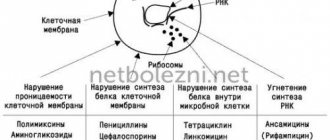
For whom is it intended and for whom is it contraindicated?
The drug is used to suppress the reaction to poisoning:
- cyanide;
- hydrocyanic acid;
- lead;
- cadmium;
- mercury;
- arsenic;
- lithium;
- aluminum, etc.
Sodium thiosulfate is used in the treatment of lupus erythematosus, neuralgia, arthritis, allergies, and scabies.
The only contraindication for medical procedures is individual intolerance to its component composition. During treatment, side effects may occur in the form of allergies or discomfort in the area where the medication was administered.
Receipt
Natural springs
Sodium sulfate occurs in the form of the mineral thenardite, and the crystalline hydrate Na2SO4.10H2O occurs in the form of mirabilite or Glauber's salt.
Laboratory methods of obtaining
Sodium sulfate is prepared by reacting sulfuric acid with sodium hydroxide or carbonate:
H2SO4 + 2NaOH = Na2SO4 + 2H2O;
H2SO4 + Na2CO3 =Na2SO4 + H2O + CO2↑.
Production of sodium sulfate in industry
In industry, sodium sulfate was prepared from sodium chloride and sulfuric acid:
H2SO4 + 2NaCl =Na2SO4 + 2HCl↑,
but now this does not make sense - natural sources are enough.
Features of sodium thiosulfate therapy
The instructions recommend the following methods and dosages:
- Topical application is used for scabies mites. A 60% solution is rubbed into the skin of the entire body. After it dries, additional treatment is carried out with a 6% solution of hydrochloric acid.
- Intravenous administration is used to cleanse the body of poisonous and toxic substances. 30% of the drug is administered intravenously, 5-50 ml. The exact dosage depends on the severity of the disease and the type of toxic compound.
- Oral – for procedures a 10% composition is used, a single dosage is equal to 2-3 g of medication.
In gynecological practice, the drug is part of complex therapy:
- endocrine infertility;
- ovarian cysts;
- genital tuberculosis.
If necessary, sodium thiosulfate is included in microenemas. This approach is used to detect adhesions in the pelvic area and inflammation of the reproductive tract. A 10% solution is suitable for enemas; 30 to 50 doses of medication are sufficient for one procedure.
Treatment for psoriasis involves taking medication orally. Cleansing the body has a positive effect on the immune system and facilitates the course of many chronic diseases. Therapy for psoriasis continues for 5-12 days; you can take from 10 to 20 ml of the product per day. The exact dosage depends on the weight and tolerance of the component composition.
A measured amount of medicine is diluted in half a glass of water and consumed before going to bed. If the medicine provokes a laxative effect, then the dose is reduced to 10 ml per day.
Sodium thiosulfate can be used to cleanse the circulatory and lymphatic systems. The procedures can improve the condition of nail plates and hair, get rid of allergies, depression, and improve general condition.
Cleansing procedures last 10 days; half an ampoule can be used at one time; the solution is diluted in half a glass of water. The first procedure is designed for the morning - half an hour before breakfast, the second - an hour before dinner.
Properties of sodium sulfate
Physical properties
| Property | Description |
| Appearance | White crystalline substance |
| Molar mass | 142.04 g/mol |
| Density | 2.68 g/cm3 |
| Melting temperature | 883°C |
| Standard molar enthalpy of formation at 298K ΔH°298, kJ/mol | −1387.9 (t)2 |
| Standard molar entropy at 298 K S°298, J/(mol•K) | 149.58 (t) |
| Standard molar heat capacity at 298 K Cp298, J/(mol•K) | 127,3 |
| Solubility in water, g/100 g | at 0°C - 4.5 at 20°C - 19.2 at 32.4°C - 49.8 at 100°C - 42.3 |
Chemical properties
When dissolved in water, sodium sulfate dissociates into ions:
Na2SO4↔ 2Na++ SO42-.
