To the reference book Wegener's granulomatosis involves damage to the upper respiratory tract.
Author:
- Oganesyan Tigran Sergeevich
ENT pathology expert
5.00 (Votes: 1)
Wegener's granulomatosis is a granulomatous vasculitis characterized by damage to the upper respiratory tract, first described in the first third of the 20th century by the German physician Friedrich Wegener, for which it received its name.
The disease is predominantly necrotic in nature; with a long course, the lungs and kidneys are involved in the process.
Clinical picture
There are several forms of pathology - acute, subacute and chronic. The development of the disease also describes three main stages:
- initial - changes in the upper respiratory tract are local in nature (the mucous membranes of the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and sometimes the middle ear are affected);
- generalized - the process of damage involves internal organs, lungs and kidneys in particular;
- terminal - the most severe, aggravated by the addition of renal, pulmonary and heart failure.
In this regard, patients complain about:
- nasal congestion (usually one half);
- purulent nasal discharge mixed with blood;
- brown-brown crusts form on the mucous membrane, after removal of which it has a thinned appearance and is covered with bleeding lesions.
In the case of further progression of the disease, perforation of the cartilaginous and then the bone part of the septum occurs (saddle-shaped perforation of the nose). After which nearby tissues, especially the paranasal sinuses, are destroyed. A distinctive feature of granulomatosis from syphilis is the absence of destruction of the hard palate, which in this case remains unchanged.
The generalized stage of the pathology is usually diagnosed after several months or even after several years. Damage to the lungs will be marked by the appearance of cough, shortness of breath, and characteristic chest pain. The skin also signals changes occurring in the body; ulcerative necrotic rashes appear on it.
Severe, terminal stage granulomatosis is life-threatening. The symptoms of azotemic uremia are accompanied by signs of pulmonary and heart failure, which together are the cause of death.
Causes and course of the disease
Currently, the causes of this disease are not fully understood, but most researchers are of the opinion that it is an autoimmune disease, in the occurrence of which viruses such as cytomegalovirus and herpes virus play an important role.
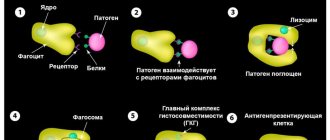
An equally important factor is the genetic peculiarity of the immune system, especially since with this disease in the blood of patients there is an increased content of the HLA-A8 antigen, which is responsible for the genetic predisposition to the development of autoimmune diseases. In the pathogenesis of Wegener's granulomatosis, immunological disorders such as deposition of immune complexes in the walls of blood vessels and impaired cellular immunity are of great importance. Patients experience necrotizing vasculitis, which affects medium- and small-caliber arteries and is accompanied by the formation of polymorphic cell granulomas that contain giant cells.
Medicines
When treating the disease use:
- "Cyclophosphamide", "Methotrexate" and "Azathioprine", which are part of the group of cytostatics.
- "Dexamethasone" and "Prednisolone" are part of the group of glucocorticoids.
- Anticytokine therapy.
- Hemodialysis, cascade plasma filtration, extracorporeal pharmacotherapy, plasmapheresis.
- Antibiotics, which are prescribed to prevent the occurrence of infectious complications.
- Immunoglobulins. May be prescribed if there is a relapsing course of the disease.
Diagnostics
In patients with a developed clinical picture, the diagnosis is usually simple, but due to the variety of forms and course options, difficulties arise in the early stages of the disease. Approximately 25% of patients in the initial stage have no signs of lung or kidney damage.
Classification criteria for the diagnosis of Wegener's granulomatosis
| Criterion | Definition |
| 1. Inflammation of the nose and mouth | Ulcers in the mouth. Purulent or bloody discharge from the nasal cavity |
| 2. Changes in X-ray examination of the lungs | Nodules, infiltrates or cavities |
| 3. Changes in urine | Microhematuria (>5 red blood cells per field of view) or accumulations of red blood cells in urine sediment |
| 4. Biopsy | Granulomatous inflammation in the arterial wall or in the perivascular and extravascular spaces |
If two or more criteria are present, the sensitivity of diagnosis is 88% and the specificity is 92%. To confirm the diagnosis, the presence of classical antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (cANCA) in the blood is determined.
