Granuloma is a serious dental problem that can lead to the loss of a healthy-looking tooth. This pathology is an inflammation of the periodontium near the root apex with the formation of a capsule filled with pus.
In the early stages, the disease does not manifest itself in any way, and tangible symptoms appear only at an advanced stage. Previously, dental granuloma was dealt with radically: the diseased tooth was removed along with the purulent formation. Today, in the fight against the disease, modern dental methods are used, which make it possible to eliminate the purulent focus and preserve the dentition in its original form.
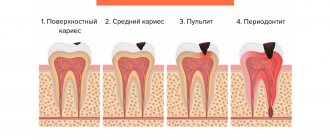
Cyst and granuloma of the tooth
Previously, it was generally accepted that if a neoplasm on the root of a tooth measures up to five millimeters, it is a granuloma, and if it is more than ten millimeters, then it is a dental cyst. Some dentists also distinguish a certain transitional stage - cystogranuloma, but practice shows that there are granulomas reaching even twelve millimeters, so an accurate diagnosis cannot be made only by the size of the formation and its shape. In addition to X-rays, histological examination of tissues is necessary.
The question often arises of how a granuloma differs from a dental cyst. The fact is that a cyst is a bladder filled with fluid or pus, with a shell formed by connective tissue and lined on the inside with endometrium. Secretory fluid is produced by the membrane, and due to this the cyst increases in size. Granuloma grows due to the growth of tissues containing infected cells.
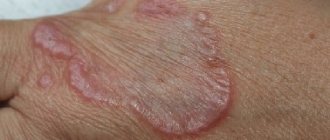
Pyogenic granuloma (PG; synonyms: telangiectatic granuloma, botryomycomoma, granulation-type hemangioma) is a common disease that is a reactive benign tumor-like formation of the skin and mucous membranes. The highest incidence is observed among children and adults under the age of 30 years. This pathology affects men and women equally often. Clinically, PG is a polyp-like formation with an erythematous granular or smooth surface, sometimes having a lobulated structure, often painless, and bleeding easily after minor trauma. The formation is often localized on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity or on the skin of the trunk and extremities [1]. According to the literature, dentists most often encounter this pathology.
At present, the etiology and pathogenesis of PG have not been fully studied. There are suggestions that this disease occurs in response to various stimuli, such as chronic minor local irritation, traumatic injury, certain types of medications, or hormonal dysfunctions [2]. PG often occurs and develops during pregnancy, puberty, menopause, or while taking contraceptives. The last factor is due to the fact that estrogens and progesterone lead to increased vascularization, proliferation of endothelial cells and increased vascular permeability. These changes lead to greater tissue susceptibility to damaging factors, which results in a tendency to inflammatory and other processes, including PG [3, 4].
Some authors suggest that an important link in the development of PG is tissue proliferation and angiogenesis under inflammatory conditions. Factors involved in angiogenesis and influencing the growth rate of PGs are inducible NO synthetase (iNOS), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), basic fibroblast growth factor or connective tissue growth factor, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), interleukin-10 (IL-10) [5].
The action of COX-2 is associated with the proangiogenic properties of certain eicosanoids, including PgE1, PgE2 and thromboxane (Tx) A2. IL-10 is a regulator of the expression of COX-2, PgE2 [5].
In 1980, M. Davies et al. [6] identified inclusions in fibroblasts that lead to disruption of protein metabolism. They suggested that the cause of PG is a disruption in the organization of germinal tissue as a result of depression of certain genes of papillary fibroblasts, for example due to retroviral infection. The rate of tumor growth depends not only on the proliferative activity of tumor cells, but also on the frequency of cell death. It is assumed that the low level of apoptosis in PG is closely related to its rapid growth and is regulated by proteins of the Bcl 2 family [7]. Proteins encoded by Bcl 2 genes control the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis induction. It is assumed that Bcl2, located in mitochondrial membranes, blocks channels through which cytochrome C and other apoptogenic molecules are transported. Survivin, which, like Bcl 2, is present in the basal layer of the epidermis, also has an inhibitory effect on apoptosis. A special feature of survivin is the type of expression of this protein: it is found in the cells of embryonic tumors, is absent in almost all differentiated cells of the adult organism, and begins to be expressed again in the cells of many tumors, including in 70-95% of cases of skin tumors. One of the reasons for the reactivation of survivin expression in tumor cells is an increase in the activity of signaling pathways controlled by proteins of the Ras family and positively regulating the transcription of its gene. An increase in survivin expression can also be induced by inactivation of p53, which represses the latter gene, suppressing transcription [8, 9].