The solution has a neutral reaction.
When interacting with acids, it forms acid salts:
Na2SO4 + HСl = NaHSO4 + NaCl.
Enters into exchange reactions to form insoluble sulfates:
Na2SO4 + CaCl2 = 2NaCl + CaSO4↓,
Na2SO4 + SrCl2 = 2NaCl + SrSO4↓,
Na2SO4 + BaCl2 = 2NaCl + BaSO4↓.
Manufacturer's instructions
The instructions draw attention to the following nuances:
- combination with iodides and bromides leads to their lack of effectiveness;
- combination with drugs that cause rhodanization weakens their effectiveness;
- immediate administration of sodium thiosulfate is necessary in case of cyanide intoxication; delay causes death;
- The powder of the drug has a specific smell, reminiscent of the aroma of sodium acetate - you can check the authenticity of the product with iodine, a chemical reaction will lead to its discoloration.
Therapeutic measures for poisoning require constant supervision by the attending physician. If symptoms of intoxication resume after their initial disappearance, it is necessary to repeat the procedure with half the dose.
SODIUM SULPHATE. Natrium sulfas.Synonyms: sodium sulfate, Glauber's salt.
Properties.
It is colorless, transparent, air-weathering crystals with a bitter-salty taste. Easily soluble in water (in cold 1:3 and 3:1 at a temperature of 33°C), insoluble in alcohol. Contains about 50% water of crystallization. When heated, it melts in its water of crystallization. Incompatible with lime, barium, lead, and mercury salts.
Release form. Available in powder form.
Store in a well-closed container.
Action and application.
Sodium sulfate in small doses irritates the receptors of the stomach and intestines, increasing secretion, revitalizes motor skills and improves digestion, and has an anti-catarrhal effect.
In large doses, the drug helps to increase osmotic pressure in the intestines, where large amounts of water accumulate, which dilutes the chyme and reflexively enhances peristalsis. This is also facilitated by irritation of the intestinal mucosal receptors by the drug solution. When using salt in a concentrated solution, dehydration occurs. The laxative effect occurs after 8-14 hours and manifests itself throughout the intestines.
Sodium sulfate also stimulates bile formation and peristalsis of the excretory tract, which promotes the excretion of metabolic products with bile.
When used externally, hypertonic solutions of sodium sulfate promote cleansing of the wound surface and rapid healing of wounds.
Sodium sulfate is prescribed orally as a laxative with plenty of water for intestinal blockage and colitis, overfeeding, flatulence, deworming and poisoning with various substances; as a distracting and dehydrating agent for inflammation of the brain, pulmonary congestion and pleurisy, peritonitis, arthritis, dropsy and rheumatic inflammation of the hooves in horses (with a small amount of water).
Together with herbal bitters and sodium chloride, the drug is prescribed to improve appetite and digestion, for catarrh of the stomach and intestines; for liver disease, it is used as a choleretic and a means of treating and preventing gallstone disease.
In the form of a 1% sodium sulfate solution, it is used for hypotension and atony of the proventriculus by washing the rumen. Used as an antidote for poisoning with barium, mercury, and lead salts.
Sodium sulfate is prescribed orally
animals in the following doses (g): as a laxative - horses 300-500; cattle 400-800, deer 100-300, sheep 50-100, pigs 25-50, dogs 10-25, cats 3-10, chickens 2-4, foxes and arctic foxes 5-20, minks 5-15; as a choleretic agent - horses 150-250, cattle 250-600, dogs 10-15; to improve digestion - horses and cattle 25-50, sheep 5-12 g, pigs 3-5 g, dogs 0.2-0.5 g.
The dose of anhydrous sodium sulfate is 2 times less.
In recommended doses, sodium sulfate does not cause complications and has no side effects.
