Pleurisy is a pathology of the chest cavity in which the inflammatory process affects the pleura - the membranes that cover our lungs. The disease can be primary, but most often develops as a secondary complication of other infectious diseases of the lower respiratory tract, such as pneumonia.
It is always accompanied by a characteristic clinical picture - shortness of breath, chest pain, non-productive cough, fever. To eliminate the symptoms of pulmonary pleurisy and stop inflammation, intensive conservative treatment is required, and in rare cases even surgical.
Causes of pulmonary pleurisy
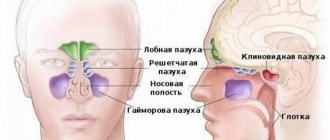
The pleura covering our lungs consists of two layers - outer and inner. Pleurisy is the presence of inflammation between these two layers covering the lungs.
All causes of the disease are divided into two large groups - infectious and non-infectious.
The number of infectious provoking factors includes:
- bacteria - staphylococci, pneumococci;
- fungi, including candida;
- viruses;
- parasitic microorganisms;
- tuberculosis;
- typhus;
- syphilis;
Non-infectious provoking factors:
- chest injuries or previous operations - in these conditions there is an increased risk of secondary infection and the development of effusion pleurisy.
- systemic vasculitis, rheumatism;
- pancreatitis;
- tumors in the lower respiratory tract, including metastases;
- heart disease, such as heart attack;
The significant difference between these two conditions is that in non-inflammatory processes, for example, in cancer, systemic diseases and heart pathology, there is a violation of the permeability of lymphatic and blood vessels, which initiates the release of fluid from them and the start of inflammation.
Infectious pleurisy of the lungs in adults is associated with infection on the pleura, for example, with prolonged pneumonia, lung abscess and other infectious diseases of the lower respiratory tract.
Why does pleurisy occur?
Provocateurs of the disease are inflammatory processes in the body and infections. Inflammatory
pleurisy is caused by:
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- arteritis;
- rheumatism;
- Libman-Sachs disease;
- scleroderma;
- pulmonary embolism;
- pulmonary edema or infarction;
- metastases in the pleural area;
- mesothelioma;
- lymphoma;
- leukemia;
- hemorrhagic diathesis;
- ovarian cancer;
- breast cancer;
- acute pancreatitis.
Infectious
sources of pleurisy:
- syphilis;
- tuberculosis;
- parasites;
- typhoid fever and other dangerous infections;
- microbes;
- staphylococcus, pneumococcus, E. coli, etc.;
- influenza, herpes and other viruses;
- candidiasis and other fungal infections;
- penetration of microbes into open wounds.
Classification
Depending on the nature of the disease, two groups are also distinguished.
- Dry (fibrinous) type. Fibrin deposits form on the surface of the pleura, which stick together the sheets and form adhesions.
- Exudative. During the inflammatory process, effusion, liquid with purulent or hemorrhagic contents, forms between the layers of the pleura.
Symptoms of pulmonary pleurisy in adults: fibrinous form
Dry pulmonary pleurisy is a complication of other pathologies. Its symptoms can completely overlap the clinical picture of the primary disease, which makes diagnosis difficult.
Main signs of pathology:
- stabbing pain in the chest;
- dry cough that gets worse with deep breaths;
- shallow breathing;
- temperature rise to low-grade levels;
- increased sweating at night.
With the fibrinous form of the pathology, the patient is forced to give up activity and spare himself. At rest, lying on the affected side, the pain is less disturbing, since the chest is fixed in one position.
Symptoms and signs of pulmonary pleurisy in adults: exudative form
The accumulation of exudate in the cavities of the organ provokes pronounced symptoms. Main features:
- dull pain on the affected side;
- nonproductive reflex cough;
- breathing noise;
- heaviness in the chest;
- shortness of breath during exercise and at rest;
- general weakness;
- temperature 38 degrees and above;
- loss of appetite;
- sweating
The more exudate accumulates in the cavities, the more pronounced the clinical picture. If you ignore the symptoms of pulmonary pleurisy and do not start treatment, especially in older people, the likelihood of complications is high.
