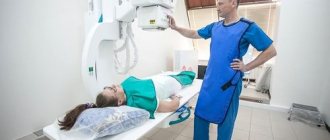
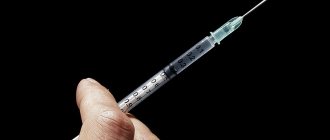
A complex drug based on calcium salt helps restore metabolism and prevent the development of many pathologies. Affordable and effective, it restores the normal level of one of the main macroelements in the body, relieving a variety of painful symptoms.
Composition and dosage form
Calcium chloride (CaCl2) is formed during the production of baking soda. The substance is used not only in medicine, but also in cooking, cosmetology, and the chemical industry. Without it, it is impossible to produce healthy calcined cottage cheese and hard cheeses.
The pharmaceutical form of calcium chloride is a water-based injection solution. Available in transparent glass ampoules of 5 or 10 ml. The cardboard packaging of the drug contains 10 such ampoules. The concentration of the medicinal compound in 1 ml of solution is 100 mg.
Use of the substance in the food industry
On the territory of the Russian Federation, the use of this substance is not prohibited, but is strictly controlled by law. The European Union also considers calcium chloride a fairly safe product and it is legally used in the medical and food industries.
As a food additive, calcium chloride is included in a wide variety of food products to stabilize some of their properties, and also as an emulsifier and preservative. Most often it can be found in dairy and fermented milk products, especially in dry cream and pasteurized milk. But it is also found in cottage cheese and various types of cheeses.
Other products in the manufacture of which calcium chloride is used include: caviar, canned vegetables and fruits, various jellies and marmalades, condensed milk, dry mashed potatoes, chocolate and beer.
This substance is used in the food industry for the following processes:
- When pasteurizing cream, adding calcium chloride to it significantly reduces the acidity, which facilitates the process of making butter.
- It is indispensable as a thickening component in the production of milk powder. The fact is that calcium ions help better adhesion of proteins to each other. This substance allows you to normalize the coagulation process of dairy products during pasteurization and improves the formation of the curd. Adding it to milk increases its final yield and leads to a significant improvement in quality.
- An additive marked E509 acts as a stabilizer in the production of chocolate, preventing it from hardening.
- When making cottage cheese, calcium chloride helps milk coagulate better.
- When making marmalade, calcium chloride also acts as a stabilizer.
- This substance prevents the softening of vegetables and fruits during the preservation process, and also normalizes the taste, bringing it to the desired salting level.
- In the production of beer and soft drinks, this product is used to reduce water hardness and improve its performance, as well as to regulate acidity.
How does calcium chloride work?
The product exhibits anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, detoxifying properties, stabilizes the blood formula, helps strengthen vascular walls, and reduces their permeability. Calcium in the drug ensures normal functioning of the muscles and heart, regulates the conduction of nerve impulses, bone tissue synthesis, increases resistance to infections, participates in the absorption of vitamins and minerals, and maintains the necessary balance of electrolytes. Calcium chloride also normalizes the condition of the kidneys, somewhat increases diuresis, relieves and prevents swelling, helps restore the functioning of the adrenal glands, and promotes the release of adrenaline.
After use, about half the dose of the drug binds to blood proteins. Part of it is absorbed by the body. The transformation of calcium chloride occurs in the liver, the excess is excreted in the intestinal contents and urine. The intensity of excretion and absorption of the drug depends on age-related changes, dietary habits, the presence of calcium-containing foods in the diet, and hormonal status.
Preparation of a chemical compound
Calcium chloride does not occur in free form in nature. It is synthesized chemically.
Natural Sources
In nature, calcium chloride occurs exclusively in the form of crystalline hydrate with the chemical formula CaCl2 6H2O. Under the influence of high temperatures when heated above 29.8°C, crystalline hydrate loses water molecules.
Artificial sources of obtaining
In laboratory conditions, calcium chloride is synthesized by reacting calcium hydroxide with ammonium chloride.
2NH4Cl + Ca(OH)2 → 2NH3↑ + CaCl2 + 2H2O
The chemical reaction discussed underlies the industrial production of soda. The second reaction product is ammonia, and water is released as a by-product.
An alternative method is to treat calcium-containing raw materials (crystalline calcium carbonate) with hydrochloric acid.
CaCO3 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + CO2↑ + H2O
Indications for use
It is recommended to use a 10% solution of the drug:
- with calcium deficiency caused by malnutrition, systemic diseases, endocrine disorders, intestinal disorders;
- when there is a need for increased doses of calcium: age-related changes, periods of active growth, postpartum complications, general physical exhaustion;
- for bleeding of various origins;
- with nutritional edema;
- for hepatitis;
- with rickets, osteomalacia;
- for tuberculosis;
- for kidney inflammation;
- for allergic reactions;
- in case of intoxication with fluorine, magnesium, oxalic acid preparations.
