The acidity regulator and preservative “sodium acetates” received the code designation E262 in the industry. It is an inexpensive, safe additive for humans and the environment, and is used not only in food production, but has a much wider range of applications. Housewives at home can independently obtain this substance by preparing baking dough - it is obtained from soda slaked with vinegar. If the resulting solution is evaporated and crystallized, you get a kind of homemade analogue of the food preservative E262. For production purposes, it is mined by other methods.
Information sources:
Alf. index: 1-9 AZ
More on the topic:
- SODIUM ACETATE - chemical encyclopedia
- Sodium acetate - medications
Characteristics of chemical properties and method of obtaining additive E262
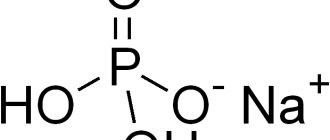
In terms of their structure, sodium acetates are salts of acetic acid, since it is from this raw material that it is obtained: sodium carbonates or hydroxides are reacted with acid.
Oddly enough, part of the production of the substance is associated with the distillation and processing of wood. Content:
- Characteristics of chemical properties and method of obtaining additive E262
- Areas of application of the substance by humans
- Requirements for packaging of additive E262
- Impact on human health
The additive is in the form of a crystalline powder that has a faint vinegar smell. May have a whitish, light yellow or brown tint. The substance is highly soluble in water, less soluble in alcohols and ether. In addition, it is not subject to combustion.
The main properties of sodium acetates, for which industrialists value it so much, are the ability to regulate the acidity level of a chemical environment, preserve and stabilize substances. The additive helps preserve the shape and texture of products, their taste and aroma characteristics, and can improve the consistency of raw materials.
Few supplements can boast that they are found in nature. Just sodium acetates can: they exist as an element of animal and plant cells, as a component of acids in fruits, and are present in fermented milk products as a result of bacterial fermentation.
Links[edit]
- "Sodium acetate". International Chemical Safety Cards
. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. 2018-09-18. - ^ abc "sodium acetate trihydrate". chemister.ru
. - Seidell, Atherton; Linke, William F. (1952). Solubility of inorganic and organic compounds
. Van Nostrand. - ^ abcdef "sodium acetate". chemister.ru
. - ^ abc Sigma-Aldrich Co. , Sodium acetate. Retrieved June 7, 2014.
- ^ ab Acetic acid, sodium salt in Linstrom, Peter J.; Mallard, William G. (ed.); NIST Chemistry Webbook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69
, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg (MD), https://webbook.nist.gov (retrieved May 25, 2014) - Acetic acid, sodium salt, hydrate (1:1:3) in Linstrom, Peter J.; Mallard, William G. (ed.); NIST Chemistry Webbook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69
, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg (MD), https://webbook.nist.gov (retrieved May 25, 2014) - Clayden, Jonathan; Greaves, Nick; Warren, Stuart; Waters, Peter (2001). Organic chemistry
(1st ed.). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-850346-0. - "Potato chips increase concrete durability". Science Daily
. August 8, 2007 - AG, Jungbunzlauer Suisse. "Sodium Diacetate - Jungbunzlauer". www.jungbunzlauer.com
. - “Dietary Supplement” Sodium Acetate (Anhydrous) “| Products" . Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation
. Retrieved September 16, 2021. - Mohammadzadeh-Agdash, Hossein; Sohrabi, Youssef; Mohammadi, Ali; Shanehbandi, Dariush; Dehgan, Parvin; Ezzati Najad Dolatabadi, Jafar (August 15, 2021). "Evaluating the Safety of the Food Additives Sodium Acetate, Sodium Diacetate, and Potassium Sorbate". Food chemistry
.
257
: 211–215. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.03.020. ISSN 0308-8146. PMID 29622200. Retrieved September 16, 2021. - ^ a b Ibrahim Dincer and Mark A. Rosen. Thermal Energy Storage: Systems and Applications, page 155
- Courty JM, Kierlik E, Les chaufferettes chimiques, Pour la Science, December 2008, pp. 108-110
- "Crystallization of supersaturated sodium acetate". Journal of Chemical Education. 2015-07-19.
- “How do sodium acetate heating pads work?” . HowStuffWorks. April 2000. Retrieved September 3, 2007.
Reactions[edit]
Sodium acetate can be used to form an ester with an alkyl halide such as bromoethane:
CH 3 COONa + BrCH 2 CH 3 → CH 3 COOCH 2 CH 3 + NaBr
Sodium acetate undergoes decarboxylation to form methane (CH 4 ) under forced conditions (pyrolysis in the presence of sodium hydroxide):
CH 3 COONa + NaOH → CH 4 + Na 2 CO 3
Calcium oxide is a typical catalyst used for this reaction. Cesium salts also catalyze this reaction. [ citation needed
]
The product's name
The chemical substance in the international codification of food additives is listed under the index E 262 (in other documents the spelling E-262 may appear).
GOST 54626–2011 established the definition of Sodium acetates (an international synonym for Sodium Acetates).
Food grade sodium acetates are presented in two chemical types:
- Sodium acetate:
- Sodium Acetatei;
- sodium acetate (chemical name);
- E 262i.
