates into the plaque, the blood clotting process is activated and a blood clot is formed, which can partially or completely block the vessel.
A significant role in the development of IHD is played by disturbances in the movement of blood through the vessels and changes in the rheological properties of blood (the ability of blood to flow).
The formation of a blood clot, especially against the background of vessel spasm, can lead to complete or partial blockage.
In 5% of cases, the cause of IHD is congenital anomalies of the origin of the coronary arteries, Marfan and Ehlers-Danlos syndromes with aortic root dissection, coronary vasculitis in systemic connective tissue diseases, Kawasaki disease and Hurler syndrome, infective endocarditis, overdose of vasoconstrictor drugs and certain narcotic drugs, syphilitic mesaortitis and other conditions.
There are factors that provoke the development of coronary heart disease that can be influenced: dyslipoproteinemia (violation of the normal ratio of blood lipids); arterial hypertension; diabetes; smoking; low physical activity; obesity; stress. And also those risk factors for the development of coronary artery disease that cannot be changed: male gender, age, family history of cardiovascular diseases (myocardial infarction or ischemic stroke in close relatives: in women - up to 65 years, in men - up to 55 years).
Classification of IHD
I. Acute myocardial infarction (MI).
- According to the stage of the disease:
- developing – from 0 to 6 hours;
- acute – from 6 hours to 7 days;
- healing (scarring) – from 7 to 28 days;
- healed - starting from the 29th day.
- According to the depth of the lesion:
- transmural MI (necrosis of the entire thickness of the heart muscle);
- Q-wave (Q wave appears on the ECG);
- not Q-generating.
- By localization:
- front;
- lower;
- myocardial infarction of other specified locations;
- myocardial infarction of unspecified localization.
- Based on the presence or absence of persistent ST segment elevation on the ECG:
- myocardial infarction with ST segment elevation on ECG;
- myocardial infarction without ST segment elevation on ECG.
II. Unstable angina (a period of ischemic heart disease that threatens the development of myocardial infarction).
- New-onset angina.
- Progressive angina.
- Variant angina (Prinzmetal's angina).
III. Chronic ischemic heart disease.
- Angina pectoris I-IV FC (functional class).
- Previous myocardial infarction.
Symptoms of coronary heart disease
Coronary heart disease can have a relatively benign course over many years. The progression of atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels leads to the development of the disease.
The most common form of coronary artery disease is angina pectoris, in which the most common complaint of patients is squeezing or pressing pain in the chest. The pain can radiate to the left arm, back or neck, lower jaw, less often to the area under the xiphoid process, and last from 2 to 5 or even 20 minutes. It occurs during physical exertion or severe psycho-emotional stress. After stopping physical activity or 1-3 minutes after taking nitroglycerin, the pain quickly disappears.
As the disease progresses, there comes a time when even minimal exertion is enough for an angina attack, and finally, attacks begin to occur at rest. Some patients may experience pain while lying down due to increased blood flow to the heart.
It is necessary to take into account that pain that occurs with other diseases (neuralgia, gastralgia, cholecystitis, etc.) can provoke and intensify existing angina.
When the blood circulation of the heart muscle is disrupted with the development of a focus of necrosis (tissue death), myocardial infarction occurs. A heart attack (from the Latin infarcire - to stuff, stuff) is the necrosis of organ tissue due to an acute lack of blood supply.
The pain of myocardial infarction is significantly greater in intensity and duration than a normal angina attack.
The pain is not relieved by nitroglycerin and its duration can vary - from 1 hour to several days. Sometimes myocardial infarction is accompanied by weakness, dizziness, headache, vomiting, fainting, and loss of consciousness. The patient looks pale, his lips are blue, and he is sweating.
Diagnosis of coronary heart disease
The diagnosis of “coronary heart disease” is established by a combination of complaints, information about the course of the disease, data from laboratory and instrumental examination methods.
For all patients with suspected ischemic heart disease, the following questions are asked:
- current or past smoking;
- the presence of cardiovascular diseases and/or deaths from cardiovascular diseases in the patient’s immediate relatives (father, mother, siblings);
- previous cases of seeking medical help and the presence of previously registered electrocardiograms, studies and conclusions;
- comorbidities to assess additional risks;
- medications taken.
The following studies are recommended for all patients with coronary artery disease or suspected coronary artery disease at initial consultation:
- clinical blood test: general analysis, leukoformula, ESR (with microscopy of a blood smear in the presence of pathological changes);
Diagnostics
At the initial appointment, the cardiologist collects anamnesis and clarifies the symptoms. Next, the patient is examined to identify edema and cyanosis of the integument. By listening, murmurs and heart rhythm disturbances are determined.
