Symphysitis is a manifestation of instability of the cartilaginous connection of the bones of the pubis (symphysis) as a result of hormonal changes in the body. Most often, symphysitis appears during pregnancy under the influence of hormones that prepare the woman’s body for childbirth. The mobility of the joint leads to pain in the pelvic area, which occurs even during any movement. There are many ways to help reduce the intensity of pain. In most cases, after childbirth, symphysitis goes away on its own.
As a result, symphysitis appears
A woman's body undergoes many changes during pregnancy. One of them is changes in hormonal levels. Hormones are produced that are responsible for the preservation of pregnancy and the safe bearing of the baby. The hormone relaxin helps soften ligaments. Thanks to this, the pubic symphysis becomes mobile, and the internal size of the small pelvis increases by several millimeters. This facilitates the easiest passage of the fetus through the birth canal. In most cases, symphysitis appears in the third trimester of pregnancy, in rare cases - much earlier, around 22-24 weeks of pregnancy.
When the first symptoms of symphysitis appear, you should consult a doctor monitoring your pregnancy. This is necessary in order to exclude diseases that are dangerous for the mother and child - urinary tract infections or inflammation of the pelvic organs.
Prevention
special method for preventing symphysitis . To prevent the development of anomaly it is necessary:
- control weight;
- to live an active lifestyle;
- perform exercises to maintain the muscle corset and reduce pain ;
- eat a balanced diet, introducing foods high in K, Ca, Mg into your diet;
- take vitamin and mineral supplements outside the season of natural fruits and vegetables;
- avoid pelvic injuries.
exercises , which increase blood supply to the pelvic organs, stimulate the process of ossification, and strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, can prevent symphysitis .
Aggravating factors
In addition to hormone production, there are several factors that provoke sprains of the pubic ligaments:
- disturbance of calcium-phosphorus metabolism;
- lack of vitamin D;
- increase in body mass index
- history of three or more pregnancies;
- injuries to the pelvic bones, even old ones;
- hereditary diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- high fetal weight (the expected weight of the child at the time of birth is 4 kg or more);
- insufficient amount of physical activity of the mother.
Folk remedies
Photo: yandex.ru
Symphysitis should be treated by a qualified specialist. The use of various traditional medicines is strictly prohibited.
At home, a woman who has the problem in question should monitor her diet. First of all, preference should be given to dairy products (cheese, cottage cheese, milk, etc.), which are rich in calcium. You should also be careful about flour products and fatty foods, as their excess consumption leads to weight gain. In turn, excess weight increases the load on the pelvic ring, and as a result, pain increases.
With symphysitis, it is important to reduce excessive physical activity, refrain from climbing stairs, fast walking, and staying in one position for a long time (over 30 minutes - 1 hour). It is also recommended to perform specially designed physical exercises daily that strengthen the gluteal, thigh and perineal muscles. We suggest the following exercises, which should be performed several times a day:
- Take a lying position. Place your feet as close to your buttocks as possible. Then spread your bent knees to the sides as far as possible and stay in this position for a few seconds, after which you close your knees again. It is necessary to repeat this exercise from 5 to 10 times, gradually increasing the number of exercises.
- Take a lying position. Bend your knees and lift your pelvis so that you form a straight line with your body. It is recommended to perform this exercise 5 to 10 times daily, gradually increasing the number of exercises. If pain occurs, you should stop doing the exercise.
- Get on your knees and place your palms on the floor so that they point forward. The correct position should look like this: arms straight, knees bent at right angles to the body, back straight. As you inhale, round your back as much as possible and lower your head down. As you exhale, slowly return to your starting position. Then, while inhaling, bend your body down as much as possible. As you exhale, return to the starting position. The exercise should be repeated 5 – 10 times.
The information is for reference only and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor.
How to recognize symphysitis
The main clinical manifestations of symphysitis during pregnancy are:
- sharp shooting pains in the pelvic area;
- aching pain in the lumbar region, radiating to the abdominal cavity and inner thigh;
- the occurrence of acute pain when raising a leg, transferring weight from one leg to another, or spreading the legs;
- the occurrence of pain with the slightest physical activity, even when walking;
- a pronounced click when performing sudden movements in the pubic area;
- pain in the pubic symphysis during sexual intercourse;
- severe fatigue and fatigue.
The level of pain with symphysitis during pregnancy can vary from mild, almost unnoticeable, to very severe. The pain becomes significantly stronger at the following moments:
- when lifting objects;
- during physical activity in which the hips are actively involved;
- while maintaining a static body position for a long time without changing posture.
Diagnostics
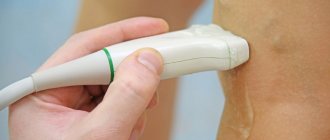
Diagnosis of symphysitis may well be limited to radiography. The pictures clearly show the size of the diastasis and the location of the bones. When a rupture occurs, fragments of ligaments or cartilage may also be visible.