In addition, it is assumed that during the development of PG, as well as other skin tumors, inactivating mutations in the genes of pro-apoptotic proteins Bax/Bak or suppression of their expression due to dysfunction of regulatory protein molecules play a certain role in the pathogenesis [7].
The endothelium is one of the most critical sites for the control of apoptosis during vascular injury and angiogenesis. Under conditions of inflammation, a heterogeneous group of protective genes is activated, preventing cell death and the development of inflammatory changes in endothelial cells due to induction by cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-α. Inhibition of apoptosis also occurs during vascular remodeling and angiogenesis. VEGF and basic fibroblast growth factor also contribute to the maintenance of endothelial cell viability (the mechanism is not fully understood) [10].
We present our own clinical observations.
A woman came to see a dermato-oncologist at the Moscow Research and Clinical Center with complaints of a formation on the scalp. She considered herself sick for about 1 month when she first noticed a tumor in the occipital region. Having appeared the size of a pea, the neoplasm rapidly increased to 2.0×1.5 cm (Fig. 1, a).
Figure 1. A patient with a giant PG of the scalp before (a) and after removal of PG using the Surgitron device in the “fully straightened wave incision/coagulation” mode (b). From the medical history it is known that the patient has been suffering from type 2 diabetes mellitus since 2009. Upon examination, a light pink polyp-like formation with a wide base and a rough surface was noted on the scalp in the parietal region, bleeding easily when touched.
Taking into account the medical history and clinical picture of the disease, we diagnosed PG of the scalp. The method of treatment chosen was high-frequency radio wave surgery using a portable radiosurgical device called Surgitron
("Ellman International"), operating at a frequency of 3.8 MHz.
The formation was removed in “II” mode, which allows simultaneous incision and coagulation of vessels, taking into account the anatomical features of the vascularization of this area (see Fig. 1, b)
.
The use of this equipment also makes it possible to obtain material for pathomorphological examination due to the small heating zone. An exophytic proliferation of thin-walled vessels of various sizes in the edematous dermis with the formation of a lobular structure separated from the adjacent tissues by a “collar” of the epidermis was established (Fig. 2).
Figure 2. Pathomorphological picture of PG. Hematoxylin and eosin staining (×200).
The patient underwent the postoperative period safely. Despite the concomitant pathology, no complications were noted.
We also observed a 36-year-old patient who came to the appointment with complaints of a mass in the chest area. The patient noted frequent trauma to this area due to wearing massive metal jewelry. At the time of examination, the pathological process was of a limited, non-inflammatory nature, represented by a tumor-like papular formation of a pale red color with clear boundaries and a smooth shiny surface. The diagnosis of PG is questionable. A diagnostic total biopsy was performed, the results of which confirmed the diagnosis of PG. The patient underwent surgical treatment (Fig. 3, a, b).
Figure 3. Fragment of surgical treatment (a) and the cosmetic effect achieved during surgical treatment (b) of a patient with PG.
The use of the chosen method of patient management makes it possible to achieve a complete cure, despite severe concomitant somatic pathology.
Tooth granuloma - symptoms and causes
Is it possible to live with dental granuloma? Yes, but you may not know about its existence for quite a long time: it is often asymptomatic and is detected only on an x-ray, which is performed for a completely different reason. However, it can be assumed if pain occurs when pressing on a tooth or getting into solid food. This condition should not be ignored, as it shows that an inflammatory disease is developing in the oral cavity. It can lead to a decrease in bone volume, resorption of tooth roots and ultimately to tooth loss. The consequences of advanced dental granuloma can be much more serious: perimaxillary abscess, phlegmon, jaw ostiomyelitis.
The hole after tooth extraction is a potential source of infection, which without treatment can lead to the formation of granuloma. Careful treatment of the hole by a doctor and following his recommendations after surgery will protect you from the disease.
