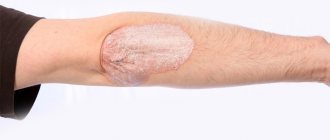
Oral leukoplakia is a disease of the oral mucosa in which plaques of whitish, gray or yellowish shades form. They (plaques) are localized on the tongue, the inner surface of the cheeks, the palate, and also in the corners of the lips. The keratinized epithelium rises slightly above the mucous membrane and brings a lot of physical and aesthetic discomfort to the patient. Plaques can form from 7 days to several months. The risk group for this disease is men aged 30-40 years, but recently the disease has also been diagnosed in young children. The main threat of oral leukoplakia is the prospect of transformation into a cancerous tumor. That is why, in case of alarming symptoms, it is necessary to urgently contact an experienced dentist.
Leukoplakia of the oral cavity: causes of the disease
The reasons causing the development of the disease include:
- Smoking. When using tobacco, the oral cavity is exposed to various irritants, including thermal (incoming smoke has a temperature of about 60 degrees Celsius) and chemical (nicotine, tar and combustion products). No less dangerous is chewing tobacco, which is also a provoking factor.
- Eating either very hot or very cold food on a regular basis for a long time.
- Mechanical trauma (bad bite, sharp edges of teeth, orthopedic structures installed with violations).
- Metal seals that cause galvanic currents.
- Inhalation of vapors of gasoline, benzene, varnishes and paints, as well as other resins.
- Hormonal imbalance, constant stress and lack of retinol.
Causes
Medicine cannot give a definite answer as to what causes the nonspecific process. It can be assumed that there is a cause-and-effect relationship with local inflammation over a long period.
Long-term trauma can be identified as the main causes:
- Mechanical injury;
- Chemical injury;
- Physical injury;
- Operating trauma.
The development of the process against the background of a form of chronic trauma to the mucous membrane occurs due to:
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Infection with papilloma virus, caries;
- Generalized process of infection;
- Decreased immunity;
- Metabolic diseases.
Hereditary predisposition to degenerative processes also initiates the development of the process of keratinization disorders.
Symptoms
The first signs of the disease often go unnoticed because they do not cause any pain or discomfort in the patient. Nevertheless, a specialist will be able to determine the onset of leukoplakia by the appearance of the mucous membrane, lips and the area where the teeth meet.
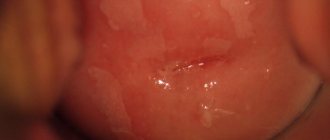
The first sign of the disease is the appearance of a keratinized gray area, which can appear on the palate (in smokers), in the corners of the mouth, on the inside of the cheek, etc. An easily removable white plaque forms in this area, but after a few days the formation makes itself felt again . The patient may feel tightness in the mouth, but, as practice shows, most people simply do not pay attention to this.
Plaques with a diameter of no more than 4 centimeters are formed. They may appear:
- on the inner surface of the cheeks;
- on the tongue (on the back or sides);
- in the sky;
- on the gums;
- in the corners of the mouth.
The process of plaque formation takes up to one month. At the first stage, the area of the future formation seems slightly swollen; when you feel it with your fingers, the compaction is not felt. However, over time, another symptom of oral leukoplakia appears - the mucous membrane at the site of the swelling loses its original shine and becomes rough, which is noticeable when touched.
There is no pain in this case: only sometimes a feeling of dryness at the site of the outbreak is possible.
Gradually, the color of the spots changes from gray to bright white. The spots in most cases have clear boundaries. Their increase is possible when the disease enters its second stage, called verrucous.
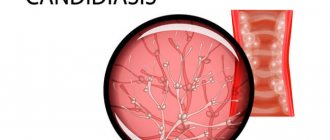
The disease often causes candidiasis and malignant cancers. In an advanced state, leukoplakia is very difficult to treat: the affected areas become even more keratinized, ulcers can form, and the infection gradually spreads to other areas of the mouth.