- Sodium diacetate:
- Sodium Acetateii;
- sodium hydroacetate;
- sodium acetate, acidic (chemical name);
- Sodium Hydrogen Acetate (Sodium Diacetate);
- E 262ii.
German names: Natriumacetat, Natrium salz der Essigsaure.
French: Acetate de Sodium, Sel de Sodium de l'aside acetique.
Areas of application of the substance by humans
There are several types of sodium acetates: technical and food grade. The first variety is used in the production of chemical heating pads and heaters, as an integral part of the “hot ice” mixture. In the construction industry, sodium acetates provide an anti-frost effect for concrete and are used in the construction of monolithic structures.
The textile industry uses the substance for dyeing fabrics and tanning leather. The additive is also used in the field of photography and electroplating, in the production of coloring products, hygiene products, and in the chemical industry.
In its structure, technical sodium acetate is a trihydrate of sodium salt of acetic acid, which has the appearance of flakes or pieces of various shapes.
In general, people are familiar with two types of E262 additive:
- sodium acetate E262i;
- sodium diacetate E262ii.
Substances have different chemical formulas, but differ little from each other in their properties.
In food production, edible sodium acetate has found application, mainly in the following foods:
- in bakery products (to protect raw materials from “potato disease” bacteria);
- in canned vegetables and fruits (to improve the taste of the product);
- in potato chips (to give them a more pleasant taste and aroma).
In the medical industry, the additive is used in the manufacture of diuretics and other drugs.
How to make sodium acetate at home
Even a person who is far from deep knowledge of chemistry can obtain this substance on his own. To do this, you only need two elements: baking soda and acetic acid. The chemical reaction equation for combining these products is as follows:
- NaHCO3 + CH3COOH = CH3COONa + H2CO3.
In other words, making acetate at home is called “quenching soda.” As a result of this chemical reaction, an unstable compound is obtained that instantly decomposes into water and carbon dioxide. During evaporation of the resulting solution, crystalline sodium acetate is formed. As a rule, to obtain it, take soda and acid in the following ratios: 84 g of sodium bicarbonate with 750 g of wine vinegar (8%) or with 86 g of vinegar essence (70%). In the latter case, evaporation will not be necessary. The reaction produces about 80 g of sodium acetate.
Negative properties of the substance
Although sodium acetate is low-toxic, excessive consumption can still cause significant harm to human health. Thus, it is not recommended for people suffering from the following diseases: arterial hypertension, vegetative-vascular dystonia, dysbacteriosis. Those who have problems with the intestines, urinary tract, liver, and gall bladder should significantly limit the consumption of products containing E262. This is due to the fact that sodium acetate in the intestines is often converted into toxic nitrates, which have a carcinogenic effect. That is why doctors warn that excessive consumption of products containing E262 can lead to the formation of malignant tumors, poisoning and allergic reactions. Sodium acetate cannot be used in the production of children's food products, so the presence of the E262 marking on the packaging is a serious reason for refusing to purchase them.
Main manufacturers
Sodium acetates are supplied to the domestic market by: the Ural Industrial Chemicals Plant (Magnitogorsk), the plant named after.
Y. M. Sverdlova and Organika LLC (both city of Dzerzhinsk, Nizhny Novgorod region). A large volume of products is produced by the Chinese company Fooding, which includes 35 chemical enterprises from several regions of the country.
The products of the German company W. Urlich GmbH, which has a 70-year history of development, are distinguished by their high quality.
The statement that when ingested by the body, the food additive E 262 turns into carcinogenic nitrites does not stand up to criticism.
Sodium acetates are found inside the cells of plants and living organisms. They are natural preservatives for all fermented milk products as a direct result of bacterial fermentation. If you don’t use spoons of soda or drink liters of vinegar, the food additive E 262 will be a useful and safe component of products.
Package
According to GOST 54626–2011, the following can be used for packaging food sodium acetates:
- grocery woven bags made of polypropylene (most often used);
- boxes for confectionery products made of corrugated cardboard;
- multilayer paper bags.
A mandatory requirement is the presence of an additional liner made of durable polyethylene intended for food packaging.
It is allowed to pack food preservatives in other safe containers (barrels, canisters, containers).
In addition to the standard labeling, there must be a “Keep away from moisture” sign.
Benefits and harms
Sodium acetates have pronounced bactericidal and disinfectant properties. Food preservative E 262 is well absorbed by the body. Sodium acetate is recognized as absolutely safe (class 4 according to GOST 12.1.007–76).
Sodium diacetate is classified as a moderately hazardous product (class 3) . Prolonged inhalation of vapors or ingestion of large quantities may:
- provoke conjunctivitis;
- have a negative effect on the skin;
- cause mild allergic reactions;
- irritate the upper respiratory tract;
- disrupt metabolism.
People sensitive to vinegar should use products with code E 260 with caution.
Children and pregnant women should exclude food coloring E151 from their diet!
Children's lunch boxes are very beautiful and colorful. If you often organize children's parties in your establishment, then this type of tableware is a must-have for you! Read more in this article.
Formaldehyde should not be used in food production as it is a very dangerous preservative. You can read more about it here.