The next step is to take blood tests, including cholesterol and glucose levels. The greatest accuracy of diagnosis is provided by instrumental methods that allow you to determine the main signs of coronary heart disease.
Depending on the clinical picture, the doctor prescribes:
- electrocardiogram;
- ultrasonography;
- stress tests under load and with drug stimulation:
- Holter ECG;
- coronary angiography.
We have equipment for digital X-ray diagnostics and electrocardiography at our disposal. We perform a treadmill test to determine how the heart functions during physical activity. During the procedure, the person is asked to walk on a treadmill. After three minutes, increase the inclination and speed of movement. The equipment records blood pressure and ECG parameters, as well as blood oxygen saturation, and counts the heart rate. Using equipment, the body’s resistance to a certain intensity and duration of stress is determined. During the test, the functional diagnostics doctor monitors the patient’s condition and prevents overload.
Holter monitoring allows long-term recording of cardiac performance indicators. The device collects data throughout the day, under typical human conditions, due to which it helps to determine with high accuracy what exactly provokes an ischemic attack.
Based on the results obtained, the doctor can establish a connection between an acute attack of coronary artery disease and a person’s lifestyle, using data from the diary kept by the patient during the examination. One advantage is the ability to detect “silent” ischemia at night. 24-hour studies are also widely used to adjust treatment.
Timely diagnosis allows you to prevent consequences, deterioration and death from IHD. Screening is recommended for adults for preventive purposes, starting from the age of 20 every 4-6 years and more often (in old age).
Prognosis and care
Coronary heart disease is a progressive disease with a rapid transition to the chronic phase and a conditionally unfavorable prognosis. High-quality treatment can slow down the development of pathology, but not completely stop it.
If a heart attack develops as a result of coronary artery disease, a person requires serious treatment and long-term recovery. With severe damage, patients may experience anxiety-depressive reactions and changes in behavior. General weakness, fatigue, and excitability cannot be ruled out. In these conditions, you should strictly, on time, follow the doctor’s instructions, follow the regimen and diet. Working relatives do not always have the opportunity to provide proper help and care. For this, people turn to special medical institutions.
A good example is the private boarding house “Idyll” in Yekaterinburg. Here, guests live in comfortable rooms under the 24-hour supervision of qualified doctors and medical staff. Each type of disease has its own rehabilitation program. Sick people receive full care, including the help of a psychologist. They can walk and spend pleasant leisure time.
Treatment
The goal of therapy is to normalize blood supply and improve the quality of life of patients. Conservative and surgical treatment is used.
Drug treatment
The doctor prescribes a set of medications that help control the onset of symptoms and improve the prognosis for the development of chronic pathology.
Typically this is:
- antiplatelet agents - they reduce thrombus formation;
- B-blockers;
- calcium antagonists;
- nitrates;
- receptor blockers;
- statins to control cholesterol.
Surgery
Depending on the results of diagnosing coronary heart disease, the doctor may refer you to a hospital for:
- Myocardial revascularization with laser. The procedure restores blood flow to the heart;
- Installation of stents in coronary arteries. The operation is performed under local anesthesia through an artery in the forearm or groin. A stent is placed in the narrowed area of the vessel, which presses the plaque against the wall to restore patency;
- Coronary artery bypass surgery is an open-heart surgery to restore blood supply. The method involves changing the direction of blood flow past narrowed areas. The patient's veins and arteries serve as coronary bypass grafts.
The treatment strategy depends on the severity of the disease and health status. When choosing an approach, the doctor takes into account the risks for the patient for 10 years after treatment.
Why does pathology occur?
The main cause of the disease is damage to the coronary arteries by atherosclerosis, in which cholesterol plaques appear in the vessels. After some time, a blood clot may form at the site of the plaque, which partially or completely blocks the artery, blocking the supply of oxygen to the heart muscle.
As a rule, narrowing of the lumen of the vessel up to 50% occurs without any clinical manifestations. Vivid symptoms appear when the artery is blocked by 70% or more.
Very rarely (up to 5% of cases) IHD is caused by:
- congenital anomalies of the origin of the coronary arteries;
- Marfan, Ehlers-Danlos syndromes - hereditary pathologies of connective tissue;
- infective endocarditis - inflammation of the inner lining of the heart caused by pathogenic pathogens;
- Kawasaki syndrome is a systemic vasculitis affecting medium and small arteries;
- syphilitic aortitis is a complication of syphilis, in which inflammation of individual layers or the entire thickness of the aortic wall occurs;
- overdose of vasoconstrictors, narcotic drugs.
