Prevention of influenza, ARVI and coronavirus is a single set of measures aimed at preventing morbidity. The words of Hippocrates are relevant today: “It is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it.” Compliance with preventive measures helps protect against infection, reduce the risk of large-scale spread of infection, and save people’s lives.
With the advent of the pandemic, the whole world has felt the importance of preventing respiratory infections. COVID-19 has forced humanity to take a fresh look at ways to stay healthy. On a par with coronavirus infection are influenza and ARVI, which people encounter in the fall and spring. As practice shows, seasonal diseases sometimes cause complications no less severe than Covid. Prevention of influenza and ARVI, developed by epidemiologists, helps protect against infection and its consequences. Read about the characteristics of respiratory viruses, means and methods of protection against infection in our article.
Ways to get a respiratory infection
Respiratory viruses are a large family of ultramicroscopic intracellular parasites. Some of them become noticeably more active during the demi-season, causing epidemics of ARVI (acute respiratory viral infection). These are paramyxoviruses, picornaviruses, adenoviruses, coronaviruses, parainfluenza viruses, influenza A, B, C.
Pathogens of infectious respiratory diseases are highly contagious (infectious), but they can only enter the body through the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract. The main method of infection is aerogenic or airborne droplets. Viral particles fly through the air with droplets of liquid that escape from the mouth of a sick person when sneezing or coughing. The second method of infection is through household contact. The direct route is through a handshake with a carrier of the infection, the indirect route is through contaminated (infected) surfaces. Having picked up the virus in your hands, it is easy to carry it into your nose, your mouth is the “entrance gate” of ARVI.
VIFERON – complex antiviral drug
VIFERON® is a complex broad-spectrum antiviral immunomodulatory drug for children and adults, which is used to combat ARVI, including influenza, and other infectious diseases. The drug is available in the form of suppositories (candles), gel and ointment.
Human recombinant interferon alpha-2b, which is part of the drug VIFERON, has antiviral, immunomodulatory properties and suppresses the replication of RNA and DNA viruses. Antiviral therapy against influenza can be started at any phase of the disease. This will help improve the condition and prevent the development of complications3. The drug VIFERON includes generally recognized highly active antioxidants: in suppositories these are vitamins E and C, in ointments - vitamin E, in gel - vitamin E, citric and benzoic acids. Against the background of such antioxidant support, an increase in the antiviral activity of interferons is noted.
The drug VIFERON Candles (suppositories) can be used during pregnancy (from the 14th week), as well as during breastfeeding and in the treatment of newborns.
Also, the drug VIFERON Suppositories is used for chronic viral hepatitis B, C, D in children as part of complex therapy, including in combination with the use of plasmapheresis and hemosorption for chronic viral hepatitis of severe activity, complicated by cirrhosis of the liver. For children under 6 months of age, 300,000-500,000 IU/day is recommended; at the age of 6 to 12 months – 500,000 IU/day. For children aged 1 to 7 years, 3,000,000 IU per 1 m2 of body surface area/day is recommended. The drug is used 2 times a day after 12 hours for the first 10 days daily, then three times a week every other day for 6-12 months. The duration of treatment is determined by clinical effectiveness and laboratory parameters.
Reference and information material
Author of the article
Belyaev Dmitry Alexandrovich
General doctor
- Guidelines for Pharmacological Management of Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1) 2009 and other Influenza Viruses. Revised February 2010. Part I: Recommendations.
- Here and further in the text, INNs of medicinal products are used. TM is indicated only if the drug VIFERON is mentioned
- Nesterova I.V. “Interferon drugs in clinical practice: when and how,” “Attending Physician,” September 2021.
Loading...
Take other surveys
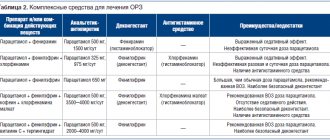
Means for the prevention of acute respiratory viral infections and influenza
Preventive measures against acute respiratory infections are divided into specific and nonspecific. Specific prevention is vaccination. The Russian Federation is immunizing the population against influenza and coronavirus. There is no vaccine for other viruses, of which medical virology numbers more than two hundred. Non-specific methods include drug protection of the body, home remedies to strengthen the immune system, rules for the prevention of influenza and ARVI, recommended by WHO.