But during pregnancy , using x-rays is dangerous for the developing embryo, so today the Manual Medicine Clinic “Galia Ignatieva MD” uses modern imaging methods:
- Ultrasound;
- MRI, CT.
MRI is most often used in sports medicine.
Rice. 2. Ultrasound of the symphysis during pregnancy
However, differential diagnosis cannot be limited to instrumental studies. To exclude a number of pathologies during pregnancy with similar symptoms , the following is carried out:
- clinical blood and urine tests;
- biochemical blood tests (PCR, enzyme immunoassay);
- assessment of calcium in the blood.
Symphysitis will also be determined on a gynecological chair - examination with a mirror and palpation examination, if the diastasis is significant. The doctor may detect swelling of the pubis and a depression in the form of a vertical strip between the bones.
is the best way to identify symphysitis. The screen clearly visualizes areas represented by different types of cartilage, the condition and integrity of ligaments and soft tissues. The method helps to predict the behavior of the symphysis pubis during childbirth and promptly choose the method of delivery - natural or cesarean section.
Severity of the condition
In modern medicine, three degrees of the disease are expressed
- 1st degree - the width of the divergence of the bones of the pubic symphysis is 5-9 mm. The condition is tolerated quite easily; the pregnant woman experiences minor pain that occurs during long walks or during physical activity;
- 2nd degree - the width of the divergence of the bones of the pubic symphysis is 10-19 mm. Pain appears, noticeable with any intense movement;
- Grade 3 - the width of the divergence of the bones of the pubic symphysis is 2 centimeters or more. Painful sensations appear even at rest.
Description and causes
The pelvis consists of paired pelvic bones, the coccyx and the sacrum. The symphysis pubis (PS) is one of 3 joints that ensure mobility of the pelvic bones during the passage of the fetus during childbirth. The symphysis pubis is formed by the fibrocartilaginous interpubic plate and 4 ligaments. The most detailed description of the morphology and anatomy of the drug was made in 1962 by M.F. Eisenberg. He pointed out that the pubic symphysis has sexual and individual characteristics. The pubic symphysis can be represented by different types of joints - from synchondrosis to a real joint. Its structural features and condition in women are in close connection with the endocrine and functional processes occurring in her body .
The structure of the interpubic plate is heterogeneous. Most of it is formed by hyaline cartilage, and on the periphery - fibrous cartilaginous tissue. The older a woman , the smaller the area of hyaline cartilage. In some cases, it can be detected in the form of separate island areas.
Relaxation of the connective tissue apparatus in the pubic area during pregnancy is a physiological process. woman’s body begins to prepare for labor by increasing the synthesis of progesterone and relaxin. Both hormones affect many tissues of the reproductive and non-reproductive systems. Connective tissue fibroblasts have specific receptors for relaxin. Under the influence of hormones, swelling occurs and the tissues in the symphysis area become loosened, which causes them to relax, and the ends of the pubic bones acquire greater mobility than before pregnancy . The discrepancy between the bones may be 1-2 cm.
Rice. 1. Symphysitis
Pathology can also be detected outside of gestation. The reasons for its appearance are infectious and autoimmune diseases :
- hepatitis C;
- tuberculosis;
- arthritis;
- hemorrhagic diathesis;
- syphilis, etc.
In addition, the disease can be caused by other reasons such as bad habits, low mobility, excess weight , and pelvic injuries. If a woman had an anomaly in a previous pregnancy , then the disease will most likely be detected in subsequent ones.
Factors causing symphysitis in pregnant women can also be obstetric complications. When a large fetus through the birth canal, the weakened tissue can not only stretch excessively, but even rupture. In sports medicine, dysfunction is often found with injuries to the ligamentous apparatus of the pelvic ring, hip and lower back .
Disorders of calcium play a major role in the development of pathology. Even with a physiologically occurring pregnancy, an imbalance of calcium , phosphorus, magnesium and vitamin D occurs. The functional restructuring of the hormonal system also affects the absorption and metabolism of these nutrients. Minerals are used to build the fetal skeletal system. If their intake into the pregnant woman’s or absorption is impaired, calcium is “washed out” from the pregnant woman’s . The disturbance of phosphorus-calcium metabolism is evidenced by manifestations characteristic of their deficiency. In 17% of cases, symphysitis is accompanied by signs of calcium imbalance:
- paresthesia;
- convulsive twitching;
- muscle spasms;
- bone pain
- change in gait, etc.
They appear 2-3 months before birth.
The factor causing pathological bone diastasis is a genetic disorder of connective tissue. The formation processes of this type of tissue are a complex and multi-stage mechanism. Any failure - abnormal proliferation, caused, for example, by genetic defects in structural genes, excessive degradation of collagen, can lead to connective tissue dysplasia and weakening of the articulation .