Preventive measures
Patients with coronary artery disease are advised to change their lifestyle:
- reduce weight in case of obesity;
- include active sports;
- adhere to proper nutrition;
- stop smoking;
- comply with night sleep standards.
Preventing the development of a disease is easier than treating it. To prevent narrowing of the arteries, doctors recommend monitoring blood pressure, reducing stress levels, and not triggering depression. It is necessary to reduce the consumption of alcohol, fried, fatty, smoked and salty foods. It is advisable to walk more, do exercise therapy, exercise, and swimming. Physical activity strengthens the walls of blood vessels and reduces the risk of weight gain.
An important measure for the prevention of coronary heart disease is regular visits to a cardiologist to prevent the development of pathological processes. In our center you can undergo all the necessary examinations and tests to determine the state of your cardiovascular system.
Therapy methods
Treatment for coronary heart disease is aimed at normalizing blood supply to the muscle tissue of the heart. Therapeutic measures reduce the intensity of angina pectoris and prevent the development of myocardial infarction. Treatment tactics depend entirely on the clinical form of the disease.
A number of pharmacological drugs are used for drug therapy, including antiplatelet agents, adrenergic blockers, anticoagulants, diuretics and many other types of drugs. When diagnosing IHD, patients are advised to keep nitroglycerin preparations in their home medicine cabinet to quickly relieve angina attacks.
Non-drug treatment includes a number of modern techniques.
- Enhanced external counterpulsation. Artificially creates body effects that are observed in well-trained or physically active people. Improves coronary blood flow.
- Quantum therapy. Laser effects on organs and tissues. Vasodilation, normalization of metabolic processes in the myocardium. Improving blood microcirculation.
- Shock wave therapy. Exposure to low frequency sound pulses. Dilates and strengthens blood vessels, improves blood flow. Gives a long-term effect. Reduces the frequency of pain attacks.
- Introduction of stem cells. An experimental technique that WHO notes as promising.
Surgical assistance for coronary heart disease is provided under certain parameters, based on the results of coronary angiography - examination of the vascular bed of the myocardium using X-ray irradiation. Surgeons' preferred treatment methods include endovascular intervention or coronary artery bypass grafting.
How to make an appointment with a cardiologist
You should not ignore the primary symptoms, no matter how insignificant they may seem. Preventing IHD is much easier than treating it. By signing up for a consultation today, you will ensure longevity and confidence in the future.
By calling the numbers listed on the website, you can find out the cardiologist’s appointment schedule, the cost of services and the location of the nearest IMMA clinic. Caring staff will help you calm down before an important examination and provide all the necessary information about diagnostic methods.
The clinic has the opportunity to call a cardiologist at home to provide emergency assistance.
High quality of service, competitive prices, the best specialists and highly qualified staff distinguish IMMA clinics from similar medical institutions. Trust your health to professionals!
Who is at risk
The risk of coronary heart disease is determined by a number of circumstances that create favorable conditions for the development of pathology. Since the main cause is dysfunction of the coronary blood vessels, the following indicators are used to classify the groups:
Biological factors
- Age. The older a person is, the higher the risk of IHD. Natural aging causes wear and tear of blood vessels, the acquisition of side diseases, etc.
- Gender. In men, the disease is diagnosed much more often.
- Heredity. If blood relatives had IHD, the risk doubles.
Physiological predisposition
- Poor nutrition. Eating large amounts of fried, smoked, pickled, spicy foods, fast food, processed foods, sausages, etc. leads to an increase in cholesterol levels and the appearance of plaques on the walls of blood vessels.
- Diabetes. The clinical picture of the disease is primarily characterized by impaired patency of blood vessels.
- Blood diseases. Coagulability indicators are of great importance. This affects the possibility of blood clots forming in the vessels.
- Chronic high blood pressure. The blood flow in the vessels is disrupted, the heart begins to work unstably, resulting in coronary heart disease.
Lifestyle and social risks
- Obesity. Excess body weight, more than 15% higher than normal, leads to the covering of the myocardium with a thick layer of fatty plaque. This has an extremely negative impact on the functioning of the heart.
- Static lifestyle. Lack of activity, office work, and constant presence at the computer do not have the best effect on the cardiovascular system.
- Bad habits. Smoking, alcohol abuse and other antisocial addictions lead to the development of IHD.
- Psychological factors. Stress, chronic fatigue syndrome, and depression very often result in a diagnosis of coronary heart disease.
Each factor, or a combination of several, creates a favorable environment for the development of the disease. The list affects almost any person, regardless of gender and age. Therefore, it is extremely important to undergo regular examinations and completely eliminate, or minimize, all negative components.