Patients often wonder if dental granuloma can go away on its own? The answer to this question is no. It only indicates that an inflammatory process is occurring somewhere nearby, and if you don’t get rid of it, the consequences can be sad. Granuloma under a tooth is tissue saturated with capillaries. It isolates the infection within itself, preventing it from spreading further throughout the body. If the infection is not eliminated, it will continue to grow.
It should be noted that it itself is not a source of infection. This is just the body's reaction to an infection in the tooth. Accordingly, if you get rid of the source of infection, then the granuloma will go away by itself as unnecessary.
Prevention in children
Any granuloma in a child is treated only after consultation with a dermatologist. There are no special methods of prevention. Granuloma annulare in children has variable causes for the development of the disease. Taking into account the influence of immunity on the occurrence of formations, it is necessary to undergo timely treatment. It is necessary to take into account the infectious nature and metabolism in the body. Any disease should receive therapy to reduce risks. This is what prevention consists of – eliminating factors that can provoke the disease.
Treatment of dental granuloma: what to do?
Today, therapeutic treatment of dental granuloma is successfully carried out; in some cases, dental granuloma is treated with a laser, which does not require tooth extraction. As a rule, it is necessary to carry out high-quality endodontic treatment of the canals: cleaning, rinsing with an antiseptic and filling. They must be carefully sealed so that infection cannot enter from the oral cavity. Subsequently, the dentist monitors the condition of the tooth and the tissues around it. After five to six months, an x-ray should be taken, and if the tumor decreases in size or disappears, the therapy is considered successful. If it continues to grow, this makes it possible to diagnose not a granuloma under the tooth crown, but a dental cyst and re-treatment, which is carried out by a surgeon.
Symptoms
In dental granuloma, most often the symptoms are not very clear, so the patient may not be aware of the pathology for a long time. The tooth itself will not hurt, only when biting and exposure to hot foods - symptoms suitable for all types of periodontitis.
With a decrease in immunity (hypothermia, infection, surgery), the inflammatory process may worsen. This is how they appear:
- sharp, shooting pain that intensifies when biting one unit;
- swelling of gingival tissue (accumulation of pus) in the projection of the root apex;
- pain in the gums when pressed.
The period of exacerbation of granuloma of a tooth with a pin may subside over time, and then the pathological process will become chronic.
Removal of tooth granuloma
If therapeutic treatment of dental granuloma does not help, surgical intervention is used. From the outside, through the bone, access is made to the tooth root, the granuloma is scraped out, the place of its attachment is carefully processed, and the mucous membrane is sutured. In some cases, the infected root tip of the tooth is excised. Subsequently, the bone is restored, and the tooth continues to serve for a long time. Sometimes it is necessary to remove the entire root. This is also a common operation today. In this case, the desired root is excised along with the coronal part, and if the remaining roots are able to withstand the required load, a prosthesis is installed in this place.
If a tooth granuloma has been removed, but pain or inflammation remains, and it is painful to press on the tooth, you should contact a dentist in Moscow again. The situation when a tooth hurts after treatment or removal of a granuloma is common. The pain may persist for a long time, but you should make sure that there is no inflammation and that this pain is truly residual and not an indicator of another problem.
Complications
If a pathological process is started, then the first thing to do is remove the unit. But there are also more serious complications:
- Cyst - encapsulation of a formation with pathological bacteria;
- periostitis (flux) - suppuration of the periosteum;
- fistulous tract - formation of purulent discharge through the gingival tissue;
- subcutaneous abscess - occurs when pus enters soft tissue structures.
Suppuration is a dangerous process. If you make lotions from home remedies, many problems will arise. An area of inflammation may lead to resorption of the jaw bone or part of the root system. Suppuration of the formation may be followed by tooth extraction with granuloma, necrosis of surrounding tissues and sepsis. Therefore, it is important to consult a therapist or surgeon in time and find out how to treat dental granuloma. Only highly qualified specialists can carry out diagnostic measures and remove granuloma. West Dental doctors will be happy to help with this.
Treatment of dental granuloma with antibiotics and physiotherapy
Dentists often suggest treating dental granuloma with antibiotics. As a rule, this is only a temporary solution to the problem, since it does not eliminate the source of inflammation, and after some time the disease will return. Dentists successfully use physiotherapeutic treatment methods. For example, depophoresis works great for curved or complex tooth canals. Its action consists in the effect of a weak electric current on a suspension with copper hydroxide, which relieves inflammation, penetrating into all corners of the tooth.