Two groups of antiviral drugs
According to experts from the Food and Drug Administration (USA), only drugs that have a direct direct effect on the reproduction of the virus can be called antiviral, i.e., the action of these drugs is aimed at destroying the virus and preventing its reproduction.
According to many scientists, all currently existing drugs that fight viruses can be divided into two groups: drugs that act on the viruses themselves, and drugs that activate the body’s own immune defense.
Nonspecific prevention
To prevent influenza and ARVI, two types of pharmacological drugs have been developed:
• Direct acting drugs. They block enzymes on the surface of the virus. Because of this, the infectious agent loses the ability to reproduce its RNA and proteins. • Agents that stimulate the production of protective interferons to increase the body's resistance to infections.
Antiviral medications are available in the form of tablets, capsules, and powders. For children, there are syrups, suspensions, and drops that are convenient to take.
The TOP 5 drugs include:
• Arbidol. Active against most pathogens of acute respiratory viral infections, including influenza viruses. For prevention, take twice a week, for treatment - 4 times a day. In powder form it is allowed for children from 2 years old, in tablet form - from 6 years old. • Ergoferon. A fast-acting immunomodulator with proven effectiveness against respiratory viruses. Tablets for sublingual administration are prescribed: 5 pcs per day. within 2 hours, on subsequent days - 1 pc. three times. • Ingavirin. An innovative antiviral agent with high anti-inflammatory activity. Used for all types of acute respiratory viral infections, including coronavirus infection. In pediatrics it is used from 7 years of age. To achieve results, 1 capsule per day is enough. • Kagocel. A powerful immunostimulant, it causes the synthesis of interferons by all cells of the body that participate in the antiviral response. Allowed for children from 3 years old. Prevention is carried out in cycles: 2 days, 2 tablets - 5 days break - 2 days, 2 tablets. • Anaferon. Increases the production of interferon, prescribed for the prevention and treatment of acute respiratory viral infections. In pediatrics, a specially developed children's version of the drug is used.
Unlike antibiotics, antivirals are sold without a doctor's prescription.
Organization of home prevention of ARVI and influenza includes:
• Nutrition correction. Foods high in ascorbic acid—vegetables, wild berries, fruits, herbs—help stimulate the formation of interferon. Protein is the building material for immune cells, so the diet should contain a sufficient amount of meat, fish, dairy products, and cereals (millet, oats, buckwheat). The main helper of immunity is vitamin D. It is found in egg yolk, seaweed, and cod liver. • Hardening, physical activity. It is recommended to start hardening procedures in the summer - before the start of seasonal epidemics. Sports activities saturate the blood with oxygen, accelerate hemodynamics, and increase blood supply to organs. This allows you to maintain the functionality of immune system cells to produce interferons.
• Use of folk remedies. Products with antimicrobial effects (garlic, ginger, onions), as well as plants with immunostimulating properties (ginseng root, rose hips, echinacea, sage, lemon balm) help protect against seasonal diseases.
To prevent illness, it is important to adhere to a rational work and rest regime. Doctors recommend getting enough sleep, walking daily, avoiding conflict situations that lead to stress, and taking vitamin and mineral supplements.
Direct acting antiviral drugs for hepatitis C
Direct-acting drugs that fight the hepatitis C virus and are effective in treating this disease can be classified according to the way they affect different stages of the life cycle of the virus:
- Protease inhibitors —drug names ending in “-previr”—include drugs being developed by various pharmaceutical companies: boceprevir, telaprevir, simeprevir, asunaprevir, danoprevir, faldaprevir, sovaprevir, ABT-450, MK-5172.
- Polymerase inhibitors —drug names ending in “-buvir”—include nucleoside/nucleotide analogues such as sofosbuvir, mericitabine, and ALS-2200 (VX-135), as well as non-nucleoside drugs such as deleobuvir, setrobuvir, ABT-072, ABT- 333, BMS-791325 and VX-222.