How to treat hairy leukoplakia
Before starting treatment, you need to conduct a number of studies. The patient is referred to a therapist at the clinic. There, the doctor can prescribe laboratory tests: biochemical blood test, testing for sexually transmitted diseases, etc.
If a person is diagnosed with HIV infection, antiretroviral therapy is administered. With long-term use of drugs, the patient’s well-being improves, and the disease in the mouth goes away.
The dental clinic provides oral examinations, dental diagnostics, and professional hygiene. If sharp edges of fillings or failed prostheses are detected, they are replaced. Treatment of caries and its complications is carried out. Recommendations are given for home dental care: personal hygiene products (brushes, pastes, dental floss, rinses) are selected.
Keratolytic drugs are suitable for local treatment. In advanced cases, they resort to surgical manipulations: excision of the affected areas with a laser.
Kinds
- The most common is simple or, as it is also called, flat leukoplakia . It is usually discovered by chance during an examination by a dentist, since the patient does not experience any subjective sensations. A burning sensation occurs extremely rarely, and the appearance of the mucous membrane may change. If the disease affects the tongue, loss of taste may occur.
- Hairy leukoplakia of the tongue resembles stomatitis. The shape of the spot that appears, as well as its size, can be different, the color - from pale gray to white. The surface of the mucous membrane at the site of the lesion becomes slightly rough, which can be felt to the touch. On the cheeks it appears as solid or broken lines. It can also be found on the lips, where it looks like thin paper pasted on.
- Verrucous leukoplakia is the second stage of the development of the disease. The keratinization thickens, the affected area seems to rise above the nearby tissues. When you touch it with your fingers, you feel a compaction.
- Erosive form . Untimely diagnosis of the two previous stages of the disease leads to a worsening of the situation - the person feels pain when exposed to any irritants, erosions or ulcers are visible in the mouth.
- Soft leukoplakia is a type of cancer. Its distinctive feature is peeling of tissue in the area of the lesion. To clarify the diagnosis, a histological method of studying cells is required.
- Tappeiner's leukoplakia . This form of the disease affects people who abuse smoking. According to studies, daily smoking 10 cigarettes a day increases the chance of developing the disease by 50 times (as the number of cigarettes increases, the risk also increases)
The disease begins with the formation of lesions on the roof of the mouth (sometimes they appear on the gums). The mucous membrane changes its color to a pronounced gray or bluish, which is noticeable to the naked eye, folds appear on it. Reddish nodules may begin to appear, which is accompanied by infectious inflammation of the oral cavity (caused by the accumulation of salivary gland secretions in the tissues).
Chemical coagulation
For leukoplakia of the tongue, more gentle therapy should be chosen than for lesions of the cheeks or lips, since the soft tissues of the tongue are much easier to damage and take longer to heal. In such cases, the affected area is exposed to a special chemical composition . It does not affect healthy cells, but has a detrimental effect on atypical ones, which leads to their death and the gradual restoration of healthy epithelial cells.
This method also has a significant drawback: the chemical composition kills not only the affected cells, but also beneficial bacteria, as a result of which candidiasis can begin after or even during treatment. To combat this complication, the doctor usually prescribes concurrent use of antifungal drugs.
Diagnosis of oral leukoplakia
Treatment of any disease begins with diagnosis: leukoplakia is no exception in this regard.
During the examination, the doctor interviews the patient to determine the factors contributing to the development of the disease. These include regular exposure to tobacco smoke, working in hazardous conditions, recent dental surgery, etc.
Next, laboratory tests are prescribed. The following procedures can be carried out:
- tissue sampling (biopsy). Accompanied by anesthesia;
- examination of the collected material under a microscope. The method allows you to determine the presence or absence of cancer cells in the formation;
- a smear of the mucous membrane is taken;
- A Schiller test is done (the mucous membrane is stained with a solution consisting of water and iodine - foci of leukoplakia are not stained);
- blood is taken for analysis (an increase in ESR may indicate the presence of malignant neoplasms).
