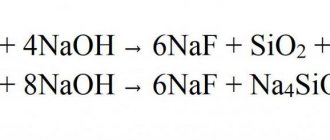Salts obtained from sodium hydroxide and phosphoric acid are collectively called sodium phosphates. This food supplement is of completely synthetic origin and is not found in nature in any form.
In food products it is most often used as an antioxidant and preservative, although it also has the properties of an emulsifier and stabilizer. In addition, the substance also acts as an acidity regulator, as it affects the establishment and maintenance of a certain level of acidic environment in the product. It also has a moisture-retaining effect.
Having encountered code E339 in the selected food, the buyer can determine for himself that the product has been treated with sodium phosphates and decide whether it is worth buying and consuming. According to international standards and regulations, the substance is classified as a low-hazard food additive.
Properties of sodium phosphate
Physical properties
| Property | Description |
| Appearance | White crystalline substance |
| Molar mass | 163.941 g/mol |
| Density | 2.536 g/cm3 |
| Melting temperature | 1340°C |
| Standard molar enthalpy of formation at 298K Δ G \Delta G ΔG °298, kJ/mol | -1922,8 |
| Standard molar Gibbs energy of formation at 298 K Δ\Delta Δ kJ/mol | -1819 |
| Standard molar entropy at 298 K S°298, J/(mol•K) | 224,7 |
| Solubility in water, 100 g | at 0°C - 5.4 at 25°C - 14.5 at 100°C - 94.6 |
Chemical properties
In aqueous solutions it hydrolyzes at the anion:
Na3P04 + H2O = Na2HP04 + Na0H.
The solution is alkaline.
When interacting with acids, it forms acid salts:
Na3P04 + HСl = Na2HP04 + NaCl,
Na3P04 + H2SO4 = NaH2P04 + Na2SO4.
Enters into exchange reactions to form insoluble phosphates:
2Na3P04 + 3CaCl2 = 6NaCl + 2Ca3(P04)2↓,
Na3P04 + AlCl3 = 3NaCl + AlP04↓,
Na3P04 + 3AgNO3 = 6NaCl + Ag3P04↓.
The latter reaction is a qualitative reaction to soluble alkali metal and ammonium phosphates. When a solution of silver nitrate AgNO3 is added to their solution, a yellow precipitate of silver phosphate Ag3P04 precipitates. And sodium can be detected by coloring the flame yellow.
Properties
| Index | Standard values |
| Color | white |
| Compound | phosphoric acid salt |
| Appearance | powder, granules or crystalline substance |
| Smell | absent |
| Solubility | good in water; do not dissolve in ethanol |
| Main substance content | from 92 to 98% |
| Taste | pleasantly sour |
| Density | not constant |
| Other | the anhydrous form is hygroscopic; heat resistant |
Preparation of a chemical compound
Laboratory methods of obtaining
Sodium phosphate is prepared by reacting phosphoric acid with sodium hydroxide or carbonate:
H3PO4 + 3NaOH = Na3PO4 + 3H2O; 2H3PO4 + 3Na2CO3 =2Na3PO4 + 3H2O + 3CO2↑.
Production of sodium phosphate in industry
In industry, sodium phosphate is produced in two stages.
First, by reacting soda ash Na2CO3 with phosphoric acid H3PO4, sodium hydrogen phosphate Na2HP04 is obtained:
Н3Р04 + Na2C03 = Na2HP04 + С02↑+ Н20,
and then by reacting sodium hydroxide NaOH with the resulting sodium hydrogen phosphate Na2HP04, sodium phosphate Na3PO4 is obtained:
Na2HP04 + Na0H = Na3P04 + H20.
After cooling the neutralized solutions to 30°C, sodium phosphate crystallizes in the form of Na3PO4·12H2O. It melts at 70°C. To obtain anhydrous sodium phosphate, the crystalline hydrate is calcined for 2 hours at a temperature of 120°C, and then for 30 minutes at a temperature of 800°C.
Main manufacturers
Food grade sodium phosphates produce:
- Group (head office in St. Petersburg);
- Voskresensk phosphoric acid plant;
- Kazphosphate (Kazakhstan);
- CHEMICO GROUP (China).
Scientists around the world are demanding a ban on the use of phosphoric acid and its salts in washing powders: additives destroy cell membranes, change the composition of the blood, and provoke serious diseases.
But for some reason, no one raised the issue of banning sodium phosphates in food products, citing the fact that the substance is added in small quantities.