To determine the degree of progression of the physiological and pathological process at the Clinic of Manual Medicine “Galia Ignatieva MD”, specialists use the classification of L.V. Vanina:
- Physiological discrepancy of the joint in a pregnant woman :
- Ⅰ degree – 5-9 mm;
- ⅠⅠ degree – 10-20 mm;
- Ⅲ degree – > 20 mm;
- Symphysiopathy (sacroileopathy) is excessive mobility of the pubic symphysis of the pelvis.
- Rupture of the pubic and sacroiliac joint .
- Symphysitis and sacroiliitis.
The author of the classification believes that if an anatomical anomaly is detected on an x-ray image in the absence of the woman’s , the case should be regarded as a variant of the norm. And when complaints are presented, it is treated as a pathology, the severity of which is assessed in 3 degrees .
How to reduce pain intensity
After confirming the diagnosis, the doctor leading the pregnancy should give some tips and recommendations that will help reduce the level of pain.
Most often this is:
- use of a special bandage;
- taking medications containing calcium and vitamin D;
- monitoring weekly weight gain and monitoring weight in case of excessive work, as excess weight increases pain;
- adherence to a sleep and rest regime, in some cases complete physical rest should be adhered to;
- applying a warm heating pad to the area of the ligaments (here the doctor must tell you about the importance of maintaining a thermal regime);
- light massage at home;
- use of a special orthopedic pillow for the pelvic area;
- lightweight gymnast;
- swimming in the pool (in the absence of contraindications from the doctor).
In some cases, it is permissible to take painkillers. They are prescribed by a doctor. Self-administration of medications during pregnancy without consulting a specialist is prohibited.
Causes of symphysitis
Instability of the pubic symphysis often develops with repeated births, especially if less than three years have passed between pregnancies.
Doctors associate the appearance of symphysitis with two reasons: calcium and vitamin D deficiency and excessive production of relaxin.
Factors predisposing to symphysitis:
Calcium deficiency is detected by blood tests. Eliminated by a diet that includes hard cheese, cottage cheese, nuts, fish, green vegetables, prunes and other foods rich in calcium.
Osteopathic correction is a painless and effective way to restore the normal tone of the ligaments of the pubic symphysis.
Epidemiology/Etiology
There are several theories about the origin of symphysis pubis dysfunction:
Aslan et al. They say that the etiology of the disease is unknown. During pregnancy, the load on the pelvis changes, ligaments and muscles weaken. This leads to spinopelvic instability, which manifests itself as DLS.
In early pregnancy, the corpus luteum produces large amounts of the hormone relaxin and progesterone. From the 12th week, this function is taken over by the placenta and the decidua of the uterus. Relaxin breaks down collagen in the sacroiliac joints, causing tissue softening. Progesterone has a similar effect. However, there is no correlation between relaxin levels and the degree of symphysis pubis dysfunction. A Norwegian study found that genetic predisposition to DLS may be caused by defects in relaxin secretion. It may seem that relaxation of the ligamentous apparatus directly indicates the presence of a hormonal basis for the disease. However, there is not enough data to support this theory.
The influence of stress and cortisol levels on pelvic pain.
Other factors leading to DLS include physically exhausting work during pregnancy, as well as pathological fatigue, poor posture and lack of exercise. Excess weight, multiple pregnancies, older pregnancies, a history of difficult labor, and shoulder dystocia may also play a role.
Effective adaptation of joints to a given load requires adequate joint compression and coordinated efforts of muscles and ligaments. This is the key to effective joint reactions to changing conditions. During pregnancy, ligaments and muscles become weaker and cannot perform their functions as they did before. As a result, the pelvic tilt changes, which leads to spinopelvic instability, most often manifested in dysfunction of the pubic symphysis.
In short, the causes of this instability are hormonal (influence of the hormone relaxin), metabolic (calcium metabolism), biomechanical (stress during pregnancy and exercise), underdeveloped muscles, body composition (weight), anatomical and genetic variations.
- The pelvic floor is made up of three layers of muscles. The superficial layer innervated by the pudendal nerve includes the bulbocavernosus muscle, the ischiocavernosus muscle, the superficial transverse perineal muscle, and the external rectal sphincter.
- The deep layer is the urogenital diaphragm, which is also innervated by the pudendal nerve. These include the urethral sphincter, constrictor bladder muscle, urethrovaginal sphincter and deep transverse perineal muscle.
- The pelvic diaphragm is made up of the following muscles: the levator ani muscle (pubococcygeus muscle, also known as pubo-prostatic, pubovaginal, pubo-anal, puborectal, iliococcygeus), coccygeus muscle, piriformis muscle and obturator internus muscle. These muscles are innervated by the sacral roots of the spinal cord (S3-S5).