Prevention
Prevention is necessary in order to protect yourself and your health from various complications arising from serious illnesses.
First, you need to protect yourself from tuberculosis as much as possible. To do this, you need to stop communicating with sick people in person, and also start taking immunomodulatory drugs. The same applies to protection from pneumonia, so as not to get pneumonia. To do this, you should not overcool, especially in the back area, or stay in a damp room for a long time. If necessary, it is better to change jobs or activities, but not to expose yourself to the risk of developing such a disease every time. The same applies to rheumatism: you should protect yourself from cold temperatures and dampness as much as possible. And then there is every chance of not getting pleurisy as a secondary disease. It is important to learn to dress according to the weather to avoid constant overheating, which threatens subsequent hypothermia of sweaty skin. It is worth avoiding places where there is a lot of smoking, where harmful chemicals are released, so that the respiratory organs are not subject to dangerous attacks. A complete, healthy diet, which contains all the vitamins and mineral nutrients, is also of great importance for a person and his well-being.
Prevention can be done by regular breathing exercises. It trains the lungs, expanding their volume, making them elastic and strong, resistant to various infectious agents. At the same time, there is protection against adhesions, which are impossible if the lungs fully contract and work at full strength. For personal peace of mind and prevention, it is worth undergoing fluorography at least once a year. It is imperative to immediately and effectively treat pulmonary diseases, respiratory diseases and not remain indifferent even to a common cold, which can develop into something more complex and dangerous.
Diagnosis of pathology
To clarify the diagnosis, a consultation with a pulmonologist is necessary. The specialist will assess the intensity of clinical manifestations and conduct a physical examination, during which the following will be determined:
- bulging of the spaces between the ribs;
- chest asymmetry;
- lag in respiratory movements on one side;
- dullness of percussion sound;
- weak, shallow breathing.
To clarify the extent of pleural damage, instrumental studies are required - chest X-ray, X-ray, ultrasound of the pleural cavity, pleural puncture. It is recommended to take a general and biochemical blood test.
Forecast
The prognosis for pleurisy is favorable, although it directly depends on the underlying disease. Inflammatory, infectious, post-traumatic pleurisy can be successfully cured and does not affect the quality of future life. Unless, during the rest of your life, pleural adhesions will be noted on radiographs.
The exception is dry tuberculous pleurisy, as a result of which fibrous deposits can calcify over time, forming the so-called armored pleurisy. The lung becomes encased in a “stone shell,” which interferes with its full functioning and leads to chronic respiratory failure.
To prevent the formation of adhesions that form after removal of fluid from the pleural cavity, after treatment, when the acute period subsides, the patient should undergo rehabilitation procedures - this is physiotherapy, manual and vibration massage, daily breathing exercises are required (according to Strelnikova, using a Frolov breathing simulator) .
Pleurisy of the lungs: treatment in adults
What is pulmonary pleurisy, how to treat the pathology - these issues are resolved with a pulmonologist during a face-to-face consultation. The tactics of therapy are selected individually and depend on the general condition of the patient, the presence or absence of contraindications, and provoking factors. For example, if pleurisy of the lungs develops against the background of pneumonia of bacterial origin, antibiotics will be prescribed.
In most cases, the pathology can be successfully corrected with timely conservative treatment of the underlying disease, but with “dry” pleurisy, the patient is additionally prescribed rest, tight bandaging of the chest, anti-inflammatory and hormonal therapy. Ozone therapy, blood laser therapy (ILBI and UVB), and magnetic therapy are used as additional measures. This approach allows you to improve blood circulation in the chest and quickly cope with the disease.
The tactics of helping patients with exudative pleurisy are fundamentally different from the treatment of “dry” pleurisy, depending on the nature of the fluid accumulating between the layers of the pleura and its volume, but always begins with invasive manipulation - pleural puncture and installation of drainage. Treatment in this case is carried out only in a hospital.
In one procedure, no more than 1-1.5 liters of liquid are removed. In case of purulent contents, active rinsing of the cavity with antiseptics and administration of antibiotics is recommended. To prevent the negative consequences of pulmonary pleurisy, breathing exercises, exercise therapy, and physical therapy are recommended.