Treatment
This disease is interesting because the patient almost plays the lottery. The fact is that about 30% of cases of the disease resolve on their own and without any additional intervention. And one could say that there is no need to rush, you can wait until everything gets better on its own. But the problem is that the same 30% of patients face serious complications of sarcoidosis - even death, if help is not started on time. So in this case, you definitely shouldn’t refuse treatment or delay visiting a doctor. No one knows what percentage of patients it will fall into, and delaying time can be truly dangerous.
It is important to understand that when the disease progresses without complications, doctors often leave time for observation. They analyze the condition of patients and understand that in some cases it is necessary to wait and see how the disease develops. And only in a situation where it is clear that the body cannot cope on its own, treatment is prescribed.
Treatment of sarcoidosis includes steroid hormones, anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, antioxidants, and vitamins. The patient is also prescribed a protein diet (when taking hormonal medications) and is recommended to reduce the amount of salt. An important point for recovery is the complete cessation of such a bad habit as smoking.
After the onset of remission, the patient remains registered for several years and is observed by his attending physician.
If you have already been diagnosed or suspect that you have pulmonary sarcoidosis, contact the Meditsina JSC clinic in Moscow: our pulmonologists and therapists are always happy to help, advise, prescribe additional examinations and adjust or develop a treatment plan for you.
Stages
There are three stages of sarcoidosis. At the first stage, there is an increase in lymph nodes, lung damage is either unilateral or symmetrical. The second stage is characterized by the spread of the disease through the lymphatic tract. The granulomas are still small, and the lung tissue gradually begins to be replaced by tissue of higher density.
At the third stage, connective tissue grows in the alveoli and scars form. The risks of complications such as emphysema and pneumosclerosis are high. Often granulomas grow simultaneously in the lungs and in other parts of the body.
Possible complications of Wegener's disease
Wegener's granulomatosis affects not only the kidneys and respiratory organs, but also other organs, including the skin, eyes, ears, spinal cord, and heart.
Complications may be as follows:
• Hearing loss that occurs due to granulomas in the middle ear. • Scars on the skin left by deep ulcers caused by disease. • Myocardial infarction as a result of damage to the coronary arteries. • Kidney failure. Progressive Wegener's disease often affects the kidneys, leading to glomerulonephritis. This impairs the kidneys' ability to filter toxins and excess water from the blood. Toxic products accumulate in the body, swelling and hypertension occur. Kidney failure is the leading cause of death in Wegener's disease.
Wegener's granulomatosis - Diagnosis in Israel
When a patient is diagnosed with suspected Wegener's granulomatosis, medical history data is carefully collected, and a number of studies are performed:
- Blood test - with Wegener's granulomatosis, an increase in ESR, anemia, leukocytosis, and an increase in the number of immunoglobulins are observed. Rheumatoid factor is also found in the blood.
- Urinalysis - detects proteinuria, hematuria, cylindruria when the kidneys are affected by the pathological process.
- Immunological examination - helps to detect antibodies to protease-3 in the cytoplasm of neutrophils, a decrease in the content of complement fractions.
- Bronchoscopy - allows you to examine the surface of large bronchi and perform a biopsy. In tissue samples taken from the lungs and upper respiratory tract with Wegener's granulomatosis, vasculitis and the presence of granulomas are always detected.
- X-ray examination of the chest - if the lungs are damaged, nodular formations, cavities, and foci of infiltration are visible on the x-ray.
Types of granulomatosis
In addition to the pathological changes that characterize the described forms of the disease, the progression of Wegener's syndrome can be divided into four stages:
- granulomatous necotic vasculitis;
- pulmonary parenchyma;
- generalized inflammation of the entire respiratory and cardiovascular systems, as well as the kidneys and gastrointestinal tract;
- pulmonary-cardiac and renal failure.
The first stage passes rapidly, with the formation of purulent and ulcerative rhinosinusitis, laryngitis or otitis. Infections have a destructive effect on the cartilaginous tissue of the nasal septum and orbit. The pathological process continues with the lung parenchyma and moves to the next stage, in which inflammation of the lungs, blood vessels and kidneys progresses. The final terminal stage is characterized by the development of heart and kidney failure, which without proper treatment leads to the death of the patient.
