Rotovirus infection is an acute form of pathology in which the gastrointestinal tract is damaged and a clear clinical picture develops. Symptoms include dyspeptic disorders, intoxication and dehydration. The condition is common, occurring in adults and children.
Causes of rotavirus infection
The main cause of the infectious disease is a viral pathogen of the rotavirus genus. The latter, when it enters the human body, contributes to the formation of all kinds of combinations, causing a wide variety of rotavirus strains. The most significant in the occurrence of the disease is considered to be the serotype of group A, which includes 4 different combinations.
Externally, the virus has the shape of a circle, 65-70 nm in size. It has a core, double RNA and a protein shell.
The pathogen is highly contagious and very resistant to adverse external factors. The virus remains viable at low temperatures, exposure to ultraviolet rays, antibacterial drugs, chemotherapy drugs and disinfectants. However, rotavirus does not tolerate heat, acid or alkali. In the environment, the pathogen can be active for 10-30 days, and in the stool of a sick person it retains the ability to infect for a maximum of 6 months.
Infection with the pathology occurs predominantly through the fecal-oral route, also by air, household and contact.
Contributing factors to the disease are dirty dishes, hands, contaminated water and food.
Among food products, dairy dishes, raw vegetables, fruits and drinks pose the greatest health hazard.
Prevention
The key measure to prevent rotavirus is to observe the rules of personal hygiene - timely washing of hands, eating only thoroughly washed and properly processed foods, using only filtered boiled water for drinking. Water used for domestic purposes must be treated or chlorinated.
Rotarix and RotaTek vaccines show high effectiveness in preventing rotavirus infection.
- Rotarix is a live monovalent vaccine of an attenuated strain of human rotavirus. The vaccination course consists of two doses. The first dose should be given to the baby from 6 weeks of age. The interval between doses should be at least 4 weeks. The vaccination course is preferably completed by 16 weeks of age and must be completed by 24 weeks of age.
- RotaTek is a live oral pentavalent vaccine containing five live reassortant strains of rotavirus. The vaccination course consists of 3 doses with an interval between doses of 4 to 10 weeks. The course must be completed before the baby reaches 32 weeks of age.
Symptoms of rotavirus
The occurrence of infection begins with the penetration of the pathogen into the human body. There it becomes embedded in the digestive tract and provokes the development of symptoms. The first signs are observed after the incubation period, which lasts 2-3 days, a maximum of a week.
In most cases, the disease occurs in an acute form with a clear clinical picture. Symptoms of an infectious condition are:
- Increase in body temperature. As a rule, it lasts no longer than 4-5 days and is accompanied by general weakness, malaise, headache and lack of appetite.
- Vomiting is characteristic of rotavirus and can occur in mild, moderate and severe forms. Lasts 1-2 days. When profuse vomiting occurs, it causes dehydration.
- Diarrhea - develops separately or together with vomiting. The stool is very copious, liquid, similar to water, with foam and various impurities, even streaks of blood. Sometimes mucus is present, and the stool has an unpleasant sour smell. The duration of diarrhea is 4-5 days, with a frequency of up to 5 times a day. Diarrhea is almost always accompanied by flatulence.
- Pain syndrome. Has a different nature of intensity and localization. More often the pain is acute, less often it is cramping.
- Dehydration of the body. Appears against a background of vomiting and diarrhea. In severe cases, fluid loss leads to the development of seizures and loss of important electrolytes with fluid. This condition is very dangerous and requires timely treatment.
- Catarrhal phenomena. Characterized by cough, impaired nasal breathing, throat hyperemia and soreness.
How can a child become infected?
There are certain conditions under which a child may get this infection. The occurrence of the disease will be facilitated by:
- Irregular and inadequate nutrition of the child;
- Poor hygienic and sanitary conditions in which the child and his family live;
- The child eating low-quality or stale foods;
- Presence of stomach and intestinal diseases;
- The presence of immunodeficiency conditions (the child often suffers from colds or is often treated with antibiotics)
The source of infection for rotavirus disease is a person who already has this disease. It is dangerous to others from the appearance of the first symptoms until the end of the disease (5-7 days).
This infection is transmitted through the digestive system. A child can become infected while swimming in a pond where there is rotavirus in the water. Infection can occur through dirty hands, dishes, towels, napkins, toys and other items if they were used by a sick person. The disease can also occur in a baby when consuming foods that contain rotavirus - most often these are various dairy products.
Rotavirus infection most often occurs in autumn or spring. A person can get this disease several times during his life.
From the moment of infection to the appearance of vomiting, abdominal pain or diarrhea in the child, it takes from several hours to several days.
Methods for treating rotovirus
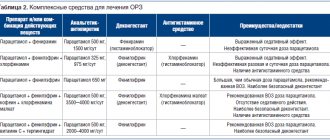
To treat rotavirus pathology, symptomatic and etiological therapy is prescribed. Patients are also prescribed a diet and auxiliary methods.