Analogs
Sodium thiosulfate can cause reactions in the body. The appearance of side effects or signs of intolerance to the medication requires its replacement. The list of popular analogues is presented:
- Algisorb, Amyl nitrite, Braidan;
- Glation, Dipiroxime, Carboxim;
- Lobelin, Naloxone, Sodium nitrite;
- Pelixim, Pentacin, Unithiol;
- Ferrocin, Amber-antitox.
Independent replacement of medication is strictly prohibited. The selection of an analogue is carried out by the attending physician, based on diagnostic data and the reasons that necessitated the need to change the therapeutic course.
Magnesium sulfate as a laxative
For 1 glass of boiled water you need to take 15-30 g of powder, stir everything and drink. To enhance the laxative effect, you need to consume as much warm liquid as possible. In this case, you will be able to notice the result within 30-40 minutes.
In no case should you take magnesium sulfate for several days in a row, otherwise you can damage the gastric mucosa, which can lead to serious consequences. For acute constipation, the product is used once. To empty the bowel, it is sometimes used together with anthelmintic drugs. For chronic constipation, enemas are done using a solution. To do this, you need to take 25 g of powder and dilute it in half a glass of water.
Combination with alcohol
Sodium thiosulfate is actively used in the treatment of alcohol dependence. Treatment involves taking medication and alcohol at the same time to cause certain symptoms:
- attacks of vomiting with nausea;
- hand trembling;
- increased sweating;
- disturbances in heart rate;
- cough, etc.
This approach allows us to develop an aversion to ethanol. Therapeutic procedures take 16-20 days, take place every day, then three times a week and once a month. The drug solution is administered intravenously, the dosage is selected for each patient separately.
Indications for use
Like other drugs, sodium sulfate has both indications for use and contraindications.
To make sure that you need this particular drug, or you are not sure of the correct diagnosis, you should definitely consult a specialist.
So, among the indications for the use of sodium sulfate are the following:
- treatment of acute constipation (including the drug is effective and is often used to cleanse the intestines before carrying out any therapeutic procedures, examination, surgery and other manipulations in the intestinal cavity);
- elimination of the consequences of food poisoning (the drug not only effectively cleanses the intestines, but also prevents the absorption of toxins, poisons, etc. into the blood);
- cleansing the intestines after anthelmintic therapy (removes the remains of dead parasites and their waste products, which prevents possible intoxication);
- cleansing the intestines before therapeutic fasting (removes food debris that may prevent the patient from feeling comfortable, especially when the fasting technique is used by a person for the first time).
The main property of this drug is the effective cleansing of the intestinal cavity. There is even a special method of cleansing the body using Glauber's salt, which allows you to cleanse not only the gastrointestinal tract, but also the liver, and also lead to weight loss.
Mode of application
Sodium sulfate (also called Glauber's salt or sodium sulfate) is available as a powder. It is white, like regular table salt, but its granules are smaller.
The powder must be dissolved in a small amount (recommended in one or two glasses) of water at a comfortable temperature.
The amount of powder is primarily determined by the age of the patient. For adults, this is from 15 to 30 grams, depending on the severity of the situation, and for children, this is 1 gram for one year of life.
It is advisable to take the solution on an empty stomach, taking it at a time.
The effect of the laxative occurs 4 or 6 hours after use.
Interaction with other drugs
The drug does not have a complex chemical composition , its interaction with all medications does not manifest itself in any way. The only thing that needs to be understood is that, as in the case of using other laxatives, during the period of action of Glauber’s salt, taking other tablets is simply pointless, since the medicine will leave the body without having time to act at all or having worked partially.
Therefore, the pain that may appear during bowel movements cannot be eliminated or mitigated with the help of painkillers.
Contraindications
You should avoid taking magnesium sulfate if:
- bleeding in the rectum;
- dehydration of the body;
- intestinal obstruction;
- inflammation of appendicitis.
Should be taken under medical supervision if:
- inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract;
- respiratory problems;
- renal failure.