In addition, the doctor may additionally prescribe a urine test, conduct a biochemical blood test and request the result of fluorography. You may need to consult an oncologist (if cancer is suspected), a therapist (to rule out infectious diseases) and a dermatologist (to look for other foci of disease).
Electrocoagulation
Treatment using electrocoagulation is one of the cheapest. However, today few doctors recommend this traumatic procedure. The fact is that during electrosurgery the surrounding healthy tissues are also damaged, healing occurs very slowly and there remains a risk of recurrence of the disease and its further spread.
For example, leukoplakia of the oral mucosa can develop into a lesion of the larynx if the affected areas were not completely cauterized. And since leukoplakia of the throat is much more dangerous than damage to the oral mucosa, it is better to choose treatment that guarantees a 100% recovery result.
Leukoplakia of the oral cavity: treatment with medications
Treatment involves the complete elimination of irritating factors that led to the development of the disease:
- to give up smoking;
- grinding down sharp edges of teeth;
- sanitation of the oral cavity;
- replacement of fillings;
- use of products to protect the surface of the lips.
Additionally, a course of vitamin A is prescribed, lasting at least a month, which inhibits the process of tissue keratinization.
If the measures taken do not cause complete disappearance of the manifestations of the disease, surgical intervention is allowed: the lesion is excised, depending on the degree of development of the disease, cryodestruction or electrocoagulation is used.
Ulcers deserve special attention, as they can develop into cancerous tumors. For their treatment, drugs are prescribed that enhance the process of tissue regeneration and epithelization. If there is no positive dynamics, surgical intervention cannot be avoided.
A person with leukoplakia must constantly visit the dentist for examination to prevent malignant degeneration of the cells.
In addition to quitting smoking, the patient’s diet is adjusted: during treatment, spicy and too salty foods are excluded from the diet, and it is recommended to eat more vegetables and fruits.
Drugs prescribed:
- products that restore the epithelium (the most effective was 30 percent tocopherol acetate, which is applied to damaged areas three times a day for 15 minutes, after which it is washed off with water);
- antiseptics (after each meal it is recommended to rinse your mouth with a solution of chlorhexidine at a concentration of 0.05%);
- analgesics (their use is justified in the presence of pain. Lidocaine, applied to the mucous membrane before meals, has worked well).
Under no circumstances should you use drugs that have an irritating effect, as otherwise this can lead to the formation of cancer cells.
If there is no improvement within a couple of weeks, surgery is prescribed: this can be either excision with a scalpel or the application of cold in the form of a liquid stream of nitrogen.
Treatment and prevention of the disease
If you find any manifestations that resemble leukoplakia, you should immediately consult a doctor! Since this disease is a type of precancerous condition, it is critically important to identify it in time and carry out a set of treatment measures. One of the important reasons for timely treatment of leukoplakia is the fact that more than thirty percent of cancer patients diagnosed with squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue and oral mucosa were previously diagnosed with oral leukoplakia. Often, as a result of histological analysis of leukoplakic plaques, it turns out that the patient has cancer.
Treatment of leukoplakia must be comprehensive. The dentist must clean the oral cavity (sanitation), as well as identify and eliminate traumatic factors - fragments of teeth, uneven edges of fillings and crowns. The patient, in turn, must be aware of the importance of giving up alcohol and smoking in the early stages of treatment. Most likely, incorrectly installed dentures and fillings will be removed. It is also necessary to avoid spicy and solid foods.
The patient will have to undergo studies to identify possible somatic diseases that accompany leukoplakia in most cases. Thus, you should prepare for an appointment not only with a dentist, but also with an endocrinologist, therapist and, first of all, with an oncologist.
Oral leukoplakia: how to treat it at home
In addition to drug treatment, oral leukoplakia can be treated with traditional medicine.
