© designer491 — stock.adobe.com
Share:
Modern fashion for healthy lifestyle dictates its own rules. People are increasingly resorting to diet correction and, of course, exercise, which is understandable. Indeed, in large cities it is very difficult to provide oneself with the necessary level of physical activity. Striving for health, many additionally introduce sources of amino acids (AA), in particular threonine, into the menu.
Description of amino acid
Threonine has been known since 1935. The discoverer was the American biochemist William Rose. It was he who created the structural characteristics of the monoaminocarboxylic amino acid and proved its indispensability for human immunity. Threonine is present in the muscles of the heart, skeletal muscles and the central nervous system. At the same time, it is not produced by the body and comes exclusively from food (source - Wikipedia).
There are 4 threonine isomers: L and D-threonine, L and D-allothreonine. The most important is the first one. It promotes protein synthesis and is a component of elastin and collagen. Needed for the process of formation and further preservation of tooth enamel. The best digestibility of this isomer is observed in the presence of nicotinic acid () and pyridoxine (). For correct absorption, the proper level of magnesium in the body is required.
Note! There are known genetic diseases caused by the body's immunity to threonine. In such cases, it is necessary to take medications containing glycine and serine.
© Gregory — stock.adobe.com
How is it absorbed by the body?
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
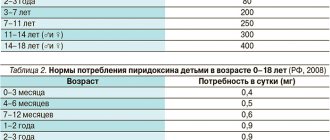
Usually, the body easily absorbs threonine, but for this it needs the presence of B vitamins, in particular, and are the most useful for this. In addition, it is important to monitor the concentration of magnesium in the body, since the correct absorption of the amino acid also depends on this trace element.
Meanwhile, some people with genetic diseases may not absorb threonine from food at all. In such cases, it is important to more intensively take serine and glycine - amino acids for which threonine actually serves as a “precursor”.
Threonine: benefits and properties
This amino acid is necessary at any age. It ensures the correct functioning of the physiological systems of the body. Toddlers and teenagers need AK to grow. With its regular intake, normal development is ensured. One of the most important functions is the synthesis of antibodies to provide immunity.
In an adult body, the amino acid has a positive effect on the gastrointestinal tract and helps cure peptic ulcers (source in English - scientific journal Gastroenterology, 1982). Moreover, by reacting with methionine and aspartic (aminosuccinic) acid, it promotes the breakdown of fats in the human liver and improves the absorption of dietary protein. Has a lipotropic effect. For therapeutic purposes, this AK activates muscle tone, heals wounds and postoperative scars, affecting the exchange of collagen and elastin.
Note! Threonine deficiency causes growth retardation and weight loss (source - scientific journal Experimental and Clinical Gastroenterology, 2012).
The main functions of threonine:
- maintaining the correct functioning of the central nervous system, immune and cardiovascular systems;
- presence in proteins and enzymes;
- ensuring growth;
- assistance in assimilation of other useful elements;
- normalization of liver function;
- muscle strengthening.
The effect of vitamin B6 in combination with the amino acid threonine
The manifestation of personal qualities often depends on the metabolism of biologically active substances at the molecular level. Vitamin B6 and the amino acid threonine are precisely those molecules that help you remain yourself in the most difficult circumstances, making the most of all your capabilities.
Biological role of vitamin B6 and threonine
The benefits of vitamin B6, or pyridoxine, for the nervous system have been confirmed: it is involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, in particular serotonin, stimulates cellular respiration and accelerates the elimination of toxins. All this improves mood, helps cope with stress, treat insomnia, neurological diseases in children and adults.
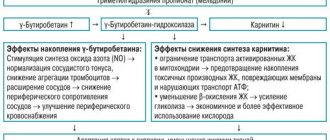
Threonine is an essential amino acid that, when entering the body, reacts and breaks down into glycine and acetaldehyde, which are also involved in the activation of processes in the Krebs cycle. Glycine is a neurotransmitter that activates protective inhibition processes. In the presence of vitamin B6, all transformations of threonine occur much faster, and both substances potentiate the effect of each other, so it is important for them to enter the body simultaneously. In this case, the potential of the nervous system and stress resistance are significantly increased.
Modern drug Biotredin®
Neither vitamin B6 nor threonine are produced in the body, so they need to be regularly supplied with food or as part of medications. To what extent can this be achieved under modern conditions, and is it possible to simultaneously maintain sufficient concentrations of both pyridoxine and threonine?
The drug Biotredin® was developed specifically to solve this problem: it consists of vitamin B6 and L-threonine, which are found here in an optimal ratio.
The effect of Biotredin® on the body is complex: the drug improves metabolism in the brain, increasing the efficiency of thinking, improving attention, memory, while helping to cope with psychological stress, activating protective inhibition.
Acetaldehyde, which is formed as a result of threonine metabolism, is a marker of craving for alcohol, and its entry into the blood before ethanol intake helps reduce the desire to drink alcohol. Therefore, the use of Biotredin® in the treatment of alcoholism helps to solve several problems at once: reduce cravings for alcohol, identify hidden cravings during remission, improve the general condition due to participation in metabolism, reduce psycho-emotional stress and increase motivation for treatment.