The main goal of treatment is to prevent dehydration. For this purpose, rehydration drugs are used for parenteral and oral administration. Such drugs prevent large fluid loss, improve well-being and relieve intoxication syndrome. Representatives are: Regidron, Acesol, Kvartasol, Refortan.
To remove pathogenic pathogens from the body, sorbents are prescribed. They accelerate the restoration of the mucous membrane, suppress pain and flatulence. Activated carbon, Polysorb, Enterosgel, Karbolen are prescribed.
Antiviral drugs based on interferon are indicated as etiotropic treatment.
To improve the normal intestinal microflora, probiotics are prescribed - Acipol, Linnex, Enterol, Bifiform.
Additionally, patients with rotavirus pathology are prescribed painkillers, antiemetics and antipyretics.
Treatment12
Drug treatment for rotavirus infection is prescribed by a doctor. In most cases the following are used:
- To remove toxins: activated carbon, Smecta, Enterosgel.
- To restore the functions of the gastrointestinal tract: digestive enzymes (Festal, Somilase, Solizim).
- To reduce the temperature (in cases where it rises above 38 ºС): antipyretic drugs (Ibuprofen, Paracetamol).
- To relieve stomach pain: antispasmodics (No-Shpa, Enterofuril).
- To suppress bacterial infections that often accompany rotavirus gastroenteritis: antibiotics.
- To restore electrolyte balance: probiotics.
General recommendations:
- Drink small amounts of fluid frequently to prevent dehydration. You should drink clean boiled water, dried fruit compotes, berry fruit drinks, and unsweetened tea.
- The patient's menu should include light, quick-to-digest, protein-rich foods - dairy-free cereals, steamed poultry and fish cutlets, fruit and vegetable purees. From the patient’s diet it is necessary to exclude everything fried, smoked and salted, sweets, foods high in fats and carbohydrates, flour products (including pasta), millet and pearl barley porridges, milk and fermented milk products, spices, coffee, legumes (and other products , which can cause flatulence).
Rotovirus infection in children
The course of the infectious process in childhood is almost no different from the clinical course in adults. The symptoms are similar, but there are some differences. In children, when the temperature rises, generalized convulsions are often observed, which lead to loss of consciousness and encephalitic signs are recorded.
In newborn children, rotavirus infection is often latent in nature without pronounced symptoms of gastrointestinal upset and high fever. However, with mass infection of babies, the disease can acquire a severe clinical form with profuse vomiting, diarrhea and dehydration.
As a rule, the incubation period of rotoavirus in newborns is short, only 1-2 days, after which clear signs of the disease are observed.
The risk group for the development of infectious pathology includes children 1-3 years old; moderate and severe forms of the disease predominate in them. Rotavirus infection is more easily tolerated by children aged 3-7 years; at this age, the symptoms are less pronounced and the condition is mild.
Most often, such a disease lasts 3-5 days.
Possible complications8
Rotavirus infection poses the greatest danger to young children from the first days of life to 3-5 years and pregnant women:
- At an early age, intestinal flu is a deadly disease - severe dehydration of the body can lead to death.
- Dehydration caused by rotavirus gastroenteritis during pregnancy leads to the risk of miscarriage.
Possible complications of rotavirus infection:
- Pancreatitis, gastritis, enlarged pancreas.
- Intestinal inflammation.
- Hemorrhagic gastroenteritis.
- Acute renal failure.
- Circulatory disorders.
- Gasser syndrome.
- Necrotizing enterocolitis.
To minimize the risk of the disease and prevent the development of complications, it is important to promptly diagnose rotavirus infection and begin adequate treatment.
Diagnostics
In order for a doctor to diagnose rotavirus infection, it is necessary to conduct a stool test for the presence of particles of the virus genome in it (this method is called “polymerase chain reaction”). In addition, various other tests are performed on blood, urine and stool. This allows you to detect infection earlier and prevent complications in the child.
Under domestic conditions, it is very difficult to diagnose this infection for an ill family member. Therefore, consultation with a doctor is necessary in any case, no matter how confident a person is in this diagnosis and methods of its treatment. There are a large number of infectious and non-infectious diseases that occur with symptoms similar to rotavirus infection.
For example, parents may mistake non-infectious diseases of the liver, stomach, intestines, and pancreas for a manifestation of rotavirus infection. With them, the sick child complains of nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain after certain (fatty, spicy, fried) foods, or indicates that all manifestations are disturbing only on one side of the body and began after severe emotional stress.
Similar signs of the disease can occur in case of poisoning with drugs or poisonous plants (more often it is children who suffer from this if they are left alone at home and can get to the home first aid kit, or walk unattended and can try different berries).
Read more about food poisoning in children in our article “Recommendations from a pediatrician for food poisoning in a child.”
Online consultation with pediatrician Olga Nikolaevna Tekutyeva
Registration online
During the consultation, you will be able to voice your problem, the doctor will clarify the situation, interpret the tests, answer your questions and give the necessary recommendations.