During childbirth, calcium chloride is necessary to prevent eclampsia and to stimulate contractile activity of the uterus.
Nosological classification (ICD-10)
- D69.0 Allergic purpura
- E20 Hypoparathyroidism
- E83.5 Disorders of calcium metabolism
- K73 Chronic hepatitis, not elsewhere classified
- L29 Itching
- L30.9 Dermatitis, unspecified
- L40 Psoriasis
- L50 Urticaria
- O15 Eclampsia
- O62.2 Other types of labor weakness
- T56 Toxic effects of metals
- T66 Unspecified radiation effects
- T78.3 Angioedema
- T78.4 Allergy, unspecified
When is calcium chloride contraindicated?
The injection drug should not be used in cases of increased blood clotting, thrombosis, vascular atherosclerosis, or in conditions of hypercalcemia. Pregnancy and breastfeeding are also contraindications. An exception may be an individual indication when the benefit to the mother outweighs the risks to the child.
It is necessary to refuse therapy if you have an allergic reaction. Its possible signs: increased swelling, severe skin itching following administration, bronchospasm, suffocation.
Links[edit]
- ^ abcdefghi Leede, David R., ed. (2009). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics
(90th ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4200-9084-0. - "Calcium Chloride (Anhydrous)". ICSC
. International Program on Chemical Safety and the European Commission. - Seidell, Atherton; Linke, William F. (1919). Solubility of inorganic and organic compounds (2nd ed.). New York: D. Van Nostrand Company. paragraph 196.
- ^ abcdef Anatolyevich, Kiper Ruslan. "Properties of the substance: calcium chloride". chemister.ru
. Retrieved July 7, 2014. - ^ B s d e e Pradyot, Patnaika (2019). Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals
. McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. page 162. ISBN. 978-0-07-049439-8. - ^ abcd Müller, Ulrich (2006). Inorganic structural chemistry. wiley.com
(2nd ed.). England: John Wiley & Sons Ltd. p. 33. ISBN 978-0-470-01864-4. - ^ abc Sigma-Aldrich Co. , calcium chloride . Retrieved July 7, 2014.
- Donald E. Garrett (2004). Handbook of Lithium and Natural Calcium Chloride. item 379. ISBN 978-0080472904. Retrieved August 29, 2018. Its oral toxicity is confirmed by a test on rats: oral LD50 (rat) is 1.0–1.4 g/kg (lethal dose for half of the experimental animals, in this case rats...)
- "Safety Data Sheet for Calcium Chloride". fishersci.ca
. Fisher Scientific. Retrieved July 7, 2014. - ^ ab Robert Kemp, Suzanne E. Keegan "Calcium Chloride" in Ullman Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2000, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. DOI: 10.1002/14356007.a04_547
- "Binary phase diagram: calcium chloride - water system". Aqueous solutions of Aps. October 2021. Retrieved April 20, 2021.
- "humantouchofchemistry.com Keeping Things Dry". Archived from the original on October 26, 2014. Retrieved October 23, 2014.
- “Dust: don’t eat! Control it!” . Journal of Highway Facilities and Engineering
. US Roads (TranSafety Inc.). June 1, 1998 Archived from the original on October 29, 2007. Retrieved August 9, 2006. - Profile of the Initial Assessment of Calcium Chloride SIDS, UNEP Publications, SIAM 15, Boston, 22–25 October 2002, pp. 13–14.
- 21 CFR § 184.1193
- 7 CFR § 205.602
- "Apple caviar technique". StarChefs Studio
. StarChefs.com. April 2004. Retrieved August 9, 2006. - "Cork Stain and the Bitter Pit of Apples," Richard K. Fant and Michael A. Ellis, Ohioline.osu.edu/factsheet/plpath-fru-01
- "CPG 7117.02". FDA Compliance Articles
. US Food and Drug Administration. March 1995. Retrieved December 3, 2007. - "Accelerating the setting time of concrete". Federal Highway Administration. June 1, 1999. Retrieved January 16, 2007.
- National Research Council (USA). Construction Research Institute (1962). Adhesives in construction: selection and application; Pressure sensitive tapes
. National Academy of Sciences - National Research Council. pp. 24–5. - Koger, November 1977, "Calcium Chloride, a Practical Necrotic Agent", Journal of the American Association of Beef Practitioners (USA)
, (November 1977), v. 12, pp. 118–119 - Yana, K.; Samantha, P. C. (2011). "Clinical evaluation of non-surgical sterilization of male cats by a single intratesticular injection of calcium chloride". BMC Vet. Res
.
7
: 39. DOI: 10.1186/1746-6148-7-39. PMC 3152893. PMID 21774835. - Smith, Michael; Simpson, Cam. "Addicts fight new war on drugs over Texas company's base chemical". Bloomberg
. Retrieved October 26, 2021. - "Product Safety Assessment (PSA): Calcium Chloride". Dow Chemical Company. May 2, 2006 Archived from the original on September 17, 2009. Retrieved July 22, 2008.