The consumer is forced to rely on the integrity of the manufacturers.
Application
Sodium phosphate is used in everyday life as a cleaning agent, as it perfectly removes grease. Due to this property, it is also included in detergents. In addition, sodium phosphate softens water by converting hardness salts into insoluble phosphates:
3Ca(HCO3)2 + 2Na3P04 = 6NaHCO3 + Ca3(P04)2↓, 3Mg(HCO3)2 + 2Na3P04 = 6NaHCO3 + Mg3(P04)2↓. It is also used in the glass industry to produce optical glasses.
In construction, sodium phosphate is used to strengthen concrete. Its addition also increases the moisture resistance of concrete, as it becomes less porous.
In medicine, sodium phosphate is occasionally used as a laxative and heartburn remedy.
In the food industry it is known as food additive E339(iii). Sodium phosphate is used as an emulsifier, stabilizer, and moisture-retaining agent. It is added to mayonnaises and ketchups, processed cheeses and baked goods, although hydrogen phosphate (food additive E339(i)) and sodium dihydrogen phosphate (food additive E339(iii)) are more often used. Sodium phosphate is used to treat chicken legs, meat and fish to retain water and maintain weight.
It belongs to low-hazard substances (hazard class 4), but when overdosed in food products it leads to digestive disorders, and in children it often causes agitation and hyperactivity.
The product's name
The main name of the substance is sodium phosphates E 339 ( GOST R 52823-2007 ). The digital index (another spelling E–339) indicates the European code assigned to the food additive.
International synonym: Sodium phosphates.
There are names:
- food grade monosodium phosphates;
- sodium orthophosphates;
- sodium phosphate;
- Phosphate de sodium (French name);
- Mononatrium-phosphat, Natriumdihydrophosphat (German synonyms).
What can be replaced?
Food additive E339 can be replaced by :
- E452 - polyphosphates, food additive of the stabilizer category, are inhibitors;
- E450 - pyrophosphates, a food additive of the stabilizer category, excessive consumption threatens to deteriorate the absorption of calcium;
- E343 - magnesium orthophosphates, food additive of the antioxidant category, available both natural and synthesized;
- E340 - orthophosphates, food additive of the antioxidant category;
- E333 - calcium citrates, a food additive in the antioxidant category, are both natural and synthesized additives.
If there is no food additive E339 on the product label, it means that one of the substitutes listed above will be present.
Effect on the body
No harmful effects on the body have been officially proven , nor has the opposite been proven. Therefore, scientists decided to consider the food additive as a low-hazard substance. Specific consumption standards that are safe for humans have also not been established.
Benefit
Benefits of dietary supplement E339:
- used as a laxative;
- added to dietary supplements and sports drinks.
Harm
Harm of food additive E339:
- interferes with calcium absorption;
- flushes water from the body, thereby harming the gastrointestinal tract;
- allergic reactions, severe rash, hyperactivity, aggressiveness are possible.
The dietary supplement is not recommended for use by children under 10 years of age.
Acceptable daily intake
By default, the daily norm is 70 g of supplements per 1 kg of human weight.
Chemical properties
- With hot water it forms various acidic salts:
NaPO3 →H2O,100oC Na3H2P3O10, Na2H2P2O7, NaH2PO4
- With a hot alkaline solution forms different sodium phosphates:
NaPO3 →NaOH,40−100oC Na3P3O9, Na3PO4, Na5P3O10, Na4P2O7, Na6P4O13
- Enters into metabolic reactions:
NaPO3 + AgNO3 → AgPO3↓ + NaNO3
| Sodium compounds | |
| |
How to identify an additive in a product?
Signs of an excessive dosage of sodium phosphates are a metallic or astringent taste and a “soapy” cut on the product (when cut, a feeling of stickiness and excessive moisture).
Based on its appearance, the presence of the food additive E339 in the product cannot be determined by eye. But the peculiarity of E339 is to protect food products from burning and preserve their natural color during heat treatment.
Can be determined by the inscription on the label. Possible names of food additives when labeling products can be:
- sodium salts of orthophosphoric acid;
- trisodium orthophosphate;
- monosubstituted sodium orthophosphate;
- disubstituted sodium orthophosphate;
- Monosodium Orthophosphate (II);
- Disodium Orthophosphate (iii);
- Trisodium Orthophosphate;
- Sodium Orthophosphates;
- sodium tripolyphosphate;
- Sodium phosphates;
- Sodium phosphates;
- Sodium phosphate;
- E 339, E-339, E339.