- NS5A inhibitors —drug names ending in “-asvir”—include daclatasvir, ledipasvir, and ABT-267.
In each class there are drugs that are more or less effective in terms of potency, stability of results and side effects. Clinical studies are currently underway to determine the best regimens for using these drugs for various patient groups.
Drug trials
The first direct-acting drugs that fight viruses and are effective in treating hepatitis C underwent clinical trials relatively recently, in 2012. These are hepatitis C virus protease inhibitors – boceprevir and telaprevir. They were recommended for use in combination with pegylated interferon and ribavirin. Pegylated interferon is a long-acting interferon that maintains the concentration of the substance in the human body significantly longer.
Based on the results of clinical studies and experience with therapy, it was found that these drugs can significantly shorten the duration of treatment and increase sustained virological response (SVR) in patients with hepatitis.
Currently, dozens of new drugs against hepatitis C are under development and testing, but not all of them have confirmed their effectiveness. Particular attention is paid to the interaction between drugs that are part of the treatment of hepatitis C. First of all, this is important for people with progressive fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Flu and its dangers
Besides coronavirus, the most dangerous causative agent of acute infections is the influenza virus. It differs from its respiratory “relatives” in its high virulence - its ability to quickly spread throughout the body, causing severe complications - even lethality. The risk group includes people of advanced age, young children, patients with chronic cardiac and pulmonary pathologies.
The influenza virus provokes infectious and inflammatory diseases of the heart, nervous system, and brain. With a heavy viral load, intoxication quickly develops, the permeability of the vascular walls increases, hemodynamics are disrupted, the lungs lose their ability to absorb oxygen, and respiratory failure occurs, which can be fatal. The most effective prevention of influenza is the introduction of an influenza vaccine before the start of the epidemic season. Children are vaccinated from 6 months of age.
Are there any limitations and disadvantages of using interferon-free treatment regimens?
Thus, interferon-free regimens for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C differ from interferon-alpha-containing regimens in higher efficiency and safety, as well as a shorter duration of therapy and ease of use.
With the introduction of interferon-free treatment regimens, significant groups of patients have a chance to be cured in whom interferon-alpha-containing therapy had contraindications (these are patients with various autoimmune diseases, other severe concomitant pathologies) or was carried out but was ineffective (this group contains “difficult” to treat patients, including patients with liver cirrhosis).
The use of interferon-free treatment regimens has virtually no restrictions, with the exception of cases of incompatibility of direct antiviral drugs with certain medications taken by the patient for another disease, if these medications cannot be replaced or temporarily discontinued.
It is also important to know that some drugs with direct antiviral action are eliminated from the body primarily by the kidneys and may have limitations in their use in patients with severe renal failure, while some are eliminated primarily by the liver, which limits their use in patients with severe liver failure.
The choice of the optimal treatment regimen, assessment of drug interactions, as well as determination of the duration of treatment and the advisability of combining therapy with ribavirin are determined by a hepatologist.
Vitamins to strengthen the immune system
Special blood tests help determine which vitamins the body lacks. The main marker of stable immune function is considered to be normal levels of vitamin D hormone. It enters the body with food and is synthesized by skin cells under the influence of sunlight. Considering the deficiency of ultraviolet radiation in most Russian regions, it is recommended to take the vitamin hormone in the form of a dietary supplement. To prevent respiratory diseases, the immune system needs B vitamins, ascorbic acid, and fat-soluble vitamins A and E.
Products that contain vitamins for the prevention of ARVI and influenza
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C):
- sauerkraut
- bell pepper
- citrus
- cranberry
- currant
- rose hip
Group B:
- nuts
- milk
- legumes
- buckwheat
- oats
- tomatoes
Tocopherol (E):
- sea buckthorn
- spinach
- broccoli
- bran
- eggs
- vegetable oils
Retinol (A):
- carrot
- green onions
- parsley
- peaches
- apricots
- melon
Replenishing vitamin reserves through nutrition alone is an impossible task. To maintain the immune system in a state of combat readiness, an additional source is needed - pharmacy vitamin complexes:
• Supradin Immuno Forte; • Doctor More; • Multi-tabs Immuno Plus; • Pediakid syrup; • Superum Echinacea Vitamin C Complex.