The initial mechanisms and causes of granulomas are not fully known to scientists. The pathology can be traced in people who have previously suffered from various respiratory infections. It is based on the synthesis of protein antibodies that fight harmful microorganisms. Subsequently, they tend to settle on the walls of blood vessels, which leads to the release of chemical active substances.
There is chronic Wegener's granulomatosis, which is described by the inability of leukocytes to produce reactive oxygen species and the inability to phagocytose microorganisms. Manifests itself in different ways:
- in the form of recurrent infections;
- noticeable changes in the lungs, liver, kidneys, lymph nodes and other organs;
- abscesses;
- lymphadenitis;
- anemia.
In half of the cases, the occurrence of Wegener's chronic granulomatosis is due to heredity. This method of infection is achieved through an autosomal recessive type or a linked molecule to the X chromosome. This type of granulomatosis is characterized by defective white blood cells that have ceased to produce oxygen peroxide and superoxide. This leads to disruption of the phagocytosis of microorganisms by cells that are unable to completely destroy pathogens and fungi.
Differential diagnosis
For the purpose of correct diagnosis, diseases that also occur with pulmonary-renal syndrome should be excluded: microscopic polyangiitis, Churg-Strauss syndrome, periarteritis nodosa, Goodpasture syndrome, hemorrhagic vasculitis, systemic lupus erythematosus; rarely - streptococcal pneumonia with glomerulonephritis. A differential diagnosis is also carried out with other diseases: lymphoid granulomatosis, angiocentric malignant lymphoma, malignant tumors, median granuloma of the nose, sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, berylliosis, systemic mycoses, syphilis, leprosy, AIDS, etc. With a predominantly renal course, differential diagnosis is carried out with idiopathic rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis .
Symptoms
Symptoms of sarcoidosis include the following:
- Labored breathing. This is especially noticeable at first during physical activity - even quite moderate ones.
- Problems with appetite, sudden weight loss.
- Weakness in muscles, tendency to fatigue.
- Dry cough, expectoration of blood.
- Painful sensations in the chest.
- Redness of the skin as a result of a strong rush of blood.
All these symptoms of sarcoidosis should immediately alert the patient and force him to seek specialist help. Pulmonologists deal with this disease, but if you doubt the first signs of the disease, you can also contact a general practitioner, who will then refer you to the right doctor.
Wegener's granulomatosis - Treatment in Israel
Treatment of Wegener's granulomatosis is a difficult task, involving a number of components:
- Drug therapy is based on the use of cytostatic drugs that suppress the proliferation of immune system cells that cause the development of the disease. Glucocorticoids are also prescribed to combat inflammation in tissues.
- Extracorporeal hemocorrection - hemodialysis, hemosorption, plasmapheresis, cryomodification of autoplasma, extracorporeal antibacterial therapy are used.
- Radiation therapy is used for local granulomatous process.
- Surgical treatment is used when complications of the disease develop. For example, in case of respiratory failure (asphyxia) due to laryngitis, a tracheostomy is performed. In severe cases of ulcerative-necrotic rhinitis, a “saddle-shaped” deformation of the nasal dorsum often develops, which is subject to surgical correction. If a granuloma forms in the soft tissues of the orbit, threatening vision loss, it is removed.
Despite the fact that the disease is prone to recurrence, with adequate quality treatment, patients with Wegener's granulomatosis can prolong their lives.
Attention! All form fields are required. Otherwise we will not receive your information. Alternatively use
Description of the pathology
In the walls of blood vessels, Wegener's disease (photo in the article) is characterized by giant cell granulomatous-necrotizing inflammation. First of all, the formation of granulomas occurs in the vessels and tissues that surround the respiratory tract and eyes, after which they begin to develop in the kidneys, skin, heart and nervous system.
Granulomatosis received its name thanks to its discoverer, who identified this systemic vasculitis as a separate nosology. This happened in the thirties of the last century.
There are several forms of Wegener's disease (we'll look at the symptoms later).