Application of Biotredin® in pediatrics
Prescribing Biotredin® in adolescence helps to survive the crisis and at the same time reduce the likelihood of deviant behavior. A key need of adolescence is to accept oneself and to be accepted by peers. But its satisfaction is complicated by increased nervous tension, irritability, and anxiety, which are caused at this age by hormonal changes, psychological crisis, and relative deficiency of vitamins and amino acids. Taking a complex of vitamin B6 and threonine helps optimize biochemical processes in a teenager’s body.
The body of a primary school student faces similar problems: when the need for active molecules is greater than the ability to obtain them, stress from studying inhibits metabolism in the nervous tissue, which further reduces adaptive capabilities. Biotredin® solves the problem of lack of energy, improves emotional state and helps adapt to new difficult conditions.
The prescription of Biotredin® for neurological problems and mental retardation is also justified by its metabolic activity. At the same time, regular use of the drug has a therapeutic effect not only during therapy, but also helps to establish one’s own regulatory mechanisms, which can be relied upon in the future.
Sources of threonine
The record holder for threonine content is protein foods:
- meat;
- eggs;
- dairy products;
- fatty fish and other seafood.
@AINATC – stock.adobe.com
Herbal suppliers of AK:
- beans;
- lentils;
- cereals;
- seeds;
- mushrooms;
- nuts;
- leafy greens.
The above products, as a rule, are always available, and therefore must be constantly present in the diet.
Food sources
Threonine is an essential amino acid, and in order to provide the body with it, it is necessary to introduce meat, dairy products, and eggs into the diet. Vegetarians can supplement their supply from nuts, grains, beans, seeds and some vegetables.
Sources of animal origin: almost all types of meat (lamb, beef, horse meat, chicken, turkey, grouse), dairy products (many varieties of hard cheese, feta cheese), fish (sea, fatty) and eggs.
Plant sources: leafy vegetables, lentils, barley, wheat, buckwheat, beans, mushrooms, sprouted grains, rye, seeds, nuts, leafy vegetables.
Table of amino acid content in some foods
| Product (100 g) | Threonine (mg) |
| Egg | 368 |
| Shellfish | 214 |
| Beef | 160 |
| Pork | 151 |
| Turkey meat | 133 |
| Anchovies | 127 |
| Sesame | 74 |
| Lentils | 33 |
| Milk | 16 |
| Champignon mushrooms) | 11 |
Deficiency and excess of threonine: dangerous disturbances of harmony
If threonine levels are exceeded, uric acid begins to accumulate in the body. Its excessive concentration leads to dysfunction of the kidneys, liver and increased stomach acidity. Therefore, it is necessary to strictly control the content of AA, avoiding oversaturation with it.
Amino acid deficiency is a rare occurrence. It is noted due to malnutrition and mental disorders.
Symptoms of threonine deficiency are:
- decreased concentration, loss of consciousness;
- depression;
- rapid weight loss, dystrophy;
- muscle weakness;
- slower development and growth (in children);
- poor condition of skin, teeth, nails and hair.
Daily norm and rules of consumption
The range of recommended daily intakes of threonine is quite wide: from 500 mg to 3 g.
But when taking an amino acid in the form of a bioactive supplement, you should be aware that high doses of the drug can cause liver dysfunction and increase the level of urea in the body, and therefore ammonia, which has a toxic effect.
Lack of amino acid causes emotional agitation, confusion, indigestion and fatty liver. In addition, the lack of this substance leads to an imbalance of all amino acids that are produced on the basis of threonine.
People who are actively involved in sports, or whose work involves heavy physical labor, should take care of additional amino acid intake. Also, a higher concentration of the substance should be maintained in a growing body. Threonine is also useful for people suffering from depression. A slight increase in the daily norm will help them cope with psycho-emotional disorders. But for vegetarians, whose diet is extremely poor in proteins, it makes sense to think about taking threonine in the form of a dietary supplement.
Over the years, the body's need for this amino acid decreases slightly. There is also an opinion that in some cases threonine can cause a decrease in lung performance. Meanwhile, there is no exact scientific evidence of this yet.
Threonine and sports nutrition
The amino acid is invaluable in the context of sports nutrition. Threonine helps build and strengthen muscle mass. Helps withstand increased stress and quickly recover from it. AK is indispensable for weightlifters, runners, and swimmers. Therefore, constant monitoring and timely correction of amino acid levels are important factors in sports success.
Note! Threonine stimulates brain function. It also alleviates the manifestations of toxicosis in pregnant women.
Proteins and amino acids
Proteins are absolutely necessary substances for the existence of the body. They participate in metabolic processes, they make up hormones and antibodies, blood cells and muscle fibers. However, a piece of well-fried beef by itself will never become the building material for bodybuilder Kolya’s biceps. First, the meat must be digested - that is, with the help of digestive enzymes, the protein contained in the meat must be broken down into its constituent amino acids, and then new proteins must be assembled from these “building blocks” - already in the coli muscle.