The most modern and effective means for strengthening the immune system can be ordered with home delivery.
Description
Antiviral drugs, when they enter the body, begin to fight the virus, they help the immune system cope with the disease, or destroy it on its own. Let's consider 2 main types of such drugs.
Kinds
- Immunomodulators. These medications, when entering the baby’s body, do not fight the virus directly; they strengthen and support the immune system and the body itself copes with the disease. They are more beneficial for the immune system; after defeating the virus on your own, the immune system becomes stronger, and the likelihood of re-infection decreases several times. However, frequent use of such medications can have the opposite effect and the body stops fighting on its own.
- Virus suppressive substances. These are antiviral agents with an extended spectrum of action. Depending on the active substance included in the drug, they fight directly against the virus itself, killing it on their own. In this case, immunity has a auxiliary effect, the risk of recurrent disease is not reduced.
Release forms
- Nasal drops. These drops are convenient for use by children aged 2 years.
- Pills. This form is convenient to give to children from 5 years of age, who can already consciously swallow a tablet.
- Rectal suppositories. Suitable for the youngest patients. When an infant needs quick help, these candles effectively cope with their task.
- Powder for preparing a solution. Convenient to take with you, a teenager at the age of 10 can already dilute the powder and take medicine on his own.
- Syrup. They can be used at any age, most often they come with various flavoring additives, they are pleasant to take.
What to do if you get sick?
Fever, weakness, soreness, lacrimation are early signs of infection. When they appear, it is not recommended to leave the house. Firstly, so as not to spread viruses, and secondly, so as not to worsen your health. You can call a therapist or pediatrician by phone. In case of extreme temperatures, it is better to call an ambulance. Before the doctor arrives, the sick person must be put to bed and given warm tea (fruit juice). It is advisable to put a medical mask on the patient, provide him with a separate room, dishes, and hygiene items. To prevent complications, it is important to follow medical prescriptions - take medications, drink plenty of fluids, ventilate the room, eat foods rich in vitamins, phytoncides, and protein. In the first days of illness it is necessary to observe bed rest. If you have the flu, physical activity can trigger the development of acute respiratory distress syndrome, an extremely life-threatening condition.
Criterias of choice
Let's look at what to look for to avoid mistakes when choosing products:
- Age. The main criterion for selecting medications is the age of the child. The dosage inside the tablet or syrup is designed so that a certain amount of the drug falls on a certain weight (age). If a 3-year-old child is given a drug for the age of 6, there will be a severe overdose; if done the other way around, the effect of taking it will be minimal.
- Precautionary measures. It is necessary to strictly follow the instructions for use, which indicate how to give the baby the medicine and in what quantity.
- Active substance. Pay attention to the composition of the medicine. The active substance in it must correspond to the virus that your baby is sick with, otherwise there will be no effect from taking it.
- Where can I buy. Buying from an online store can significantly reduce your time costs, and sometimes medications are cheaper there than in a pharmacy. Ordering online is not difficult; you can have it delivered to your home or picked up at your nearest pharmacy.
- Which one is better to buy? The popularity of a model is not always justified by the effectiveness of the drug. Sometimes time-tested but not overly advertised products help more effectively than popular models and new products that constantly appear on the market.
- Doctor's prescription. Be sure to consult your doctor about possible contraindications before purchasing. Also, if the medicine is a prescription, your doctor will write a prescription.
- Price. Inexpensive (budget) products are sometimes not inferior to their expensive counterparts. Therefore, initially consult your doctor which medicine will be more effective. Don't overpay for the brand. Children's medications on the market have the highest percentage of counterfeits. Therefore, be careful to ask the seller for a certificate for the product.