There are many recipes, here are just the main ones:
- rinsing with herbs (infusions of oregano, chamomile, ginseng and other adaptogens that reduce the inflammatory process and increase the body’s resistance to harmful factors are suitable);
- regular consumption of nuts and tinctures based on them;
- rinsing with decoctions of calendula, St. John's wort, eucalyptus. Alternation works well - once the oral cavity is rinsed with a soda solution, after a couple of hours - with an infusion of herbs. This procedure should be repeated at least 5 times a day;
- lubricating the lesions with sea buckthorn and olives (the fruits must first be mashed in your hands so that the juice appears).
Timely detection of the disease and compliance with all doctor’s recommendations is the key to recovery in the shortest possible time and reducing the risk of complications. If you start treatment at the initial stage, you can reduce the likelihood of complications to almost zero.
Uterus and reproductive organs
The female reproductive system is represented by the mammary glands and pelvic organs.
The main function of these organs is procreation. The gonads produce regulatory substances that affect the development of the reproductive system and other organs. The most important structures are the ovaries, in which the maturation of female germ cells occurs. During ovulation, the reproductive cell leaves the ovarian follicle and enters the fallopian tube. The fusion of male and female reproductive cells in this organ leads to the formation of the rudiment of a new organism. The remaining stages of embryo development occur in the lumen of the uterus. The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located next to the rectum, vagina, ovaries and bladder. The uterine cavity is connected to the external environment through the cervical canal and the vaginal opening. The fallopian tubes allow the fertilized egg to migrate to the uterus. Attachment of the embryo to the inner layer (endometrium) of the organ is necessary for the formation of embryonic organs.
The main part of the cervix is the narrow cervical canal, which connects the vaginal opening to the uterine cavity. This anatomical structure is necessary for the transport of sperm into the fallopian tubes. The mucous membrane of the cervical canal contains a large number of glands that secrete a special fluid. Gynecologists include the functions of cervical mucus as protection against pathogenic microorganisms and ensuring the transportation of sperm. Smooth muscle and elastic fibers of the cervix provide expansion of the cervical canal during childbirth.
Risk factors
In addition to the direct causes of cervical leukoplakia, gynecologists recognize the importance of certain forms of predisposition to the disease associated with heredity, individual history and a woman’s lifestyle.
Known risk factors:
- unprotected sexual intercourse;
- menstrual irregularities;
- drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking;
- radiation therapy of the pelvic organs;
- insufficient intake of vitamins and microelements from food;
- metabolic diseases;
- uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs;
- detection of leukoplakia or cervical carcinoma in a close relative.
Eliminating some of the risk factors listed above is an effective method of preventing the disease.
Forms of leukoplakia
Leukoplakia on the cervix is divided into simple and proliferative.
A simple form of cervical leukoplakia is a background change - hyperkeratosis or parakeratosis, manifested by thickening of the surface layer of the epithelium and its keratinization. Unlike the proliferative form, here the basal and parabasal cells do not change in any way. Simple leukoplakia of the cervix, unlike the proliferative form, does not have impaired differentiation of all cell layers and atypical elements.
The proliferative form (precancer) is also called cervical intraepithelial dysplasia.
Now, knowing the forms of leukoplakia, everyone knows how leukoplakia differs from dysplasia.
What is leukoplakia
Leukoplakia of the cervix is a pathological condition, which is presented in the form of keratinization and thickening of the upper layer of the epithelium of the cervix. The severity of epithelial thickening can vary: from hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis to acanthosis. When examined, leukoplakia of the cervical epithelium looks like whitish plaques that rise above the mucous membrane of the cervix, but if leukoplakia is in the cervical canal, it can only be diagnosed using colposcopy.
Cervical disease leukoplakia occurs in 5% of all cervical pathologies, and this number is women of reproductive age. Its danger is associated with a high degree of oncological alertness and malignant degeneration (according to statistics, every third woman diagnosed with leukoplakia and lack of treatment develops oncology).