The function of the pelvic floor muscles is to support the organs lying on it. The sphincters (anal and urinary) allow conscious control of the bowel and bladder. Thanks to this, we can consciously control the excretion of feces or fatus, as well as urine.
When contracted, the pelvic floor muscles are able to lift the internal organs and compress the openings of the sphincters of the vagina, anus and urethra. When the pelvic floor muscles relax, urine may leak and feces may be released uncontrollably. Pregnancy changes the functioning of these muscles, as well as their function.
The effect of symphysitis on pregnancy
Symphysiopathy does not affect pregnancy in any way. But the condition of a pregnant woman, due to specific symptoms, will be worse than it could be. Remember that stretching the symphysis pubis can lead to its excessive thinness, which is why cartilage rupture occurs during the birth of the baby. This, as we have already written, is called symphysiolysis. A woman who has given birth will lose her ability to work for 2 or more months.
There is a high risk of rupture of the joint in those expectant mothers who have a narrow pelvis (male body type), and at the same time their baby is heavy. If your doctor has diagnosed second or third degree symphysiopathy, he may recommend a cesarean section instead of a natural birth. The same can happen if it is revealed that the fetus is very large and can damage the mother’s birth canal.
What is the danger of symphysis rupture?
The divergence of the symphysis pubis after or before childbirth causes a lot of unpleasant symptoms in a young mother. However, this condition is not a threat to health or life. But if the divergence of the pelvic bones leads to rupture of the symphysis pubis during childbirth, then we are talking about a serious injury, that is, a pelvic fracture .
Photo of where the pubic bone is located
Provided that the bones have separated by 2 cm, we are talking about a stable fracture that rarely provokes complications. But if the symphyosis has diverged by 5 cm or more, then this condition seriously threatens health. Therefore, treatment of symphysitis after childbirth depends on the woman’s condition – sometimes surgical intervention is required.
After all, when the edges of the bones rupture, they sometimes damage the bladder, urethra, and clitoris. Hemorrhages sometimes develop in the joint area, and this subsequently leads to the development of arthritis . True, such a serious condition requiring surgery is quite rare.
Treatment of symphysiolysis in newborns
Pain relief is needed because this is one of the main symptoms. The doctor prescribes NSAIDs. These are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. These drugs include ibuprofen and paracetamol. But the drug itself and the dosage must be determined by the doctor, because it is very individual. NSAIDs are prescribed only if the pain is very severe. The drugs have side effects. If taken for a long time and without medical supervision, liver pathology or stomach ulcers may develop.
If you feed your baby naturally, consult your doctor about taking NSAIDs. Not all medications from this group can be taken during lactation, because they can harm the newborn.
The next component of complex therapy for symphysiolitis after childbirth: a gentle regimen. Physical stress on a woman’s body should be minimized. Canes can be used for walking. In some cases, the doctor prescribes wearing a bandage that will capture the trochanters of the femur. This will reduce pain and prevent bone separation in the future. Thanks to the bandage, the symphysis will heal faster.
Physiotherapeutic methods of treatment are used, including magnetic therapy. It is important to combine this method with fixation of the pelvic bones and bed rest. The doctor prescribes strict bed rest for those women in labor whose bones have severely eroded and the symphysis has torn. To speed up the fusion process, you need a special hammock with weights suspended crosswise. Thanks to it, the reduction of the pubic bones will be ensured. A controlled pelvic girdle may also be needed for treatment. It enhances the hammock effect mentioned above.
Old tears can only be treated with surgery. To make the pelvis whole again, plastic materials and rods are used.
Therapeutic methods
Treatment of arthrosis of the pubic joint must necessarily be comprehensive. Its main task is to eliminate etiological factors. The first thing the doctor recommends that the patient do is to reduce the load on the problem joints, for which you need to avoid staying in one position for a long time and get a fixing bandage. Conservative therapy involves the use of the following pharmaceuticals:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They alleviate the patient’s condition, but are characterized by an exclusively symptomatic effect.
- Hormonal drugs. Prescribed for severe pain syndrome. It is not recommended to use for a long time.
- Chondoprotectors. They have a targeted effect on the affected cartilage tissue, promoting its regeneration.
- Muscle relaxants. Relieve muscle tension and reduce pain.
- Vasodilators. Designed to improve blood circulation in tissues, so that joints receive more nutrients.
Physiotherapy, massage, and acupuncture are useful to activate metabolic processes in the symphysis pubis. A set of gymnastic exercises perfectly helps to improve joint mobility, restore blood circulation and strengthen muscle fibers. An individual training program is developed for each patient, taking into account the stage of the disease and the degree of damage to the joint.
The operation is indicated for advanced forms of arthrosis, when traditional methods of treatment are powerless. Endoprosthesis replacement is carried out after a comprehensive clinical examination, which confirms the irreversible nature of the destruction.