Prevent severe disease. How does the cure for COVID-19 work?
In the updated recommendations of the Ministry of Health for the diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19, the antiviral drug favipiravir is first mentioned - in Russia it is produced under the names “Areplivir”, “Coronavir” and “Avifavir”. Judging by clinical trials here and abroad, it effectively combats the multiplication of the virus in the body, shortens the treatment period and is suitable for outpatients. However, local doctors are skeptical about the new medicine and are in no hurry to prescribe it. RIA Novosti, together with experts, understands how the drug works and why medicine gives it the green light.
What Japanese scientists found out
With the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, scientists immediately began to look for a remedy against the causative agent of the disease. Creating a specific medicine from scratch is a long process; it will take years, so we analyzed existing ones.
One candidate was favipiravir, developed by the Japanese company Toyama Chemical in 2002 as a treatment for influenza. It disrupts the reproduction processes of RNA-containing viruses, which include SARS-CoV-2, and triggers the processes of their self-destruction in the body. In test mode, the drug was given to patients with COVID-19.
A preliminary report from an observational program in Japan conducted in May on more than 2,000 people found that those taking favipiravir felt better as early as the seventh day of treatment. Positive dynamics were observed in 73.8% of mild patients, 66.6% of moderate patients and 40.1%, among whom were people with cardiovascular problems, diabetes and chronic lung disease.
A total of 39 clinical trials of favipiravir have been registered worldwide. It has been approved for treatment in China, India, and Thailand. It is also recommended in Russia. However, medical practitioners have mixed opinions about the drug.
Doubts and evidence
“They treat it differently - some strictly follow the recommendations of the Ministry of Health, others do not prescribe it at all, because they are not too confident in its effectiveness,” notes Pavel Nikitin from the N. N. Burdenko National Medical Research Center for Neurosurgery.
According to him, favipiravir did demonstrate antiviral activity against other RNA viruses in preclinical studies. But in order to definitely recommend it, deeper and more detailed research is needed according to the standards of evidence-based medicine. “Scientific data, in my opinion, is still not enough,” says the scientist.
Dmitry Rosukhovsky, a vascular surgeon and chief physician at the Lastikmed clinic in St. Petersburg, is also skeptical: “Already a year has passed since the start of testing potentially reliable remedies for coronavirus. And everyone is not efficient enough.”
Wariness towards favipiravir, he believes, is explained by negative experience with the use of other drugs that affect the cause of the disease.
Doctors who tested favipiravir-based drugs in the clinic have a different opinion.
“We deal with Areplivir as soon as it appeared. The experience of use was gained from the staff of the Department of Infectious Diseases - they were the first to admit patients with COVID-19. Since September we have been monitoring data from the regional hospital. We have an idea of how the drug works from both a practical point of view and a scientific one, since colleagues from the university participated in clinical trials,” says Candidate of Medical Sciences Lyudmila Tverdova, an endocrinologist of the highest category, associate professor at the Ryazan State Medical University named after Academician Pavlov.
During the randomized trial, patients were given antiviral drugs or standard therapy drugs recommended by the Ministry of Health. It turned out that those who received Areplivir as part of complex treatment spent less time in the hospital and got back on their feet faster.
“Ideally, clinical trials take years to plan, recruit hundreds of patients, and look at targets for molecules to act on. But we have a unique situation. There is not a single drug developed specifically for COVID-19. Medicines for malaria, despite the side effects, were used in practice in our country. Favipiravir has never been used in Russia. Yes, it is registered in Japan, and many scientific articles describe its successful action against various RNA viruses - say, influenza or even Ebola. But Russian doctors are not yet very familiar with it, which largely explains their skepticism. The only way is clinical research,” says Kira Zaslavskaya, national medical manager of Promomed LLC, which produces Areplivir.