Methods of treating the disease
Granuloma annulare in children requires restrained treatment. The characteristics of the body allow us to expect spontaneous resolution. According to statistics, in 75% of cases, granulomas regress within 2 years. A granuloma may reappear on the skin of a child in 40% of patients. It is important that recurrent tumors behave benignly. For painful symptoms, corticosteroid ointment with a pronounced anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effect is used. Another treatment method is superficial scarification. How to treat granuloma annulare in a child without harm to health is an important topic. The methods are based on the use of physiotherapeutic procedures: PUVA therapy, ultraviolet irradiation and phototherapy, pulsed laser. The treatment of pyogenic neoplasm is characterized by excessive proliferation of blood capillaries. With this diagnosis, it is recommended to be treated by excision, curettage, liquid nitrogen and electrocoagulation. Granuloma annulare in children is treated within a month. The need for manipulation and use of ointments is determined individually.
Is it possible to put a crown on a granuloma on the root of a tooth?
Dental prosthetics imposes special requirements on the doctor and the patient. If we are talking about installing a crown on a tooth of which no more than 1/3 remains, that is, only the root, then it must be carefully prepared: the canals are sealed, the infection is eliminated. A granuloma under a tooth is an indicator that an inflammatory process is occurring in the tooth, and before dental prosthetics it is necessary to get rid of it, or sooner or later the granuloma will still have to be treated, since it can become inflamed under the crown. So why not do this right away, before installing a denture?
Causes
There are two main reasons for the formation of the pathological process:
- Consequences of untreated pulpitis (inflammation of the neurovascular bundle). The formation of a carious cavity leads to further destruction of the hard structures of the tooth and the accumulation of microorganisms, which subsequently destroy the pulp. Inflammation and noticeable pain occur. The formation of dental granuloma occurs when the patient endures unpleasant sensations for a long time and the root canals are not treated. The pulp becomes necrotic and pathogens go beyond the unit through the root tips - an intraosseous complication occurs - periodontitis. Also, pathology may appear if caries is treated and a filling is placed without following the protocols - secondary caries. Then the deep cavity will be hidden from view under the filling.
- Violation of the endodontic treatment protocol. Signs of granuloma may appear at the root of the unit, treated and with canals filled with gutta-percha pins. Most often, underfilling leads to the formation of conditions for inflammation of the space left without filling material.
There are also rare provoking factors:
- To be treated with orthodontic equipment without following the doctor’s recommendations;
- traumatization of the unit in the past;
- Inflammatory processes in the maxillary area, infecting through the blood/lymph.
Tooth granuloma and folk remedies: will there be any benefit?
As we have already found out, granuloma occurs as the body’s response to inflammation that occurs in the tooth canals or periodontal tissues: a kind of tubercle of tissue appears under the tooth, absorbing and processing microbes. Is it possible to cure dental granuloma without seeing a doctor? At home, treating granuloma on the root of a tooth with folk remedies can be a dangerous undertaking. It is unlikely that with the help of herbal decoctions you will be able to get rid of infection in the dental canals. You can alleviate the condition by rinsing with tinctures based on calamus and propolis. Sage, chamomile, eucalyptus, calendula, oak bark have an antiseptic and antibacterial effect, and rinsing with decoctions of these herbs can alleviate the symptoms of the disease, but this is a temporary measure, since dental granuloma cannot be cured in this way. All this should be used in complex treatment after consultation with a dentist-therapist.
Available diagnostic methods
At JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic) near the Mayakovskaya metro station, you can comprehensively examine the health of adults and children. The latest equipment (ultrasound, MRI, CT) and advanced diagnostic methods, specially equipped rooms - everything is there to confirm or refute granuloma annulare in children. In the early stages of development, neoplasms cannot be detected. Symptoms appear when lesions appear on the surface of the epidermis. A diagnostic examination by a dermatologist is carried out when there are complaints of skin changes. Only after this do they turn to laboratory and histological analyzes of skin biopsies from lesions in case of suspicion of deep forms of lesions.