- "Possible side effects of calcium chloride".
- Profile of the Initial Assessment of Calcium Chloride SIDS, UNEP Publications, SIAM 15, Boston, 22–25 October 2002, p. 11.
- https://www.mindat.org/min-3673.html
- https://www.mindat.org/min-251.html
- https://www.ima-mineralogy.org/Minlist.htm
- https://www.mindat.org/min-43592.html
- https://www.ima-mineralogy.org/Minlist.htm
- https://www.mindat.org/min-1020.html
- https://www.mindat.org/min-3865.html
- https://www.ima-mineralogy.org/Minlist.htm
- https://www.mindat.org/min-3446.html
- https://www.ima-mineralogy.org/Minlist.htm
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of elements
(2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
Side effects
When an injection is administered, the following body reactions are likely:
- burning pain along the veins;
- redness of the skin of the face, a feeling of heat in the mouth, face, neck and throughout the body;
- decreased heart rate, arrhythmia;
- pain in the stomach, abdominal cavity;
- nausea, vomiting.
Within 20–30 minutes after the medicine enters the bloodstream, the discomfort weakens and passes. If the injection is administered too quickly, cardiac problems may occur.
Lack of calcium
Insufficient calcium in the body leads to health problems. This substance affects the functioning of basic systems. Calcium ions improve performance:
- of cardio-vascular system;
- central and peripheral nervous system;
- circulatory systems;
- promote muscle contraction.
If the plasma contains an insufficient amount of calcium, this indicates pathological processes occurring in the body. An insufficient amount of calcium leads to severe tetany (tension, numbness, cramp). To cope with the malaise, you need to drink a medicine containing calcium.
In the blood, calcium is present in ionized form. When administered artificially, it is deposited in bone tissue. Excess substances are excreted by the kidneys or through the intestines.
How to use calcium chloride according to instructions
In most cases, calcium chloride injections are prescribed by infusion: through droppers, at a rate of no more than 6 drops per minute. This way the drug causes fewer painful side effects. Jet injection is practiced less frequently. Intravenous injections are given slowly: administering the dose over 3–5 minutes. Subcutaneous and intramuscular injections of the drug are prohibited. The product does not dissolve in soft tissues, forming compactions and foci of necrosis.
The daily dose depends on the age and physical condition of the patients:
- For adults, the drug is administered in a volume of 5–10 ml per day;
- Children are dosed from 0.5 to 4–5 ml.
It is allowed to divide the daily dose into several parts and administer them at equal time intervals. In emergency cases, it is allowed to take calcium solution orally: consume the contents of the ampoules orally:
- for children and adolescents, the maximum dose is about 5 ml of the drug at a concentration of 10%;
- Adults can drink about 10–15 ml of the product per day.
The exact scheme, as well as the duration of the course of therapy, is determined individually.
Contraindications
Not everyone can use calcium chloride; there are contraindications for use. It is not prescribed if there is a diagnosis such as atherosclerosis. Also, you should not take this remedy if the calcium content in the body is exceeded. If a person has a tendency to form blood clots, then calcium chloride is contraindicated for use.
Concomitant use with the following substances is prohibited:
- phosphates;
- salicylates;
- salts of lead and silver;
- carbonates;
- sulfates.
During the therapeutic course, it should be taken into account that the medicine reduces the absorption of tetracyclines and drugs containing iron. Do not take it with digoxin. The medicine is not prescribed to children under one year of age.
Calcium chloride in cosmetics
The drug solution is popular as part of masks for deep cleansing of facial skin. You can use them at home:
- Apply the contents of the ampoule with a cotton swab to clean skin, repeat the procedure several times after each layer has dried;
- wash your hands with solid, fragrance-free toilet soap and apply foam to your face;
- rub the soap over the skin until characteristic pellets appear under the palms;
- Continue massaging until the entire mass is peeled off the skin.
This “rolling” removes dead particles of the epidermis, dissolves remaining sebum, softens and eliminates various imperfections, and narrows pores. Regular use normalizes sebum secretion and eliminates inflammatory processes. The mask is especially useful for dull, oily and problematic skin.
Application in other areas
Due to its beneficial qualities, calcium chloride is widely used in various areas of life. This is a popular product in the medical and pharmaceutical industries; it is often included in various medications aimed at improving blood clotting, as well as antihistamines.
Food emulsifier E509 is used for the following processes:
- production of latex goods and rubber products;
- for the production of lactic acid;
- in the production of glue;
- for the production of rubber products;
- when laying asphalt, improving its adhesion;
- used as an anti-dust and de-icing agent;
- in preparation for gas transportation;
- in the production of calcium metal;
- when the dew point decreases and gas drying occurs at gas distribution stations and autogas filling compressor units.