Medicines for COVID-19 are being tested using an accelerated procedure. This reduces bureaucratic difficulties, Zaslavskaya notes, but does not detract from the value of the results, which in any case should have statistical significance. The Areplivir study involved 206 people, and the Coronavir study - 168. For the third trial, 540 participants were announced, the results have not yet been published. “All data, both Russian and international, goes into the piggy bank. “Soon we will receive the highest level of evidence of the results of clinical studies of favipiravir,” the expert emphasizes.
"Effective in the early stages"
“We noticed that the drug Areplivir is more effective in the first five days of the disease, in the early stages. In our opinion, it is better to use it on an outpatient basis, and not just in a hospital, where patients are admitted with moderate and severe forms. In addition, it reduces the effectiveness of infection,” Lyudmila Tverdova shares her observations.
The fact that medications based on favipiravir can be used not only in hospitals, but also in outpatient settings is also stated in the temporary recommendations of the Ministry of Health.
“To reduce the risk of severe disease and, accordingly, the burden on the healthcare system, it is necessary to use effective drugs. Favipiravir acts directly on the virus reproduction mechanism, and now it is the only one. In the Areplivir study, which was conducted on moderately ill patients, after a course of administration, 98% of patients experienced elimination of the virus. This was demonstrated in a study by our colleagues,” says Zaslavskaya.
Antiviral therapy is needed to prevent a mild form from becoming moderate, and a moderate form from becoming severe. Of course, sooner or later the elimination of the virus occurs on its own. But if by this moment there are large-scale lesions and hyperactivation of the immune system, then the risk of serious complications is very high, explains a representative of Promomed.
The company will soon launch observational studies of the use of Areplivir in routine clinical practice. Doctors will receive new data on the safety and effectiveness of the drug.
Effective, but affordable?
So, manufacturers and researchers of favipiravir are optimistic, but until recently it was distributed only in hospitals; it was almost impossible to buy at retail even in Moscow. In the regions there are still problems with ordering through online services - medicines are simply “out of stock”.
Now the situation has begun to change. The drugs appeared in pharmacies, but only in those connected to the digital labeling system introduced on July 1 of this year in Russia. Now the manufacturer applies a unique QR code to each package so that it can be tracked at every stage from the conveyor to the consumer. Distributors and pharmacy chains must read the label and enter it into the federal database - IS MDLP.
In practice, all this resulted in chaos: the system regularly crashed, documents were not processed for a long time, calls to technical support remained without resolution. In fact, there is no shortage of medicines; often they are already in the supplier’s warehouse, but they cannot be sold. “The problem also affected medications used to treat covid infection; in some companies, the circulation of these drugs has been suspended,” the press service of the Association of Russian Pharmaceutical Manufacturers (ARPP) explained to RIA Novosti.
Officials have received many complaints and requests regarding the work of the new labeling system from both manufacturers and pharmacy chains. Only ARFP sent three letters to M.V. Mishustin, V.I. Matvienko, V.V. Volodin, where they proposed “to establish a special procedure for working with IS MDLP during the COVID-19 epidemic in order to ensure the unimpeded movement of products in the supply chain.” As a result, on October 27, the Ministry of Industry and Trade met halfway and simplified the procedure for working with the system.
Now the drug costs about 5,500 rubles per package. Often this is enough for a course of treatment, because the main task is to stop the spread of the virus. Self-medication is unacceptable - the medicine is dispensed only as prescribed by a doctor.
“Outpatient patients can purchase the drug using prescription form number 107 (not strict reporting) from a local physician, or a pulmonologist, or a general practitioner. There shouldn’t be any difficulty in getting a prescription,” explained Lyudmila Tverdova.
However, favipiravir drugs will be provided free of charge to those receiving treatment at home. Moscow is already doing this, and the regions are next. The government recently decided to allocate five billion rubles for this purpose. Funds have been transferred to the constituent entities of the Federation, and procurement has begun. “By the end of the year, at least 640,500 patients will be provided with free medicines from the federal budget, excluding the city of Moscow,” says the official statement of the Russian Ministry of Health.
As RIA Novosti was told by Promomed LLC, the plant has doubled its capacity, which is enough to meet the needs of the regions, and is now actively shipping goods.