If conservative treatment is ineffective, doctors resort to surgery - pleurectomy.
Characteristic signs
The disease is always accompanied by chest pain and difficulty breathing. This means that pleurisy has recognizable symptoms. In this case, pain during the development of a pathological condition begins suddenly.
When coughing and sudden movements, the acute pain intensifies. In most cases, it is localized on one side and radiates to the shoulder region. Shallow, slow breathing may improve the patient's condition. Pain decreases when fluid accumulates in the pleural cavity. This is explained by a decrease in friction between the inflamed surfaces of the pleura. But with a large amount of liquid, there is a risk of respiratory dysfunction.
Often, pulmonary pleurisy, the symptoms of which are always obvious, is accompanied by an increase in body temperature and a debilitating dry cough. If the disease is viral, headaches, general malaise and muscle pain are additionally noted.
Prognosis for pulmonary pleurisy
A small amount of exudate resolves on its own in 2-4 weeks. Pathology with the formation of purulent effusion requires more intensive and prolonged treatment. In its absence, the risk of complications increases - adhesions, pleurosclerosis, respiratory failure.
Patients who have had illnesses should undergo preventive examinations for 2-3 years after recovery. In order to prevent relapses, it is necessary to eliminate exposure to harmful factors, including toxic compounds and nicotine, avoid hypothermia, and eat a balanced diet.
Causes of pleural effusion
| Transudate | Exudate |
| Congestive heart failure Nephrotic syndrome Liver cirrhosis Pericardial diseases Myxedema | Tuberculosis Viral infections Fungal infections Rheumatoid arthritis Parasitic infections SLE Meigs syndrome Chylothorax Hemothorax Pleural mesothelioma Dressler's syndrome Metastatic lesions of the pleura Actinomycosis |
In most cases, pleurisy is a complication of an underlying disease, for example, congestive heart failure, nephrotic syndrome, liver cirrhosis, sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, viral, fungal infections, rheumatoid arthritis and many other various nosologies. The most important aspect of differential diagnosis is the division of pleural effusion into exudate or transudate, taking into account the concentration of protein, LDH and cellular components.
The Light criteria are considered generally accepted in the diagnosis of exudative pleurisy: 1) The ratio of protein in pleural effusion to protein in blood plasma is >0.5. 2) The ratio of LDH in pleural effusion to plasma LDH is >0.6. 3) LDH in the pleural effusion >2/3 of the upper limit of normal for plasma LDH.
Treatment in Kaliningrad
Cough, shortness of breath, high temperature may indicate dangerous respiratory diseases. One of them is pulmonary pleurisy: only a specialist can tell you what it is, what the symptoms are and how it is treated. Make an appointment with a pulmonologist in Kaliningrad.
Our Pulmonology Center offers:
- diagnosis of lung diseases based on laboratory parameters;
- help with any pathologies: treatment of COPD, asthma, bronchitis;
- rehabilitation after COVID-19;
- affordable prices for all services.
Make an appointment by calling 8 (4012) 971-961.
What types of cancer most often lead to pleurisy?
The prognosis of pleurisy in oncology depends on the organ affected by cancer. The highest survival rate has been established for malignant tumors of the breast and ovaries. The prognosis for pulmonary pleurisy in oncology is much worse. To determine the outcome, the LENT scale is used, which takes into account not only the condition, but also the patient’s functional capabilities.
Most often, pleurisy develops with cancer:
- lung (24-50% of patients);
- ovaries (up to 10%);
- breast (48%).
Less commonly, a complication occurs in the presence of a malignant process in the colon, stomach and pancreas - from 1 to 6% of cases. The prognosis and therapeutic options are determined by the prevalence and nature of the tumor process. The degree of sensitivity to drug therapy matters.
If a malignant tumor is sensitive to cytostatics, as in ovarian, breast and lung cancer, then with timely adoption of therapeutic measures it is possible to prevent relapses of exudation. If systemic therapy is ineffective, pleurodesis is performed to improve the prognosis.